Android 源码分析 ContentProvider 启动
Posted 小图包
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 源码分析 ContentProvider 启动相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ContentProvider (内容提供者) 属于四大组件之一,可以说它是在四大组件中开发者使用率最少的一个,它的作用就是进程间进行数据交互,底层采用 Binder 机制进行进程间通信。
下面我们就以分析 ContentProvider 工作流程为主来进行全面分析。
源码分析
query 到 AMS 调用过程
下面先来看一个代码示例,代码如下:
fun getContactsLists(): MutableList<String>
var contactsLists: MutableList<String> = mutableListOf<String>()
lateinit var cursor: Cursor
try
//使用 getContentResolver() 查询联系人列表
cursor = contentResolver.query(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI, null, null, null, null)
//对 cursor 进行遍历
if (cursor != null)
while (cursor.moveToNext())
//电话号码
val number = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER))
contactsLists.add("电话:$number")
cursor.close()
catch (error: Exception)
logger.error("error:$error")
return contactsLists
//测试
val contactsLists = getContactsLists()
contactsLists.forEach it -> println("通过ContentResolver获取联系人: $contactsLists")
那么这一流程内部是怎么运行的,下面进入代码分析。老规矩,还是看一下该小节分析流程,这里以时序图为主
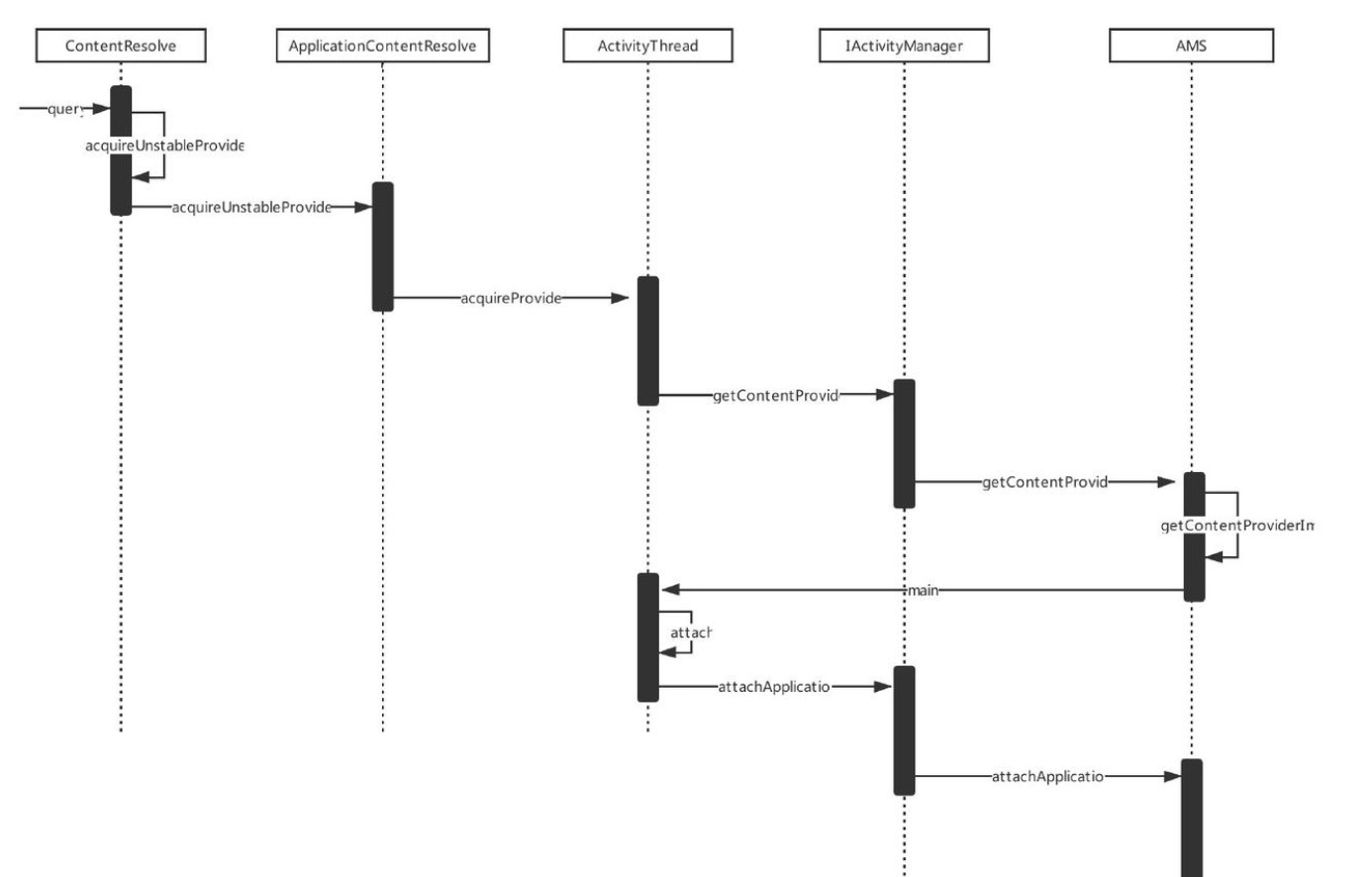
通过上面代码示例想要 query 数据先要拿到 contentResolver 对象,通过父类 getContentResolver()方法获得,代码如下:
@Override
public ContentResolver getContentResolver()
return mBase.getContentResolver();
这里的 mBase 是 Context 对象,它的实现类就是 ContextImpl 我们直接看它具体实现,代码如下:
//ContextImpl.java
@Override
public ContentResolver getContentResolver()
return mContentResolver;
这里的 getContentResolver 方法中返回了 ApplicationContentResolver 对象,它是 ContextImpl 的静态内部类,继承自 ContentResolver ,它在 ContextImpl 的构造方法中被创建,就会启动 ContentProvider,这里以上面我们示例 query 来进行分析,我们看它的具体实现,
//ContentResolver.java
public final @Nullable Cursor query(final @RequiresPermission.Read @NonNull Uri uri,
@Nullable String[] projection, @Nullable Bundle queryArgs,
@Nullable CancellationSignal cancellationSignal)
Preconditions.checkNotNull(uri, "uri");
1. 拿到 IContentProvider 对象,它是 ContentProvider 的本地代理
IContentProvider unstableProvider = acquireUnstableProvider(uri);
if (unstableProvider == null)
return null;
IContentProvider stableProvider = null;
Cursor qCursor = null;
try
try
2. 调用 IContentProvider 的 query 函数来进行 query
qCursor = unstableProvider.query(mPackageName, uri, projection,
queryArgs, remoteCancellationSignal);
catch (DeadObjectException e)
//...
return wrapper;
catch (RemoteException e)
return null;
finally
...
通过 acquireUnstableProvider 方法拿到 ContentProvider 的本地代理对象,我们先来看下注释 1 的 acquireUnstableProvider 方法怎么拿到 ContentProvider 本地代理对象,代码如下:
//ContentResolver.java
public final IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Uri uri)
if (!SCHEME_CONTENT.equals(uri.getScheme()))
return null;
String auth = uri.getAuthority();
if (auth != null)
//调用内部抽象方法
return acquireUnstableProvider(mContext, uri.getAuthority());
return null;
/** @hide */
protected abstract IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Context c, String name);
//ContextImpl.java
@Override
protected IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Context c, String auth)
return mMainThread.acquireProvider(c,
ContentProvider.getAuthorityWithoutUserId(auth),
resolveUserIdFromAuthority(auth), false);
return 返回的对象,首先拿到 mMainThread 对象,然后调用它内部的 acquireProvider 方法
//ActivityThread.java
public final IContentProvider acquireProvider(
Context c, String auth, int userId, boolean stable)
1. acquireExistingProvider 方法主要检查 ActivityThread 全局变量 mProviderMap 中是否有目标 ContentProvider 存在,有就返回,没有就通过注释 2 处获取,
final IContentProvider provider = acquireExistingProvider(c, auth, userId, stable);
if (provider != null)
return provider;
ContentProviderHolder holder = null;
try
2. 调用 IAcitivityManager 获取 ContentProviderHolder 对象
holder = ActivityManager.getService().getContentProvider(
getApplicationThread(), auth, userId, stable);
catch (RemoteException ex)
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
...
3. 用来安装 ContentProvider
holder = installProvider(c, holder, holder.info,
true /*noisy*/, holder.noReleaseNeeded, stable);
return holder.provider;
总结
1 处的 acquireExistingProvider 方法内部会检查 ActivityThread 的全局变量 mProviderMap 中是否有 ContentProvider 存在
2 处 的 IActivityManager 的 getContentProvider 方法与 AMS 进行通信来获取
3 是安装 ContentProvider,并将 ContentProvider 相关数据存储在 mProviderMap 中,起到缓存作用
我们现在来看下AMS 的 getContentProvider 方法具体实现,代码如下:
//AMS.java
@Override
public final ContentProviderHolder getContentProvider(
IApplicationThread caller, String name, int userId, boolean stable)
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("getContentProvider");
...
//调动内部 getContentProviderImpl 方法
return getContentProviderImpl(caller, name, null, stable, userId);
//AMS.java
private ContentProviderHolder getContentProviderImpl(IApplicationThread caller,
String name, IBinder token, boolean stable, int userId)
ContentProviderRecord cpr;
ContentProviderConnection conn = null;
ProviderInfo cpi = null;
..1. 获取目标 ContentProvider 应用程序进程的信息,如果进程已经启动就调用注释 2 ,否则调用注释 3
ProcessRecord proc = getProcessRecordLocked(
cpi.processName, cpr.appInfo.uid, false);
if (proc != null && proc.thread != null && !proc.killed)
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.d(TAG_PROVIDER,
"Installing in existing process " + proc);
if (!proc.pubProviders.containsKey(cpi.name))
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: scheduling install");
proc.pubProviders.put(cpi.name, cpr);
try
2. 调用 IApplicationThreadscheduleInstallProvider 函数
proc.thread.scheduleInstallProvider(cpi);
catch (RemoteException e)
else
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: before start process");
3. 启动新进程
proc = startProcessLocked(cpi.processName,
cpr.appInfo, false, 0, "content provider",
new ComponentName(cpi.applicationInfo.packageName,
cpi.name), false, false, false);
checkTime(startTime, "getContentProviderImpl: after start process");
if (proc == null)
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to launch app "
+ cpi.applicationInfo.packageName + "/"
+ cpi.applicationInfo.uid + " for provider "
+ name + ": process is bad");
return null;
cpr.launchingApp = proc;
mLaunchingProviders.add(cpr);
finally
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
....
2 位置执行流程,首先调用 ActivityThread 的内部类 IApplication 的scheduleInstallProvider 函数,然后通过 H sendMessage 通知进行安装 ContentProvider
看3位置处我们直接看 ActivityThread main 函数,代码如下
//AMS.java
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName, boolean allowWhileBooting,
boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge)
return startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags, hostingType,
hostingName, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */, keepIfLarge,
null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */, null /* entryPointArgs */,
null /* crashHandler */);
我们直接看 ActivityThread main 函数,代码如下
//ActivityThread.java
//通过反射调用执行的
public static void main(String[] args)
....
//主线程消息循环
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
//创建 ActivityThread 对象
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
//Application,Activity 入口
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null)
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
if (false)
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
主要看 ActivityThread attach 函数具体实现,代码如下:
//ActivityThread.java
private void attach(boolean system)
...
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try
关联 Application
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
catch (RemoteException ex)
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
...
从上得到 AMS 的代理类 IActivityManager ,在注释 调用 AMS 的 attachApplication 函数,并将 IApplicationThread 对象传入 AMS 保持应用进程和 AMS 跨进程通信,应用程序调用 AMS 的过程就分析完了,下面我们分析 AMS 到应用程序进程的 ContentProvider 安装过程
AMS 启动 ContentProvider 的过程
先看流程图
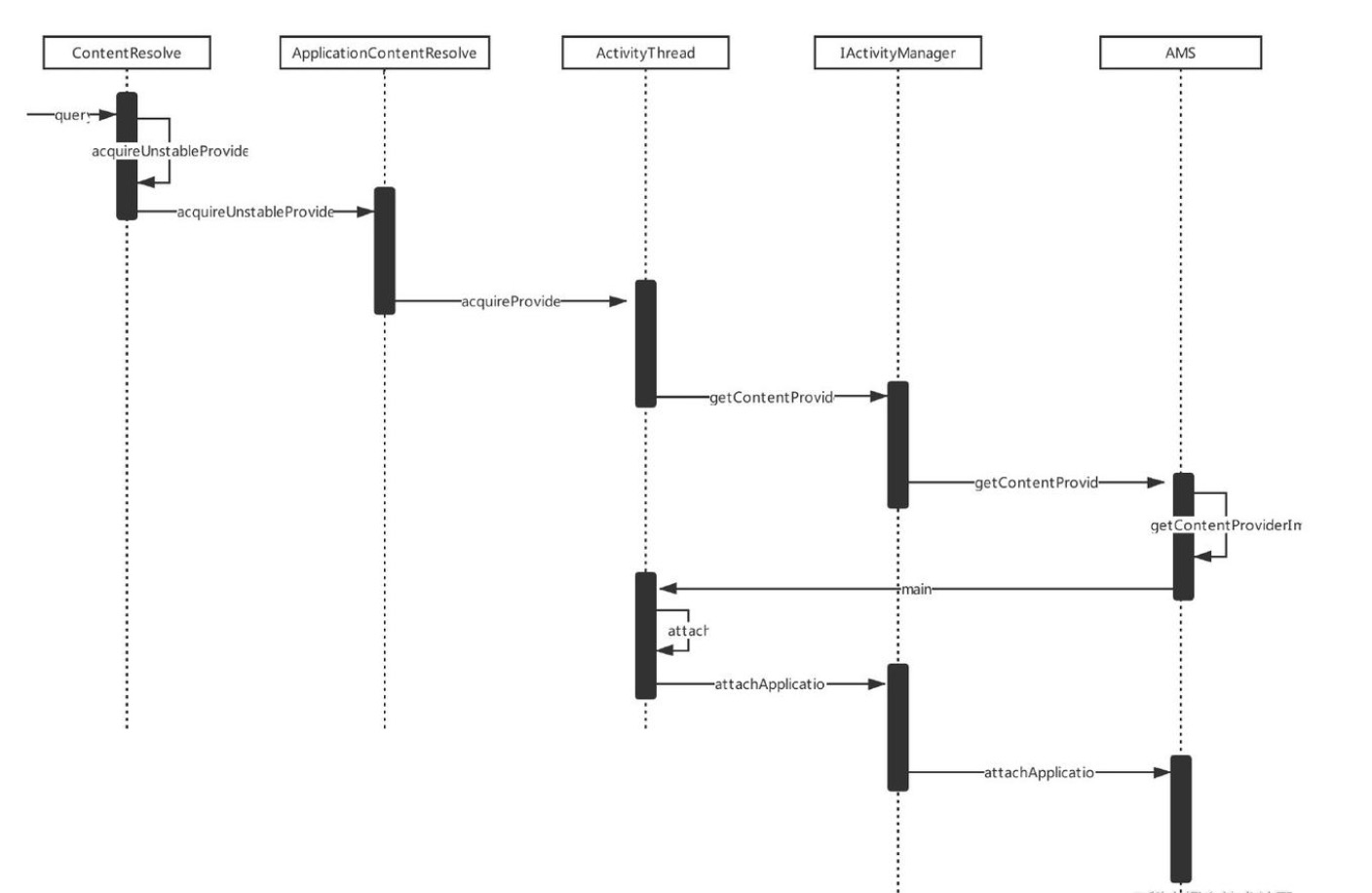
//AMS.java
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid)
...
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
...
在 attachApplicationLocked 函数中调用了 thread.bindApplication 方法,thread 是 IApplicationThread ,这里和 IActivityManager 一样采用了 aidl 进行进程间传输数据,我们回到 ActivityThread 内部类 ApplicationThread 的 bindApplication 方法
//ActivityThread.java
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial)
if (services != null)
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
data.buildSerial = buildSerial;
//发送消息给 H 类
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
ActivityThread 内部类 H 收到消息,开始处理 BIND_APPLICSTION消息,代码如下:
//ActivityThread.java
...
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
...
case BIND_APPLICATION:
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
break;
...
...
//ActivityThread.java
...
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
...
case BIND_APPLICATION:
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
break;
...
...
//ActivityThread.java
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data)
...
1. 创建 ContentImpl
final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, data.info);
...
2 通过反射创建 Instrumentation
final ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();
mInstrumentation = (Instrumentation)
cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
catch (Exception e)
...
final ComponentName component = new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name);
3 处初始化 Instrumentaion
mInstrumentation.init(this, instrContext, appContext, component,
data.instrumentationWatcher, data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);
....
try
创建 Application
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode)
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers))
5 ContentProvider 启动的
installContentProviders(app, data.providers);
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10*1000);
try
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
catch (Exception e)
...
try
6 调用 Application onCreate 生命周期方法
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
catch (Exception e)
...
注释 5 看 ContentProvider 是如何启动的,代码如下:
//ActivityThread.java
private void installContentProviders(
Context context, List<ProviderInfo> providers)
final ArrayList<ContentProviderHolder> results = new ArrayList<>();
1 遍历当前应用程序进程的 ProviderInfo 列表,得到每个 ContentProvicer 的存储信息
for (ProviderInfo cpi : providers)
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER)
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(128);
buf.append("Pub ");
buf.append(cpi.authority);
buf.append(": ");
buf.append(cpi.name);
Log.i(TAG, buf.toString());
2 调用 installProvider 方法来启动这些 ContentProvider
ContentProviderHolder cph = installProvider(context, null, cpi,
false /*noisy*/, true /*noReleaseNeeded*/, true /*stable*/);
if (cph != null)
cph.noReleaseNeeded = true;
results.add(cph);
try
3 处是将启动了的 ContentProvider 存入 AMS 的 mProviderMap 中 就是用来缓存启动过的 ContentProvidec
ActivityManager.getService().publishContentProviders(
getApplicationThread(), results);
catch (RemoteException ex)
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
现在来看调用 installProvider 方法来启动这些 ContentProvider
//ActivityThread.java
private ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context,
ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable)
....
try
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = c.getClassLoader();
1 通过反射实例化 ContentProvider 对象
localProvider = (ContentProvider)cl.
loadClass(info.name).newInstance();
provider = localProvider.getIContentProvider();
...
2处调用它的 attachInfo 方法
localProvider.attachInfo(c, info);
catch (java.lang.Exception e)
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(null, e))
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to get provider " + info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
return null;
....
在注释 2 处调用它的 attachInfo 方法,代码如下
//ContentProvider.java
public void attachInfo(Context context, ProviderInfo info)
attachInfo(context, info, false);
private void attachInfo(Context context, ProviderInfo info, boolean testing)
mNoPerms = testing;
if (mContext == null)
mContext = context;
if (context != null)
mTransport.mAppOpsManager = (AppOpsManager) context.getSystemService(
Context.APP_OPS_SERVICE);
mMyUid = Process.myUid();
if (info != null)
setReadPermission(info.readPermission);
setWritePermission(info.writePermission);
setPathPermissions(info.pathPermissions);
mExported = info.exported;
mSingleUser = (info.flags & ProviderInfo.FLAG_SINGLE_USER) != 0;
setAuthorities(info.authority);
/**
* 安装成功,调用生命周期函数 onCreate
*/
ContentProvider.this.onCreate();
public abstract boolean onCreate();
可以看到最后在 ContentProvider 的 attachInfo 函数中进行调用了抽象方法 onCreate, 那么它的子类就会进行实现 onCreate 达到启动成功的通知。
以上是关于Android 源码分析 ContentProvider 启动的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章