EDA常用模块 奇数分频 偶数分频 冒泡排序
Posted 海绵小青年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了EDA常用模块 奇数分频 偶数分频 冒泡排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、分频
1、偶数分频
.v文件
module FenPin (
input clk,
input rst,
output wire clk_10k
);
parameter f=8; //即为偶分频的分频数
reg [11:0] count=0; //存储分频计数
reg clk_10k_tmp=0;
assign clk_10k = clk_10k_tmp;
// 复位信号rst低电平有效
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if (!rst)
begin
clk_10k_tmp = 0;
count = 0;
end
else
begin
if (count == f/2-1) //偶分频数/2 - 1
begin
clk_10k_tmp = ~clk_10k_tmp;
count = 0;
end
else
begin
count = count + 1;
end
end
end
endmodule
测试文件
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module FenPin_vlg_tst();
reg clk;
reg rst;
wire clk_10k;
FenPin i1 (
.clk(clk),
.clk_10k(clk_10k),
.rst(rst)
);
initial
begin
rst=1; //模拟复位信号按下
#20 rst=0;
#20 rst=1;
#8000 $stop;
end
always
begin
#50 clk=1;
#50 clk=0;
end
endmodule
仿真结果
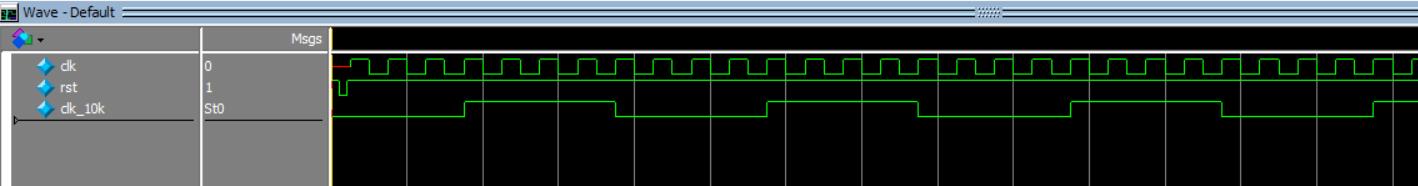
2、奇数分频
.v文件
module FenPin(clkout,clk,rst);
input clk,rst;
output clkout;
parameter f=9; //即为奇分频分频数
reg [9:0] counter1, counter2;
reg clkp1, clkp2;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst) // counter1自动计数
begin
if (~rst)
counter1<=0;
else
if (counter1==f-1)
counter1<=0;
else
counter1<=counter1+1;
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) // clk上升沿触发产生p1
begin
if(~rst)
clkp1<=0;
else
if(counter1==(f-1)/2 || counter1==f-1)
clkp1<=~clkp1;
end
always @(negedge clk or negedge rst)//counter2自动计数
begin
if(~rst)
counter2<=0;
else
if(counter2==f-1)
counter2<=0;
else
counter2<=counter1+1;
end
always @(negedge clk or negedge rst)//clk下降触发产生p2
begin
if(~rst)
clkp2<=0;
else
begin
if(counter2==(f-1)/2||counter2==f-1)
clkp2<=~clkp2;
end
end
assign clkout=clkp1|clkp2; //p1|p2使占空比等于50%
endmodule
测试文件
`timescale 1 ps/ 1 ps
module FenPin_vlg_tst();
reg clk;
reg rst;
wire clkout;
FenPin i1 (
.clk(clk),
.clkout(clkout),
.rst(rst)
);
initial
begin
rst=1; //模拟复位信号按下
#20 rst=0;
#20 rst=1;
#8000 $stop;
end
always
begin
#50 clk=1;
#50 clk=0;
end
endmodule
仿真结果
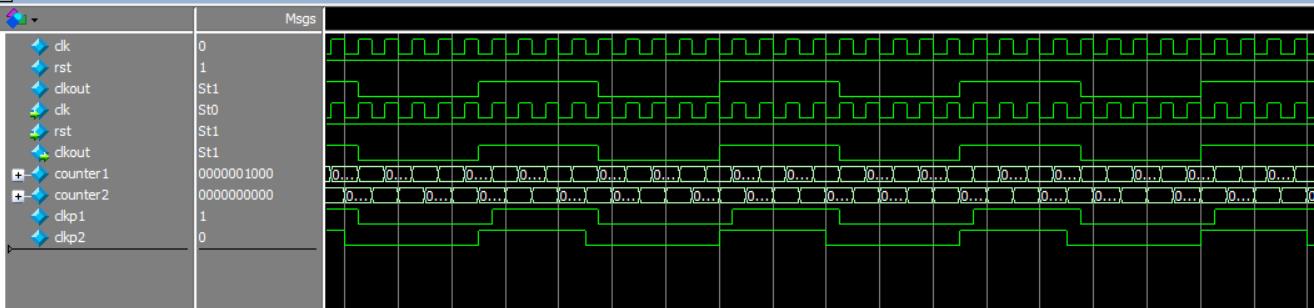
二、其他功能
1. 冒泡排序
代码
module pop(
input clk,
input rst,
input [3:0]data_in,
output reg[2:0]state,
output reg[3:0]data_out
);
reg[3:0] i,p;//计数器
reg[3:0]content[7:0];
initial
begin
state<=0;
i<=0;
p<=7;
end
always@(posedge clk or posedge rst )
begin
if(rst)begin state<=0;data_out<=0;i<=0;p<=7;end
else begin
case(state)
3'b000:begin//读取数据
content[i]=data_in;
i=i+1;
if(i==8)begin i<=0;state<=3'b001;end
end //000
3'b001:begin//冒泡排序
if(i<p) begin
if(content[i]<content[i+1])begin //如果当前位置比后面小则对调
content[i+1]<=content[i];
content[i]<= content[i+1];
end
i<=i+1;
end
else begin
i<=0; p<=p-1;
end
if (p==0&&i==0) state<=3'b010;
end//001
3'b010:begin //发送数据
data_out=content[i];
i=i+1;
if(i==8) begin i=0; state=3'b011; end
end
3'b011:begin//延时一段时间
i=i+1;
if(i==15)begin i=0;state=0;end
end//011
endcase
end//else
end//always
endmodule
测试文件
//测试文件:
`timescale 1 ns/ 1 ps
module pop_vlg_tst();
reg clk;
reg [3:0] data_in;
reg rst;
wire [3:0] data_out;
wire [2:0] state;
// assign statements (if any)
pop i1 (
.clk(clk),
.data_in(data_in),
.data_out(data_out),
.rst(rst),
.state(state)
);
initial
begin
clk=0;
#100
rst=1;
#30
rst=0;
forever #5 clk=~clk;
end
initial
begin
#130
while(1)
begin
data_in=7;
#10
data_in=5;
#10
data_in=8;
#10
data_in=11;
#10
data_in=12;
#10
data_in=14;
#10
data_in=15;
#10
data_in=9;
#1000
rst=1;
#30
rst=0;
end
end
endmodule
以上是关于EDA常用模块 奇数分频 偶数分频 冒泡排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章