从源码分析面试中经常出现的集合类问题
Posted JF Coder
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从源码分析面试中经常出现的集合类问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
从源码分析面试中经常出现的集合类问题
Collection接口
/* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Set
* @see List
* @see Map
* @see SortedSet
* @see SortedMap
* @see HashSet
* @see TreeSet
* @see ArrayList
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @see Collections
* @see Arrays
* @see AbstractCollection
* @since 1.2
集合层次结构中的根接口。集合表示一组对象,称为其元素。
一些集合允许重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。有些是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。
JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现:它提供了更多特定子接口的实现
*/
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
// Query Operations
/**
返回此集合中的元素数
*/
int size();
/**
如果此集合不包含任何元素,则返回<tt> true </ tt>
*/
boolean isEmpty();
...........
.........
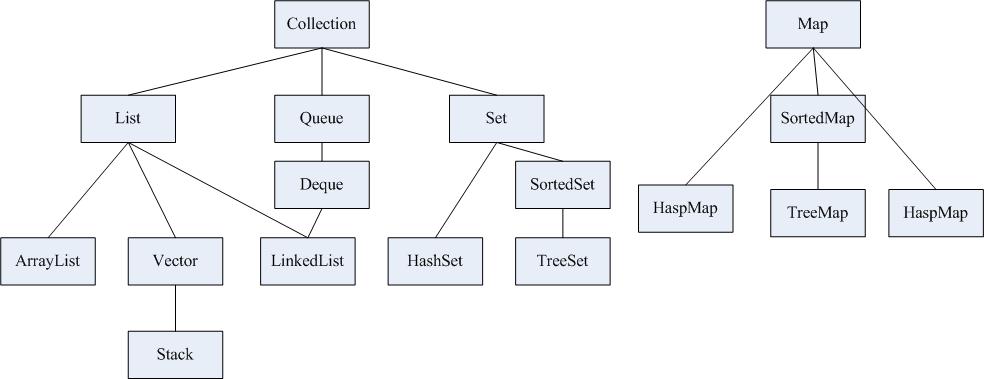
Collection接口是集合类的根接口,继承了Iterable接口,Java中没有直接提供Collection接口的实现类。但是却产生了两个接口,就是Set和List。Set中不能包含重复的元素。List是一个有序的集合,可以包含重复的元素,提供了按索引访问的方式。
List接口
1、List(有序、可重复)
List里存放的对象是有序的,同时也是可以重复的,List关注的是索引,拥有一系列和索引相关的方法,查询速度快。因为往list集合里插入或删除数据时,会伴随着后面数据的移动,所有插入删除数据速度慢。2、Set(无序、不能重复)
Set里存放的对象是无序,不能重复的,集合中的对象不按特定的方式排序,只是简单地把对象加入集合中。
/* @see Collection
* @see List
* @see SortedSet
* @see HashSet
* @see TreeSet
* @see AbstractSet
* @see Collections#singleton(java.lang.Object)
* @see Collections#EMPTY_SET
* @since 1.2
不包含重复元素的集合
*/
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E>
// Query Operations
/**
返回此集合中的元素数(其基数)
*/
int size();
/**
如果此集合不包含任何元素,则返回<tt> true </ tt>
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回<tt> true </ tt>
*/
boolean contains(Object o);
/**
返回此集合中元素的迭代器。 *元素以不特定的顺序返回(除非此集合是提供保证的某些*类的实例)。
*/
Iterator<E> iterator();
...........
.........
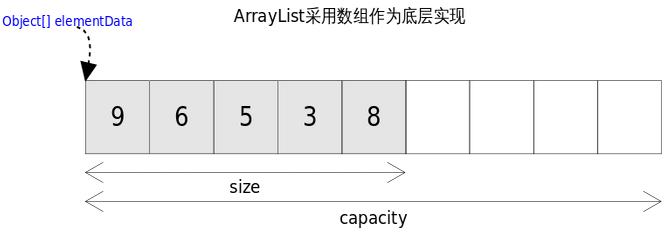
ArrayList(动态数组)
List接口的可调整大小的数组实现。实现所有可选的列表操作(实现了List的全部方法),并允许所有元素,包括null;
/* @see Collection
* @see List
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @since 1.2
List接口的可调整大小的数组实现。实现所有可选的列表操作,并允许所有元素,包括null。除了实现 List接口之外,此类还提供了一些方法来操纵内部用于存储列表的数组的大小
*/
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
默认初始容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
用于空实例的共享空数组实例
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = ;
/**
共享的空数组实例,用于默认大小的空实例。我们将其与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA区别开来,以了解添加第一个元素时需要充气多少
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = ;
/**
用于存储ArrayList元素的数组缓冲区。ArrayList的容量是此数组缓冲区的长度。添加第一个元素时,任何具有elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的空ArrayList都将扩展为DEFAULT_CAPACITY,
该elementData是真正存放元素的容器,可见ArrayList是基于数组实现的;
*/
transient Object[] elementData; //非私有,以简化嵌套类的访问
- ArrayList提供了三个构造方法
/** *构造一个具有指定初始容量的空列表。 @param initialCapacity列表的初始容量@如果指定的初始容量为负,则抛出IllegalArgumentException */
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
if (initialCapacity > 0)
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
else if (initialCapacity == 0)
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
/** *构造一个初始容量为10的空列表。 */
public ArrayList()
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
/**构造一个包含指定集合的元素的列表,其顺序由集合的迭代器返回。 @param c 要将其元素放入此列表的集合如果指定的集合为null,则抛出NullPointerException */
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0)
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
else
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
ArrayList扩容和add,set等方法
可见当初始化的list是一个空ArrayList的时候,会直接扩容到DEFAULT_CAPACITY,该值大小是一个默认值10。而当添加进ArrayList中的元素超过了数组能存放的最大值就会进行扩容。
/** ArrayList扩容
默认初始容量 DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10
*/
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity)
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
return minCapacity;
- get,add,set等方法
/** *返回此列表中指定位置的元素。@要返回的元素的索引索引 @返回此列表中指定位置的元素、@throws IndexOutOfBoundsException @inheritDoc */
public E get(int index)
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
/**
用指定的元素替换此列表中指定位置的元素。@param要替换元素的索引index @param要存储在指定位置的元素 @返回先前在指定位置的元素 @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException @inheritDoc
*/
public E set(int index, E element)
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
/**
将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾。@要附加到此列表的参数元素 @返回 true (由@link Collection#add指定)
*/
public boolean add(E e)
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
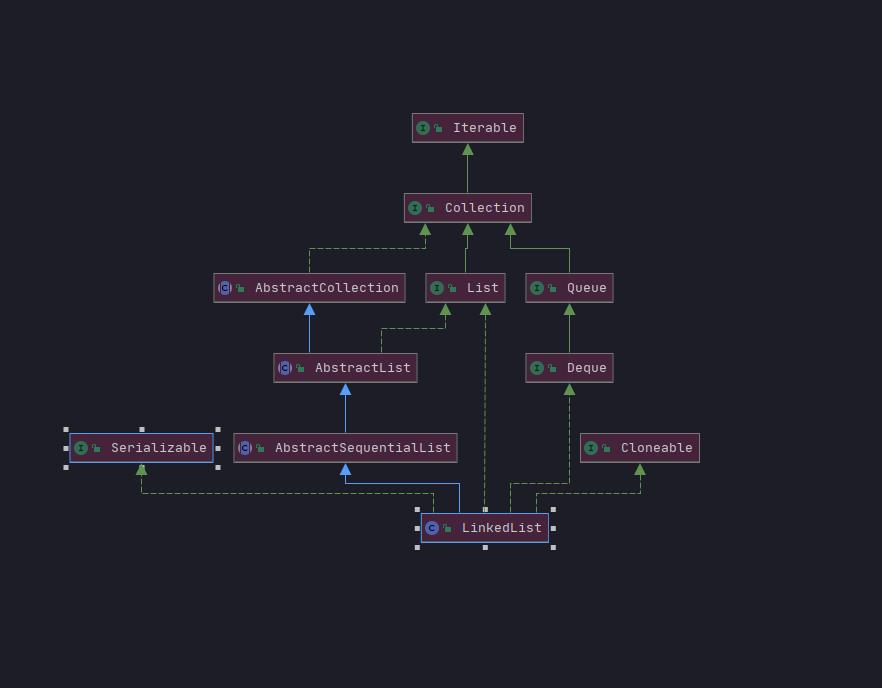
LinkedList(双向链表)
LinkedList是一种链表结构,从UML图可以看到,LinkList接口实现了Queue接口和List接口
-
进LinkList源码看看
List和Deque接口的双链列表实现。实现所有可选的列表操作(实现了List的全部方法),并允许所有元素(包括null)
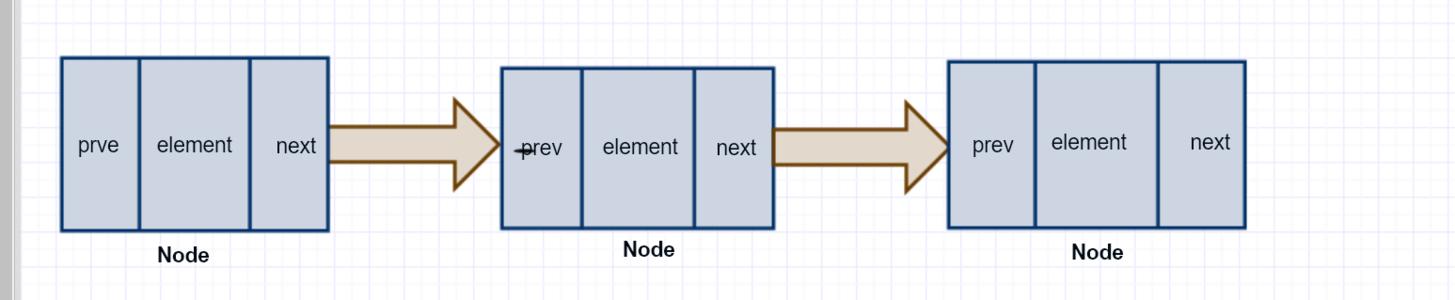
LinkedList由一个头节点和一个尾节点组成,分别指向链表的头部和尾部。
/** @code List和@code Deque接口的双链列表实现。实现所有可选的列表操作,
并允许所有元素(包括@code null)。
所有操作均按双链接列表的预期执行。索引到列表中的操作将从开头或结尾遍历列表,
以更接近指定索引的位置为准。
*/
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
transient int size = 0;
/**
指向第一个节点的指针
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
指向最后一个节点的指针
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
/**
构造一个空List
*/
public LinkedList()
/**
构造一个包含指定集合的元素的List,其顺序由集合的迭代器返回。
@param c 要将其元素放入此List的集合
如果指定的集合为null,则抛出NullPointerException
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c)
this();
addAll(c);
/** Node节点*/
private static class Node<E>
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next)
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
- 数据结构中链表的头插法linkFirst和尾插法linkLast
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e)
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ)
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
- LinkList的查询方法
/**
返回此列表中指定位置的元素,要遍历,找到节点才能拿到元素
*/
public E get(int index)
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
/**返回指定元素索引处的(非空)节点 */
Node<E> node(int index)
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1))
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
else
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
注意!ArrayList随机访问比LinkedList快的原因,LinkedList要遍历找到该位置才能进行修改,而ArrayList是内部数组操作会更快
- ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于链表的数据结构。
- 对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要遍历找节点。
- 对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。 这一点要看实际情况的。若只对单条数据插入或删除,ArrayList的速度反而优于LinkedList。但若是批量随机的插入删除数据,LinkedList的速度大大优于ArrayList. 因为ArrayList每插入一条数据,要移动插入点及之后的所有数据。
Vector
Vector类实现了对象的可增长数组。像数组一样,初始数组大小为10和ArrayList相同,它包含可以使用整数索引访问的组件。但是Vector的大小可以根据需要增大或缩小,以适应创建Vector之后的添加和删除项;
与新的集合实现不同,
Vector是同步的,线程安全的。如果不需要线程安全实现,建议使用 ArrayList代替 Vector,ArrayList是线程不安全的
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
/**
向量分量存储在其中的数组缓冲区。
向量的容量是此数组缓冲区的长度,
并且至少足够大以包含所有向量的元素。
Vector中最后一个元素之后的所有数组元素均为null
*/
protected Object[] elementData;
/**
此Vector对象中有效组件的数量
* @serial
*/
protected int elementCount;
/**
向量的容量在其大小大于其容量时自动增加的量。如果容量增量小于或等于零,
则向量的容量每次需要增长时都会加倍。
* @serial
*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
/** 使用JDK 1.0.2中的serialVersionUID来实现互操作性 */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
/**
使用指定的初始容量和容量增量构造一个空向量。 @param initialCapacity向量的初始容量
@param Capacity增大向量溢出时容量增加的数量
如果指定的初始容量为负,则抛出IllegalArgumentException
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
/**
构造一个具有指定初始容量和*容量增量等于零的空向量。
@param initialCapacity向量的初始容量
@如果指定的initialCapacity为负,则抛出IllegalArgumentException
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity)
this(initialCapacity, 0);
/**
构造一个空向量,以便其内部数据数组的大小为 10,并且其标准容量增量为零
*/
public Vector()
this(10);
/**
构造一个向量,该向量包含指定集合的元素,
并按集合的迭代器返回它们的顺序。
@param c 将元素放置在此向量中的集合
如果指定的集合为null,则抛出NullPointerException
*/
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c)
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
为什么Vector是线程安全的?
vector是线程同步的,所以它也是线程安全的,而arraylist是线程异步的,是不安全的。如果不考虑到线程的安全因素,一般用arraylist效率比较高
- 使用synchronized给方法加锁,达到线程安全的目的;
..........
public synchronized E get(int index)
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
public synchronized E set(int index, E element)
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
public synchronized boolean add(E e)
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
............
ArrayList是非线程安全的,Vector是线程安全的;
HashMap是非线程安全的,HashTable是线程安全的;
StringBuilder是非线程安全的,StringBuffer是线程安全的。
Vector和ArrayList扩容数组的区别
- ArrayList扩容数组1.5倍,扩容50%;
private void grow(int minCapacity)
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
- Vector扩容数组2倍,扩容100%;
private void grow(int minCapacity)
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
Set接口
Set里存放的对象是无序,不能重复的,集合中的对象不按特定的方式排序,只是简单地把对象加入集合中。
不包含重复元素的集合
HashSet(无序)
此类实现由散列表(实际上
是 HashMap 实例)支持的Set接口。它不保证集合的迭代顺序。特别是,它不能保证顺序会随时间保持不变。此类允许null 元素如果多个线程同时访问哈希集,并且线程中的至少一个修改了哈希集,则它必须 </ i> >从外部进行同步。 这通常是通过对自然封装了该集合的某个对象进行同步来完成的。 如果不存在这样的对象,则应使用Collections synchronized Set Collections.synchronizedSet 方法来“包装”该集合。最好在创建时完成此操作,以防止意外异步访问集合;(说明
Hashset线程不安全)
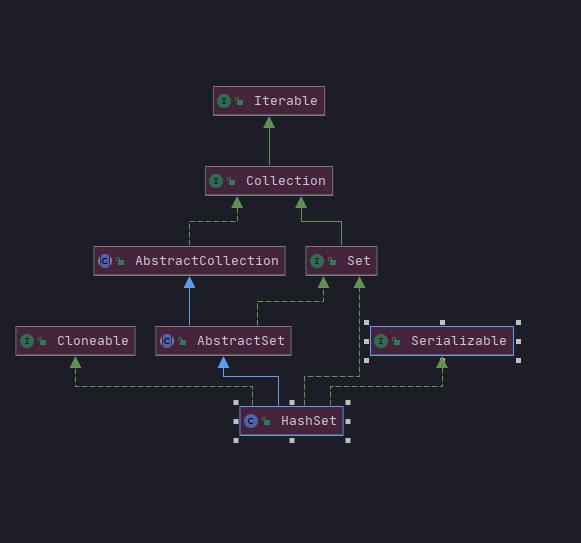
-
HashSet集合底层就是
HashMap(hashmap无序所以hashset也无序),基于二叉树的treemap,treeset有序
public class HashSet<E>
extends