spring如何开启允许循环依赖
Posted 洪宏鸿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring如何开启允许循环依赖相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
如何解决spring循环依赖
在Spring框架中,allowCircularReferences属性是用于控制Bean之间的循环依赖的。循环依赖是指两个或多个Bean之间相互依赖的情况,其中一个Bean依赖于另一个Bean,同时另一个Bean又依赖于第一个Bean。
allowCircularReferences属性默认是关闭的,即不允许循环依赖存在。如果两个或多个Bean之间存在循环依赖,Spring会抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常,以避免可能出现的死循环和性能问题。
默认情况下,Spring不允许循环依赖,如果存在循环依赖,会抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常。这是因为Spring默认使用构造函数注入或者setter注入的方式创建Bean,如果两个Bean之间存在循环依赖,则无法满足其中一个Bean的创建要求。
但是,在某些情况下,循环依赖是必要的。例如,两个Bean需要相互引用对方的属性或方法才能正常工作。这时,可以将allowCircularReferences属性设置为true,允许循环依赖的存在。
当allowCircularReferences属性设置为true时,Spring会使用一个特殊的方式创建Bean,即使用代理对象来解决循环依赖的问题。这种方式可以满足循环依赖的要求,但同时也会带来一些额外的性能开销和复杂性。
需要注意的是,循环依赖可能导致一些问题,例如无限递归、死锁等,因此建议在确保必要性的情况下才使用循环依赖。
两种解决方案
当存在循环依赖时,Spring框架提供了两种解决方案:
-
使用构造函数注入方式:这是Spring默认的注入方式,它会在Bean创建时将依赖项通过构造函数注入到Bean中。当Bean之间存在循环依赖时,Spring会抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常。
-
使用setter注入方式:这种方式通过setter方法注入依赖项,可以在Bean创建后再设置依赖项。在Bean之间存在循环依赖时,Spring可以通过setter方法暂时设置null值或代理对象,等到Bean创建完毕后再将实际的依赖项注入到Bean中。
在Spring 5.1及更高版本中,还提供了一种新的循环依赖解决方案,即SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,它提供了更细粒度的控制和处理循环依赖的方式。通过实现该接口,可以自定义Bean的实例化和初始化过程,并实现更灵活和高效的循环依赖处理方式。
开启循环依赖
在Spring Boot中,开启循环依赖可以通过在应用程序的配置文件中设置spring.main.allow-circular-references属性来实现。具体来说,可以在application.properties或application.yml配置文件中添加以下属性:
spring:
main:
allow-circular-references: true
这将启用Spring框架中默认的循环依赖解决方案,即使用代理对象来解决循环依赖问题。
需要注意的是,开启循环依赖并不代表完全避免了循环依赖的问题。
spring循环依赖
spring循环依赖主要有三种:
单例引用类型循环依赖(属性):允许
构造器的循环依赖:不允许
多例循环依赖:不允许
单例引用类型循环依赖(属性)
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
public class CirculeA
@Autowired
private CirculeB circuleB;//引用CirculeB
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
public class CirculeB
@Autowired
private CirculeA circuleA;//引用CirculeA
@org.junit.Test
public void test3()
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
System.out.println("spring启动成功");
总结:在circuleA实例化过程中触发circuleB的getBean(),此时circileA的实例已放入到三级缓存中,在circuleB的实例化过程中会触发circuleA的genBean(),直接从缓存中拿到circileA的实例,这样会优先将circuleB是实例化完成,并在circuleA触发circuleB的getBean()时返回,然后继续完成circuleA的实例化;
circuleA第一次实例化会走以下代码,第二次直接从缓存中获取不会走以下代码
单例实例化流程图: 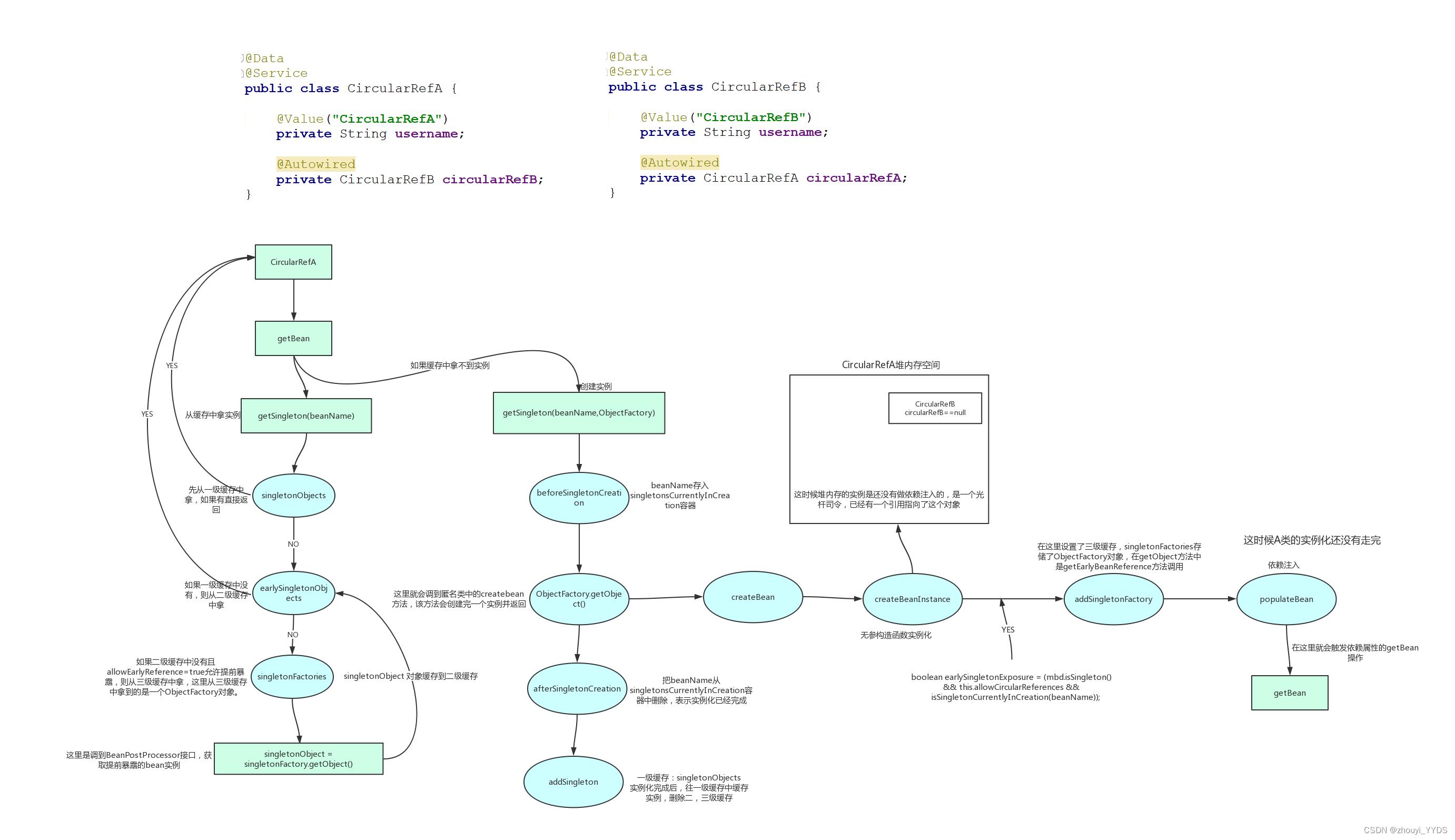
构造器的循环依赖:
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
public class CirculeB
private CirculeA circuleA;
public CirculeB(CirculeA circuleA)
this.circuleA = circuleA;
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
public class CirculeA
private CirculeB circuleB;
public CirculeA(CirculeB circuleB)
this.circuleB = circuleB;

报错:org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException:
Error creating bean with name 'circuleA' defined in file [D:\\XXX\\5.2.8\\spring_demo\\spring_test\\target\\classes\\com\\spring\\bean\\CirculeA.class]:
Unsatisfied dependency expressed through constructor parameter 0;
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException:
Error creating bean with name 'circuleB' defined in file [D:\\xxxx\\5.2.8\\spring_demo\\spring_test\\target\\classes\\com\\spring\\bean\\CirculeB.class]:
Unsatisfied dependency expressed through constructor parameter 0;
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'circuleA': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
//创建实例,在这个方法中触发circuleB的getBean()
if (instanceWrapper == null)
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class)
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock)
if (!mbd.postProcessed)
try
//AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 收集有@Autowire和@Value注解的方法和属性,
// 放入到injectionMetadataCache缓存中,包装为InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement对象,其中有member,isFiled属性相对重要
//CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 收集有@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解的方法 放入到lifecycleMetadataCache,
// 有@Resource注解的方法和属性 放入到injectionMetadataCache缓存中,
// 包装为InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement对象,其中有member,isFiled属性相对重要
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
catch (Throwable ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
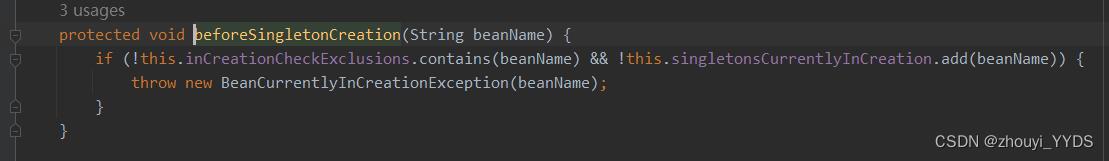
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure)
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
//放入到三级缓存中
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
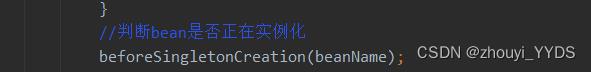

总结:在放入缓存前调用getBean(),导致缓存中没有,所以每次调用getbean()都会走beforeSingletonCreation()方法,在第二次调用时判断以下条件时(!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName))返回true,会抛出异常
多例循环依赖:
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public class CirculeB
@Autowired
private CirculeA circuleA;
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public class CirculeA
@Autowired
private CirculeB circuleB;
@org.junit.Test
public void test4()
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
CirculeA bean = context.getBean(CirculeA.class);
CirculeB bean1 = context.getBean(CirculeB.class);
System.out.println("spring启动成功");
会报错:org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException:
Error creating bean with name 'circuleA': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'circuleB';
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException:
Error creating bean with name 'circuleB': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'circuleA';
nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'circuleA': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
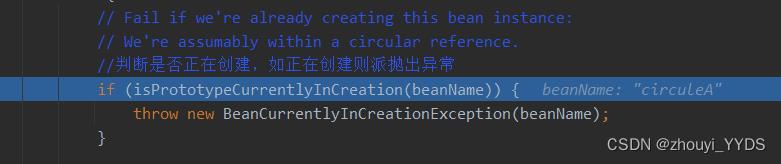
原因:第一次调用会在ThreadLocal中存放,在第二次调用以下方法时抛出异常

以上是关于spring如何开启允许循环依赖的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章