pytorch多分类的语义分割
Posted lonelyrains
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了pytorch多分类的语义分割相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基于 segmentation_models.pytorch 实现的多分类的语义分割。
github中的示例没有包含多分类的内容,网上资料比较少,就动手调了一下。
segmentation_models.pytorch\\examples\\cars segmentation (camvid).ipynb 里写了怎么做单分类的调用,用来检测Camvid数据集中的Car类型。
实现多分类目标,要做的就是训练、测试时支持多分类。主要是把原来用到二维矩阵(图像)的地方,改为三维矩阵。
笔者只有一个GPU,只实践了单GPU的场景。
代码结构很清晰:数据加载/增强/训练/验证/测试
具体代码如下:
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0'
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
DATA_DIR = r'D:\\cv_ai\\2d\\segmentation\\segmentation_models.pytorch\\examples\\data\\CamVid'
# load repo with data if it is not exists
if not os.path.exists(DATA_DIR):
print('Loading data...')
os.system('git clone https://github.com/alexgkendall/SegNet-Tutorial ./data')
print('Done!')
x_train_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train')
y_train_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'trainannot')
x_valid_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'val')
y_valid_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'valannot')
x_test_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'test')
y_test_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'testannot')
# helper function for data visualization
def visualize(**images):
"""PLot images in one row."""
n = len(images)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5))
for i, (name, image) in enumerate(images.items()):
plt.subplot(1, n, i + 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title(' '.join(name.split('_')).title())
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.data import Dataset as BaseDataset
class Dataset(BaseDataset):
"""CamVid Dataset. Read images, apply augmentation and preprocessing transformations.
Args:
images_dir (str): path to images folder
masks_dir (str): path to segmentation masks folder
class_values (list): values of classes to extract from segmentation mask
augmentation (albumentations.Compose): data transfromation pipeline
(e.g. flip, scale, etc.)
preprocessing (albumentations.Compose): data preprocessing
(e.g. noralization, shape manipulation, etc.)
"""
CLASSES = ['sky', 'building', 'pole', 'road', 'pavement',
'tree', 'signsymbol', 'fence', 'car',
'pedestrian', 'bicyclist', 'unlabelled']
def __init__(
self,
images_dir,
masks_dir,
classes=None,
augmentation=None,
preprocessing=None,
):
self.ids = os.listdir(images_dir)
self.images_fps = [os.path.join(images_dir, image_id) for image_id in self.ids]
self.masks_fps = [os.path.join(masks_dir, image_id) for image_id in self.ids]
# convert str names to class values on masks
self.class_values = [self.CLASSES.index(cls.lower()) for cls in classes]
self.augmentation = augmentation
self.preprocessing = preprocessing
def __getitem__(self, i):
# read data
image = cv2.imread(self.images_fps[i])
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
mask = cv2.imread(self.masks_fps[i], 0)
# extract certain classes from mask (e.g. cars)
masks = [(mask == v) for v in self.class_values]
mask = np.stack(masks, axis=-1).astype('float')
# apply augmentations
if self.augmentation:
sample = self.augmentation(image=image, mask=mask)
image, mask = sample['image'], sample['mask']
# apply preprocessing
if self.preprocessing:
sample = self.preprocessing(image=image, mask=mask)
image, mask = sample['image'], sample['mask']
return image, mask
def __len__(self):
return len(self.ids)
# Lets look at data we have
# 这里选择定义了两种类型:车和行人
dataset = Dataset(x_train_dir, y_train_dir, classes=['car','pedestrian'])
image, mask = dataset[4] # get some sample
visualize(
image=image,
cars_mask=mask[:,:,0].squeeze(),
ped_mask=mask[:,:,1].squeeze(),
)
# 数据增广
import albumentations as albu
def get_training_augmentation():
train_transform = [
albu.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
albu.ShiftScaleRotate(scale_limit=0.5, rotate_limit=0, shift_limit=0.1, p=1, border_mode=0),
albu.PadIfNeeded(min_height=320, min_width=320, always_apply=True, border_mode=0),
albu.RandomCrop(height=320, width=320, always_apply=True),
albu.IAAAdditiveGaussianNoise(p=0.2),
albu.IAAPerspective(p=0.5),
albu.OneOf(
[
albu.CLAHE(p=1),
albu.RandomBrightness(p=1),
albu.RandomGamma(p=1),
],
p=0.9,
),
albu.OneOf(
[
albu.IAASharpen(p=1),
albu.Blur(blur_limit=3, p=1),
albu.MotionBlur(blur_limit=3, p=1),
],
p=0.9,
),
albu.OneOf(
[
albu.RandomContrast(p=1),
albu.HueSaturationValue(p=1),
],
p=0.9,
),
]
return albu.Compose(train_transform)
def get_validation_augmentation():
"""Add paddings to make image shape divisible by 32"""
test_transform = [
albu.PadIfNeeded(384, 480)
]
return albu.Compose(test_transform)
def to_tensor(x, **kwargs):
return x.transpose(2, 0, 1).astype('float32')
def get_preprocessing(preprocessing_fn):
"""Construct preprocessing transform
Args:
preprocessing_fn (callbale): data normalization function
(can be specific for each pretrained neural network)
Return:
transform: albumentations.Compose
"""
_transform = [
albu.Lambda(image=preprocessing_fn),
albu.Lambda(image=to_tensor, mask=to_tensor),
]
return albu.Compose(_transform)
#### Visualize resulted augmented images and masks
augmented_dataset = Dataset(
x_train_dir,
y_train_dir,
augmentation=get_training_augmentation(),
classes=['car', 'pedestrian'],
)
# same image with different random transforms
for i in range(1):
image, mask = augmented_dataset[1]
visualize(image=image,
cars_mask=mask[:,:,0].squeeze(),
ped_mask=mask[:,:,1].squeeze(),)
import torch
import numpy as np
import segmentation_models_pytorch as smp
ENCODER = 'se_resnext50_32x4d'
ENCODER_WEIGHTS = 'imagenet'
DEVICE = 'cuda'
CLASSES = ['car', 'pedestrian']
ACTIVATION = 'sigmoid'
# create segmentation model with pretrained encoder
model = smp.Unet(
encoder_name=ENCODER,
encoder_weights=ENCODER_WEIGHTS,
classes=len(CLASSES),
activation=ACTIVATION,
)
preprocessing_fn = smp.encoders.get_preprocessing_fn(ENCODER, ENCODER_WEIGHTS)
train_dataset = Dataset(
x_train_dir,
y_train_dir,
augmentation=get_training_augmentation(),
preprocessing=get_preprocessing(preprocessing_fn),
classes=CLASSES,
)
valid_dataset = Dataset(
x_valid_dir,
y_valid_dir,
augmentation=get_validation_augmentation(),
preprocessing=get_preprocessing(preprocessing_fn),
classes=CLASSES,
)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
# Dice/F1 score - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/S%C3%B8rensen%E2%80%93Dice_coefficient
# IoU/Jaccard score - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jaccard_index
loss = smp.utils.losses.BCEDiceLoss(eps=1.)
metrics = [
smp.utils.metrics.IoUMetric(eps=1.),
smp.utils.metrics.FscoreMetric(eps=1.),
]
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([
'params': model.decoder.parameters(), 'lr': 1e-4,
# decrease lr for encoder in order not to permute
# pre-trained weights with large gradients on training start
'params': model.encoder.parameters(), 'lr': 1e-6,
])
# create epoch runners
# it is a simple loop of iterating over dataloader`s samples
train_epoch = smp.utils.train.TrainEpoch(
model,
loss=loss,
metrics=metrics,
optimizer=optimizer,
device=DEVICE,
verbose=True,
)
valid_epoch = smp.utils.train.ValidEpoch(
model,
loss=loss,
metrics=metrics,
device=DEVICE,
verbose=True,
)
# train model for 40 epochs
Train = False
TrainIters = 500 # 40
if Train == True:
max_score = 0
for i in range(0, TrainIters):
print('\\nEpoch: '.format(i))
train_logs = train_epoch.run(train_loader)
valid_logs = valid_epoch.run(valid_loader)
# do something (save model, change lr, etc.)
if max_score < valid_logs['iou']:
max_score = valid_logs['iou']
torch.save(model, './best_model_Iter' + str(TrainIters) + '_.pth')
print('Model saved!')
if i == 25:
optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] = 1e-5
print('Decrease decoder learning rate to 1e-5!')
# load best saved checkpoint
best_model = torch.load(r'D:\\cv_ai\\2d\\segmentation\\segmentation_models.pytorch\\best_model_Iter500_.pth')
# 如果模型中有dropout或者batchnorm的话,一定要先将模型设置为eval模式,再保存,否则在用libtorch调用后会出现随机干扰;
best_model.eval()
# 生成一个样本供网络前向传播 forward()
example = torch.rand(1, 3, 384, 480)
# # 使用 torch.jit.trace 生成 torch.jit.ScriptModule 来跟踪
traced_script_module = torch.jit.trace(best_model, example.cuda())
traced_script_module.save("best_model.pt")
# create test dataset
test_dataset = Dataset(
x_test_dir,
y_test_dir,
augmentation=get_validation_augmentation(),
preprocessing=get_preprocessing(preprocessing_fn),
classes=CLASSES,
)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset)
# evaluate model on test set
test_epoch = smp.utils.train.ValidEpoch(
model=best_model,
loss=loss,
metrics=metrics,
device=DEVICE,
)
logs = test_epoch.run(test_dataloader)
# test dataset without transformations for image visualization
test_dataset_vis = Dataset(
x_test_dir, y_test_dir,
classes=CLASSES,
)
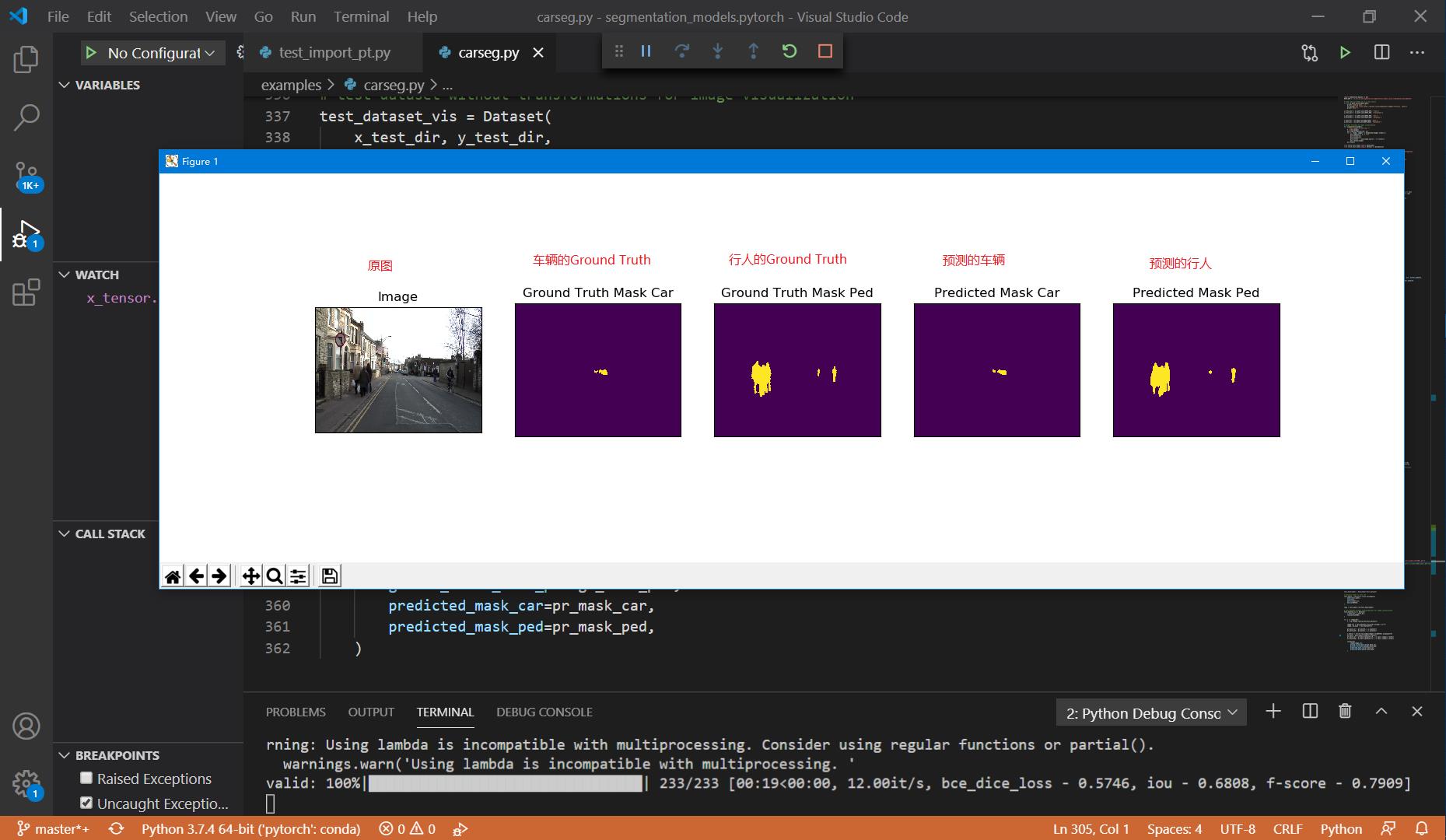
for i in range(50):
n = np.random.choice(len(test_dataset))
image_vis = test_dataset_vis[n][0].astype('uint8')
image, gt_mask = test_dataset[n]
gt_mask_car = gt_mask[0,:,:].squeeze()
gt_mask_ped = gt_mask[1,:,:].squeeze()
x_tensor = torch.from_numpy(image).to(DEVICE).unsqueeze(0)
pr_mask = best_model.predict(x_tensor)
pr_mask_car = pr_mask.squeeze()[0,:,:].cpu().numpy().round()
pr_mask_ped = pr_mask.squeeze()[1,:,:].cpu().numpy().round()
visualize(
image=image_vis,
ground_truth_mask_car=gt_mask_car,
ground_truth_mask_ped=gt_mask_ped,
predicted_mask_car=pr_mask_car,
predicted_mask_ped=pr_mask_ped,
)camvid数据集下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/15L0QAE6RMaCA4ZkZD8dbDg 提取码 57ge
验证用的编码器se_resnext50_32x4d下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hu3dW7z0ENLC0P1tY1UYkA 提取码 7489
结果示例:
以上是关于pytorch多分类的语义分割的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章