Nginx架构三之核心配置文件
Posted yangyanping20108
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Nginx架构三之核心配置文件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
nginx配置详解
安装完毕Nginx后,会有相应的安装目录,安装目录里的conf/nginx.conf为nginx的主配置文件,nginx主配置文件分为4部分,main(全局配置)、server(主机配置)、upstream(负载均衡服务器设置)以及location(URL匹配特定位置的设置)。
在 nginx.conf 的注释符号为: #
默认的 nginx 配置文件 nginx.conf 内容如下:
######## Nginx的main(全局配置)文件
#指定nginx运行的用户及用户组,默认为nobody
#user nobody;
#开启的线程数,一般跟逻辑CPU核数一致
worker_processes 1;
#定位全局错误日志文件,级别以notice显示,还有debug,info,warn,error,crit模式,debug输出最多,crir输出最少,根据实际环境而定
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#指定进程id的存储文件位置
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#指定一个nginx进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,受系统进程的最大打开文件数量限制
#worker_rlimit_nofile 65535
events
#设置工作模式为epoll,除此之外还有select,poll,kqueue,rtsig和/dev/poll模式
#use epoll;
#定义每个进程的最大连接数,受系统进程的最大打开文件数量限制。
worker_connections 1024;
#######Nginx的Http服务器配置,Gzip配置
http
#主模块指令,实现对配置文件所包含的文件的设定,可以减少主配置文件的复杂度。
include mime.types;
#核心模块指令,智力默认设置为二进制流,也就是当文件类型未定义时使用这种方式
default_type application/octet-stream;
#下面代码为日志格式的设定,main为日志格式的名称,可自行设置,后面引用
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#引用日志main
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#开启高效文件传输模式
sendfile on;
#开启防止网络阻塞
#tcp_nopush on;
#设置客户端连接保存活动的超时时间
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#开启gzip压缩
#gzip on;
#########Nginx的server虚拟主机配置
server
#监听端口为 80
listen 80;
#设置主机域名
server_name localhost;
#设置访问的语言编码
#charset koi8-r;
#设置虚拟主机访问日志的存放路径及日志的格式为main
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#设置虚拟主机的基本信息
location /
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html
root html;
# proxy the php scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \\.php$
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \\.php$
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\\.ht
# deny all;
#
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location /
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
#
#
# HTTPS server
#
#server
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location /
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
#
#
nginx 文件结构
... #全局块
events #events块
...
http #http块
... #http全局块
server #server块
... #server全局块
location [PATTERN] #location块
...
location [PATTERN]
...
server
...
... #http全局块
1、全局块:配置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等。
2、events块:配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数,选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求,是否允许同时接受多个网路连接,开启多个网络连接序列化等。
3、http块:可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,mime-type定义,日志自定义,是否使用sendfile传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等。
4、server块:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。
5、location块:配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
work process指令
用于配置Nginx生成工作进程的数量,这个是Nginx 服务器实现并发处理服务的关键所在。理论上来说workder process的 值越大,可以支持的并发处理量也越多,但事实上这个值的设定是需要 受到来自服务器自身的限制,建议将该值和服务器CPU的内核数保存一 致。
| 语法 | worker_processes num/auto; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | 1 |
| 位置 | 全局块 |
如果将worker_processes设置成2,则会看到如下内容
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx % sudo sbin/nginx -s reload -c conf/nginx.conf
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx % ps -ef |grep nginx
0 1378 1 0 10:52下午 ?? 0:00.00 nginx: master process ./sbin/nginx -q
-2 20257 1378 0 10:17下午 ?? 0:00.00 nginx: worker process
-2 20258 1378 0 10:17下午 ?? 0:00.00 nginx: worker process
502 20285 496 0 10:18下午 ttys002 0:00.00 grep nginx
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx %
daemon指令
设定Nginx是否以守护进程的方式启动。守护式进程是linux后台执行的一种服务进程,特点是独立于控制终端, 不会随着终端关闭而停止。
| 语法 | daemon on或off; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | daemon on; |
| 位置 | 全局块 |
#user nobody;
worker_processes 2;
daemon on;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
pid 指令
用来配置Nginx当前master进程的进程号ID存储的文件路径。
| 语法 | pid file; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid |
| 位置 | 全局块 |
#user nobody;
worker_processes 2;
daemon on;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
pid /usr/local/nginx/logs;
查看/usr/local/nginx/logs/pid 文件
cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/pid
1378
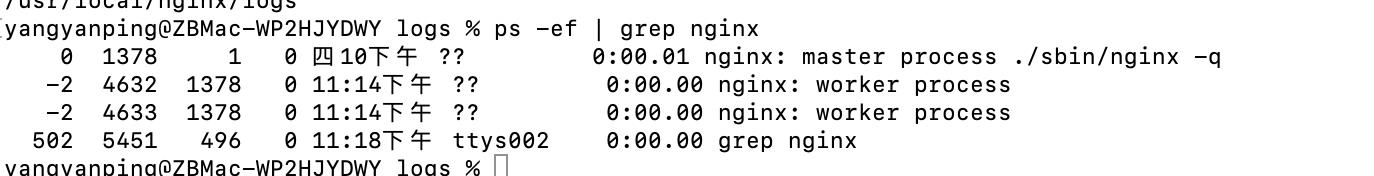
从图中可以看出pid 文件内容和主进程ID一致。
error_log
用来配置Nginx的错误日志存放路径。
| 语法 | error_log file [日志级别]; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | error_log logs/error.log error; |
| 位置 | 全局块、http、server、location |
其中日志级别的值有: debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg,翻译过来为试|信 息|通知|警告|错误|临界|警报|紧急,这块建议大家设置的时候不要设 置成info以下的等级,因为会带来大量的磁盘I/O消耗,影响Nginx的性 能。
设置日志级别为info,如下:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 2;
daemon on;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log info;
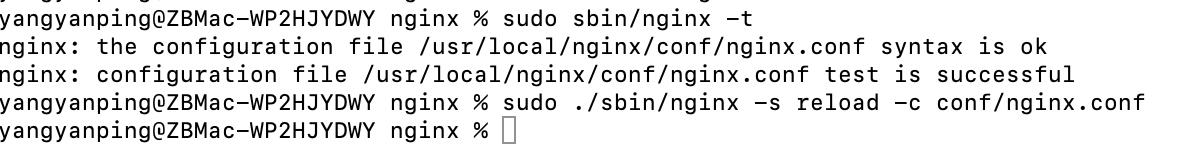
修改完毕nginx.conf文件后执行命令:
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx % sudo sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx % sudo sbin/nginx -s reload -c conf/nginx.conf
我们可以使用访问一个不存在的地址,测试错误日志
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx % curl -X GET 127.0.0.1/abc
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.17.9</center>
</body>
</html>
yangyanping@ZBMac-WP2HJYDWY nginx %
我们使用tail 命令查看error.log 文件内容
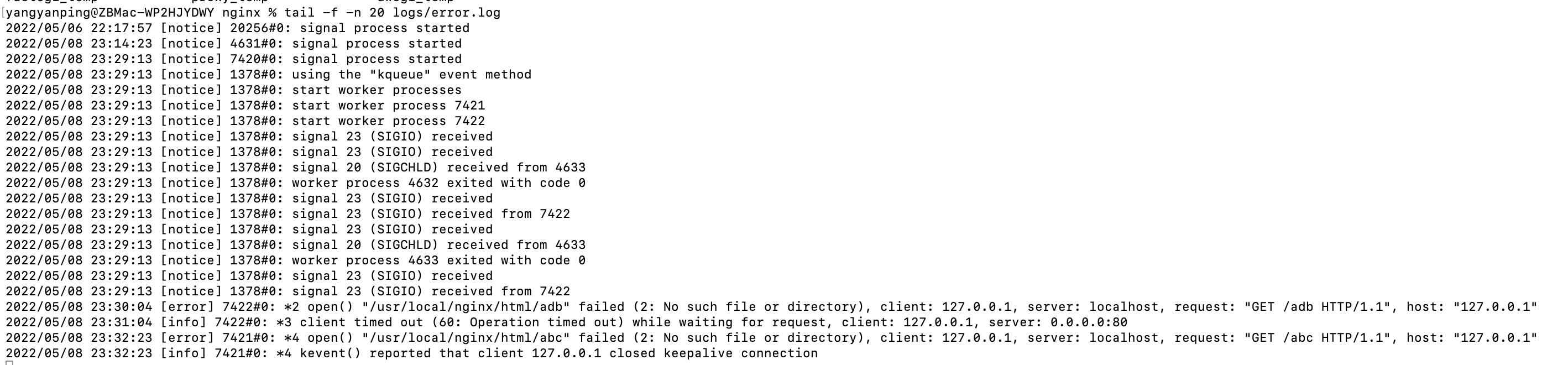
events块
accept_mutex:用来设置Nginx网络连接序列化
| 语法 | accept_mutex on或off; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | accept_mutex on; |
| 位置 | events |
这个配置主要可以用来解决常说的"惊群"问题。大致意思是在某一个时 刻,客户端发来一个请求连接,Nginx后台是以多进程的工作模式,也 就是说有多个worker进程会被同时唤醒,但是最终只会有一个进程可以 获取到连接,如果每次唤醒的进程数目太多,就会影响Nginx的整体性 能。如果将上述值设置为on(开启状态),将会对多个Nginx进程接收连接 进行序列号,一个个来唤醒接收,就防止了多个进程对连接的争抢。
multi_accept
用来设置是否允许同时接收多个网络连接。
| 语法 | multi_accept on或off; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | multi_accept off; |
| 位置 | events |
如果multi_accept被禁止了,nginx一个工作进程只能同时接受一个新的 连接。否则,一个工作进程可以同时接受所有的新连接。
events 指令演示
events
accept_mutex on;
multi_accept on;
#use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
HTTP 块
default_type
在Nginx的配置文件中,默认有两行配置
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
用来配置Nginx响应前端请求默认的MIME类型。
| 语法 | default_type mime-type; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | default_type text/plain; |
| 位置 | http、server、location |
举例来说明:
有些时候请求某些接口的时候需要返回指定的文本字符串或者json字符 串,如果逻辑非常简单或者干脆是固定的字符串,那么可以使用nginx快 速实现,这样就不用编写程序响应请求了,可以减少服务器资源占用并 且响应性能非常快。
配置参考
location /get_text
default_type " text/plain;charset=utf-8";
return 200 "系统已迁移到xxx.com";
location /get_json
default_type "application/json;charset=utf-8";
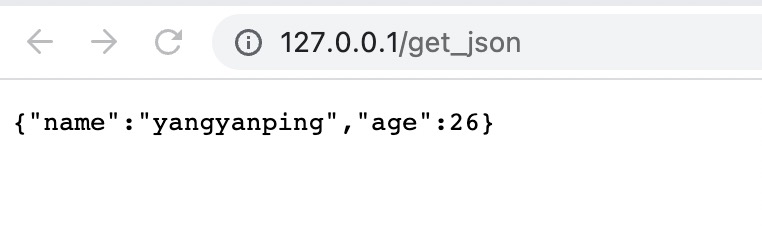
return 200 '"name":"yangyanping","age":26';
访问:http://127.0.0.1/get_text
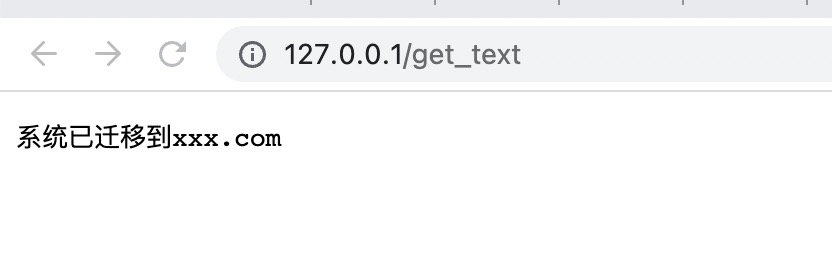
访问:http://127.0.0.1/get_json
sendfile
用来设置Nginx服务器是否使用sendfile()传输文件,该属 性可以大大提高Nginx处理静态资源的性能
| 语法 | sendfile on或off; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | sendfile off; |
| 位置 | http、server、location |
配置参考:
http
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
...
keepalive_timeout
用来设置长连接的超时时间。
- 我们都知道HTTP是一种无状态协议,客户端向服务端发送一个TCP请求, 服务端响应完毕后断开连接。
- 如何客户端向服务端发送多个请求,每个请求都需要重新创建一次连接, 效率相对来说比较多,使用keepalive模式,可以告诉服务器端在处理完 一个请求后保持这个TCP连接的打开状态,若接收到来自这个客户端的其 他请求,服务端就会利用这个未被关闭的连接,而不需要重新创建一个新 连接,提升效率,但是这个连接也不能一直保持,这样的话,连接如果过 多,也会是服务端的性能下降,这个时候就需要我们进行设置其的超时时 间。
| 语法 | keepalive_timeout time; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | keepalive_timeout 75s; |
| 位置 | http、server、location |
配置参考:
http
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
...
自定义服务日志
Nginx中日志的类型有access.log、error.log。
| 日志 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| access.log | 用来记录用户所有的访问请求。 |
| error.log | 记录nginx本身运行时的错误信息,不会记录用户的访问请 求。 |
Nginx服务器支持对服务日志的格式、大小、输出等进行设置,需要使 用到两个指令,分别是access_log和log_format指令。
access_log
| 语法 | access_log path[format[buffer=size]] |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | access_log logs/access.log combined; |
| 位置 | http, server, location |
log_format
| 语法 | log_format name [escape=default 或 json 或none] string…; |
|---|---|
| 默认值 | log_format combined “…”; |
| 位置 | http |
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
Nginx日志详解
Nginx日志主要分为两种:访问日志和错误日志。日志开关在Nginx配置文件(/nginx/conf/nginx.conf)中设置,两种日志都可以选择性关闭,默认都是打开的。
- 访问日志
访问日志主要记录客户端访问Nginx的每一个请求,格式可以自定义。通过访问日志,你可以得到用户地域来源、跳转来源、使用终端、某个URL访问量等相关信息。Nginx中访问日志相关指令主要有两条:
log_format:log_format用来设置日志格式,也就是日志文件中每条日志的格式,具体如下:log_format name(格式名称) type(格式样式)
举例说明如下:
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| $remote_addr | 远程客户端的IP地址 |
| $server_name | 虚拟主机名称 |
| - | 空白,用一个“-”占位符替代,历史原因导致还存在 |
| $remote_user | 远程客户端用户名称,用于记录浏览者进行身份验证时提供的名字,如果没有登录就是空白 |
| [$time_local] | 访问的时间与时区,比如18/Jul/2012:17:00:01 +0800,时间信息最后的"+0800"表示服务器所处时区位于UTC之后的8小时 |
| $request | 请求的URI和HTTP协议,这是整个PV日志记录中最有用的信息,记录服务器收到一个什么样的请求 |
| $status | 记录请求返回的http状态码,比如成功是200 |
| $uptream_status | upstream状态,比如成功是200 |
| $upstream_addr | 后端服务器的IP地址 |
| $http_referer | 记录从哪个页面链接访问过来的 |
| $http_user_agent | 客户端浏览器信息 |
| $http_x_forwarded_for | 客户端的真实ip,通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过$remote_addr拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的iP地址。反向代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客户端的请求的服务器地址 |
- access_log
能够使用access_log指令的字段包括:http、server、location。
需要注意的是:nginx进程设置的用户和组必须对日志路径有创建文件的权限,否则,会报错。
Nginx支持为每个location指定强大的日志记录。同样的连接可以在同一时间输出到不止一个的日志中。
access_log指令用来指定日志文件的存放路径(包含日志文件名)、格式和缓存大小,具体如下:
| access_log | path(存放路径) | [format(自定义日志格式名称) [buffer=size off]] |
|---|---|---|
| access_log | logs/access.log | main |
| access_log | off 关闭日志 |
格式参考:
access_log logs/access.log main;
日志内容
127.0.0.1 - - [07/Jan/2021:19:37:56 +0800]
"GET /proxy/hello HTTP/1.1" 200 22 "-"
"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh;
Intel Mac OS X 10_13_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)
Chrome/87.0.4280.88 Safari/537.36"
- 错误日志
错误日志主要记录客户端访问nginx出错时的日志,格式不支持自定义。通过错误日志,你可以得到系统某个服务或server的性能瓶颈等。因此,将日志好好利用,你可以得到很多有价值的信息。错误日志由指令error_log来指定,具体格式如下:
| error_log | 存放路径path | 日志等级level |
|---|---|---|
| error_log | logs/error.log | info |
| error_log | /dev/null | 关闭日志 |
path含义同access_log,level表示日志等级,具体如下:
[ debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit ]
从左至右,日志详细程度逐级递减,即debug最详细,crit最少。日志内容:
2021/01/07 18:30:39 [error]
45306#0: *507 no live upstreams while connecting to upstream,
client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost,
request: "GET /proxy/hello HTTP/1.1", upstream: "http://myweb/web/hello",
host: "www.test-nginx.com"
Web服务器群集——Nginx动态网站架构(笔记)
Nginx动态网站架构
一、fastcgi & php-fpm
静态网站 :Nginx服务器能处理的静态元素.html .jpg .mp4 .css
1.1 Nginx
ngx_fastcgi_modul
- fastcgi 快速通用网关接口
- 处理动态请求的接口
- Nginx通过ngx_fastcgi_modul模块 链接php-fpm处理动态请求
1.2 PHP
php-fpm
- PHP-FPM(FastCGI Process Manager :FastCGI进程管理器)是一个PHP GastCGI管理器
- PHP通过php-fpm接受前台nginx的动态访问请求,如向后端MySQL进行查询请求后,将查询结果返回给前台nginx
1.3 PHP-MySQL
- php-mysql是php连接mysql的接口程序
1.4 MySQL
- 存储数据
1.5 面试题
- 什么是FastCGI
- Nginx+FastCGI运行原理
- LNMP的运行原理:用户向网站请求,当请求静态元素时,由Nginx独立返回用户,当为动态请求时,将通过fastcgi模块连接php程序传达动态请求,php程序通过fpm接口管理器接受到其请求之后,再通过php-mysql程序向MySQL数据库进行数据存储(口头描述)。
二、PHP-FPM优化
2.1 了解php-fpm相关配置文件
2.1.1 核心配置文件
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/php.ini
;date.timezone = date.timezone=PRC 设置PHP的时区
;open_basedir = oepn_basedir
- open_basedir:设置PHP脚本允许访问的目录
- open_basedir 将php所能打开的文件限制在指定的目录树中,包括文件本身,当程序要使用例如fopen()或file_get_contents()打开一个文件时,这个文件的位置将会被检查,当文件在指定的目录树之外,程序将拒绝打开
2.1.2 全局配置文件
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.conf
pid = /run/php-fpm/php-fpm.pid #pid存放的位置
error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/error.log #日志存放的位置
;log_level = notice #日志级别
daemonize = yes #守护进程,将fpm转至后台允许 默认no
2.1.3 扩展配置文件
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
user = nginx
listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1 #监听允许谁访问,如分离部署填对方IP地址
listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 #fpm监听端口,即nginx中php处理的地址,一般默认值即可,可用格式'ip :port'
slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/$pool-slow.log #慢查询日志
pm = dynamic #动态模式进程管理开启
pm.start_servers = 5 #最初开启多少进程
pm.min_spare_servers = 5 #最小的多余进程数,最少空闲,用户访问会消耗进程,为了满足后续服务随时开启进程保持空闲数为5
pm.max_children = 50 #最大进程数,限定php程序最大进程数
pm.max_spare_servers = 10 #空闲进程超过35个之后 立刻杀死多余进程只保留35个进程
pm.max_requests = 500 # 每个子进程能相应的请求数量 超过500次请求立刻杀死

2.2 初始化php-fpm
生产环境下常用数值
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
#设置生产环境下常用数值
pm = dynamic #启动动态管理模式
pm.start_servers = 32 #初始启动32个进程
pm.max_children = 512 #最大进程数(子进程会在最大和最小数范围之间变化)
pm.min_spare_servers = 32 #随着用户访问的增加,保持32个空闲进程
pm.max_spare_servers = 64 #随着用户离去,杀死大量进程来节约资源
;pm.max_requests = 1500 #每个子进程处理1500个请求,默认为unlimiter(1024个)
[root@lnmp ~]# systemctl restart php-fpm
2.2.1 初始化后
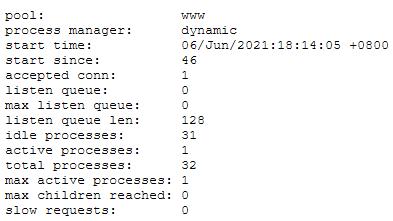
[root@lnmp ~]# ps -aux | grep php | wc -l
2.3 启动php动态监控页面功能
2.3.1 启动测试页功能
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
;pm.status_path = /status #去掉注释
pm.status_path = /php_status #更改为如前所示
2.3.2 Nginx 配置页面转发
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf #在Server中添加页面转发功能
...
location = /php_status{
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
...
[root@lnmp ~]# systemctl restart nginx php-fpm
2.3.3 访问测试页
http://192.168.100.10/php_status
三、Nginx Location
Location只影响之后带的路径!
启用身份验证模块配置到Server中,应用全局
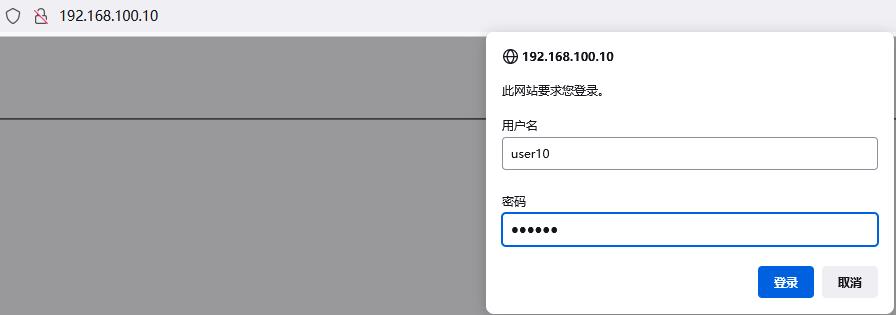
1)生成账户密码文件
[root@lnmp ~]# yum -y install httpd-tools #安装密码生成工具
[root@lnmp ~]# htpasswd -cm /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd user10
2)启用身份认证应用至server中
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server {
auth_basic "nginx access test!"; #提示消息
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd; #引用认证文件
...
[root@lnmp ~]# systemctl restart nginx
将身份认证加入status
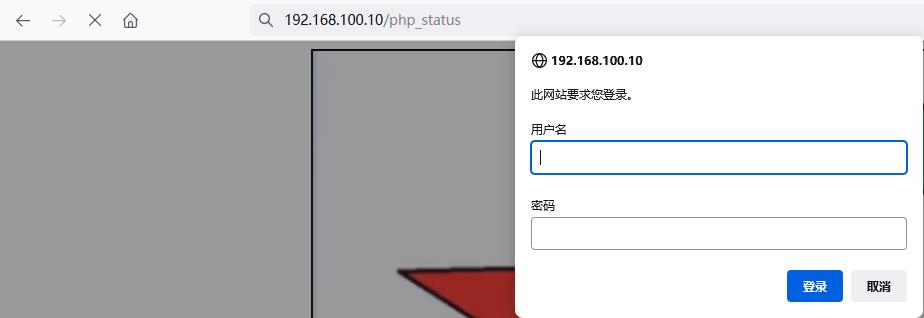
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server {
location = /php_status{
auth_basic "nginx access test!";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
...
[root@lnmp ~]# systemctl restart nginx
访问主页能够正常访问
 访问location 限制之后的php_status页面需要输入账户
访问location 限制之后的php_status页面需要输入账户
3.1 Location 语法规则
location [=|~|~*|!~|!~*|^~] /uri/{
module;
module;
}
= 表示精确匹配,优先级也是最高的
~ 区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 不区分大小写的正则匹配
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到
^~ 以某些字符串开头
!~ 非 (区分大小写的匹配的正则)
!~* 非 (不区分大小写匹配的正则)
优先级 精准匹配 > 模糊匹配 > 正则匹配 > 配
3.2 Location 示例
目的:通过不同的表达式,观察表达式之间的优先级
[root@lnmp ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# location / {
# index index.php index.html;
# } #将主配置文件部分进行注释
root /abcd; #添加如下测试页面
index index.html;
location = / { index a.html; }
location ~ / { index b.html; }
location / { index c.html; }
[root@lnmp abcd]# systemctl restart nginx

#location = / { index a.html; }
[root@lnmp abcd]# systemctl restart nginx

#location ~ / { index b.html; }
[root@lnmp abcd]# systemctl restart nginx

#location / { index c.html; }
[root@lnmp abcd]# echo index > index.html
[root@lnmp abcd]# systemctl restart nginx

四、Nginx 平滑升级
4.1 Nginx信号控制表
| 信号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| TERM,INT | 立刻停止进程 |
| QUIT | 等待进程结束后再结束进程 |
| HUP | 平滑地重读配置文件(开启一个新的worker进程读取配置文件,然后关闭旧进程) |
| USR1 | 重读日志,分割日志时使用 |
| USR2 | 平滑地升级Nginx |
| WINCH | 等待进程结束后关闭旧进程(配合USR2来进行升级) |
4.2 平滑升级流程解析
例:如平滑升级1.12版本到1.14版本
一、编译安装新版本的nginx,指定安装目录为新目录
二、查看旧的nginx的主程序号和工作进程号

三、替换旧的执行程序

四、给主程序发送USR2信号
信号 1 为立刻重启
信号 2 为工作完毕后重启

- 旧版本的主程序将重命名它的pid文件为.oldbin(例如:/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin),然后执行新版本的可执行程序,依次启动新的主程序和新的工作进程
五、给进程发送WINCH信号
等待进程结束后关闭旧进程(配合USR2来进行升级)

以上是关于Nginx架构三之核心配置文件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章