数据库LeetCode每日练习
Posted 小杰312
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据库LeetCode每日练习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
前言
mysql必知必会,详尽入门,一文帮你学会SQL必知必会_小杰312的博客-CSDN博客MYSQL基操一网打尽,详尽入门,一文帮你学会SQL必知必会 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53695360/article/details/123770512?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53695360/article/details/123770512?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
- 上面这个是一些基础的mysql入门必知必会,可以帮助sql语法不熟悉的友友快速回顾和入门各种操作
- 这个系列是小杰针对mysql的每日练习,如果您觉得对您有所帮助,麻烦关注小杰,让我们一起练习sql题目,熟练各种查询表合并操作 --- 为将来的面试打基础
题目1: 合并两个表

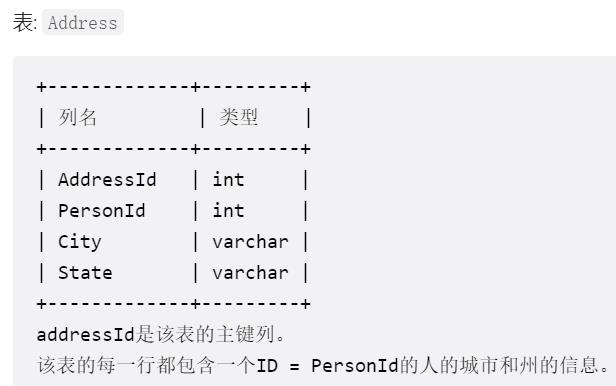
- 题目要求:
编写一个SQL查询来报告 Person 表中每个人的姓、名、城市和状态。如果 personId 的地址不在 Address 表中,则报告为空 null 。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
-
题目分析: 因为如果personId 的地址不存在 Address表中报告为 null 但是还是需要输出personId 表信息, 故而是一种外连接的方式:
select
FirstName, LastName, city, state
from
person p left outer join address a
on p.personid = a.personid
顺便回顾一下几种连接
-
inner join : 内连接 2表值都存在
-
outer join : 附表中值可能存在null的情况
总结:
- A inner join B : 取交集
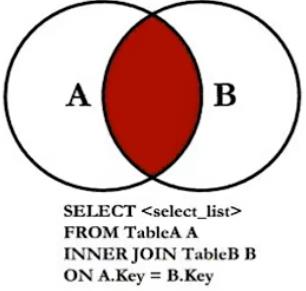
- A left join B : 取A全部,B没有对应的值,则为null
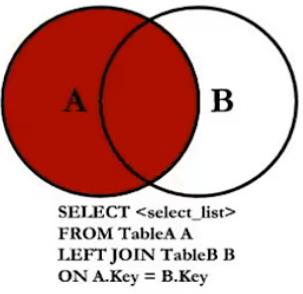
- A right join B : 取B全部,A没有对应的值,则为null

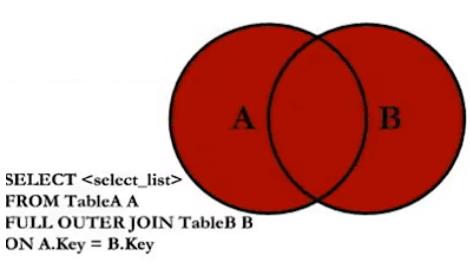
- A full outer B : 取并集, 彼此没有对应的值为 null
筛选条件 写在 on 后面
题目2:超过经理收入的员工

- 题目要求
编写一个SQL查询来查找收入比经理高的员工。
- 题目分析:要求查找收入高于经理的员工,这个是很明显的自连接问题,我们需要对比的信息是处在同一个表的,这种关系我们可以理解为自连接的题目
- 自联结:自联结字面的意思就是,自己和自己联结。此时联结所用到的表只有一张,此时我们可以把自联结想象成两张一模一样的表在进行联结。
- 这种题目常常是两条连接的信息处在同一张表中。员工经理都处在employee表中, 明显自连接题目
# 形式1
select
a.name as Employee
from
Employee a inner join Employee b
on a.managerid = b.id
where
a.salary > b.salary;
# 形式2
/*
select
a.name as Employee
from
Employee a inner join Employee b
on a.managerid = b.id && a.salary > b.salary;
*/
# 形式3
/*
select
a.name as Employee
from
Employee a, Employee b
where
a.managerid = b.id && a.salary > b.salary;
*/
题目三:查找重复的电子邮件
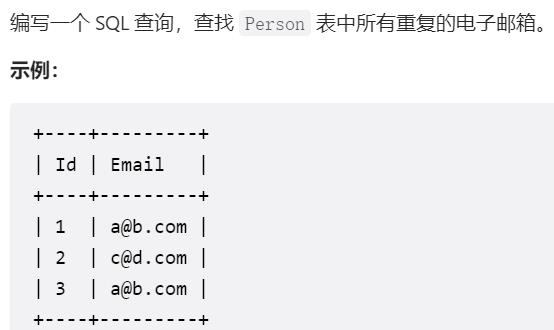
- 要求: 查找表中所有重复的电子邮件
- 思路: 竟然是重复的电子邮件,说明按照email分组之后会进行去重count,我们将count(email) > 1 的结果保留就是ans了
select
email
from
person
group by
email
having
count(email) > 1;总结
- 今日份的题目主要是回顾了几种表连接方式,表连接如何理解使用集合的交并这些来理解,内连接交集,全外连接并集,左外右外连接:左右表全部信息,没有关联的写null
- 表自连接查询,相同的一张表可以自己跟自己形成自连接进行查询
- 还有分组查询 请注意一个优先顺序: where > group by > having > order by
leetcode习题练习-每日更新
leetcode 20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','','','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
1.左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
2.左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
3.每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "()[]"
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s 仅由括号 '()[]' 组成
class Solution
public boolean isValid(String s)
int n = s.length();
if (n % 2 == 1)
return false;
Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<Character, Character>();
map.put(')', '(');
map.put(']', '[');
map.put('', '');
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (map.containsKey(ch))
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != map.get(ch))
return false;
stack.pop();
else
stack.push(ch);
return stack.isEmpty();
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例 1:
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示:
1 <= x <= 9
最多调用 100 次 push、pop、peek 和 empty
假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)
进阶:
你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为 O(1) 的队列?换句话说,执行 n 个操作的总时间复杂度为 O(n) ,即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
class MyQueue
Deque<Integer> inPutStack;
Deque<Integer> outPutStack;
public MyQueue()
inPutStack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
outPutStack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
public void push(int x)
inPutStack.push(x);
public int pop()
if (outPutStack.isEmpty())
inToOut();
return outPutStack.pop();
public int peek()
if (outPutStack.isEmpty())
inToOut();
return outPutStack.peek();
public boolean empty()
return inPutStack.isEmpty() && outPutStack.isEmpty();
private void inToOut()
while(!inPutStack.isEmpty())
outPutStack.push(inPutStack.pop());
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
提示:
1 <= x <= 9
最多调用100 次 push、pop、top 和 empty
每次调用 pop 和 top 都保证栈不为空
class MyStack
Queue<Integer> queueOne;
Queue<Integer> queueTwo;
public MyStack()
queueOne = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queueTwo = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public void push(int x)
queueTwo.offer(x);
while(!queueOne.isEmpty())
queueTwo.offer(queueOne.poll());
Queue<Integer> temp = queueOne;
queueOne = queueTwo;
queueTwo = temp;
public int pop()
return queueOne.poll();
public int top()
return queueOne.peek();
public boolean empty()
return queueOne.isEmpty();
设计一个找到数据流中第 k 大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第 k 大元素,不是第 k 个不同的元素。
请实现 KthLargest 类:
KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) 使用整数 k 和整数流 nums 初始化对象。
int add(int val) 将 val 插入数据流 nums 后,返回当前数据流中第 k 大的元素。
示例:
输入:
["KthLargest", "add", "add", "add", "add", "add"]
[[3, [4, 5, 8, 2]], [3], [5], [10], [9], [4]]
输出:
[null, 4, 5, 5, 8, 8]
解释:
KthLargest kthLargest = new KthLargest(3, [4, 5, 8, 2]);
kthLargest.add(3); // return 4
kthLargest.add(5); // return 5
kthLargest.add(10); // return 5
kthLargest.add(9); // return 8
kthLargest.add(4); // return 8
提示:
1 <= k <= 104
0 <= nums.length <= 104
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-104 <= val <= 104
最多调用 add 方法 104 次
题目数据保证,在查找第 k 大元素时,数组中至少有 k 个元素
class KthLargest
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq;
int k;
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums)
this.k = k;
pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for (int x : nums)
add(x);
public int add(int val)
pq.offer(val);
if (pq.size() > k)
pq.poll();
return pq.peek();
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
注意:若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
示例 1:
输入: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = "rat", t = "car"
输出: false
提示:
1 <= s.length, t.length <= 5 * 104s和t仅包含小写字母
class Solution
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t)
if (s.length() != t.length())
return false;
int[] table = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
table[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++)
table[t.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
if (table[t.charAt(i) - 'a'] < 0)
return false;
return true;
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-109 <= target <= 109
只会存在一个有效答案
class Solution
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target)
Map<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
if (hashMap.containsKey(target - nums[i]))
return new int[] hashMap.get(target - nums[i]), i;
hashMap.put(nums[i], i);
return new int[0];
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
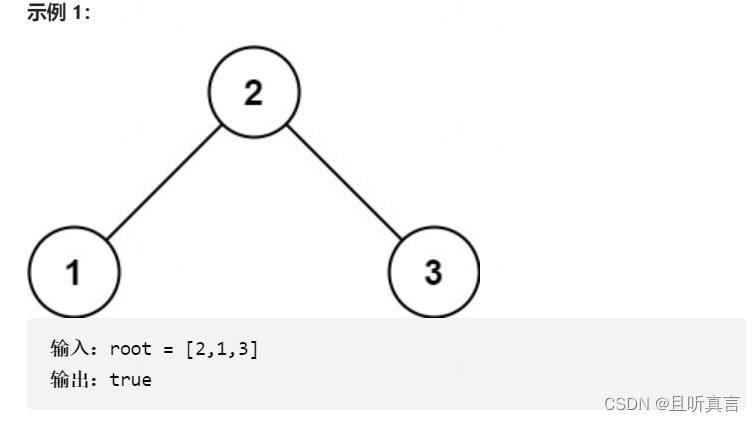

提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[1, 104]内 -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode()
* TreeNode(int val) this.val = val;
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right)
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
*
*
*/
class Solution
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root)
Deque<TreeNode> linkedList = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
double inorderValue = -Double.MAX_VALUE;
while(!linkedList.isEmpty() || root != null)
while(root != null)
linkedList.push(root);
root = root.left;
root = linkedList.pop();
if (root.val <= inorderValue)
return false;
inorderValue = root.val;
root = root.right;
return true;
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]

示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
class Solution
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode cur, TreeNode p, TreeNode q)
if (cur == null || cur == p || cur == q)
return cur;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(cur.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(cur.right, p, q);
if (left == null)
return right;
if (right == null)
return left;
return cur;
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]

方法一:广度优先搜索
class Solution
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int currrentLevelSize = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= currrentLevelSize; i++)
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right);
result.add(level);
return result;
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

class Solution
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root)
if (root == null)
return 0;
else
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
以上是关于数据库LeetCode每日练习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章