Matlab 一种计算植物面积密度的新方法(论文复现:凸包法)
Posted 大鱼BIGFISH
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Matlab 一种计算植物面积密度的新方法(论文复现:凸包法)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、简介
该方法基于水平切片和森林冠层凸包来计算出植物面积密度(PAD),具体过程如下所述:

1、第一步是对整个点云进行切片。在每个水平切割( z = z i z = z_i z
[CC]点云密度计算
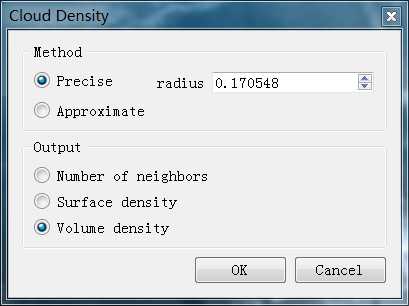
包括两种计算方法:精确计算和近似计算(思考:local density=单位面积的点数 vs local density =1/单个点所占的面积)
每种方法可以实现三种模式的点云密度计算,CC里面的点云计算依赖于 给定的近邻半径所对应的最佳八叉树层级 (通过findBestLevelForAGivenNeighbourhoodSizeExtraction()方法实现)
在GeometricalAnalysisTools类文件中实现。
//volume of a unit sphere static double s_UnitSphereVolume = 4.0 * M_PI / 3.0;
1.精确计算

1 int GeometricalAnalysisTools::computeLocalDensity( GenericIndexedCloudPersist* theCloud,
2 Density densityType,
3 PointCoordinateType kernelRadius,
4 GenericProgressCallback* progressCb/*=0*/,
5 DgmOctree* inputOctree/*=0*/)
6 {
7 if (!theCloud)
8 return -1;
9
10 unsigned numberOfPoints = theCloud->size();
11 if (numberOfPoints < 3)
12 return -2;
13
14 //compute the right dimensional coef based on the expected output
15 double dimensionalCoef = 1.0;
16 switch (densityType)
17 {
18 case DENSITY_KNN:
19 dimensionalCoef = 1.0;
20 break;
21 case DENSITY_2D:
22 dimensionalCoef = M_PI * (static_cast<double>(kernelRadius) * kernelRadius);
23 break;
24 case DENSITY_3D:
25 dimensionalCoef = s_UnitSphereVolume * ((static_cast<double>(kernelRadius) * kernelRadius) * kernelRadius);
26 break;
27 default:
28 assert(false);
29 return -5;
30 }
31
32 DgmOctree* theOctree = inputOctree;
33 if (!theOctree)
34 {
35 theOctree = new DgmOctree(theCloud);
36 if (theOctree->build(progressCb) < 1)
37 {
38 delete theOctree;
39 return -3;
40 }
41 }
42
43 theCloud->enableScalarField();
44
45 //determine best octree level to perform the computation
46 unsigned char level = theOctree->findBestLevelForAGivenNeighbourhoodSizeExtraction(kernelRadius);
47
48 //parameters
49 void* additionalParameters[] = { static_cast<void*>(&kernelRadius),
50 static_cast<void*>(&dimensionalCoef) };
51
52 int result = 0;
53
54 if (theOctree->executeFunctionForAllCellsAtLevel( level,
55 &computePointsDensityInACellAtLevel,
56 additionalParameters,
57 true,
58 progressCb,
59 "Local Density Computation") == 0)
60 {
61 //something went wrong
62 result = -4;
63 }
64
65 if (!inputOctree)
66 delete theOctree;
67
68 return result;
69 }

1 //"PER-CELL" METHOD: LOCAL DENSITY
2 //ADDITIONNAL PARAMETERS (2):
3 // [0] -> (PointCoordinateType*) kernelRadius : spherical neighborhood radius
4 // [1] -> (ScalarType*) sphereVolume : spherical neighborhood volume
5 bool GeometricalAnalysisTools::computePointsDensityInACellAtLevel( const DgmOctree::octreeCell& cell,
6 void** additionalParameters,
7 NormalizedProgress* nProgress/*=0*/)
8 {
9 //parameter(s)
10 PointCoordinateType radius = *static_cast<PointCoordinateType*>(additionalParameters[0]);
11 double dimensionalCoef = *static_cast<double*>(additionalParameters[1]);
12
13 assert(dimensionalCoef > 0);
14
15 //structure for nearest neighbors search
16 DgmOctree::NearestNeighboursSphericalSearchStruct nNSS;
17 nNSS.level = cell.level;
18 nNSS.prepare(radius,cell.parentOctree->getCellSize(nNSS.level));
19 cell.parentOctree->getCellPos(cell.truncatedCode,cell.level,nNSS.cellPos,true);
20 cell.parentOctree->computeCellCenter(nNSS.cellPos,cell.level,nNSS.cellCenter);
21
22 unsigned n = cell.points->size(); //number of points in the current cell
23
24 //for each point in the cell
25 for (unsigned i=0; i<n; ++i)
26 {
27 cell.points->getPoint(i,nNSS.queryPoint);
28
29 //look for neighbors inside a sphere
30 //warning: there may be more points at the end of nNSS.pointsInNeighbourhood than the actual nearest neighbors (neighborCount)!
31 unsigned neighborCount = cell.parentOctree->findNeighborsInASphereStartingFromCell(nNSS,radius,false);
32 //数目/体积
33 ScalarType density = static_cast<ScalarType>(neighborCount/dimensionalCoef);
34 cell.points->setPointScalarValue(i,density);
35
36 if (nProgress && !nProgress->oneStep())
37 {
38 return false;
39 }
40 }
41
42 return true;
43 }
2. 近似计算

1 int GeometricalAnalysisTools::computeLocalDensityApprox(GenericIndexedCloudPersist* theCloud, 2 Density densityType, 3 GenericProgressCallback* progressCb/*=0*/, 4 DgmOctree* inputOctree/*=0*/) 5 { 6 if (!theCloud) 7 return -1; 8 9 unsigned numberOfPoints = theCloud->size(); 10 if (numberOfPoints < 3) 11 return -2; 12 13 DgmOctree* theOctree = inputOctree; 14 if (!theOctree) 15 { 16 theOctree = new DgmOctree(theCloud); 17 if (theOctree->build(progressCb) < 1) 18 { 19 delete theOctree; 20 return -3; 21 } 22 } 23 24 theCloud->enableScalarField(); 25 26 //determine best octree level to perform the computation 27 unsigned char level = theOctree->findBestLevelForAGivenPopulationPerCell(3); 28 29 //parameters 30 void* additionalParameters[] = { static_cast<void*>(&densityType) }; 31 32 int result = 0; 33 34 if (theOctree->executeFunctionForAllCellsAtLevel( level, 35 &computeApproxPointsDensityInACellAtLevel, 36 additionalParameters, 37 true, 38 progressCb, 39 "Approximate Local Density Computation") == 0) 40 { 41 //something went wrong 42 result = -4; 43 } 44 45 if (!inputOctree) 46 delete theOctree; 47 48 return result; 49 }

1 //"PER-CELL" METHOD: APPROXIMATE LOCAL DENSITY 2 //ADDITIONAL PARAMETERS (0): NONE 3 bool GeometricalAnalysisTools::computeApproxPointsDensityInACellAtLevel(const DgmOctree::octreeCell& cell, 4 void** additionalParameters, 5 NormalizedProgress* nProgress/*=0*/) 6 { 7 //extract additional parameter(s) 8 Density densityType = *static_cast<Density*>(additionalParameters[0]); 9 10 DgmOctree::NearestNeighboursSearchStruct nNSS; 11 nNSS.level = cell.level; 12 nNSS.alreadyVisitedNeighbourhoodSize = 0; 13 nNSS.minNumberOfNeighbors = 2; 14 cell.parentOctree->getCellPos(cell.truncatedCode,cell.level,nNSS.cellPos,true); 15 cell.parentOctree->computeCellCenter(nNSS.cellPos,cell.level,nNSS.cellCenter); 16 17 unsigned n = cell.points->size(); 18 for (unsigned i=0; i<n; ++i) 19 { 20 cell.points->getPoint(i,nNSS.queryPoint); 21 22 //the first point is always the point itself! 23 if (cell.parentOctree->findNearestNeighborsStartingFromCell(nNSS) > 1) 24 { 25 double R2 = nNSS.pointsInNeighbourhood[1].squareDistd; 26 27 ScalarType density = NAN_VALUE; 28 if (R2 > ZERO_TOLERANCE) 29 { 30 switch (densityType) 31 { 32 case DENSITY_KNN: 33 { 34 //we return in fact the (inverse) distance to the nearest neighbor 35 density = static_cast<ScalarType>(1.0 / sqrt(R2)); 36 } 37 break; 38 case DENSITY_2D: 39 { 40 //circle area (2D approximation) 41 double circleArea = M_PI * R2; 42 density = static_cast<ScalarType>(1.0 / circleArea); 43 } 44 break; 45 case DENSITY_3D: 46 { 47 //sphere area 48 double sphereArea = s_UnitSphereVolume * R2 * sqrt(R2); 49 density = static_cast<ScalarType>(1.0 / sphereArea); 50 } 51 break; 52 default: 53 assert(false); 54 break; 55 } 56 } 57 cell.points->setPointScalarValue(i,density); 58 } 59 else 60 { 61 //shouldn‘t happen! Apart if the cloud has only one point... 62 cell.points->setPointScalarValue(i,NAN_VALUE); 63 } 64 65 if (nProgress && !nProgress->oneStep()) 66 { 67 return false; 68 } 69 } 70 71 return true; 72 }
以上是关于Matlab 一种计算植物面积密度的新方法(论文复现:凸包法)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
