Java数据结构与算法解析——B树
Posted 4K_WarCraft
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java数据结构与算法解析——B树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
B树简介
定义
在计算机科学中,B树(英语:B-tree)是一种自平衡的树,能够保持数据有序。这种数据结构能够让查找数据、顺序访问、插入数据及删除的动作,都在对数时间内完成。
特点
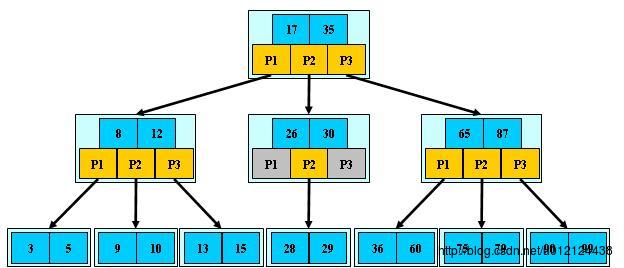
阶为M的B树是一颗具有以下特点的树:
1.数据项存储在树叶上
2.非叶子节点直到M-1个关键字以指示搜索的方向:关键字i代表子树i+1中最小的关键字
3.树的根或者是一片树叶,或者其儿子在2和M之间
4.除根外,所有非树叶节点的儿子数在M/2和M之间。
5.所有的树叶都在相同的深度上并有L/2和L之间个数据项
例如:(M=3)
查找和插入
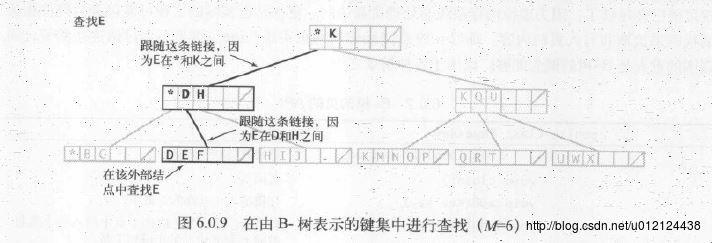
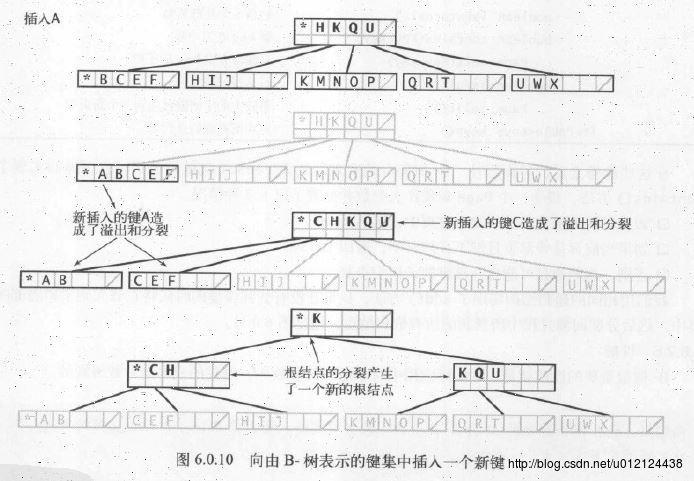
为了方便这里用了一个特殊的哨兵键,它小于其他所有键,用*表示。
一开始B树只含有一个根结点,而根结点在初始化时仅含有该哨兵键。
内部结点中的每个键都与一个结点相关联,以此结点为根的子树种,所有的键都大于等于与此结点关联的键,但小于其他所有键。
B树的实现
public class BTree2<K, V>
private static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(BTree.class);
/**
* B树节点中的键值对。
* <p/>
* B树的节点中存储的是键值对。
* 通过键访问值。
*
* @param <K> - 键类型
* @param <V> - 值类型
*/
private static class Entry<K, V>
private K key;
private V value;
public Entry(K k, V v)
this.key = k;
this.value = v;
public K getKey()
return key;
public V getValue()
return value;
public void setValue(V value)
this.value = value;
@Override
public String toString()
return key + ":" + value;
/**
* 在B树节点中搜索给定键值的返回结果。
* <p/>
* 该结果有两部分组成。第一部分表示此次查找是否成功,
* 如果查找成功,第二部分表示给定键值在B树节点中的位置,
* 如果查找失败,第二部分表示给定键值应该插入的位置。
*/
private static class SearchResult<V>
private boolean exist;
private int index;
private V value;
public SearchResult(boolean exist, int index)
this.exist = exist;
this.index = index;
public SearchResult(boolean exist, int index, V value)
this(exist, index);
this.value = value;
public boolean isExist()
return exist;
public int getIndex()
return index;
public V getValue()
return value;
/**
* B树中的节点。
*
* TODO 需要考虑并发情况下的存取。
*/
private static class BTreeNode<K, V>
/** 节点的项,按键非降序存放 */
private List<Entry<K,V>> entrys;
/** 内节点的子节点 */
private List<BTreeNode<K, V>> children;
/** 是否为叶子节点 */
private boolean leaf;
/** 键的比较函数对象 */
private Comparator<K> kComparator;
private BTreeNode()
entrys = new ArrayList<Entry<K, V>>();
children = new ArrayList<BTreeNode<K, V>>();
leaf = false;
public BTreeNode(Comparator<K> kComparator)
this();
this.kComparator = kComparator;
public boolean isLeaf()
return leaf;
public void setLeaf(boolean leaf)
this.leaf = leaf;
/**
* 返回项的个数。如果是非叶子节点,根据B树的定义,
* 该节点的子节点个数为(@link #size() + 1)。
*
* @return 关键字的个数
*/
public int size()
return entrys.size();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
int compare(K key1, K key2)
return kComparator == null ? ((Comparable<K>)key1).compareTo(key2) : kComparator.compare(key1, key2);
/**
* 在节点中查找给定的键。
* 如果节点中存在给定的键,则返回一个<code>SearchResult</code>,
* 标识此次查找成功,给定的键在节点中的索引和给定的键关联的值;
* 如果不存在,则返回<code>SearchResult</code>,
* 标识此次查找失败,给定的键应该插入的位置,该键的关联值为null。
* <p/>
* 如果查找失败,返回结果中的索引域为[0, @link #size()];
* 如果查找成功,返回结果中的索引域为[0, @link #size() - 1]
* <p/>
* 这是一个二分查找算法,可以保证时间复杂度为O(log(t))。
*
* @param key - 给定的键值
* @return - 查找结果
*/
public SearchResult<V> searchKey(K key)
int low = 0;
int high = entrys.size() - 1;
int mid = 0;
while(low <= high)
mid = (low + high) / 2; // 先这么写吧,BTree实现中,l+h不可能溢出
Entry<K, V> entry = entrys.get(mid);
if(compare(entry.getKey(), key) == 0) // entrys.get(mid).getKey() == key
break;
else if(compare(entry.getKey(), key) > 0) // entrys.get(mid).getKey() > key
high = mid - 1;
else // entry.get(mid).getKey() < key
low = mid + 1;
boolean result = false;
int index = 0;
V value = null;
if(low <= high) // 说明查找成功
result = true;
index = mid; // index表示元素所在的位置
value = entrys.get(index).getValue();
else
result = false;
index = low; // index表示元素应该插入的位置
return new SearchResult<V>(result, index, value);
/**
* 将给定的项追加到节点的末尾,
* 你需要自己确保调用该方法之后,节点中的项还是
* 按照关键字以非降序存放。
*
* @param entry - 给定的项
*/
public void addEntry(Entry<K, V> entry)
entrys.add(entry);
/**
* 删除给定索引的<code>entry</code>。
* <p/>
* 你需要自己保证给定的索引是合法的。
*
* @param index - 给定的索引
* @param 给定索引处的项
*/
public Entry<K, V> removeEntry(int index)
return entrys.remove(index);
/**
* 得到节点中给定索引的项。
* <p/>
* 你需要自己保证给定的索引是合法的。
*
* @param index - 给定的索引
* @return 节点中给定索引的项
*/
public Entry<K, V> entryAt(int index)
return entrys.get(index);
/**
* 如果节点中存在给定的键,则更新其关联的值。
* 否则插入。
*
* @param entry - 给定的项
* @return null,如果节点之前不存在给定的键,否则返回给定键之前关联的值
*/
public V putEntry(Entry<K, V> entry)
SearchResult<V> result = searchKey(entry.getKey());
if(result.isExist())
V oldValue = entrys.get(result.getIndex()).getValue();
entrys.get(result.getIndex()).setValue(entry.getValue());
return oldValue;
else
insertEntry(entry, result.getIndex());
return null;
/**
* 在该节点中插入给定的项,
* 该方法保证插入之后,其键值还是以非降序存放。
* <p/>
* 不过该方法的时间复杂度为O(t)。
* <p/>
* <b>注意:</b>B树中不允许键值重复。
*
* @param entry - 给定的键值
* @return true,如果插入成功,false,如果插入失败
*/
public boolean insertEntry(Entry<K, V> entry)
SearchResult<V> result = searchKey(entry.getKey());
if(result.isExist())
return false;
else
insertEntry(entry, result.getIndex());
return true;
/**
* 在该节点中给定索引的位置插入给定的项,
* 你需要自己保证项插入了正确的位置。
*
* @param key - 给定的键值
* @param index - 给定的索引
*/
public void insertEntry(Entry<K, V> entry, int index)
/*
* 通过新建一个ArrayList来实现插入真的很恶心,先这样吧
* 要是有类似C中的reallocate就好了。
*/
List<Entry<K, V>> newEntrys = new ArrayList<Entry<K, V>>();
int i = 0;
// index = 0或者index = keys.size()都没有问题
for(; i < index; ++ i)
newEntrys.add(entrys.get(i));
newEntrys.add(entry);
for(; i < entrys.size(); ++ i)
newEntrys.add(entrys.get(i));
entrys.clear();
entrys = newEntrys;
/**
* 返回节点中给定索引的子节点。
* <p/>
* 你需要自己保证给定的索引是合法的。
*
* @param index - 给定的索引
* @return 给定索引对应的子节点
*/
public BTreeNode<K, V> childAt(int index)
if(isLeaf())
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Leaf node doesn't have children.");
return children.get(index);
/**
* 将给定的子节点追加到该节点的末尾。
*
* @param child - 给定的子节点
*/
public void addChild(BTreeNode<K, V> child)
children.add(child);
/**
* 删除该节点中给定索引位置的子节点。
* </p>
* 你需要自己保证给定的索引是合法的。
*
* @param index - 给定的索引
*/
public void removeChild(int index)
children.remove(index);
/**
* 将给定的子节点插入到该节点中给定索引
* 的位置。
*
* @param child - 给定的子节点
* @param index - 子节点带插入的位置
*/
public void insertChild(BTreeNode<K, V> child, int index)
List<BTreeNode<K, V>> newChildren = new ArrayList<BTreeNode<K, V>>();
int i = 0;
for(; i < index; ++ i)
newChildren.add(children.get(i));
newChildren.add(child);
for(; i < children.size(); ++ i)
newChildren.add(children.get(i));
children = newChildren;
private static final int DEFAULT_T = 2;
/** B树的根节点 */
private BTreeNode<K, V> root;
/** 根据B树的定义,B树的每个非根节点的关键字数n满足(t - 1) <= n <= (2t - 1) */
private int t = DEFAULT_T;
/** 非根节点中最小的键值数 */
private int minKeySize = t - 1;
/** 非根节点中最大的键值数 */
private int maxKeySize = 2*t - 1;
/** 键的比较函数对象 */
private Comparator<K> kComparator;
/**
* 构造一颗B树,键值采用采用自然排序方式
*/
public BTree()
root = new BTreeNode<K, V>();
root.setLeaf(true);
public BTree(int t)
this();
this.t = t;
minKeySize = t - 1;
maxKeySize = 2*t - 1;
/**
* 以给定的键值比较函数对象构造一颗B树。
*
* @param kComparator - 键值的比较函数对象
*/
public BTree(Comparator<K> kComparator)
root = new BTreeNode<K, V>(kComparator);
root.setLeaf(true);
this.kComparator = kComparator;
public BTree(Comparator<K> kComparator, int t)
this(kComparator);
this.t = t;
minKeySize = t - 1;
maxKeySize = 2*t - 1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
int compare(K key1, K key2)
return kComparator == null ? ((Comparable<K>)key1).compareTo(key2) : kComparator.compare(key1, key2);
/**
* 搜索给定的键。
*
* @param key - 给定的键值
* @return 键关联的值,如果存在,否则null
*/
public V search(K key)
return search(root, key);
/**
* 在以给定节点为根的子树中,递归搜索
* 给定的<code>key</code>
*
* @param node - 子树的根节点
* @param key - 给定的键值
* @return 键关联的值,如果存在,否则null
*/
private V search(BTreeNode<K, V> node, K key)
SearchResult<V> result = node.searchKey(key);
if(result.isExist())
return result.getValue();
else
if(node.isLeaf())
return null;
else
search(node.childAt(result.getIndex()), key);
return null;
/**
* 分裂一个满子节点<code>childNode</code>。
* <p/>
* 你需要自己保证给定的子节点是满节点。
*
* @param parentNode - 父节点
* @param childNode - 满子节点
* @param index - 满子节点在父节点中的索引
*/
private void splitNode(BTreeNode<K, V> parentNode, BTreeNode<K, V> childNode, int index)
assert childNode.size() == maxKeySize;
BTreeNode<K, V> siblingNode = new BTreeNode<K, V>(kComparator);
siblingNode.setLeaf(childNode.isLeaf());
// 将满子节点中索引为[t, 2t - 2]的(t - 1)个项插入新的节点中
for(int i = 0; i < minKeySize; ++ i)
siblingNode.addEntry(childNode.entryAt(t + i));
// 提取满子节点中的中间项,其索引为(t - 1)
Entry<K, V> entry = childNode.entryAt(t - 1);
// 删除满子节点中索引为[t - 1, 2t - 2]的t个项
for(int i = maxKeySize - 1; i >= t - 1; -- i)
childNode.removeEntry(i);
if(!childNode.isLeaf()) // 如果满子节点不是叶节点,则还需要处理其子节点
// 将满子节点中索引为[t, 2t - 1]的t个子节点插入新的节点中
for(int i = 0; i < minKeySize + 1; ++ i)
siblingNode.addChild(childNode.childAt(t + i));
// 删除满子节点中索引为[t, 2t - 1]的t个子节点
for(int i = maxKeySize; i >= t; -- i)
childNode.removeChild(i);
// 将entry插入父节点
parentNode.insertEntry(entry, index);
// 将新节点插入父节点
parentNode.insertChild(siblingNode, index + 1);
/**
* 在一个非满节点中插入给定的项。
*
* @param node - 非满节点
* @param entry - 给定的项
* @return true,如果B树中不存在给定的项,否则false
*/
private boolean insertNotFull(BTreeNode<K, V> node, Entry<K, V> entry)
assert node.size() < maxKeySize;
if(node.isLeaf()) // 如果是叶子节点,直接插入
return node.insertEntry(entry);
else
/* 找到entry在给定节点应该插入的位置,那么entry应该插入
* 该位置对应的子树中
*/
SearchResult<V> result = node.searchKey(entry.getKey());
// 如果存在,则直接返回失败
if(result.isExist())
return false;
BTreeNode<K, V> childNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex());
if(childNode.size() == 2*t - 1) // 如果子节点是满节点
// 则先分裂
splitNode(node, childNode, result.getIndex());
/* 如果给定entry的键大于分裂之后新生成项的键,则需要插入该新项的右边,
* 否则左边。
*/
if(compare(entry.getKey(), node.entryAt(result.getIndex()).getKey()) > 0)
childNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex() + 1);
return insertNotFull(childNode, entry);
/**
* 在B树中插入给定的键值对。
*
* @param key - 键
* @param value - 值
* @param true,如果B树中不存在给定的项,否则false
*/
public boolean insert(K key, V value)
if(root.size() == maxKeySize) // 如果根节点满了,则B树长高
BTreeNode<K, V> newRoot = new BTreeNode<K, V>(kComparator);
newRoot.setLeaf(false);
newRoot.addChild(root);
splitNode(newRoot, root, 0);
root = newRoot;
return insertNotFull(root, new Entry<K, V>(key, value));
/**
* 如果存在给定的键,则更新键关联的值,
* 否则插入给定的项。
*
* @param node - 非满节点
* @param entry - 给定的项
* @return true,如果B树中不存在给定的项,否则false
*/
private V putNotFull(BTreeNode<K, V> node, Entry<K, V> entry)
assert node.size() < maxKeySize;
if(node.isLeaf()) // 如果是叶子节点,直接插入
return node.putEntry(entry);
else
/* 找到entry在给定节点应该插入的位置,那么entry应该插入
* 该位置对应的子树中
*/
SearchResult<V> result = node.searchKey(entry.getKey());
// 如果存在,则更新
if(result.isExist())
return node.putEntry(entry);
BTreeNode<K, V> childNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex());
if(childNode.size() == 2*t - 1) // 如果子节点是满节点
// 则先分裂
splitNode(node, childNode, result.getIndex());
/* 如果给定entry的键大于分裂之后新生成项的键,则需要插入该新项的右边,
* 否则左边。
*/
if(compare(entry.getKey(), node.entryAt(result.getIndex()).getKey()) > 0)
childNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex() + 1);
return putNotFull(childNode, entry);
/**
* 如果B树中存在给定的键,则更新值。
* 否则插入。
*
* @param key - 键
* @param value - 值
* @return 如果B树中存在给定的键,则返回之前的值,否则null
*/
public V put(K key, V value)
if(root.size() == maxKeySize) // 如果根节点满了,则B树长高
BTreeNode<K, V> newRoot = new BTreeNode<K, V>(kComparator);
newRoot.setLeaf(false);
newRoot.addChild(root);
splitNode(newRoot, root, 0);
root = newRoot;
return putNotFull(root, new Entry<K, V>(key, value));
/**
* 从B树中删除一个与给定键关联的项。
*
* @param key - 给定的键
* @return 如果B树中存在给定键关联的项,则返回删除的项,否则null
*/
public Entry<K, V> delete(K key)
return delete(root, key);
/**
* 从以给定<code>node</code>为根的子树中删除与给定键关联的项。
* <p/>
* 删除的实现思想请参考《算法导论》第二版的第18章。
*
* @param node - 给定的节点
* @param key - 给定的键
* @return 如果B树中存在给定键关联的项,则返回删除的项,否则null
*/
private Entry<K, V> delete(BTreeNode<K, V> node, K key)
// 该过程需要保证,对非根节点执行删除操作时,其关键字个数至少为t。
assert node.size() >= t || node == root;
SearchResult<V> result = node.searchKey(key);
/*
* 因为这是查找成功的情况,0 <= result.getIndex() <= (node.size() - 1),
* 因此(result.getIndex() + 1)不会溢出。
*/
if(result.isExist())
// 1.如果关键字在节点node中,并且是叶节点,则直接删除。
if(node.isLeaf())
return node.removeEntry(result.getIndex());
else
// 2.a 如果节点node中前于key的子节点包含至少t个项
BTreeNode<K, V> leftChildNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex());
if(leftChildNode.size() >= t)
// 使用leftChildNode中的最后一个项代替node中需要删除的项
node.removeEntry(result.getIndex());
node.insertEntry(leftChildNode.entryAt(leftChildNode.size() - 1), result.getIndex());
// 递归删除左子节点中的最后一个项
return delete(leftChildNode, leftChildNode.entryAt(leftChildNode.size() - 1).getKey());
else
// 2.b 如果节点node中后于key的子节点包含至少t个关键字
BTreeNode<K, V> rightChildNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex() + 1);
if(rightChildNode.size() >= t)
// 使用rightChildNode中的第一个项代替node中需要删除的项
node.removeEntry(result.getIndex());
node.insertEntry(rightChildNode.entryAt(0), result.getIndex());
// 递归删除右子节点中的第一个项
return delete(rightChildNode, rightChildNode.entryAt(0).getKey());
else // 2.c 前于key和后于key的子节点都只包含t-1个项
Entry<K, V> deletedEntry = node.removeEntry(result.getIndex());
node.removeChild(result.getIndex() + 1);
// 将node中与key关联的项和rightChildNode中的项合并进leftChildNode
leftChildNode.addEntry(deletedEntry);
for(int i = 0; i < rightChildNode.size(); ++ i)
leftChildNode.addEntry(rightChildNode.entryAt(i));
// 将rightChildNode中的子节点合并进leftChildNode,如果有的话
if(!rightChildNode.isLeaf())
for(int i = 0; i <= rightChildNode.size(); ++ i)
leftChildNode.addChild(rightChildNode.childAt(i));
return delete(leftChildNode, key);
else
/*
* 因为这是查找失败的情况,0 <= result.getIndex() <= node.size(),
* 因此(result.getIndex() + 1)会溢出。
*/
if(node.isLeaf()) // 如果关键字不在节点node中,并且是叶节点,则什么都不做,因为该关键字不在该B树中
logger.info("The key: " + key + " isn't in this BTree.");
return null;
BTreeNode<K, V> childNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex());
if(childNode.size() >= t) // // 如果子节点有不少于t个项,则递归删除
return delete(childNode, key);
else // 3
// 先查找右边的兄弟节点
BTreeNode<K, V> siblingNode = null;
int siblingIndex = -1;
if(result.getIndex() < node.size()) // 存在右兄弟节点
if(node.childAt(result.getIndex() + 1).size() >= t)
siblingNode = node.childAt(result.getIndex() + 1);
siblingIndex = result.getIndex() + 1;
// 如果右边的兄弟节点不符合条件,则试试左边的兄弟节点
if(siblingNode == null)
if(result.getIndex() > 0)