java并发设计模式
Posted halulu.me
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java并发设计模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
终止模式
两阶段终止模式(Two Phase Termination)
错误思路
1、使用线程对象的 stop() 方法停止线程
stop方法会真正杀死线程,如果这时线程锁住了共享资源,那么当它被杀死后就再也没有机会释放锁, 其它线程将永远无法获取锁
2、使用 System.exit(int) 方法停止线程
目的仅是停止一个线程,但这种做法会让整个程序都停止
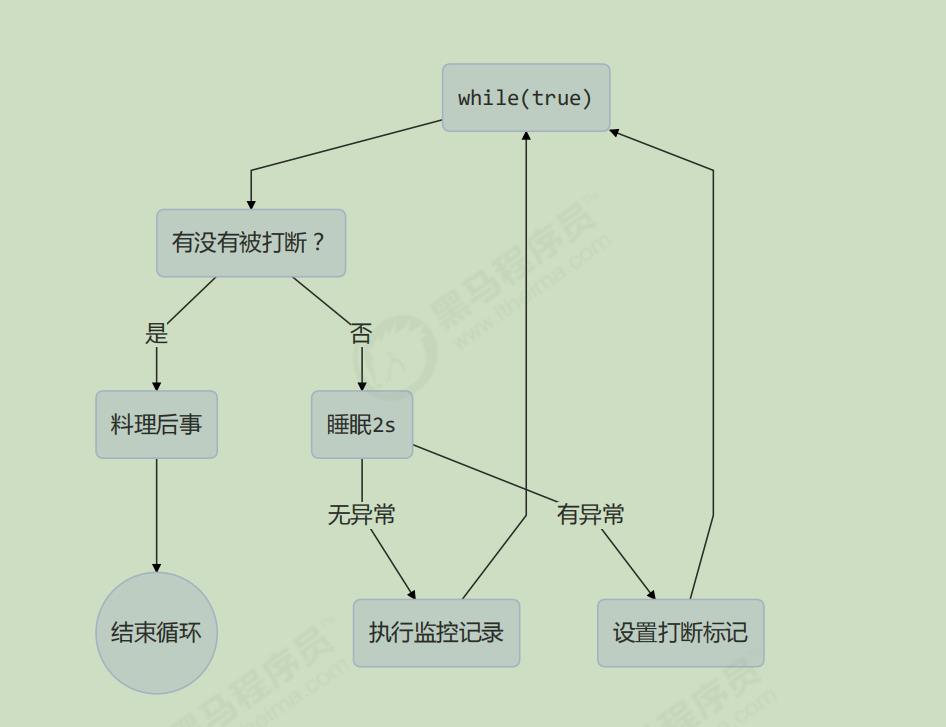
两阶段终止模式–interrupt
@Slf4j(topic = "c.tpt")
public class TwoPhaseTermination
private Thread monitor;
public void start()
monitor = new Thread("t1")
@Override
public void run()
while (true)
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted())
log.debug("处理后事");
break;
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("检测记录");
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
;
monitor.start();
public void stop()
monitor.interrupt();
两阶段终止模式—volatile
class TwoPhaseTermination
// 监控线程
private Thread monitorThread;
// 停止标记
private volatile boolean stop = false;
// 启动监控线程
public void start()
monitorThread = new Thread(() ->
while (true)
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 是否被打断
if (stop)
log.debug("料理后事");
break;
try
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("执行监控记录");
catch (InterruptedException e)
, "monitor");
monitorThread.start();
// 停止监控线程
public void stop()
stop = true;
monitorThread.interrupt();
同步模式
保护性暂停
保护性暂停即 Guarded Suspension,用在一个线程等待另一个线程的执行结果
要点
1、有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一个线程,让他们关联同一个GuardedObject
2、如果有结果不断从一个线程到另一个线程那么可以使用消息队列(见生产者/消费者)
3、JDK 中,join 的实现、Future的实现,采用的就是此模式
4、使用wait—notifyall
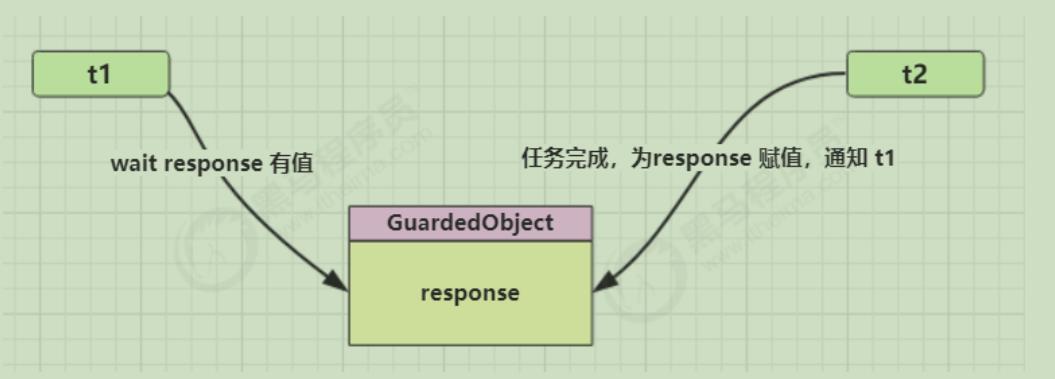
public class GuardedObject
private Object response;
private final Object obj = new Object();
public Object get()
synchronized (obj)
while (response == null)
try
obj.wait();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return response;
public void setResponse(Object response)
synchronized (obj)
this.response = response;
obj.notifyAll();
带超时版 GuardedObject
public static void main(String[] args)
GuardedObject object = new GuardedObject();
new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
object.get(1000);
.start();
new Thread()
@Override
public void run()
try
Thread.sleep(1020);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
object.setResponse(10000);
.start();
private Object response;
private final Object obj = new Object();
mill 表示要等待多久 2000
public Object get(long mill)
synchronized (obj)
//记录最初时间 15:00:00
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//已经经历的时间
long timePassed = 0;
while (response == null)
// 这一轮循环应该等待的时间
long waitTime = mill - timePassed;
log.info("waitTime:",waitTime);
// 经历的时间超过了最大等待时间时,退出循环
if(waitTime <= 0)
log.info("break");
break;
try
obj.wait(waitTime); // 虚假唤醒 15:00:01
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 求得经历时间
timePassed = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
log.info("timePassed:,response:",timePassed,response);
return response;
public void setResponse(Object response)
synchronized (obj)
this.response = response;
log.info("notify...");
obj.notifyAll();
多任务版 GuardedObject
结果产生者和结果消费者是一一对应的关系。

新增id用来标识Guarded Object
public class GuardedObject
//标识Guarded Object
private int id;
public int getId()
return id;
public GuardedObject(int id)
this.id = id;
private Object response;
public Object get(long mill)
synchronized (this)
//记录最初时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//已经经历的时间
long timePassed = 0;
while (response == null)
long waitTime = mill - timePassed;
if(waitTime <= 0)
break;
try
this.wait(waitTime);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
timePassed = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
return response;
public void setResponse(Object response)
synchronized (this)
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
中间解耦类
ublic class MailBoxes
private static Map<Integer,GuardedObject> boxes = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//产生唯一id
private static int id;
public static synchronized int generateId()
return id++;
//送信人获取邮箱--GuardedObject
public static GuardedObject getGuarderObject(int id)
//根据唯一id获取邮箱并删除
return boxes.remove(id);
//收信人创建邮箱--GuardedObject
public static GuardedObject createGuarderObject()
GuardedObject go = new GuardedObject(generateId());
boxes.put(go.getId(), go);
return go;
//获取所有id
public static Set<Integer> getIds()
return boxes.keySet();
业务代码
@Slf4j
public class PostMan extends Thread
private int id;
private String mail;
public PostMan(int id,String mail)
this.id = id;
this.mail = mail;
@Override
public void run()
GuardedObject guardedObject = MailBoxes.getGuarderObject(id);
log.info("送信id:,内容:",id,mail);
guardedObject.setResponse(mail);
@Slf4j
class People extends Thread
@Override
public void run()
GuardedObject go = MailBoxes.createGuarderObject();
log.info("开始收信 id:",go.getId());
Object mail = go.get(5000);
log.info("收到的信 id:, mail:" ,go.getId(),mail);
犹豫模式(blaking)
Balking (犹豫)模式用在一个线程发现另一个线程或本线程已经做了某一件相同的事,那么本线程就无需再做了,直接结束返回
保证线程只启动一次,实现线程的单例

顺序控制
固定运行顺序(wait-notify版)
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test25")
public class Test25
static final Object lock = new Object();
// 表示 t2 是否运行过
static boolean t2runned = false;
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->
synchronized (lock)
while (!t2runned)
try
lock.wait();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("1");
, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->
synchronized (lock)
log.debug("2");
t2runned = true;
lock.notify();
, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
固定运行顺序(park-unpark版)
public class Test26
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("1");
, "t1");
t1.start();
new Thread(() ->
log.debug("2");
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
,"t2").start();
交替输出(wait-notify版)
public class Test27
public static void main(String[] args)
WaitNotify wn = new WaitNotify(1, 5);
new Thread(() ->
wn.print("a", 1, 2);
).start();
new Thread(() ->
wn.print("b", 2, 3);
).start();
new Thread(() ->
wn.print("c", 3, 1);
).start();
/*
输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记
a 1 2
b 2 3
c 3 1
*/
class WaitNotify
// 打印 a 1 2
public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFlag)
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++)
synchronized (this)
while(flag != waitFlag)
try
this.wait();
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.print(str);
flag = nextFlag;
this.notifyAll();
// 等待标记
private int flag; // 2
// 循环次数
private int loopNumber;
public WaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber)
this.flag = flag;
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
交替输出(await-singnal版)
public class Test30
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
AwaitSignal awaitSignal = new AwaitSignal(5);
Condition a = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition b = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition c = awaitSignal.newCondition();
new Thread(() ->
awaitSignal.print("a", a, b);
).start();
new Thread(() ->
awaitSignal.print("b", b