33Java 异常掌握这些就够了(图解 Java 中的异常)
Posted JavaLearnerZGQ
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了33Java 异常掌握这些就够了(图解 Java 中的异常)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
异常文章目录
- 一、引出异常(Exception)
- 二、异常简介
- 三、try-catch 处理异常
- 四、throws 处理异常
- 五、throw 主动抛出异常
- 六、自定义异常
- 七、使用异常的好处
- 八、案例(编写断言类)
一、引出异常(Exception)
(1) 写代码会产生的错误
📝 写代码会遇到各种各样的错误:
✏️ ① 语法错误(会导致编译失败,程序无法正常运行)
✏️ ② 逻辑错误(比如需要进行加法操作时,不小心写成了减法操作)
✏️ ③ 运行时错误(程序运行过程中产生的意外,会导致程序终止运行)
(2) 案例引出异常
❓ 写代码计算三个整数的和 ❓
❓ 若输入的是 null,需要给出提示 ❓
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println(sumThree(1, null, 3));
private static Integer sumThree(Integer n1, Integer n2, Integer n3)
if (n1 == null || n2 == null || n3 == null)
System.out.println("\\n不能传入 null 值");
return -1;
return n1 + n2 + n3;

🍀 上面的代码实现了需求的功能,但不好,主要有以下三点
🍀 ① 错误提示太平淡了,仅仅是打印了错误信息,没有终止程序【假如有很多很多的代码,且后面的代码会依赖该方法的返回值。该方法报错,则后面的代码肯定也是错的,既然后面的代码肯定是错的,为啥还要执行呢❓】
🍀 ② 为了终止该方法中后面代码的执行,必须给予返回值【返回值为多少比较合适呢❓ 给多少都不合适。返回值必须是 Integer 类型,无论给什么值都有可能导致误解。没注意错误信息的人可能会以为 -1 就是三个数的和呐 ❗】
🍀 ③ 错误不够智能,没有告知错误发生在哪一行【假如一个 java 文件中有1万行代码,执行某一行出现错误的时候打印了错误信息,但没有告知是哪一行出现了错误,哪么排查错误的效率就降低了。】
🌼 Java 的异常机制可解决上面的全部问题
🌼 异常一般是红色提示(一目了然)
🌼 若开发者没有处理异常的话,产生异常的时候,后面的代码不会执行
🌼 产生异常后,程序直接退出,不用给返回值
🌼 异常会给一个用于定位错误行的链接(点击即可定位到产生错误的哪一行)
二、异常简介
(1) 异常介绍
📜 Java 中所有的错误和异常最终都继承自 java.lang.Throwable
✒️ The
Throwable classis the superclass of all errors and exceptions in the Java language.【在 Java 语言中,Throwable 类是所有的错误和异常的父类】
✒️ Throwable 是错误的祖宗 😊

📜 检查型异常(Check Exception)【这类异常一般难以避免,编译器会进行检查】
✒️ 如果开发者没有处理检查型异常,编译器将会报错
✒️ 除了 Error 和 RuntimeException 之外的都是检查型异常
📜 非检查型异常(Uncheck Exception)【这类异常一般是可以避免的,编译器不会进行检查】
✒️ 如果开发者没有处理非检查型异常,编译器也不会报错
✒️ Error 和 RuntimeException 都是非检查型异常
(2) 常见的检查型异常
🌼 下面的异常涉及到后期需要学习的知识(如 IO 流、日期类、反射 …)
🌼 了解一下这些异常,知道检查型异常都直接继承自 Exception (没有走 RuntimeException) 即可
① FileNotFoundException
FileNotFoundException: 文件找不到异常

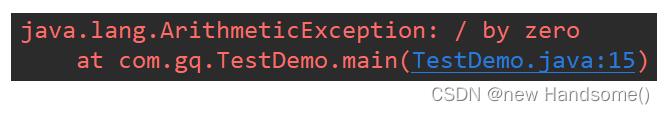
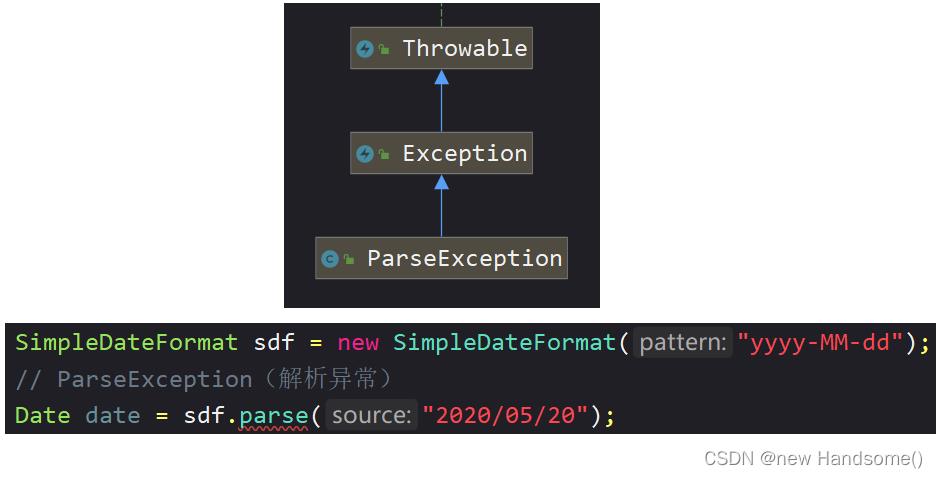
② ParseException
ParseException: 解析异常
③ InterruptedException
InterruptedException: 中断异常

④ ClassNotFoundException
ClassNotFoundException: 类找不到异常

⑤ IllegalAccessException
IllegalAccessException: 没有权限访问构造方法
InstantiationException: 没有无参构造方法

(3) 常见的非检查型异常
🌼 下面的异常很常见,需要知道其原因(为什么会产生这种异常?)
🌼 了解一下这些异常,知道非检查型异常继承自 RuntimeException 或 Error
① OutOfMemoryError【Error】
OutOfMemoryError: 内存溢出异常
public class UncheckException
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println("start");
// OutOfMemoryError(超出内存错误)
long[] longs = new long[10_0000_0000];
// 上面的代码抛出了异常, 下面的代码不会执行
System.out.println("end");

② StackOverflowError【Error】
StackOverflowError: 栈溢出异常
public class UncheckException
public static void main(String[] args)
// StackOverflowError: 栈溢出
test();
private static void test()
// 递归:方法调用自身
test();

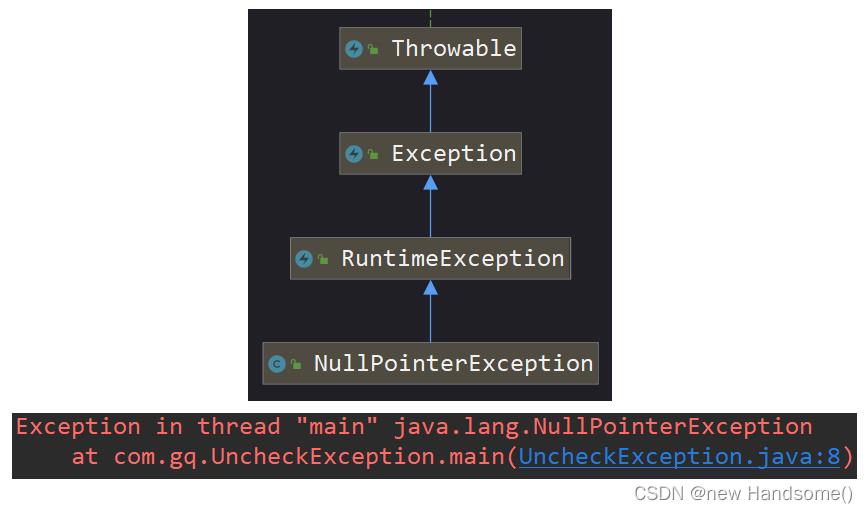
③ NullPointerException【RuntimeException】
NullPointerException: 空指针异常
public class UncheckException
public static void main(String[] args)
String s = null;
// NullPointerException: 空指针异常(用 null 调用方法)
int len = s.length();
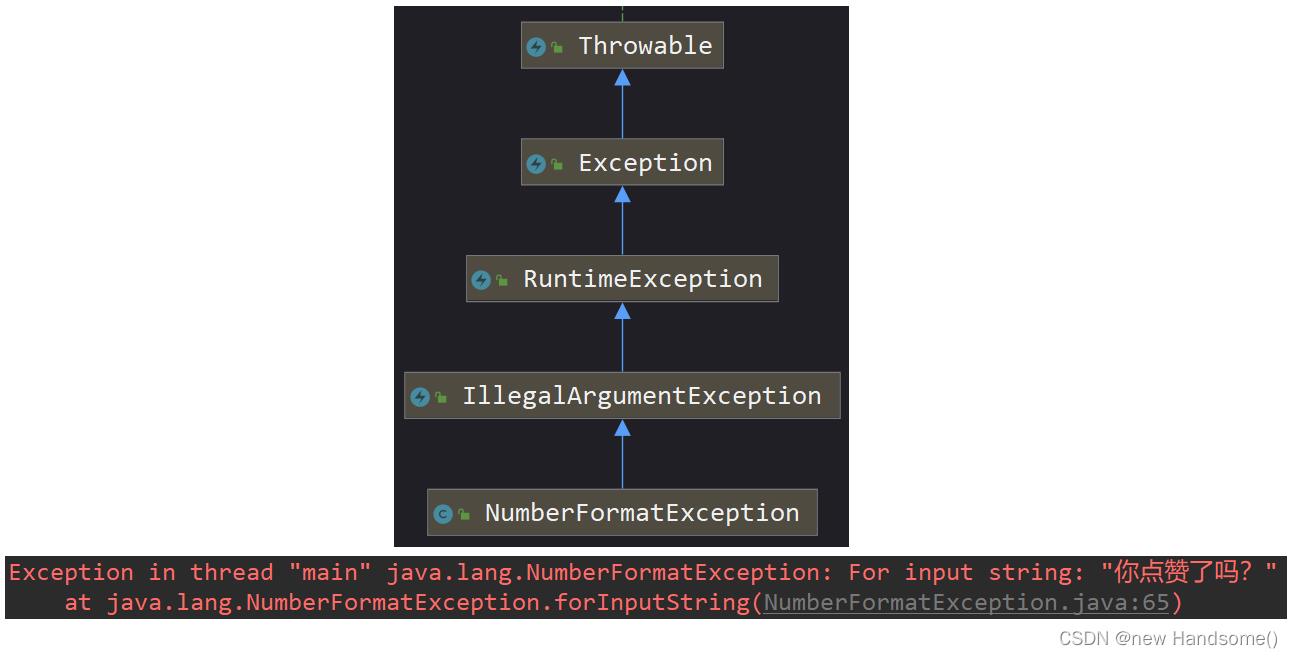
④ NumberFormatException【RuntimeException】
NumberFormatException: 数字格式化异常
public class UncheckException
public static void main(String[] args)
/*
Integer.parseInt(): 把字符串转换为数字
NumberFormatException: 数字格式化异常
原因:句子不能转换为数字
*/
int i = Integer.parseInt("你点赞了吗?");
⑤ ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException【RuntimeException】
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 数组索引越界异常
public class UncheckException
public static void main(String[] args)
int[] ints = new int[3];
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 数组越界异常
System.out.println(ints[66]);

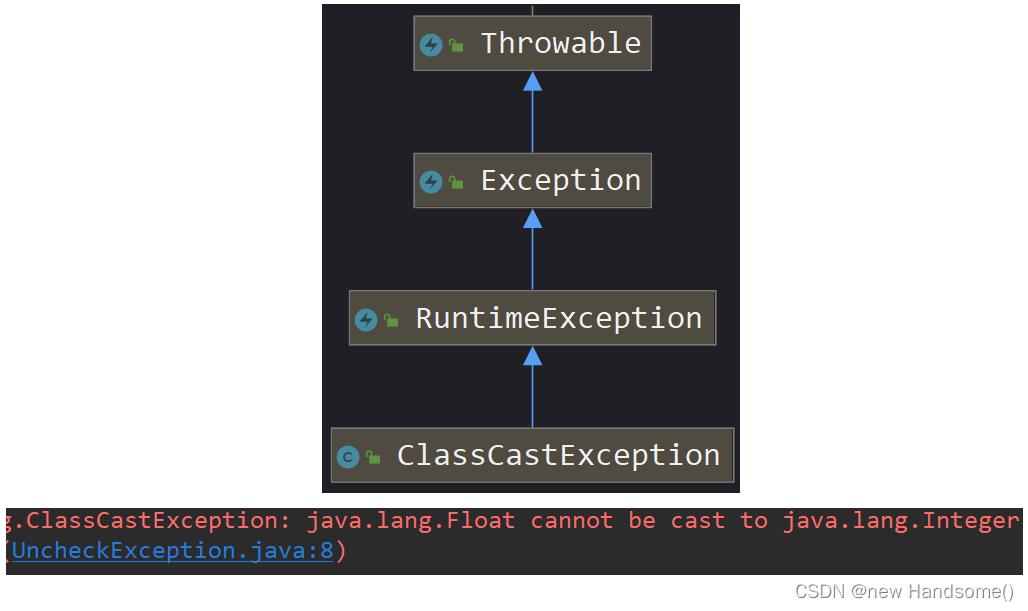
⑥ ClassCastException【RuntimeException】
ClassCastException : 类型转换异常
public class UncheckException
public static void main(String[] args)
Object o = 3.14F;
// ClassCastException 类型转换异常
int i = (int) o;
三、try-catch 处理异常
📜 程序产生了异常,有个专业的术语:抛出了异常
📜 无论是检查型异常,还是非检查型异常,只要开发者没有主动去处理它,都会导致 Java 程序终止运行
📜 处理异常有2种方式:
✒️ ①
try-catch【捕获异常】
✒️ ②throws【往上抛异常】

(1) try-catch
📜 可能抛出异常的代码放try代码块中
📜 catch代码块用于捕获不同类型的异常,并对异常做出处理
🌼
catch代码块中的代码不一定执行,除非抛出了与之相应的(相匹配的)异常
📜 父类型异常必须写在子类型异常的后面(否则会报错)
try-catch 处理异常的格式:
public class TryCatch
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println("不可能抛异常的代码1");
try
// try 代码块中放可能抛异常的代码
System.out.println("该行代码可能抛异常, 如果抛出了异常, 下面的一行代码不会被执行");
System.out.println("如果上面的代码抛出了异常, 本行代码不执行");
catch (NullPointerException e)
// 当抛出【空指针异常】的时候会来到该代码块
System.out.println("抛出了【空指针异常】");
catch (ClassCastException e)
// 当没有抛出【空指针异常】
// 但抛出【类转换异常】的时候会来到该代码块
System.out.println("抛出了【类转换异常】");
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
// 当没有抛出【空指针异常】和【类转换异常】
// 但抛出【数组下标越界异常】的时候会来到该代码块
System.out.println("抛出了【数组下标越界异常】");
catch (Throwable t) // Throwable 是所有异常的父类, 只能放子异常的后面
// 上面的异常没有抛出
// 且的确抛出了异常, 会来到该代码块
System.out.println("抛出了异常");
System.out.println("不可能抛异常的代码2");
(2) Throwable 常用方法
看下面代码,思考打印结果:
public class TryCatch
public static void main(String[] args)
try
long[] longs = new long[10_0000_0000];
catch (OutOfMemoryError e)
// output: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
System.out.println("\\n" + e);
// output: Java heap space
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
// 红色字体, 带异常行定位(控制台输出堆栈信息)
e.printStackTrace();

🌼 直接打印异常对象【e】:异常类型(
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError)和异常信息(Java heap space)
🌼 打印异常对象【e】的 getMessage() 方法的返回值:异常信息(Java heap space)
🌼 直接调用异常对象【e】的 printStackTrace() 方法 【常用】
🌼 有红色打印信息不代表程序退出了
(3) 一个 catch 捕获多种类型的异常
🌼 从 Java7 开始,当个
catch可以捕获多种类型的异常
🌼 如果并列的几个异常类型之间存在父子关系,保留父类型即可
🌼 此时异常对象【e】是隐式 final 的
public class TryCatch
public static void main(String[] args)
try
System.out.println("啦啦啦");
// 可能产生异常的代码
catch (OutOfMemoryError | NullPointerException | IndexOutOfBoundsException e)
// 产生 OutOfMemoryError 异常、NullPointerException 异常
// 或 IndexOutOfBoundsException 异常的时候都会来到该代码块
if (e instanceof OutOfMemoryError)
System.out.println(e);
else if (e instanceof NullPointerException)
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
else // 是 IndexOutOfBoundsException 异常的时候
e.printStackTrace();
(4) Exercise
① 第1题
思考下面的代码的打印结果是什么:
public class Exercise
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println(1);
Integer integer = new Integer("啦啦啦");
// 上一行代码抛异常了, 程序终止, 下面的代码不会执行
System.out.println(2);
② 第2题
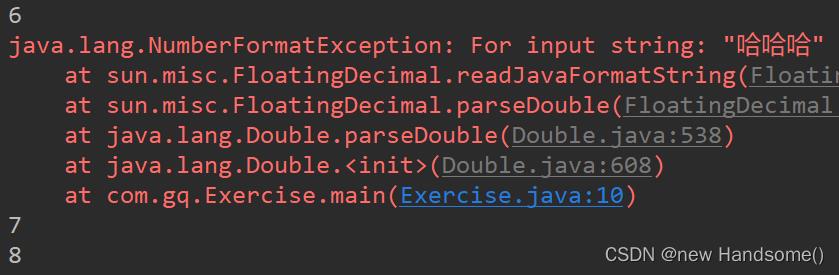
思考下面的代码的打印结果是什么:
public class Exercise
public static void main(String[] args)
int n = 6;
try
// 6
System.out.println(n++);
Double d = new Double("哈哈哈");
System.out.println(++n);
System.out.println(d);
catch (NumberFormatException e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 7
System.out.println(n++);
// 8
System.out.println(n);
③ 第3题
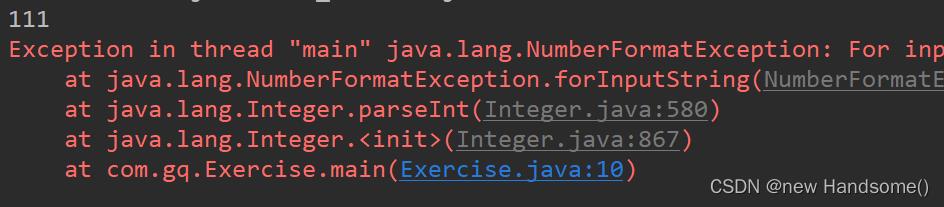
思考下面的代码的打印结果是什么:
public class Exercise
public static void main(String[] args)
int num = 1;
Integer integer1 = new Integer("111");
// 111
System.out.println(num++ + --integer1);
Integer integer2 = new Integer("嘻嘻嘻");
System.out.println(integer1 + integer2);
④ 第4题
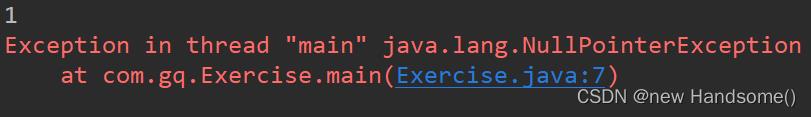
思考下面的代码的打印结果是什么:
public class Exercise
public static void main(String[] args)
Integer[] ints = 111, null, 222;
for (int integer : ints)
// 自动拆箱
// ints[n].intValue();
// 当 ints[n] 为 null 的时候就抛 NullPointerException 异常
System.out.println(integer);
// output: 111
(5) finally
✏️ try或catch代码块中的代码执行完毕后,一定会执行finally代码块中的代码
✏️ finally可以和try-catch搭配使用,也可以和try搭配使用
✏️ 作用:在finally中编写关闭、释放资源的代码(如:关闭文件)
finally 使用格式1:
public class FinallyTest
public static void main(String[] args)
try
System.out.println(1);
catch (NullPointerException e)
System.out.println(11);
finally
System.out.println(111);
/*
output:
1
111
*/
finally 使用格式2:
public class FinallyTest
public static void main(String[] args)
try
System.out.println(222);
finally
System.out.println(555);
/*
output:
222
555
*/
往文件写数据的案例:
public class FinallyTest
public static void main(String[] args)
String file = "C:\\\\Users\\\\34657\\\\Desktop\\\\fileTest.txt";
PrintWriter pw = null;
try
// 创建打印写入器(类似打开文件)
pw = new PrintWriter(file);
// 往文件中写入内容【愿你万事顺心!】
pw.write("愿你万事顺心!");
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
// 关闭文件资源
assert pw != null;
pw.close();
(6) finally 细节
✏️ 如果在执行 try 或 catch 的时候,JVM 退出或当前线程被中断(杀死),finally 代码块不会执行
✏️ 如果在 try 或 catch 中使用了 return、break、continue 等提前结束的语句的话,finally 会在 return、break、continue 之前执行
思考下面代码的执行结果:
public class FinallyTest
public static void main(String[] args)
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
try
System.out.println(i + "_try_1");
// continue: 终止此次循环, 继续下次循环
if (i == 2) continue;
System.out.println(i + "_try_2");
finally
System.out.println(i + "_finally");

思考下面代码的执行结果:
public class FinallyTest
public static void main(String[] args)
// 3
// 77
// 11
System.out.println(t());
private static int t()
try
new Integer("好");
System.out.println(1);
return 2;
catch (Exception以上是关于33Java 异常掌握这些就够了(图解 Java 中的异常)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章