机器学习-Hierarchical clustering 层次聚类算法
Posted YEN_csdn
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习-Hierarchical clustering 层次聚类算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
学习彭亮《深度学习基础介绍:机器学习》课程
假设有N个待聚类的样本,对于层次聚类来说,步骤:
- (初始化)把每个样本归为一类,计算每两个类之间的距离,也就是样本与样本之间的相似度;
- 寻找各个类之间最近的两个类,把他们归为一类(这样类的总数就少了一个);
- 重新计算新生成的这个类与各个旧类之间的相似度;
- 重复2和3直到所有样本点都归为一类,结束
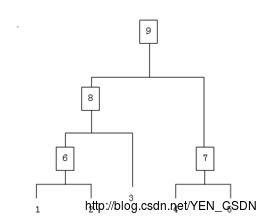
整个聚类过程其实是建立了一棵树,在建立的过程中,可以通过在第二步上设置一个阈值,当最近的两个类的距离大于这个阈值,则认为迭代可以终止。另外关键的一步就是第三步,如何判断两个类之间的相似度有不少种方法。这里介绍以下三种:
- SingleLinkage:又叫做 nearest-neighbor ,就是取两个类中距离最近的两个样本的距离作为这两个集合的距离,也就是说,最近两个样本之间的距离越小,这两个类之间的相似度就越大。容易造成一种叫做 Chaining 的效果,两个 cluster 明明从“大局”上离得比较远,但是由于其中个别的点距离比较近就被合并了,并且这样合并之后 Chaining 效应会进一步扩大,最后会得到比较松散的 cluster 。
- CompleteLinkage:这个则完全是 Single Linkage 的反面极端,取两个集合中距离最远的两个点的距离作为两个集合的距离。其效果也是刚好相反的,限制非常大,两个 cluster 即使已经很接近了,但是只要有不配合的点存在,就不相合并,也是不太好的办法。这两种相似度的定义方法的共同问题就是指考虑了某个有特点的数据,而没有考虑类内数据的整体特点。
- Average-linkage:这种方法就是把两个集合中的点两两的距离全部放在一起求一个平均值,相对也能得到合适一点的结果。Average-linkage的一个变种就是取两两距离的中值,与取均值相比更加能够解除个别偏离样本对结果的干扰。
图片分类代码

HierarchicalClustering.py
#coding=utf-8
# @Author: yangenneng
# @Time: 2018-01-21 14:06
# @Abstract:Hierarchical clustering 层次聚类算法
from numpy import *
# 定义一个结点类
class cluster_node:
# self:当前实例 <=> java中的this
def __init__(self,vec,left=None,right=None,distance=0.0,id=None,count=1):
self.left=left
self.right=right
self.vec=vec
self.distance=distance
self.id=id
self.count=count
# 距离衡量方法1:两两之间绝对值
def L1dist(v1, v2):
return sum(abs(v1 - v2))
# 距离衡量方法2:两两之间距离的平方
def L2dist(v1,v2):
return sqrt(sum(v1-v2)**2)
# 建立好树形结构
# features :numpyArray 矩阵
# distance :距离衡量方法 默认L2dist()
def hcluster(features,distance=L2dist):
distances=
currentclustid=-1
# 每一个实例自称一类 cluster_node(array(features[i]),id=i)相当于调用构造函数
clust=[cluster_node(array(features[i]),id=i) for i in range(len(features))]
# 只要聚类的数量还大于1 => 继续
while len(clust)>1:
# 初始化两个最相近的距离,后面比较再更新
lowestpair=(0,1)
closet=distance(clust[0].vec,clust[1].vec)
for i in range(len(clust)):
for j in range(i+1,len(clust)):
if(clust[i].id,clust[j].id) not in distances:
distances[(clust[i].id,clust[j].id)]=distance(clust[i].vec,clust[j].vec)
d=distances[(clust[i].id,clust[j].id)]
if d<closet:
closet = d
lowestpair=(i,j)
# 两两中的平均距离
mergevec=[(clust[lowestpair[0]].vec[i]+clust[lowestpair[1]].vec[i])/2.0 for i in range(len(clust[0].vec))]
# 创造了一个新的结点
newcluster=cluster_node(array(mergevec),left=clust[lowestpair[0]],
right=clust[lowestpair[1]],distance=closet,id=currentclustid)
currentclustid-=1
del clust[lowestpair[1]]
del clust[lowestpair[0]]
clust.append(newcluster)
return clust[0]
# 取出建立好的树形结构
# clust:建立好的树形结构
# dist:阈值
def extract_clusters(clust,dist):
clusters=
if clust.distance<dist:
return [clust]
else:
cl=[]
cr=[]
if clust.left!=None:
cl=extract_clusters(clust.left,dist=dist)
if clust.right!=None:
cr=extract_clusters(clust.right,dist=dist)
return cl+cr
def get_cluster_elements(clust):
if clust.id >= 0:
return [clust.id]
else:
cl=[]
cr=[]
if clust.left!=None:
cl=get_cluster_elements(clust.left)
if clust.right!=None:
cr=get_cluster_elements(clust.right)
return cl+cr
def printclust(clust,labels=None,n=0):
for i in range(n):print ' ',
if clust.id<0:
print '-'
else:
if labels == None:print clust.id
else:print labels[clust.id]
if clust.left!=None:printclust(clust.left,labels=labels,n=n+1)
if clust.right!=None:printclust(clust.right,labels=labels,n=n+1)
# 求树的高度
def getHeight(clust):
if clust.left==None and clust.right==None:return 1
return max(getHeight(clust.left),getHeight(clust.right))
# 求树的深度
def getDepth(clust):
if clust.left==None and clust.right==None:return 0
return max(getDepth(clust.left),getDepth(clust.right))+clust.distance
TestHierarchicalClustering.py
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw
from HierarchicalClustering import hcluster
from HierarchicalClustering import getHeight
from HierarchicalClustering import getDepth
import numpy as np
import os
def drawdendrogram(clust,imlist,jpeg='clusters.jpg'):
h=getHeight(clust)*1000
w=1200
depth=getDepth(clust)
scaling =float(w-150)/depth
img=Image.new('RGB',(w,h),(255,255,255))
draw=ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.line((0,h/2,50,h/2),fill=(255,0,0))
drawnode(draw,clust,50,int(h/2),scaling,imlist,img)
img.save(jpeg)
def drawnode(draw,clust,x,y,scaling,imlist,img):
if clust.id<0:
h1=getHeight(clust.left)*200
h2=getHeight(clust.right)*200
top=y-(h1+h2)/2
bottom=y+(h1+h2)/2
ll=clust.distance*scaling
draw.line((x,top+h1/2,x,bottom-h2/2),fill=(255,0,0))
draw.line((x,top+h1/2,x+ll,top+h1/2),fill=(255,0,0))
draw.line((x,bottom-h2/2,x+ll,bottom-h2/2),fill=(255,0,0))
drawnode(draw,clust.left,x+ll,top+h1/2,scaling,imlist,img)
drawnode(draw,clust.right,x+ll,bottom-h2/2,scaling,imlist,img)
else:
nodeim=Image.open(imlist[clust.id])
nodeim.thumbnail((50,50))
ns=nodeim.size
print x,y-ns[1]//2
print x+ns[0]
print (img.paste(nodeim, (int(x), int(y - ns[1] // 2), int(x + ns[0]), int(y + ns[1] - ns[1] // 2))))
# img.paste()
imlist=[]
folderPath=r'D:\\Python\\PyCharm-WorkSpace\\MachineLearningDemo\\HierarchicalClustering\\data'
for filename in os.listdir(folderPath):
if os.path.splitext(filename)[1]=='.jpg':
imlist.append(os.path.join(folderPath,filename))
n=len(imlist)
print n
features=np.zeros((n,3))
for i in range(n):
im=np.array(Image.open(imlist[i]))
R=np.mean(im[:,:,0].flatten())
G=np.mean(im[:,:,1].flatten())
B=np.mean(im[:,:,2].flatten())
features[i]=np.array([R,G,B])
tree=hcluster(features)
drawdendrogram(tree,imlist,jpeg='sunSet.jpg')
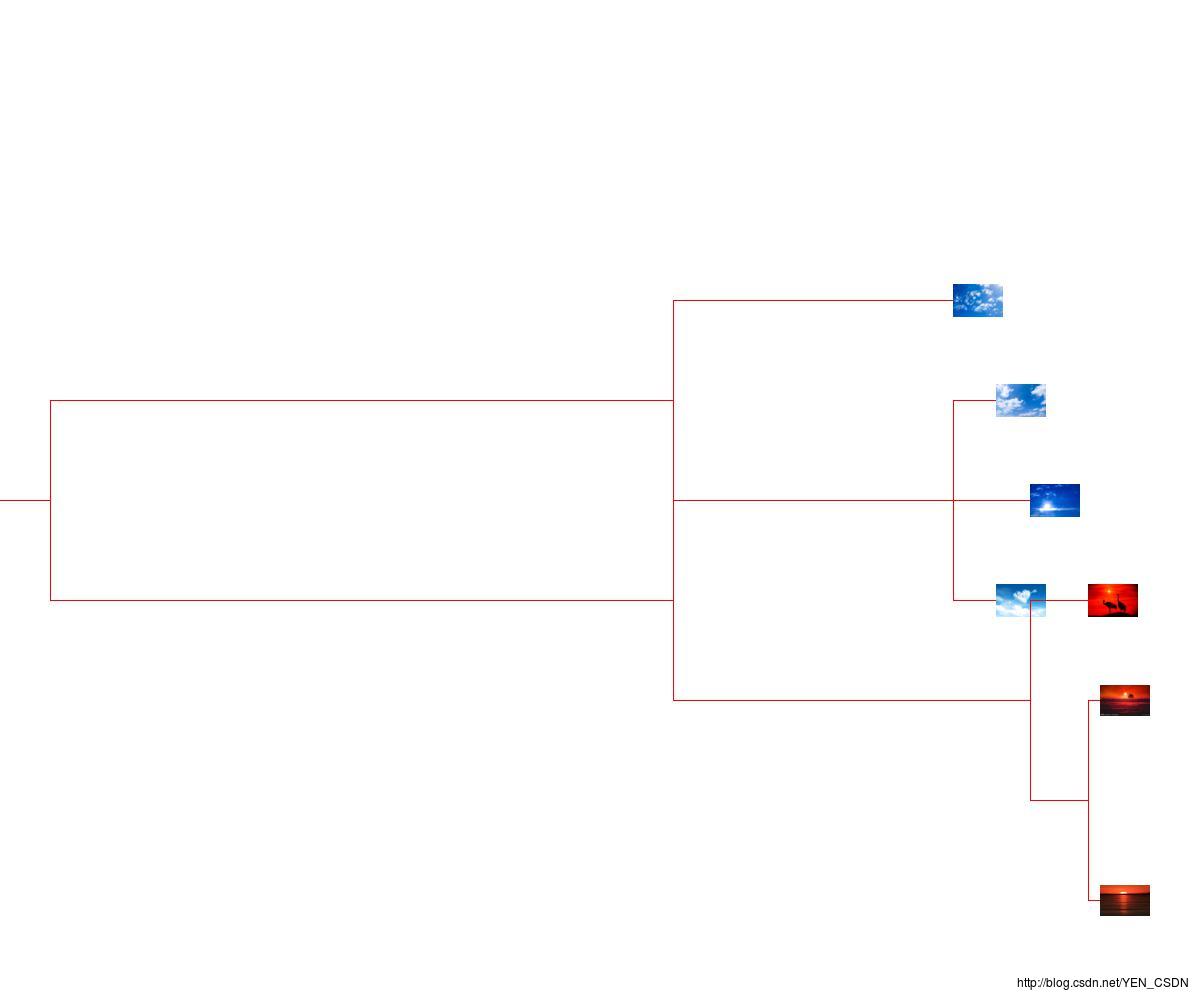
以上是关于机器学习-Hierarchical clustering 层次聚类算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章