10种优雅的MyBatis写法,同事用了都说好
Posted Javatutouhouduan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了10种优雅的MyBatis写法,同事用了都说好相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
用来循环容器的标签forEach,查看例子
foreach元素的属性主要有item,index,collection,open,separator,close。
-
item:集合中元素迭代时的别名,
-
index:集合中元素迭代时的索引
-
open:常用语where语句中,表示以什么开始,比如以'('开始
-
separator:表示在每次进行迭代时的分隔符,
-
close 常用语where语句中,表示以什么结束,
在使用foreach的时候最关键的也是最容易出错的就是collection属性,该属性是必须指定的,但是在不同情况下,该属性的值是不一样的,主要有一下3种情况:
-
如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个List的时候,collection属性值为list .
-
如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个array数组的时候,collection的属性值为array .
-
如果传入的参数是多个的时候,我们就需要把它们封装成一个Map了,当然单参数也可以封装成map,实际上如果你在传入参数的时候,在MyBatis里面也是会把它封装成一个Map的,map的key就是参数名,所以这个时候collection属性值就是传入的List或array对象在自己封装的map里面的key.
针对最后一条,我们来看一下官方说法:
注意 你可以将一个 List 实例或者数组作为参数对象传给 MyBatis,当你这么做的时候,MyBatis 会自动将它包装在一个 Map 中并以名称为键。List 实例将会以“list”作为键,而数组实例的键将是“array”。
所以,不管是多参数还是单参数的list,array类型,都可以封装为map进行传递。如果传递的是一个List,则mybatis会封装为一个list为key,list值为object的map,如果是array,则封装成一个array为key,array的值为object的map,如果自己封装呢,则colloection里放的是自己封装的map里的key值
//mapper中我们要为这个方法传递的是一个容器,将容器中的元素一个一个的
//拼接到xml的方法中就要使用这个forEach这个标签了
public List<Entity> queryById(List<String> userids);
//对应的xml中如下
<select id="queryById" resultMap="BaseReslutMap" >
select * FROM entity
where id in
<foreach collection="userids" item="userid" index="index" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#userid
</foreach>
</select>
concat模糊查询
//比如说我们想要进行条件查询,但是几个条件不是每次都要使用,那么我们就可以
//通过判断是否拼接到sql中
<select id="queryById" resultMap="BascResultMap" parameterType="entity">
SELECT * from entity
<where>
<if test="name!=null">
name like concat('%',concat(#name,'%'))
</if>
</where>
</select>
choose (when, otherwise)标签
choose标签是按顺序判断其内部when标签中的test条件出否成立,如果有一个成立,则 choose 结束。当 choose 中所有 when 的条件都不满则时,则执行 otherwise 中的sql。类似于Java 的 switch 语句,choose 为 switch,when 为 case,otherwise 则为 default。
例如下面例子,同样把所有可以限制的条件都写上,方面使用。choose会从上到下选择一个when标签的test为true的sql执行。安全考虑,我们使用where将choose包起来,放置关键字多于错误。
<!-- choose(判断参数) - 按顺序将实体类 User 第一个不为空的属性作为:where条件 -->
<select id="getUserList_choose" resultMap="resultMap_user" parameterType="com.yiibai.pojo.User">
SELECT *
FROM User u
<where>
<choose>
<when test="username !=null ">
u.username LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #username, jdbcType=VARCHAR),'%')
</when >
<when test="sex != null and sex != '' ">
AND u.sex = #sex, jdbcType=INTEGER
</when >
<when test="birthday != null ">
AND u.birthday = #birthday, jdbcType=DATE
</when >
<otherwise>
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
selectKey 标签
在insert语句中,在Oracle经常使用序列、在mysql中使用函数来自动生成插入表的主键,而且需要方法能返回这个生成主键。使用myBatis的selectKey标签可以实现这个效果。
下面例子,使用mysql数据库自定义函数nextval('student'),用来生成一个key,并把他设置到传入的实体类中的studentId属性上。所以在执行完此方法后,边可以通过这个实体类获取生成的key。
<!-- 插入学生 自动主键-->
<insert id="createStudentAutoKey" parameterType="liming.student.manager.data.model.StudentEntity" keyProperty="studentId">
<selectKey keyProperty="studentId" resultType="String" order="BEFORE">
select nextval('student')
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO STUDENT_TBL(STUDENT_ID,
STUDENT_NAME,
STUDENT_SEX,
STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
STUDENT_PHOTO,
CLASS_ID,
PLACE_ID)
VALUES (#studentId,
#studentName,
#studentSex,
#studentBirthday,
#studentPhoto, javaType=byte[], jdbcType=BLOB, typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.BlobTypeHandler,
#classId,
#placeId)
</insert>
调用接口方法,和获取自动生成key
StudentEntity entity = new StudentEntity();
entity.setStudentName("黎明你好");
entity.setStudentSex(1);
entity.setStudentBirthday(DateUtil.parse("1985-05-28"));
entity.setClassId("20000001");
entity.setPlaceId("70000001");
this.dynamicSqlMapper.createStudentAutoKey(entity);
System.out.println("新增学生ID: " + entity.getStudentId());
if标签
if标签可用在许多类型的sql语句中,我们以查询为例。首先看一个很普通的查询:
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名 -->
<select id="getStudentListLikeName" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #studentName),'%')
</select>
但是此时如果studentName为null,此语句很可能报错或查询结果为空。此时我们使用if动态sql语句先进行判断,如果值为null或等于空字符串,我们就不进行此条件的判断,增加灵活性。
参数为实体类StudentEntity。将实体类中所有的属性均进行判断,如果不为空则执行判断条件。
<!-- 2 if(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性作为where条件 -->
<select id="getStudentList_if" resultMap="resultMap_studentEntity" parameterType="liming.student.manager.data.model.StudentEntity">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.STUDENT_PHOTO,
ST.CLASS_ID,
ST.PLACE_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE
<if test="studentName !=null ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR),'%')
</if>
<if test="studentSex != null and studentSex != '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #studentSex, jdbcType=INTEGER
</if>
<if test="studentBirthday != null ">
AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #studentBirthday, jdbcType=DATE
</if>
<if test="classId != null and classId!= '' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="classEntity != null and classEntity.classId !=null and classEntity.classId !=' ' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #classEntity.classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="placeId != null and placeId != '' ">
AND ST.PLACE_ID = #placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="placeEntity != null and placeEntity.placeId != null and placeEntity.placeId != '' ">
AND ST.PLACE_ID = #placeEntity.placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="studentId != null and studentId != '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_ID = #studentId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
</select>
使用时比较灵活, new一个这样的实体类,我们需要限制那个条件,只需要附上相应的值就会where这个条件,相反不去赋值就可以不在where中判断。
public void select_test_2_1()
StudentEntity entity = new StudentEntity();
entity.setStudentName("");
entity.setStudentSex(1);
entity.setStudentBirthday(DateUtil.parse("1985-05-28"));
entity.setClassId("20000001");
//entity.setPlaceId("70000001");
List<StudentEntity> list = this.dynamicSqlMapper.getStudentList_if(entity);
for (StudentEntity e : list)
System.out.println(e.toString());
if + where 的条件判断
当where中的条件使用的if标签较多时,这样的组合可能会导致错误。我们以在3.1中的查询语句为例子,当java代码按如下方法调用时:
@Test
public void select_test_2_1()
StudentEntity entity = new StudentEntity();
entity.setStudentName(null);
entity.setStudentSex(1);
List<StudentEntity> list = this.dynamicSqlMapper.getStudentList_if(entity);
for (StudentEntity e : list)
System.out.println(e.toString());
如果上面例子,参数studentName为null,将不会进行STUDENT_NAME列的判断,则会直接导“WHERE AND”关键字多余的错误SQL。
这时我们可以使用where动态语句来解决。这个“where”标签会知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个‘where’。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或OR 开头的,则它会剔除掉。
上面例子修改为:
<!-- 3 select - where/if(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性作为where条件 -->
<select id="getStudentList_whereIf" resultMap="resultMap_studentEntity" parameterType="liming.student.manager.data.model.StudentEntity">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.STUDENT_PHOTO,
ST.CLASS_ID,
ST.PLACE_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
<where>
<if test="studentName !=null ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR),'%')
</if>
<if test="studentSex != null and studentSex != '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #studentSex, jdbcType=INTEGER
</if>
<if test="studentBirthday != null ">
AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #studentBirthday, jdbcType=DATE
</if>
<if test="classId != null and classId!= '' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="classEntity != null and classEntity.classId !=null and classEntity.classId !=' ' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #classEntity.classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="placeId != null and placeId != '' ">
AND ST.PLACE_ID = #placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="placeEntity != null and placeEntity.placeId != null and placeEntity.placeId != '' ">
AND ST.PLACE_ID = #placeEntity.placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="studentId != null and studentId != '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_ID = #studentId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
</where>
</select>
if + set实现修改语句
当update语句中没有使用if标签时,如果有一个参数为null,都会导致错误。
当在update语句中使用if标签时,如果前面的if没有执行,则或导致逗号多余错误。使用set标签可以将动态的配置SET 关键字,和剔除追加到条件末尾的任何不相关的逗号。使用if+set标签修改后,如果某项为null则不进行更新,而是保持数据库原值。
如下示例:
<!-- 4 if/set(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性更新 -->
<update id="updateStudent_if_set" parameterType="liming.student.manager.data.model.StudentEntity">
UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
<set>
<if test="studentName != null and studentName != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #studentName,
</if>
<if test="studentSex != null and studentSex != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #studentSex,
</if>
<if test="studentBirthday != null ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #studentBirthday,
</if>
<if test="studentPhoto != null ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_PHOTO = #studentPhoto, javaType=byte[], jdbcType=BLOB, typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.BlobTypeHandler,
</if>
<if test="classId != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #classId
</if>
<if test="placeId != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.PLACE_ID = #placeId
</if>
</set>
WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #studentId;
</update>
if + trim代替where/set标签
trim是更灵活的去处多余关键字的标签,他可以实践where和set的效果。
trim代替where
<!-- 5.1if/trim代替where(判断参数) -将实体类不为空的属性作为where条件-->
<select id="getStudentList_if_trim" resultMap="resultMap_studentEntity">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.STUDENT_PHOTO,
ST.CLASS_ID,
ST.PLACE_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR">
<if test="studentName !=null ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #studentName, jdbcType=VARCHAR),'%')
</if>
<if test="studentSex != null and studentSex != '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #studentSex, jdbcType=INTEGER
</if>
<if test="studentBirthday != null ">
AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #studentBirthday, jdbcType=DATE
</if>
<if test="classId != null and classId!= '' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="classEntity != null and classEntity.classId !=null and classEntity.classId !=' ' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #classEntity.classId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="placeId != null and placeId != '' ">
AND ST.PLACE_ID = #placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="placeEntity != null and placeEntity.placeId != null and placeEntity.placeId != '' ">
AND ST.PLACE_ID = #placeEntity.placeId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
<if test="studentId != null and studentId != '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_ID = #studentId, jdbcType=VARCHAR
</if>
</trim>
</select>
trim代替set
<!-- 5.2 if/trim代替set(判断参数) - 将实体类不为空的属性更新 -->
<update id="updateStudent_if_trim" parameterType="liming.student.manager.data.model.StudentEntity">
UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="studentName != null and studentName != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #studentName,
</if>
<if test="studentSex != null and studentSex != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #studentSex,
</if>
<if test="studentBirthday != null ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #studentBirthday,
</if>
<if test="studentPhoto != null ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_PHOTO = #studentPhoto, javaType=byte[], jdbcType=BLOB, typeHandler=org.apache.ibatis.type.BlobTypeHandler,
</if>
<if test="classId != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #classId,
</if>
<if test="placeId != '' ">
STUDENT_TBL.PLACE_ID = #placeId
</if>
</trim>
WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #studentId
</update>
foreach
对于动态SQL 非常必须的,主是要迭代一个集合,通常是用于IN 条件。List 实例将使用“list”做为键,数组实例以“array” 做为键。
foreach元素是非常强大的,它允许你指定一个集合,声明集合项和索引变量,它们可以用在元素体内。它也允许你指定开放和关闭的字符串,在迭代之间放置分隔符。这个元素是很智能的,它不会偶然地附加多余的分隔符。
注意:你可以传递一个List实例或者数组作为参数对象传给MyBatis。当你这么做的时候,MyBatis会自动将它包装在一个Map中,用名称在作为键。List实例将会以“list”作为键,而数组实例将会以“array”作为键。
这个部分是对关于XML配置文件和XML映射文件的而讨论的。下一部分将详细讨论Java API,所以你可以得到你已经创建的最有效的映射。
1.参数为array示例的写法
接口的方法声明:
public List<StudentEntity> getStudentListByClassIds_foreach_array(String[] classIds);
动态SQL语句:
<!-- 7.1 foreach(循环array参数) - 作为where中in的条件 -->
<select id="getStudentListByClassIds_foreach_array" resultMap="resultMap_studentEntity">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.STUDENT_PHOTO,
ST.CLASS_ID,
ST.PLACE_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.CLASS_ID IN
<foreach collection="array" item="classIds" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#classIds
</foreach>
</select>
测试代码,查询学生中,在20000001、20000002这两个班级的学生:
@Test
public void test7_foreach()
String[] classIds = "20000001", "20000002" ;
List<StudentEntity> list = this.dynamicSqlMapper.getStudentListByClassIds_foreach_array(classIds);
for (StudentEntity e : list)
System.out.println(e.toString());
2.参数为list示例的写法
接口的方法声明:
public List<StudentEntity> getStudentListByClassIds_foreach_list(List<String> classIdList);
动态SQL语句:
<!-- 7.2 foreach(循环List<String>参数) - 作为where中in的条件 -->
<select id="getStudentListByClassIds_foreach_list" resultMap="resultMap_studentEntity">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.STUDENT_PHOTO,
ST.CLASS_ID,
ST.PLACE_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.CLASS_ID IN
<foreach collection="list" item="classIdList" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#classIdList
</foreach>
</select>
测试代码,查询学生中,在20000001、20000002这两个班级的学生:
@Test
public void test7_2_foreach()
ArrayList<String> classIdList = new ArrayList<String>();
classIdList.add("20000001");
classIdList.add("20000002");
List<StudentEntity> list = this.dynamicSqlMapper.getStudentListByClassIds_foreach_list(classIdList);
for (StudentEntity e : list)
System.out.println(e.toString());
sql片段标签<sql>:通过该标签可定义能复用的sql语句片段,在执行sql语句标签中直接引用即可。这样既可以提高编码效率,还能有效简化代码,提高可读性
需要配置的属性:id="" >>>表示需要改sql语句片段的唯一标识
引用:通过<include refid="" />标签引用,refid="" 中的值指向需要引用的<sql>中的id=“”属性
<!--定义sql片段-->
<sql id="orderAndItem">
o.order_id,o.cid,o.address,o.create_date,o.orderitem_id,i.orderitem_id,i.product_id,i.count
</sql>
<select id="findOrderAndItemsByOid" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<!--引用sql片段-->
<include refid="orderAndItem" />
from ordertable o
join orderitem i on o.orderitem_id = i.orderitem_id
where o.order_id = #orderId
</select> ELK日志系统(企业用了都说好)
ELK日志系统(企业用了都说好)
一、ELK概述
1、ELK日志分析系统

2、ELK中日志处理步骤

第一步:将日志进行集中化管理(beats)
第二步:将日志格式化(Logstash),然后将格式化后的数据输出到Elasticsearch
第三步:对格式化后的数据进行索引和存储(Elasticsearch)
第四步:前端数据的展示(Kibana)
3、Elasticsearch概述
Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它基于RESTful web接口提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎。
Elasticsearch是用Java开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是第二流行的企业搜索引擎。设计用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。
(1)Elasticsearch的特性
接近实时的搜索
集群
节点
索引
索引(库)→类型(表)→文档(记录)
分片和副本
(2)分片和副本
在上述特性中,最重要的就是分片和副本,也是让es数据库(Elasticsearch)成为百度这些主流搜索引擎的主要原因,理论上能提升4倍的性能。
结合实际情况分析:索引存储的数据可能超过单个节点的硬件限制,如一个10亿文档需1TB空间可能不适合存储在单个节点的磁盘上,或者从单个节点搜索请求太慢了,为了解决这个问题,elasticsearch提供将索引分成多个分片的功能,当在创建索引时,可以定义想要分片的数量。每个分片就是一个全功能的独立索引,可以位于集群中任何节点上。
分片的特点:
水平分割扩展,增大存储量
分布式并行跨分片操作,提供性能和吞吐量
分布式分片的机制和搜索请求的文档如何汇总完全是有elasticsearch控制的,这些对用户而言是透明的
网络问题等等其他问题可以在任何时候不期而至,为了健壮性,强烈建议要有个故障切换机制,无论何种故障以防止分片或者节点不可用,为此,elasticsearch让我们将索引分片复制一份或多份,称为分片副本或副本
副本的特点:
高可用性,以应对分片或者节点故障,出于这个原因,分片副本要在不同的节点上
性能加强,增加吞吐量,搜索可以并行在所有副本上执行
4、LogStash概述
一款强大的数据处理工具
可实现数据传输、格式处理、格式化输出
数据输入、数据加工(如过滤,改写等)以及数据输出
常用插件:Input、Filter Plugin、Output
Input:收集源数据(访问日志、错误日志等)
Filter Plugin:用于过滤日志和格式处理
Output:输出日志
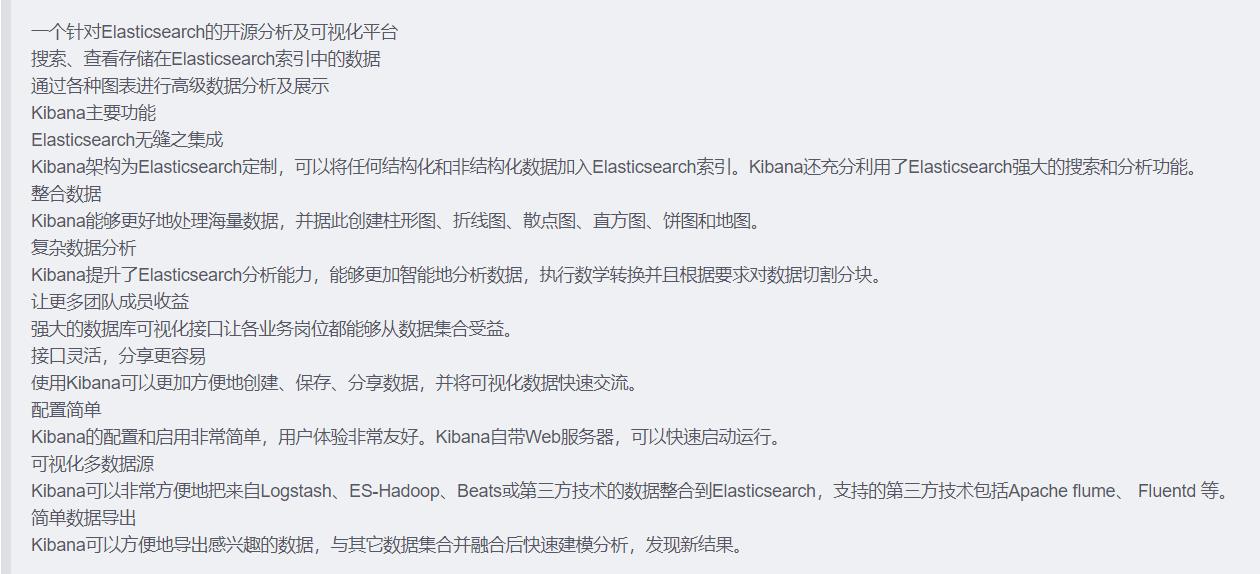
5、Kibana概述
二、部署ELK日志分析系统
需求描述
配置ELK日志分析集群
使用Logstash收集日志
使用Kibana查看分析日志
案例环境
配置和安装ELK日志分析系统,安装集群方式,2个elasticsearch节点,并监控apache服务器日志
实验准备
主机 操作系统 IP地址 软件
node1 CentOS7 192.168.221.20 Elasticsearch/Kibana
node2 CentOS7 192.168.221.30 Elasticsearch
apache CentOS7 192.168.221.100 httpd / Logstash
客户机(宿主机) Windows10 192.168.221.188
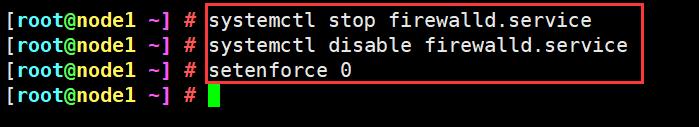
1、关防火墙和系统安全机制
更改主机名
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl disable firewalld.service
setenforce 0
hostnamectl set-hostname 主机名
2、配置elasticsearch环境
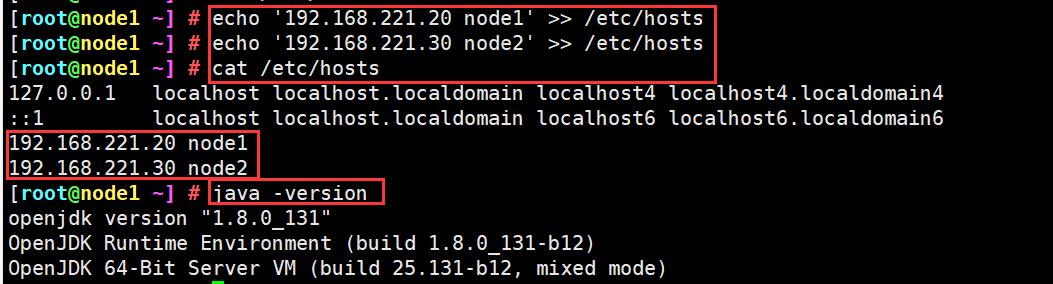
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
echo '192.168.221.20 node1' >> /etc/hosts
echo '192.168.221.30 node2' >> /etc/hosts
java -version #如果没有安装,yum -y install java
3、部署elasticsearch软件
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
(1)安装elasticsearch—rpm包
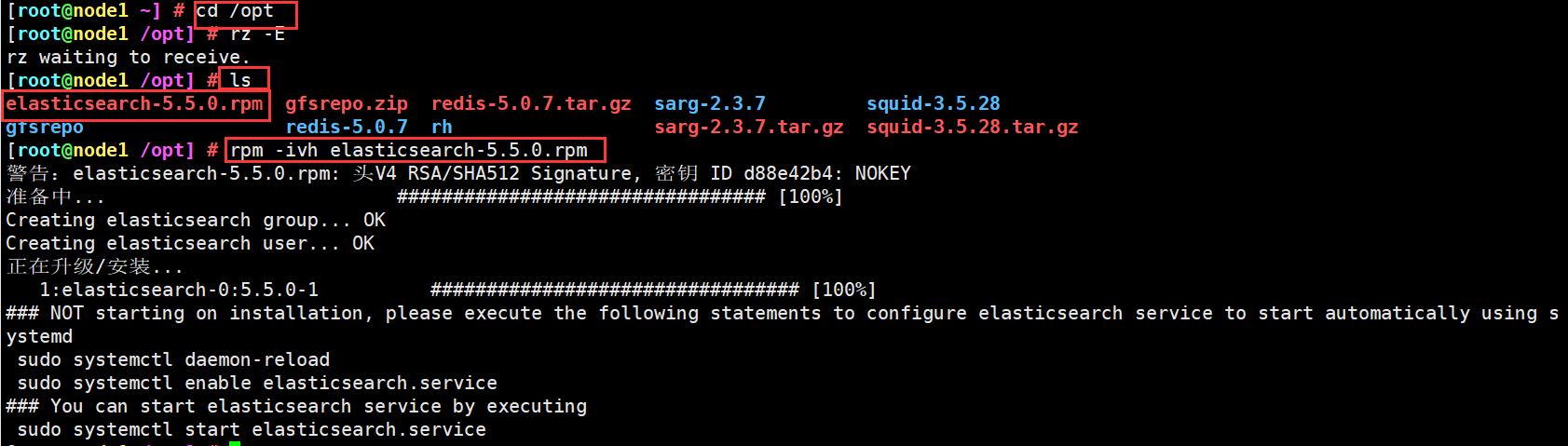
上传elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm到/opt目录下
cd /opt
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm
(2)加载系统服务
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable elasticsearch.service

(3)更改elasticsearch主配置文件
cp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.bak
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
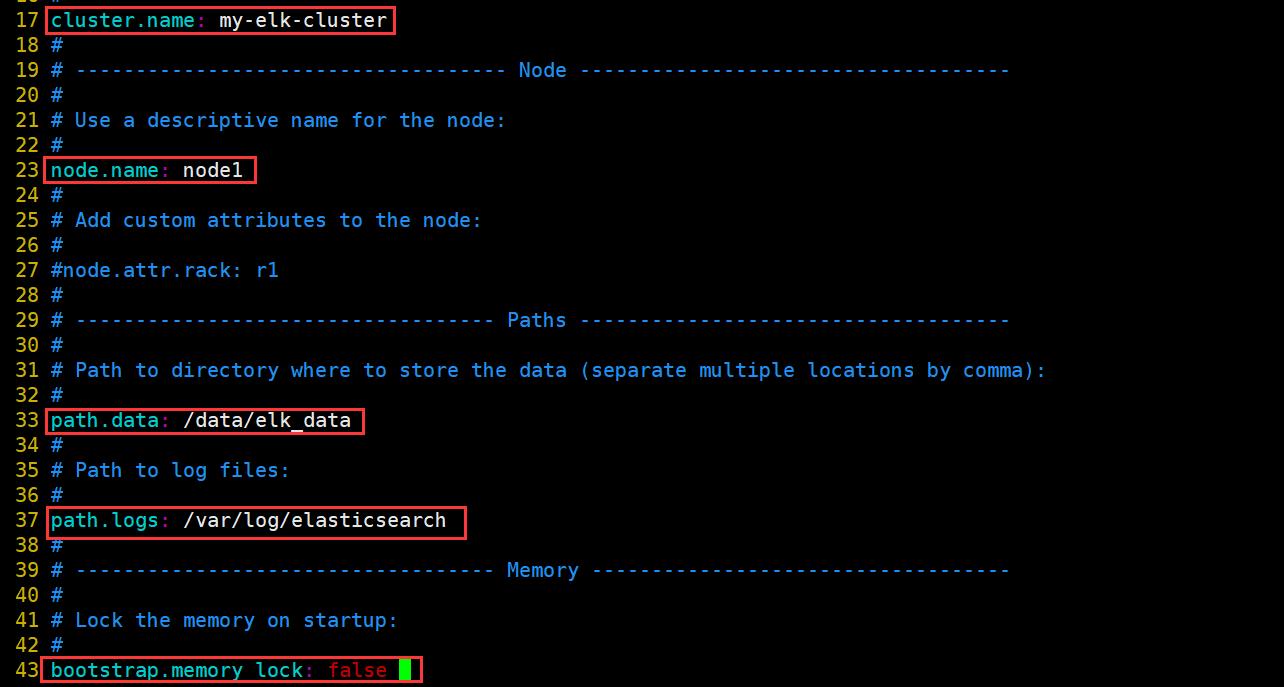
#17行;取消注释,修改;集群名字
cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
#23行;取消注释,修改;节点名字(node2修改成node2)
node.name: node1
#33行;取消注释,修改;数据存放路径
path.data: /data/elk_data
#37行;取消注释,修改;日志存放路径
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
#43行;取消注释,修改;不在启动的时候锁定内存
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
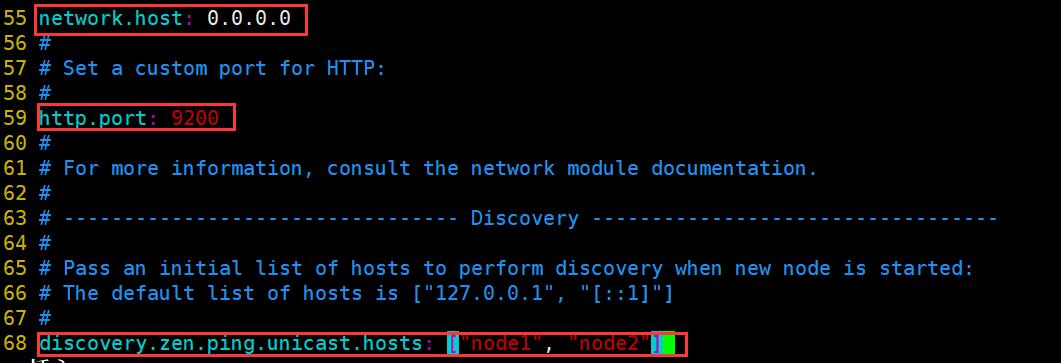
#55行;取消注释,修改;提供服务绑定的IP地址,0.0.0.0代表所有地址
network.host: 0.0.0.0
#59行;取消注释;侦听端口为9200(默认)
http.port: 9200
#68行;取消注释,修改;集群发现通过单播实现,指定要发现的节点 node1、node2
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"]
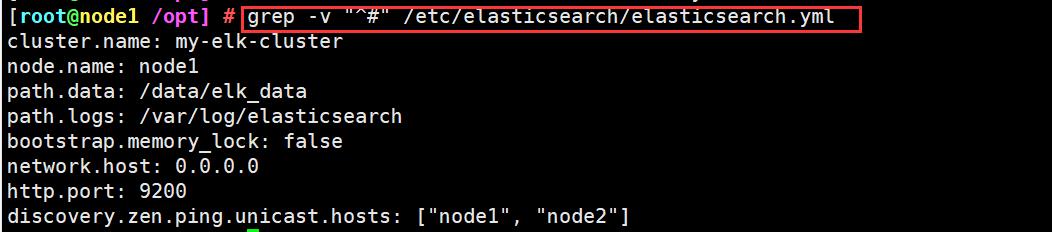
检验配置
grep -v "^#" /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
(4)创建数据存放路径并授权
mkdir -p /data/elk_data
chown elasticsearch:elasticsearch /data/elk_data/

(5)启动elasticsearch是否成功开启
systemctl start elasticsearch
netstat -antp |grep 9200
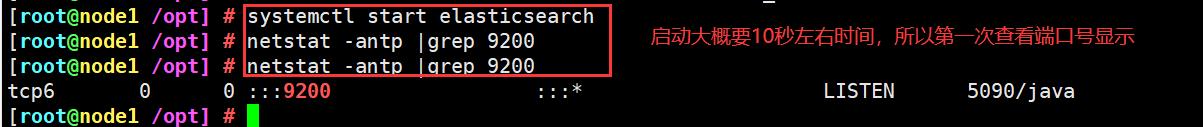
(6)查看节点信息
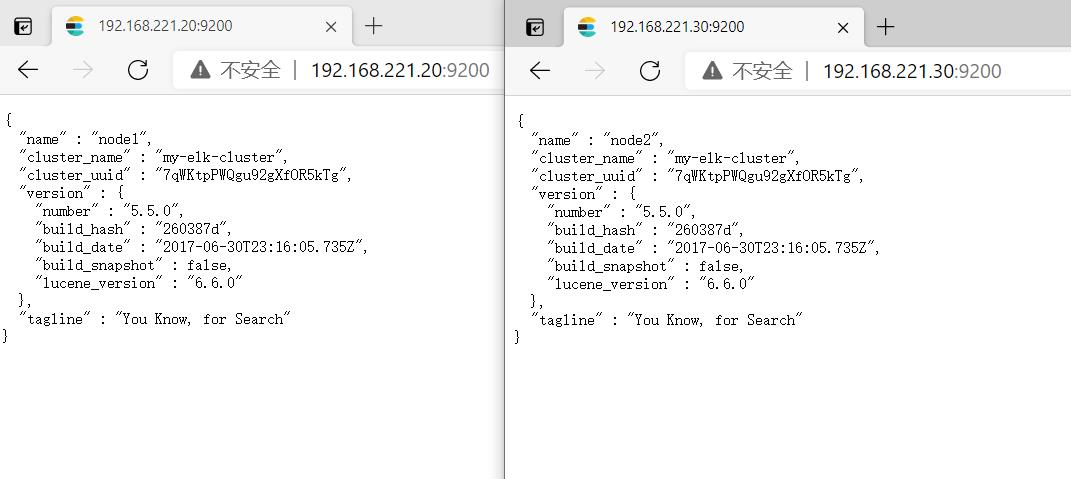
在宿主机192.168.221.188上访问
http://192.168.221.20:9200
http://192.168.221.30:9200
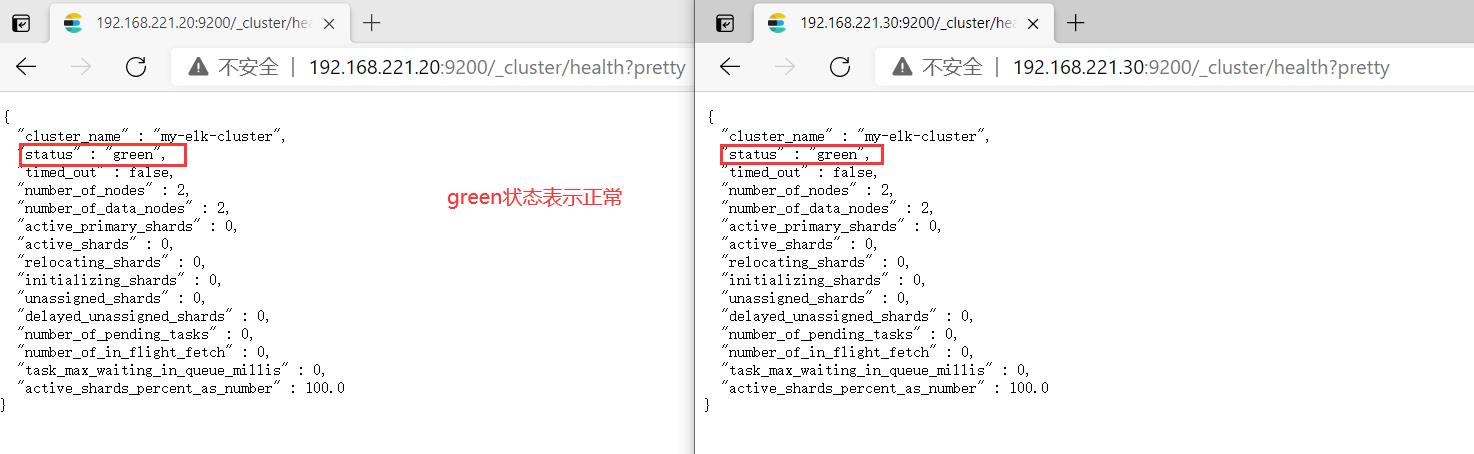
2、真机检测集群健康、查看集群状态
http://192.168.221.20:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
http://192.168.221.30:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
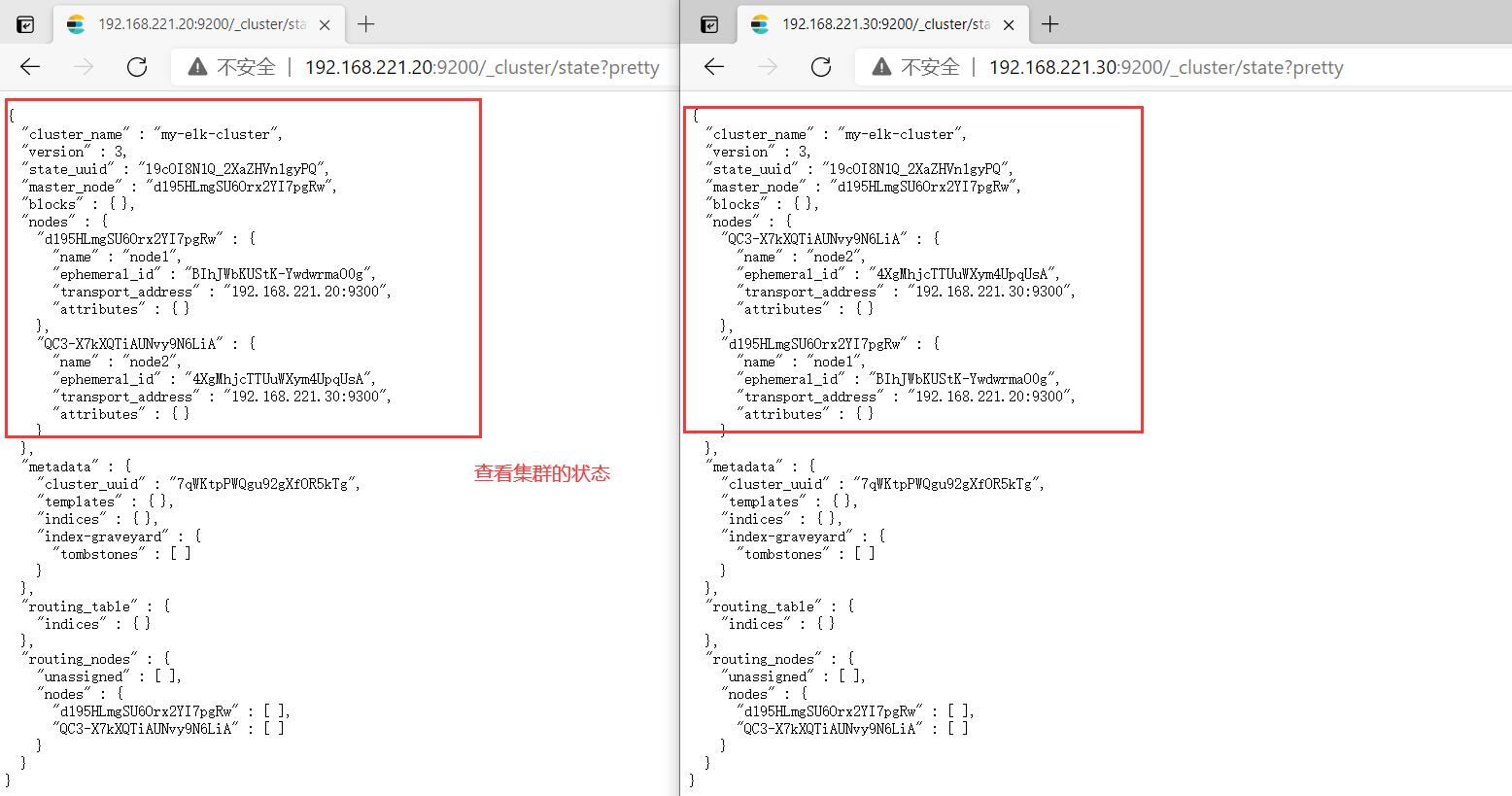
http://192.168.221.20:9200/_cluster/state?pretty
http://192.168.221.30:9200/_cluster/state?pretty
4、安装elasticsearch-head插件
安装elasticsearch-head插件,用于管理集群
(1)编译安装node组件依赖包
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make
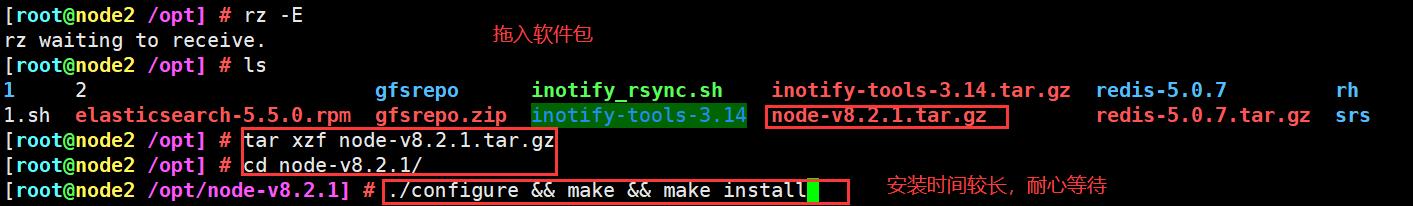
上传软件包 node-v8.2.1.tar.gz 到/opt
cd /opt
tar zxvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz
cd node-v8.2.1/
./configure && make && make install
这里耗时比较长估计20-30分钟
(2)安装phantomjs(前端框架)
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
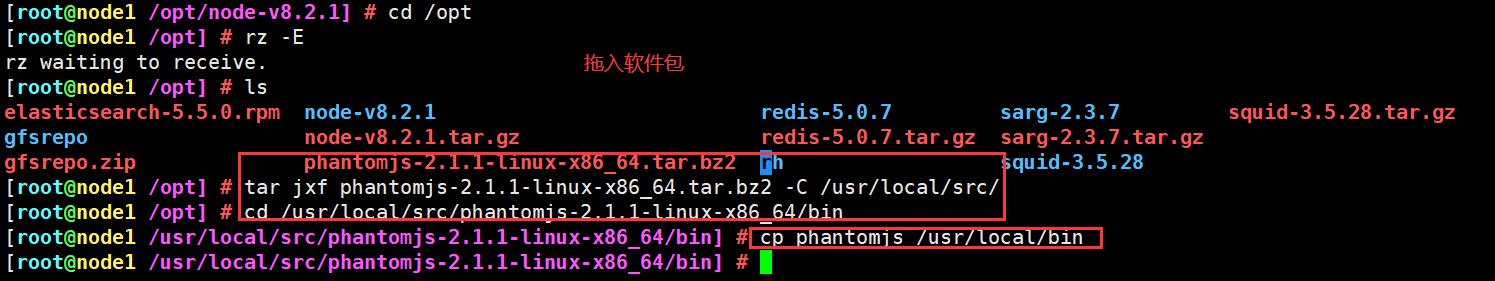
上传软件包 phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2 到/opt目录下
cd /opt
tar jxf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2 -C /usr/local/src/
cd /usr/local/src/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin
cp phantomjs /usr/local/bin
(3)安装elasticsearch-head(数据可视化工具)
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
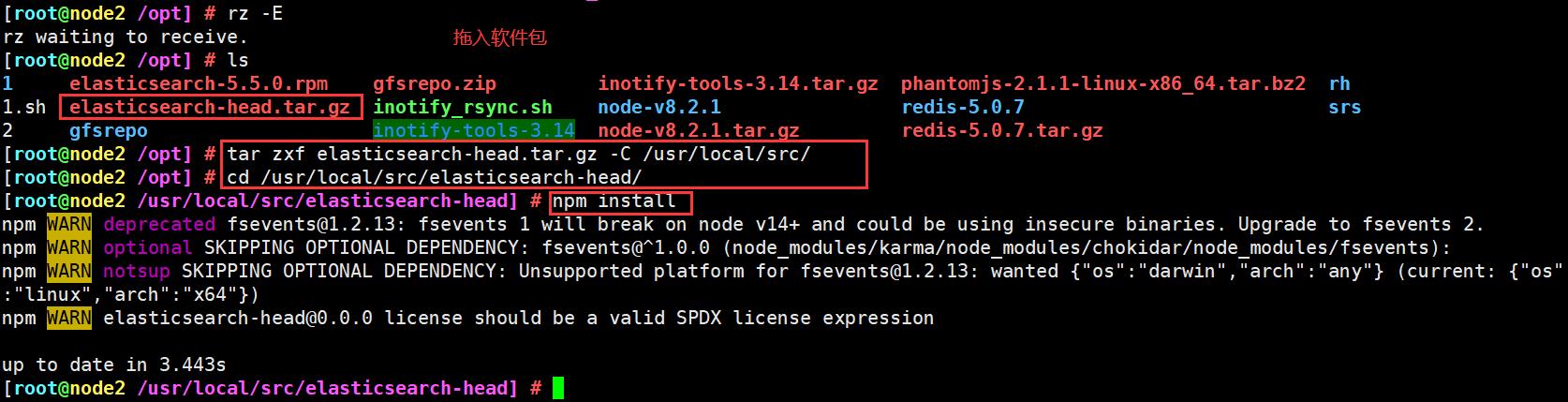
上传软件包 elasticsearch-head.tar.gz 到/opt
cd /opt
tar zxf elasticsearch-head.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
npm install
(4)修改主配置文件
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
......
#-------末尾;添加以下内容--------
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
#-----------参数解释-----------------------------
http.cors.enabled: true #开启跨域访问支持,默认为 false
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #指定跨域访问允许的域名地址为所有
systemctl restart elasticsearch.service

(5)启动elasticsearch-head
node1(192.168.221.20)
node2(192.168.221.30)
必须在解压后的 elasticsearch-head 目录下启动服务,进程会读取该目录下的 gruntfile.js 文件,否则可能启动失败。
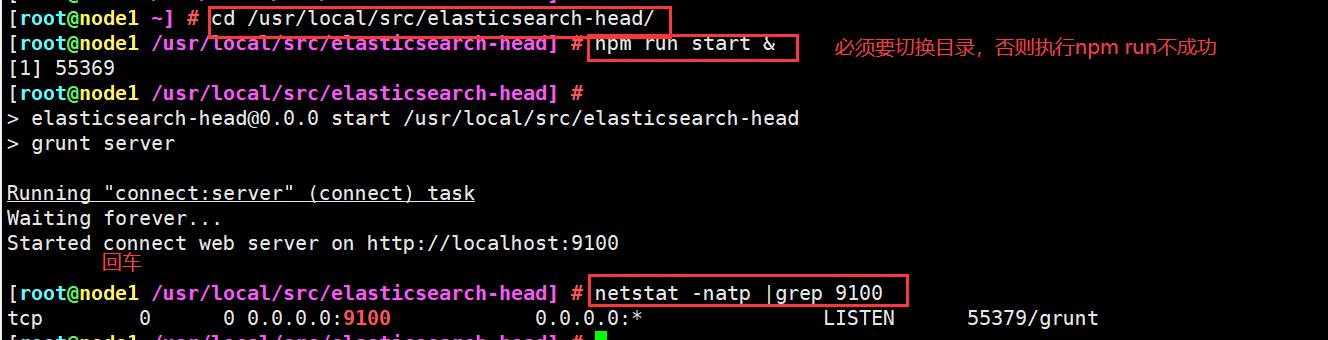
cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
npm run start &
> elasticsearch-head@0.0.0 start /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head
> grunt server
Running "connect:server" (connect) task
Waiting forever...
Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100
elasticsearch-head 监听的端口是 9100
netstat -natp |grep 9100
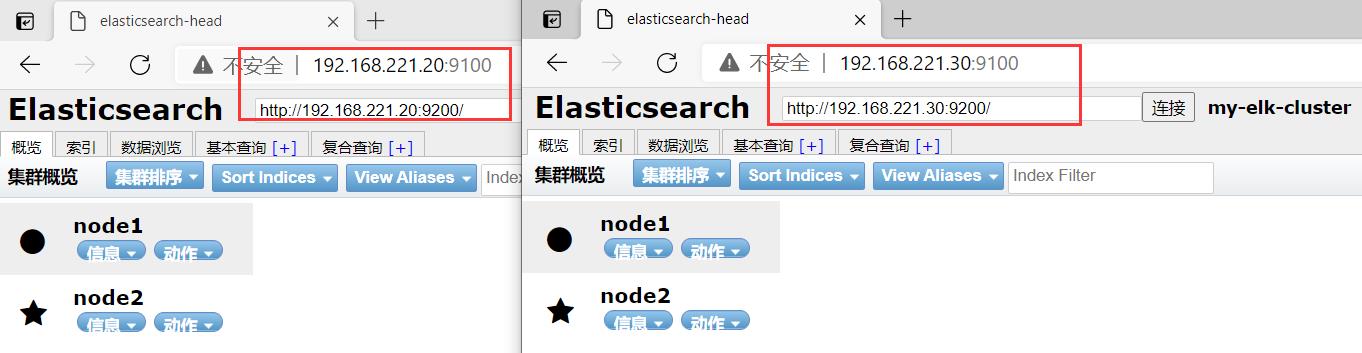
(6)使用elasticsearch-head插件查看集群状态
在宿主机192.168.221.188上访问
http://192.168.221.20:9100
在Elasticsearch 后面的栏目中输入
http://192.168.221.20:9200
http://192.168.221.30:9100
在Elasticsearch 后面的栏目中输入
http://192.168.221.30:9200
(7)创建索引
node1(192.168.221.20)
创建索引为index-demo,类型为test
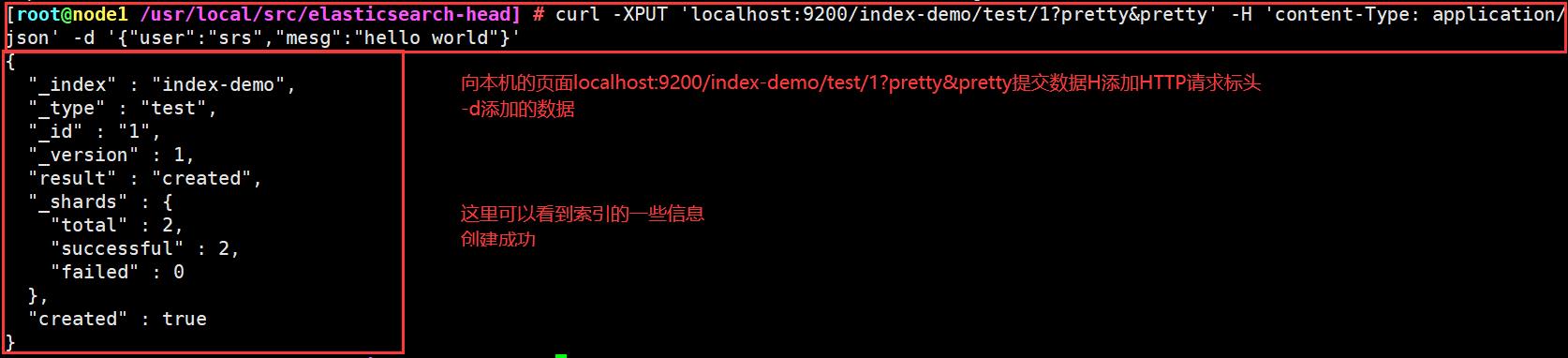
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"srs","mesg":"hello world"}'
向本机的页面localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty提交数据H添加HTTP请求标头-d添加的数据
回到宿主机192.168.163.1
打开浏览器输入地址,查看索引信息
http://192.168.163.11:9100
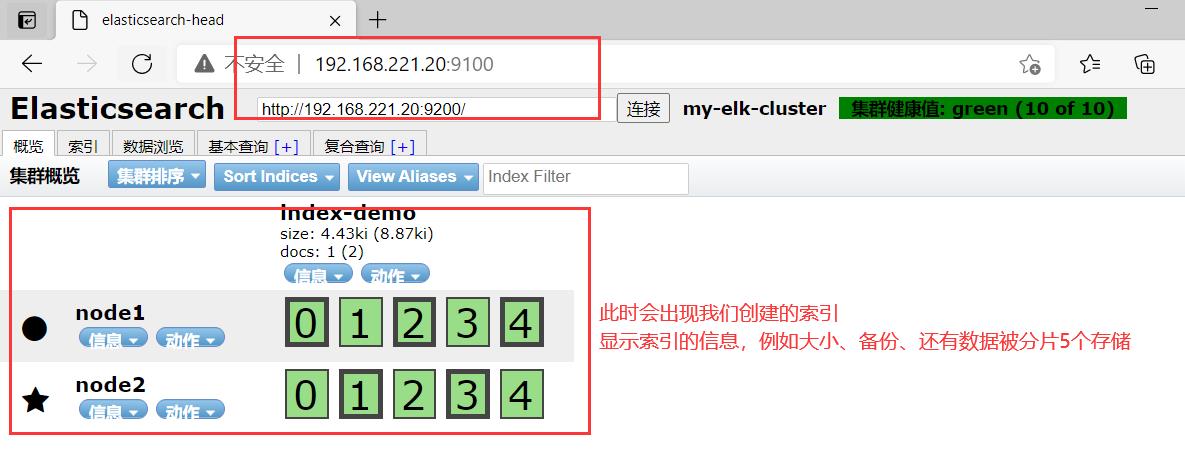
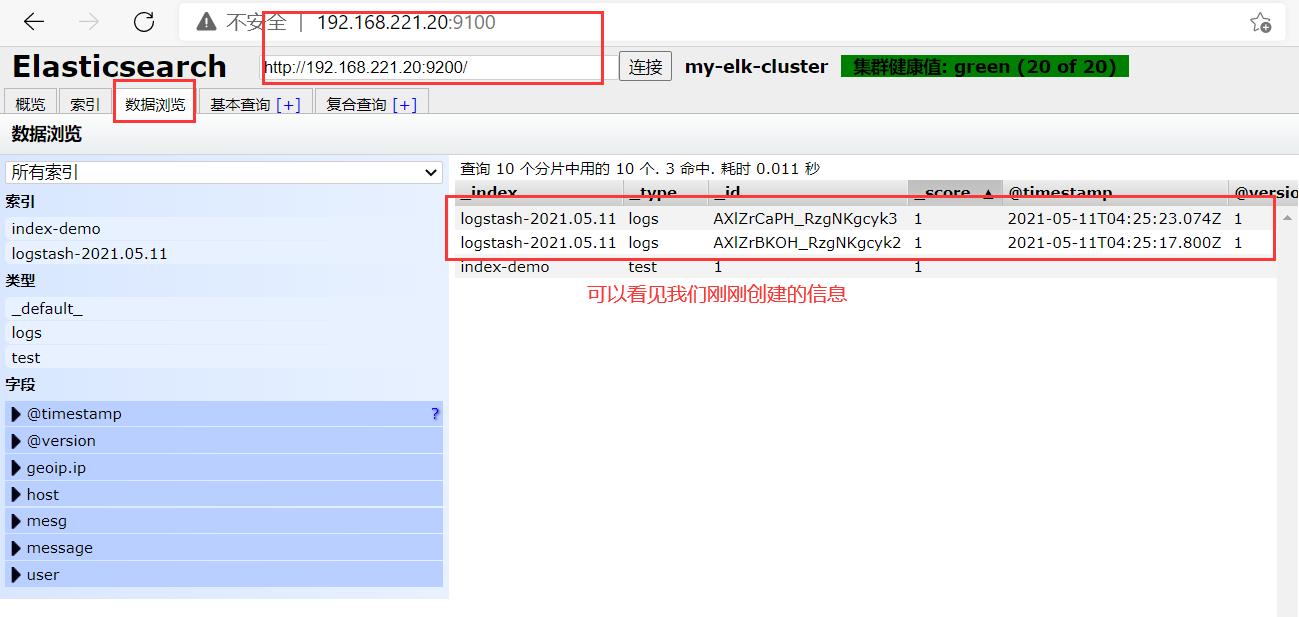
可以看见索引默认被分片5个,并且有一个副本
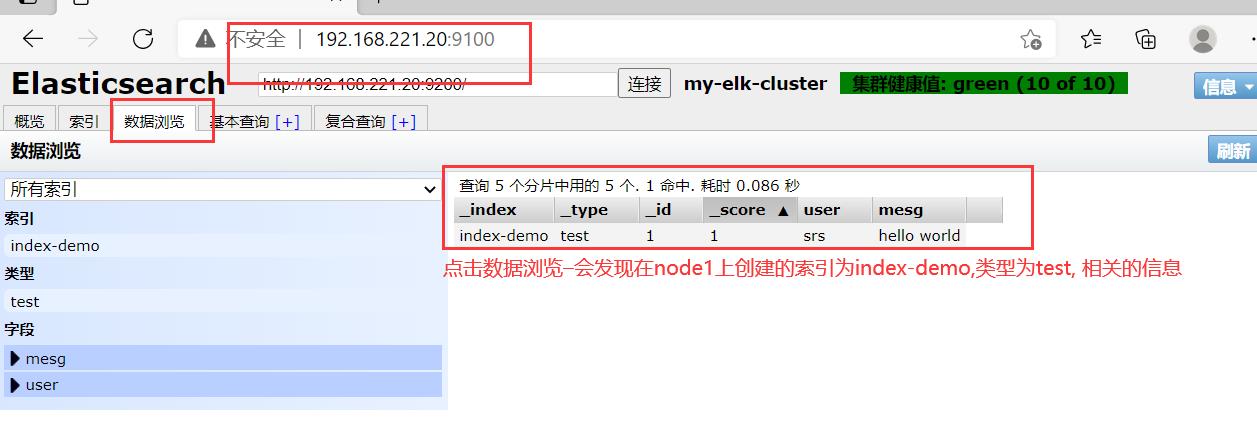
点击数据浏览–会发现在node1上创建的索引为index-demo,类型为test, 相关的信息
5、安装logstash
收集日志输出到elasticsearch中
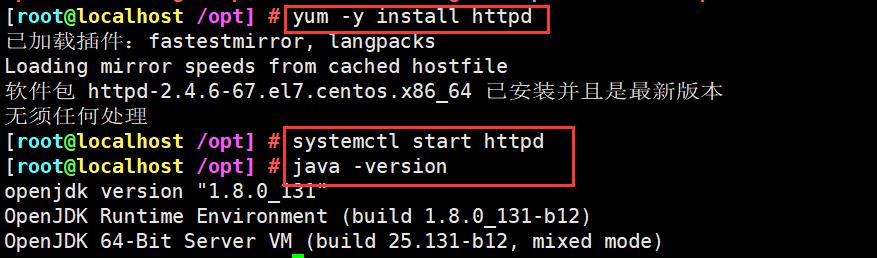
(1)安装Apahce服务(httpd)和Java环境
apache(192.168.221.70)
yum -y install httpd
systemctl start httpd
java -version ###如果没有装 安装yum -y install java
(3)安装logstash
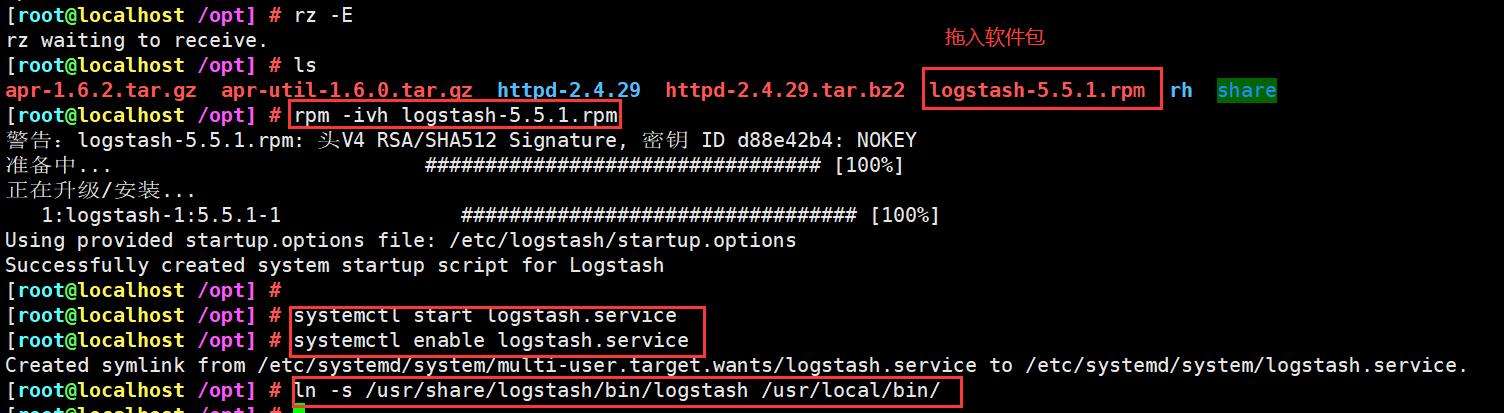
apache(192.168.221.70)
上传logstash-5.5.1.rpm到/opt目录下
cd /opt
rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.1.rpm
systemctl start logstash.service
systemctl enable logstash.service
#建立logstash软连接
ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/
(4)测试logstash命令
apache(192.168.163.13)
字段描述解释:
-f 通过这个选项可以指定logstash的配置文件,根据配置文件配置logstash
-e 后面跟着字符串 该字符串可以被当做logstash的配置(如果是” ”,则默认使用stdin做为输入、stdout作为输出)
-t 测试配置文件是否正确,然后退出
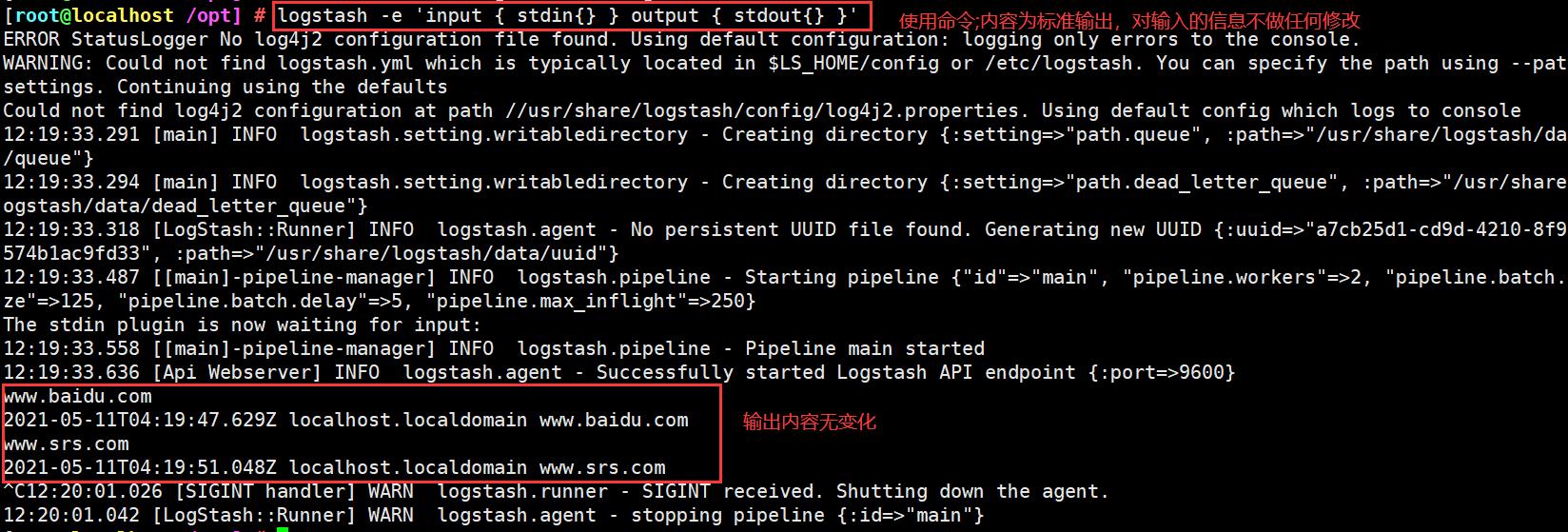
定义输入和输出流:
输入采用标准输入,输出采用标准输出(类似管道)
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'
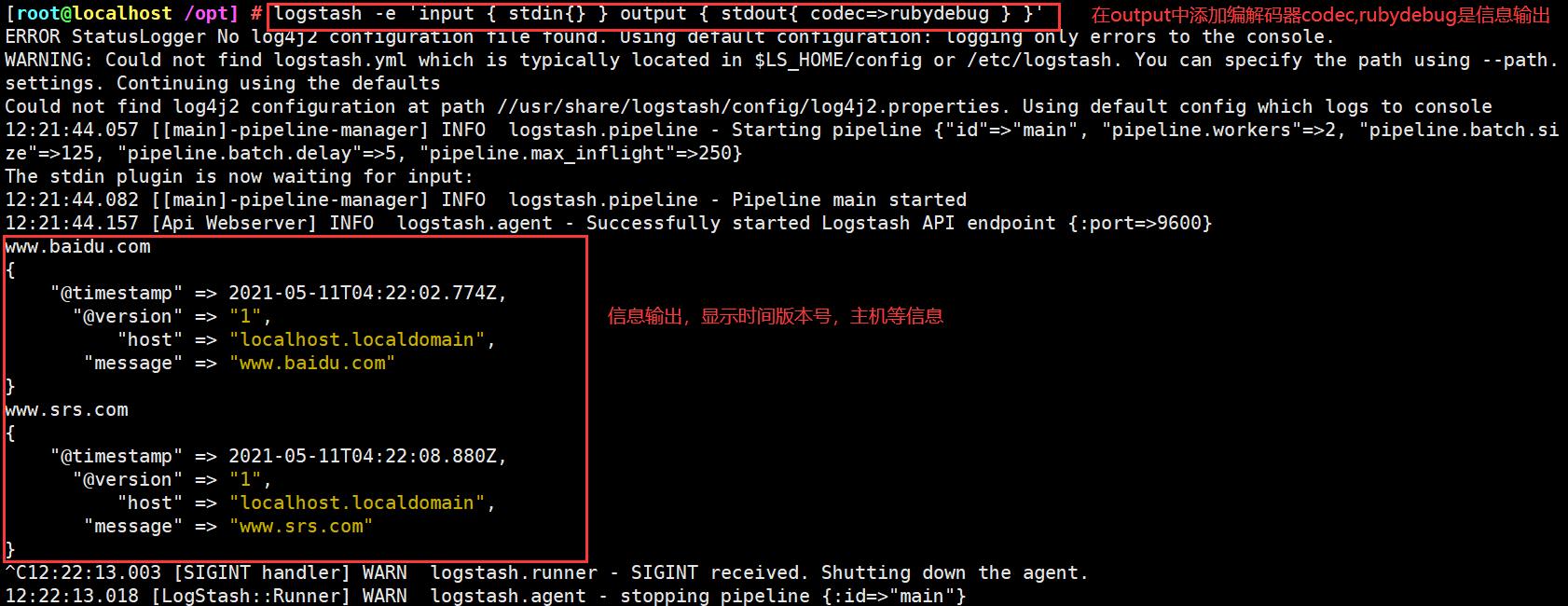
使用rubydebug显示详细输出,codec为一种编解码器
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'
使用 Logstash 将信息写入 Elasticsearch 中
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.221.20:9200"] } }'
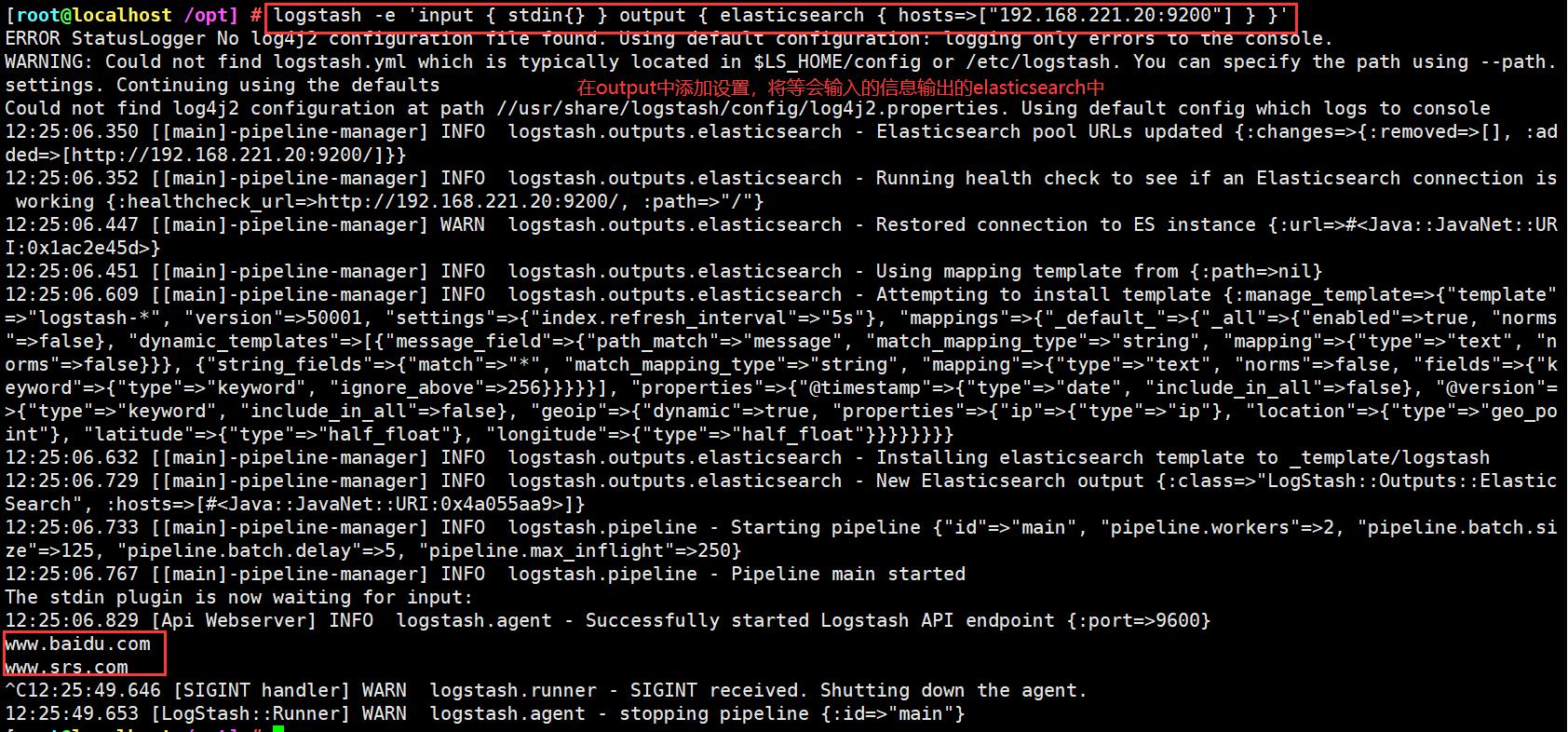
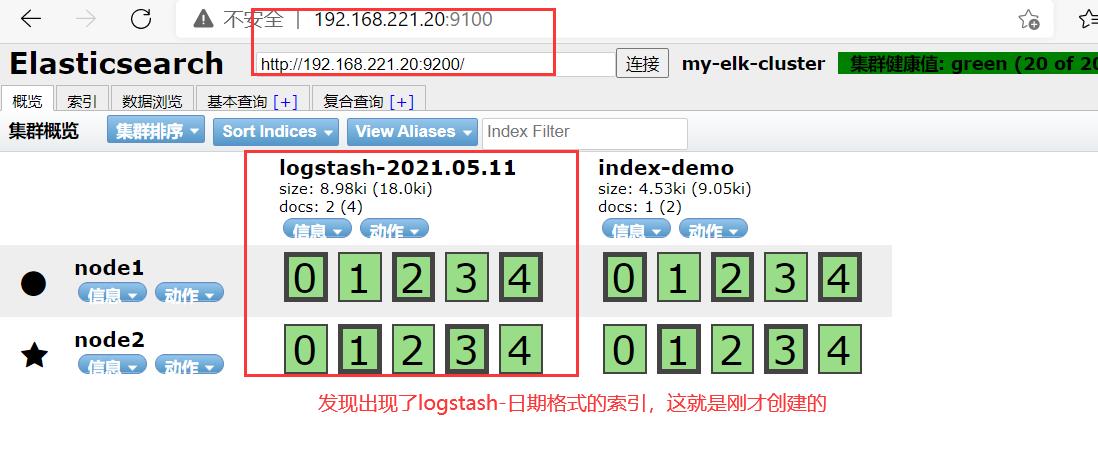
在宿主机192.168.221.188上访问
查看索引信息
多出 logstash-日期
http://192.168.221.20:9100
(5)在Apache主机上做对接配置
apache(192.168.163.13)
Logstash配置文件主要由三部分组成:input、output、filter(根据需要)
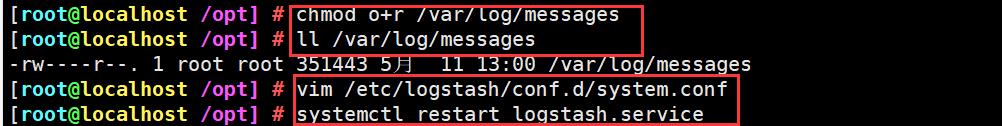
chmod o+r /var/log/messages
ll /var/log/messages
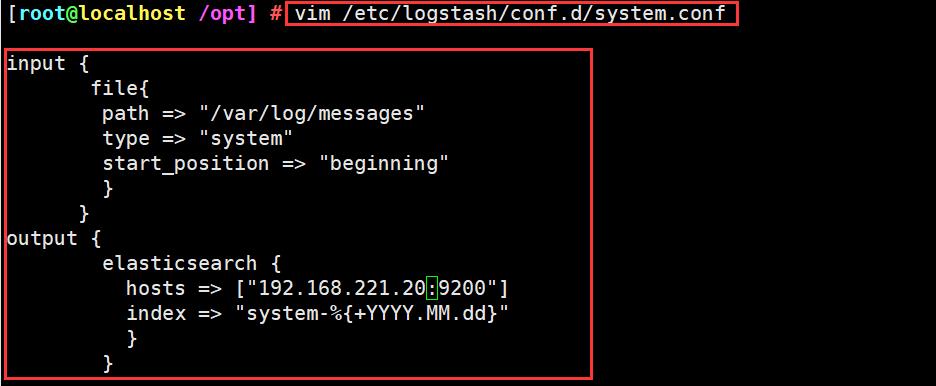
vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf
input {
file{
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.221.20:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
systemctl restart logstash.service
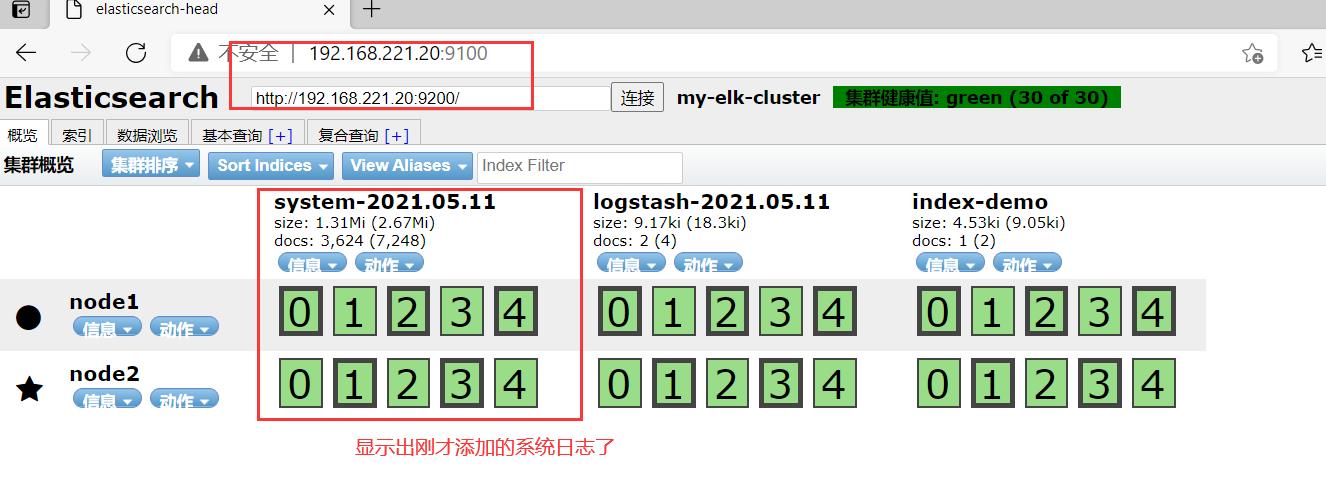
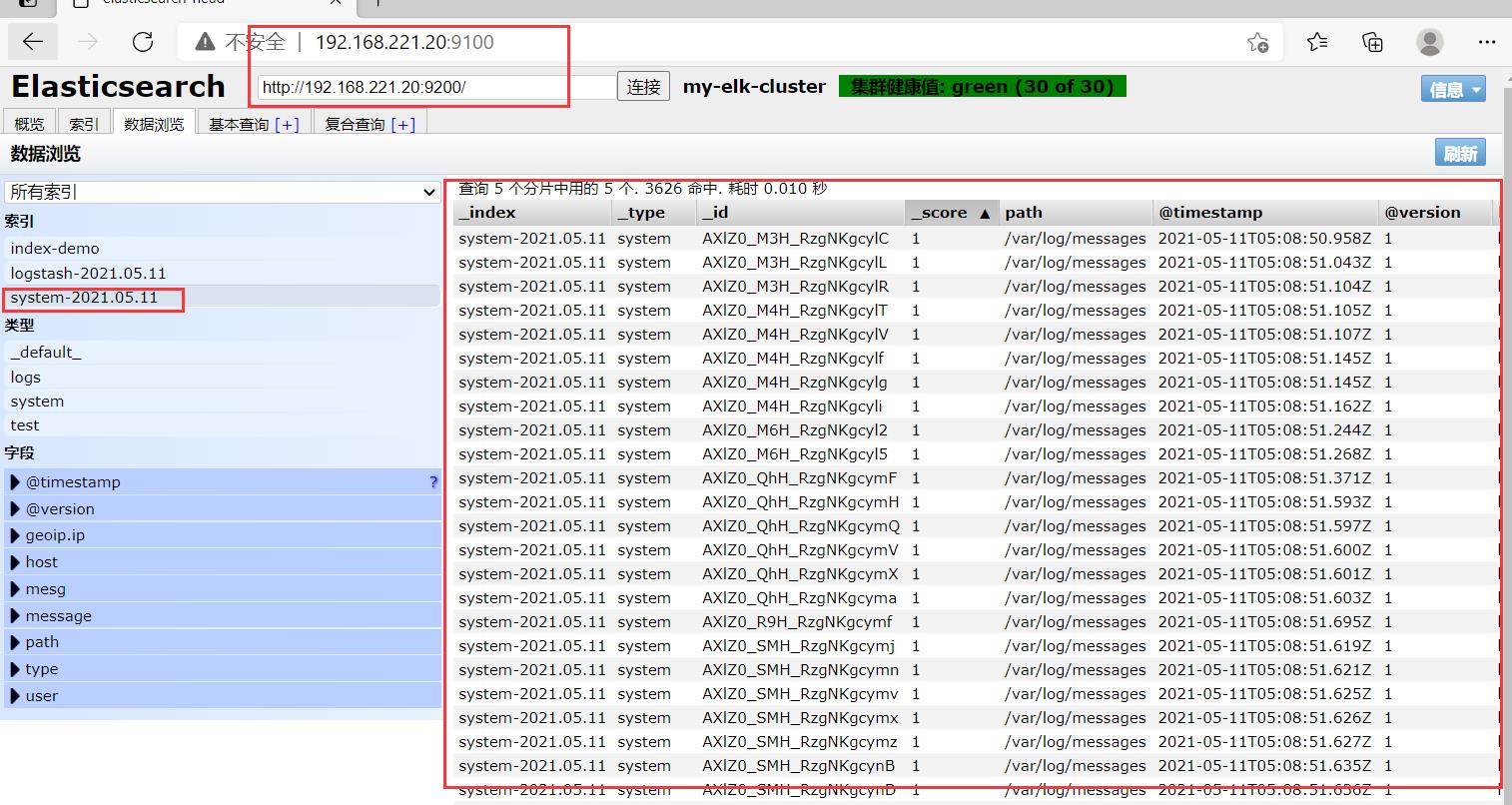
在宿主机192.168.221.188上访问
查看索引信息
多出 system-日期
http://192.168.221.20:9100
6、安装kibana
node1(192.168.221.20)
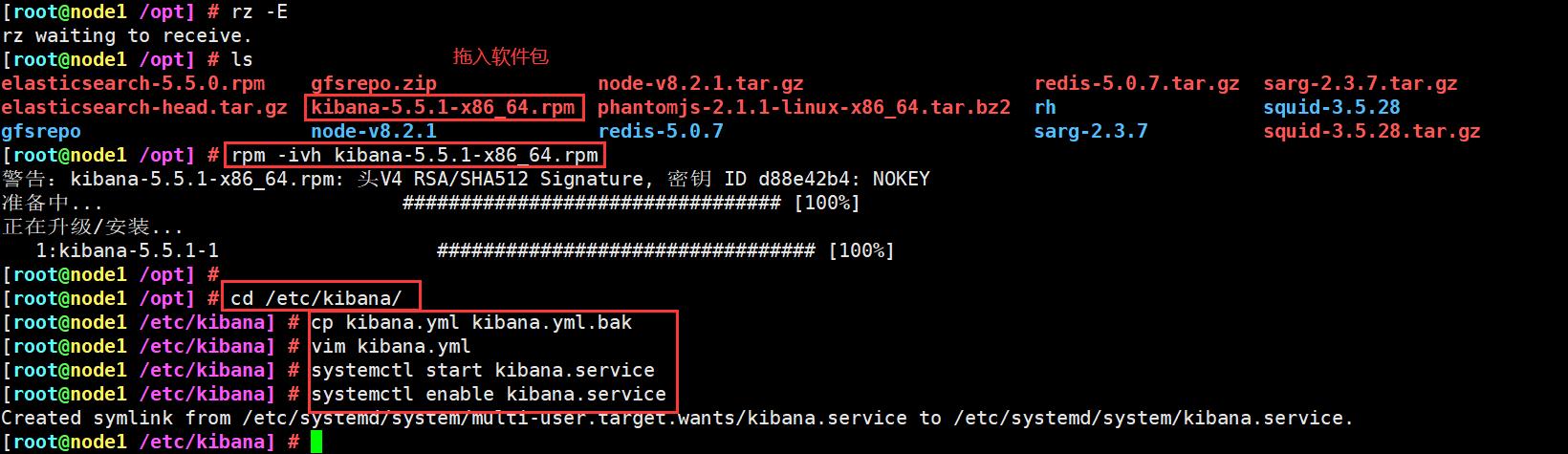
上传kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm 到/opt目录
cd /opt
rpm -ivh kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
cd /etc/kibana/
cp kibana.yml kibana.yml.bak
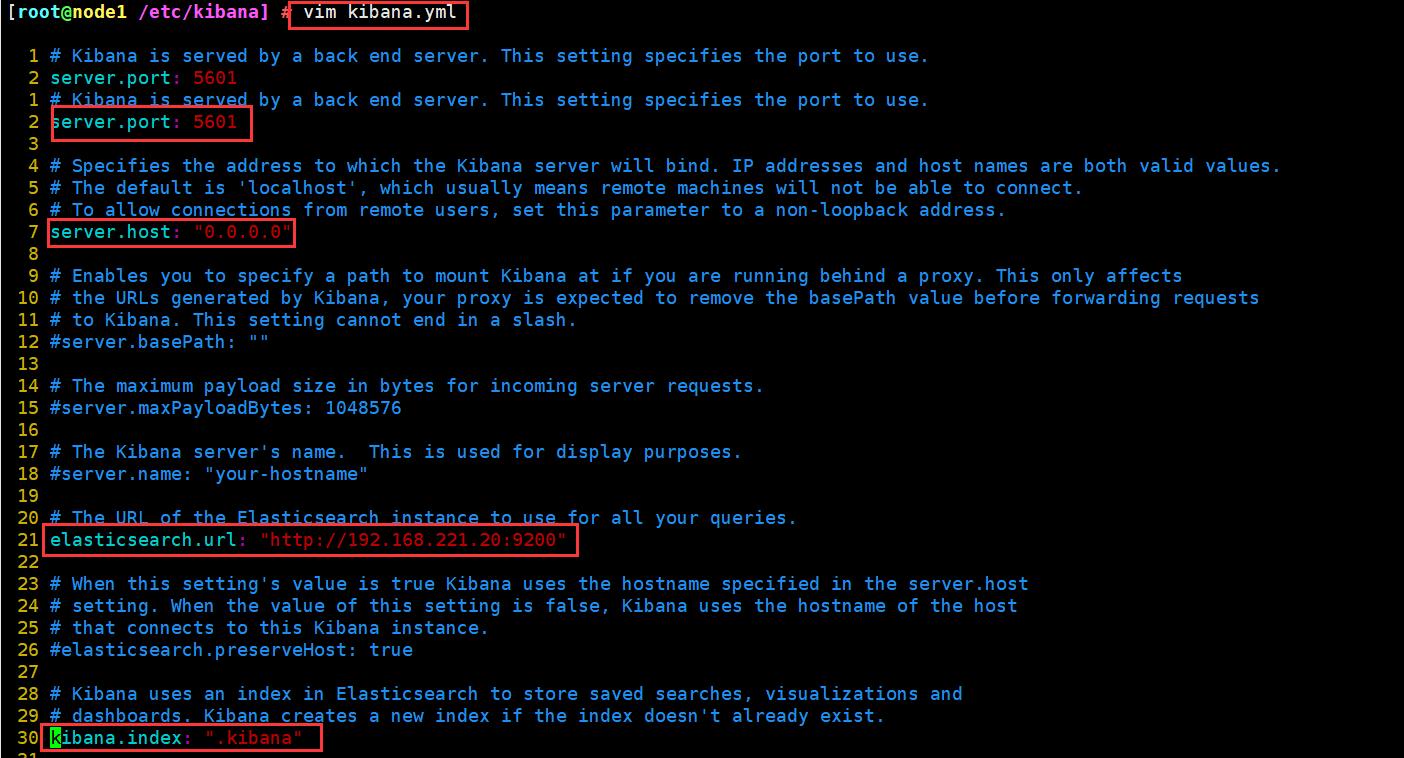
vim kibana.yml
#2行;取消注释;kibana打开的端口(默认5601)
server.port: 5601
#7行;取消注释,修改;kibana侦听的地址
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
#21行;取消注释,修改;和elasticsearch建立联系
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.221.20:9200"
#30行;取消注释;在elasticsearch中添加.kibana索引
kibana.index: ".kibana"
systemctl start kibana.service
systemctl enable kibana.service
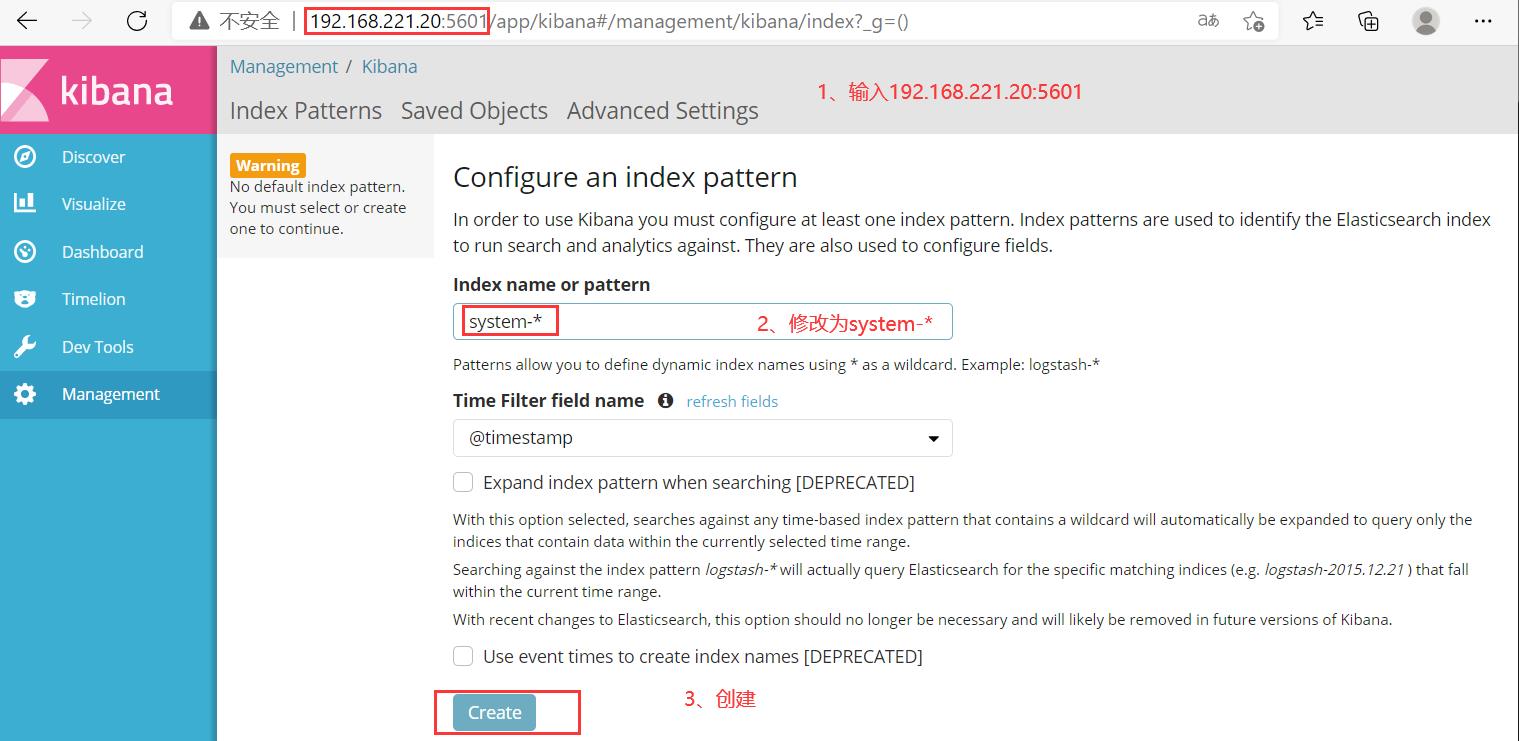
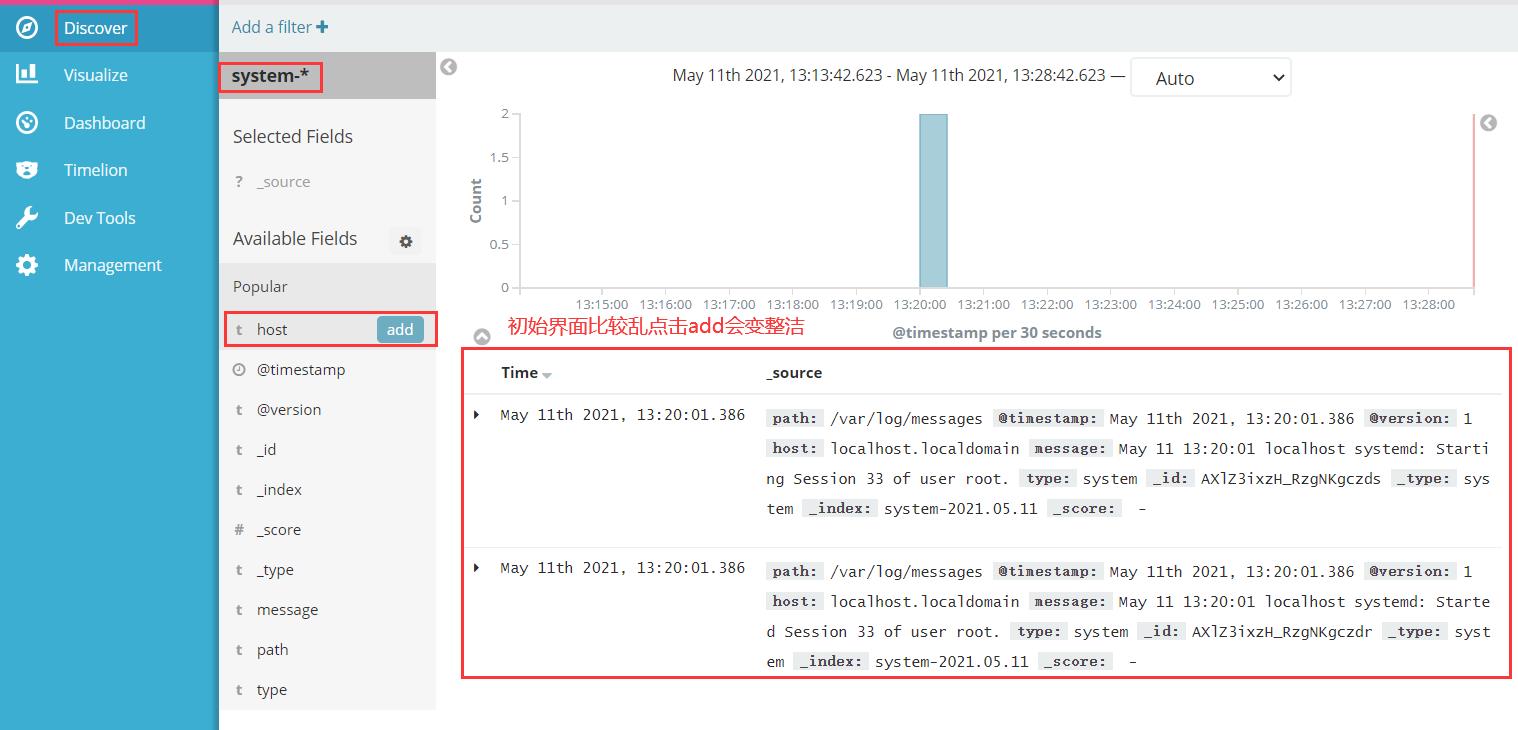
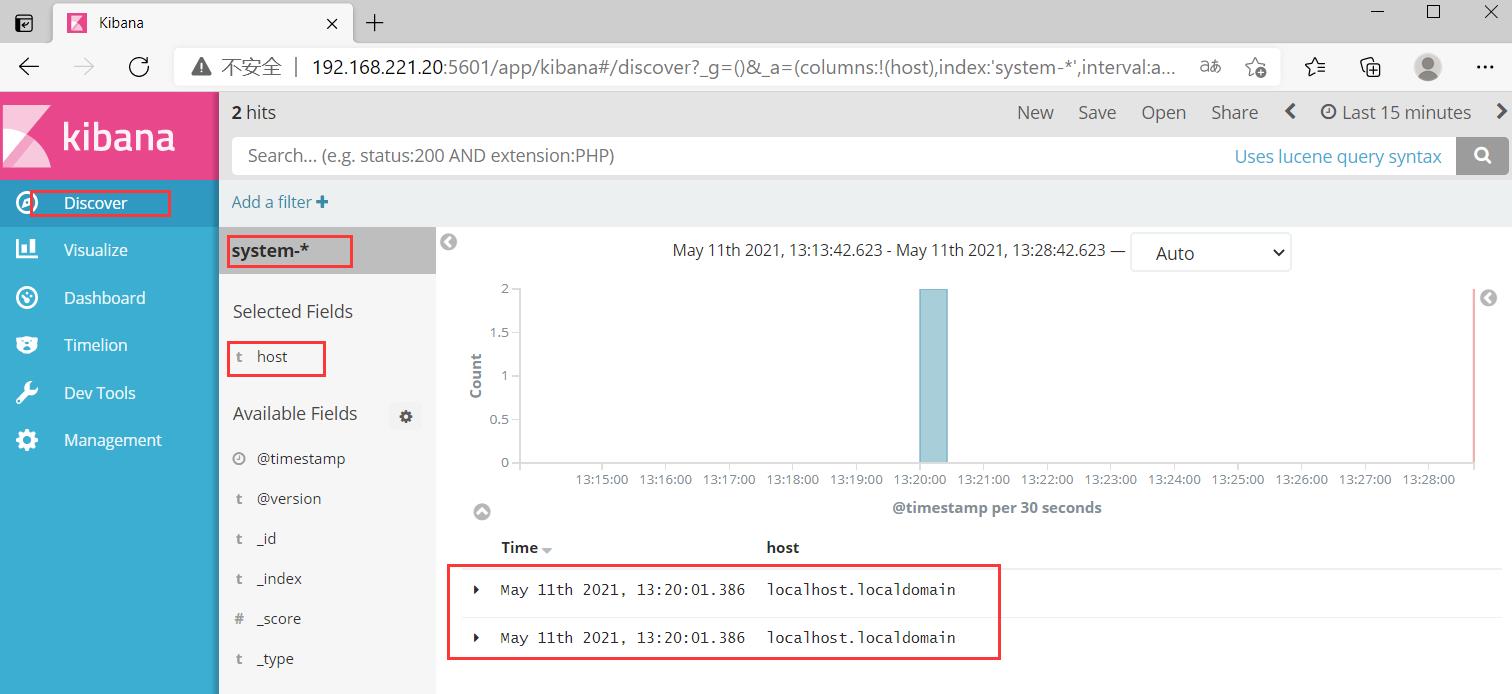
在宿主机192.168.221.188上访问
192.168.221.20:5601
首次登录创建一个索引 名字:system-* (这是对接系统日志文件)
然后点最下面的出面的create 按钮创建
(6)对接Apache主机的Apache 日志文件(访问日志、错误日志)
apache(192.168.221.70)
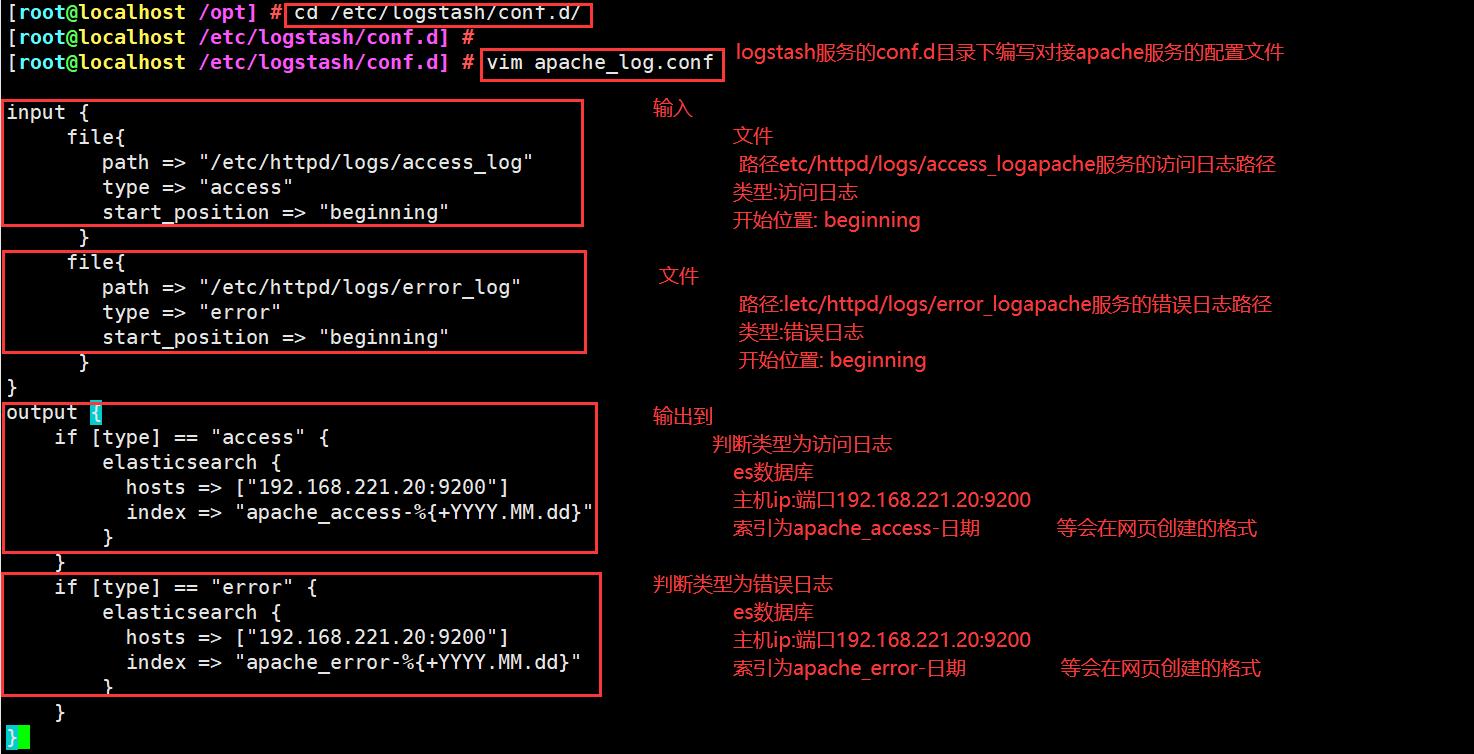
cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
vim apache_log.conf
input {
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/access_log"
type => "access"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/error_log"
type => "error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "access" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.221.20:9200"]
index => "apache_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.221.20:9200"]
index => "apache_error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f apache_log.conf
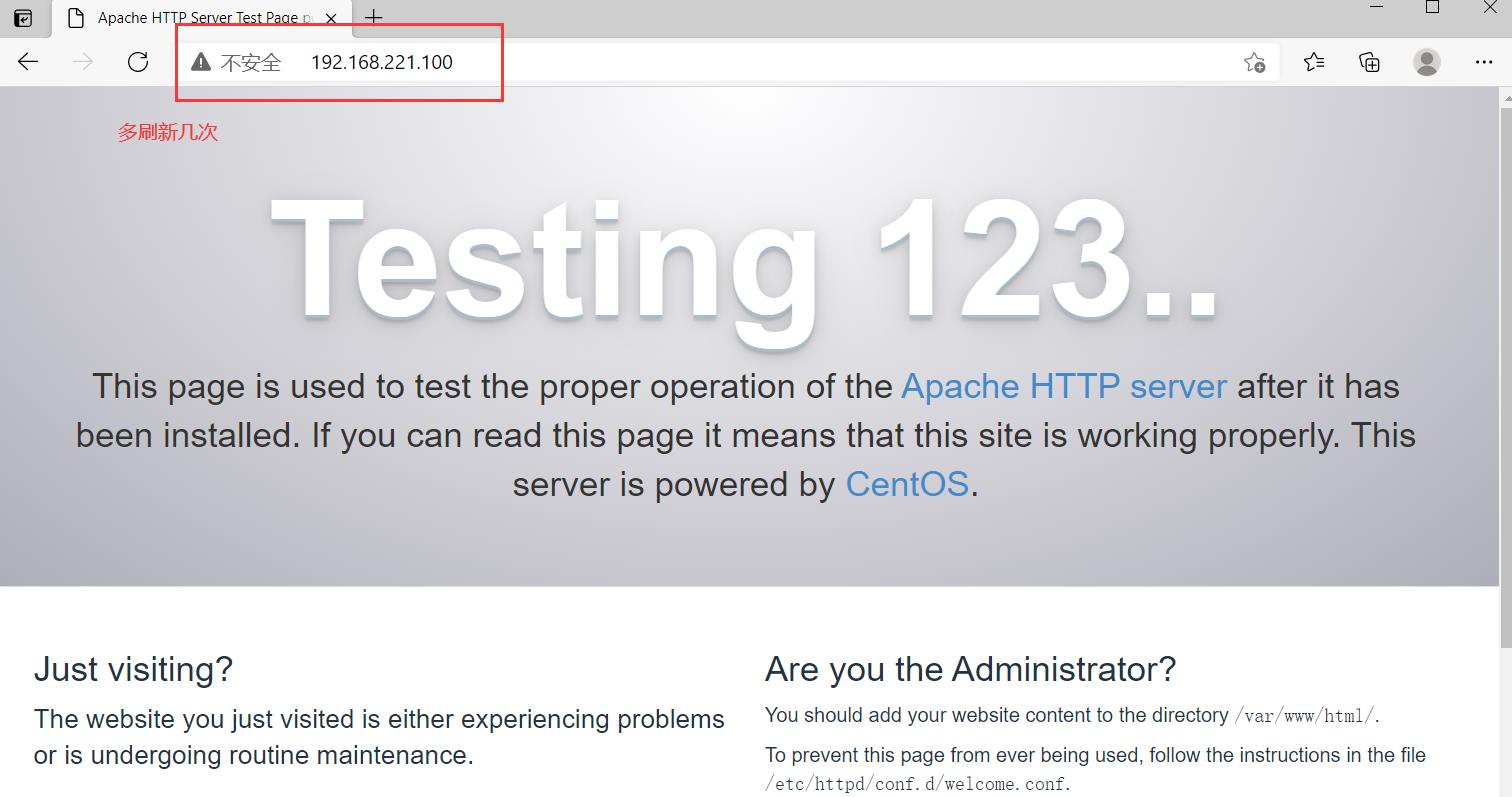
在宿主机192.168.221.188上访问
打开输入http://192.168.221.100,制造点访问记录
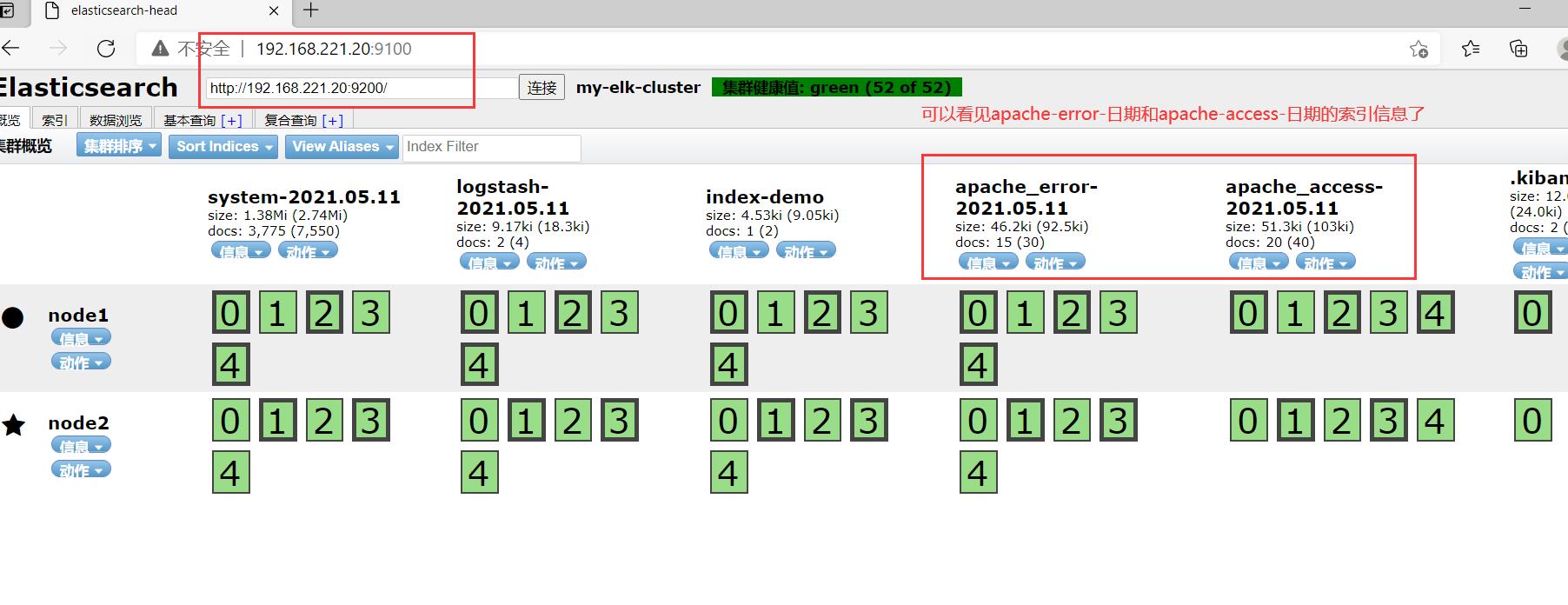
打开浏览器 输入http://192.168.221.20:9100/ 查看索引信息
能发现apache_error-2021.03.04和apache_access-2021.03.04
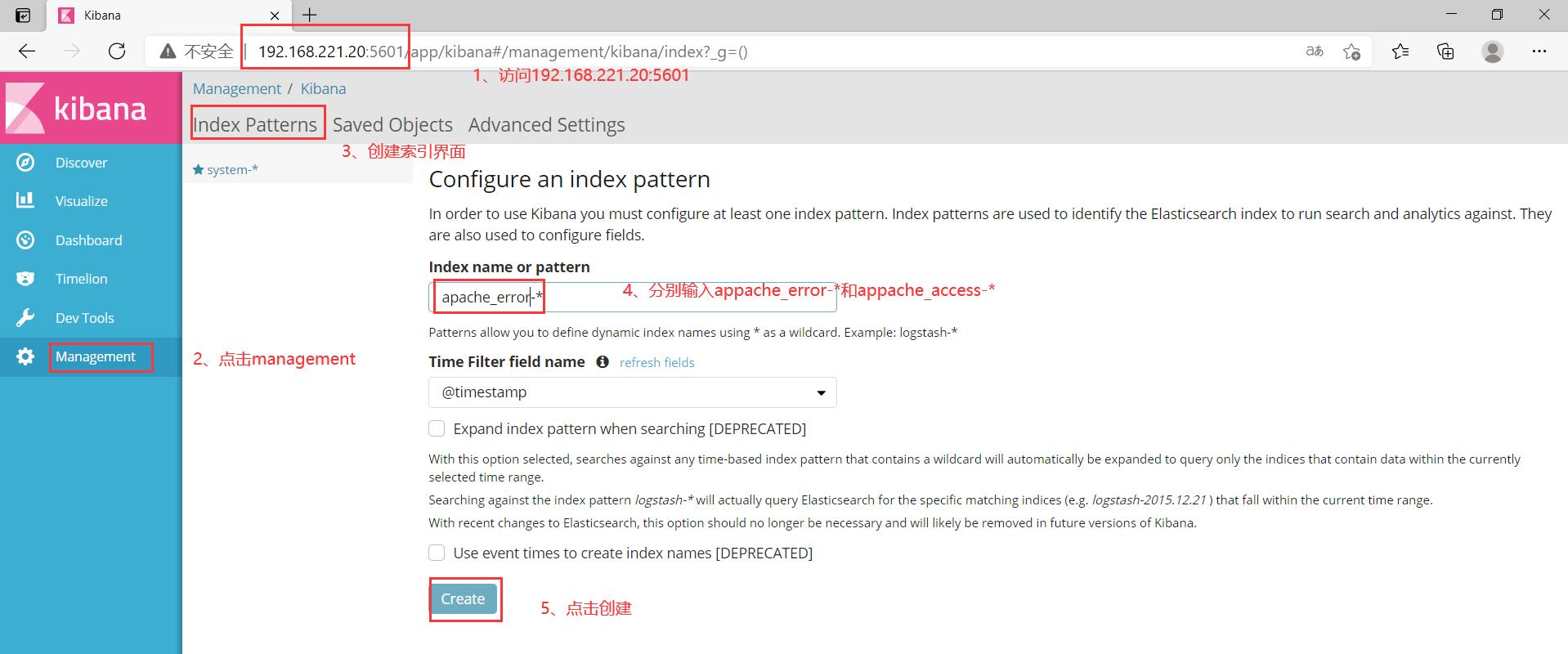
打开浏览器 输入http://192.168.163.11:5601
点击左下角有个management选项—index patterns—create index pattern
分别创建apache_error-* 和 apache_access-* 的索引
总结
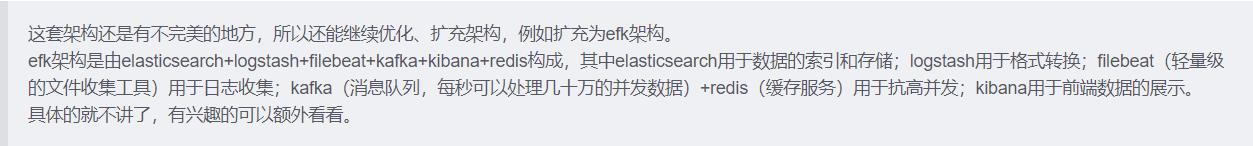
以上是关于10种优雅的MyBatis写法,同事用了都说好的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章