Java网络编程——NIO的阻塞IO模式非阻塞IO模式IO多路复用模式的使用
Posted 胡玉洋
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java网络编程——NIO的阻塞IO模式非阻塞IO模式IO多路复用模式的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
NIO虽然称为Non-Blocking IO(非阻塞IO),但它支持阻塞IO、非阻塞IO和IO多路复用模式这几种方式的使用。
同步IO模式
NIO服务器端
@Slf4j
public class NIOBlockingServer
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(true); // 设置SocketChannel为阻塞模式(默认就是阻塞模式)
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (true)
// 如果没有接收到新的线程,这里会阻塞,无法及时处理其他已连接Channel的请求
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
log.info("receive connection from client. client:",socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(true); // 设置SocketChannel为阻塞模式(默认就是阻塞模式)
// 如果读不到数据,这里会阻塞,无法及时处理其他Channel的请求
int length = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
log.info("receive message from client. client: message:",socketChannel.getRemoteAddress(),new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,length,"UTF-8"));
byteBuffer.clear();
NIO客户端
@Slf4j
public class NIOClient
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args)
SocketChannel socketChannel=SocketChannel.open();
try
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080));
log.info("client connect finished");
ByteBuffer writeBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
log.info("client send finished");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
socketChannel.close();
NIO阻塞模式的使用,乍一看怎么跟BIO的使用方法很像?不是很像,简直是一模一样~
按照 《Java网络编程——BIO(Blocking IO)》 中的步骤:
- 以Run模式启动NIO服务端
- 在客户端的
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);处打上断点,以Debug模式运行一个客户端A,执行到断点时,服务端已经接收到客户端A的请求(在控制台打印了receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:64334) - 再以Debug模式运行一个客户端B,服务端没反应,因为这时客户端A还没发送数据,所以服务端目前是在
int length = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)的地方阻塞了(还在等着接收客户端A发送数据) - 再以Debug模式运行一个客户端C,服务端同样没反应
- 让客户端A继续运行完,发现服务端读取到客户端A的数据(打印了
receive message from client. client:/127.0.0.1:64334 message:hello)后,才能接收到客户端B的连接(打印了receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:64358) - 让客户端B继续运行完,发现服务端读取到客户端B的数据(打印了
receive message from client. client:/127.0.0.1:64358 message:hello)后,才能接收到客户端C的连接(打印了receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:64369)
因此,NIO的阻塞IO模式跟BIO一样,最大的缺点就是阻塞。
异步IO模式
通过前面的学习我们知道,异步IO和同步IO最大的区别就是:
同步IO在做完一件事(比如:处理客户端连接请求+写请求)之前,只能等待,无法做其他事情;
而异步是在客户端某个事件没有就绪时,我服务端可以先处理其他的客户端请求,不用一直等着。
BIO服务端
@Slf4j
public class NIONonBlockingServer
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
List<SocketChannel> socketChannelList = new ArrayList<>();
while (true)
// 如果没有接收到新的线程,这里不会阻塞,会返回null,可以让线程继续处理其他Channel的请求
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (Objects.nonNull(socketChannel))
log.info("receive connection from client. client:", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannelList.add(socketChannel);
for (SocketChannel channel : socketChannelList)
// 如果没有读到数据,这里也不会阻塞,会返回0,表示没有读到数据,可以让线程继续处理其他Channel的请求
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
int length = channel.read(byteBuffer);
if (length > 0)
log.info("receive message from client. client: message:", channel.getRemoteAddress()
, new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, length, "UTF-8"));
byteBuffer.clear();
// 为了避免没有客户端请求时循环过于频繁,把所有就绪的事件循环处理完后,停顿1秒再继续执行
Thread.sleep(1000);
NIO客户端
@Slf4j
public class NIOClient
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args)
SocketChannel socketChannel=SocketChannel.open();
try
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080));
log.info("client connect finished");
ByteBuffer writeBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
log.info("client send finished");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
socketChannel.close();
- 以Run模式启动NIO服务端
- 在客户端的
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);处打上断点,以Debug模式运行一个客户端A,执行到断点时,服务端已经接收到客户端A的请求(在控制台打印了receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53004) - 再以Debug模式运行一个客户端B,服务端也接收到客户端B的请求(在控制台打印了
receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53032) - 再以Debug模式运行一个客户端C,服务端也接收到客户端B的请求(在控制台打印了
receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53032)
如下图:

继续运行客户端A、B、C,可以看到服务端也可以正常接收它们发来的数据:
2022-07-30 16:31:07.987 INFO [danny-codebase,,,,,main] com.code.io.blog.NIONonBlockingServer - receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53004
2022-07-30 16:31:13.014 INFO [danny-codebase,,,,,main] com.code.io.blog.NIONonBlockingServer - receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53032
2022-07-30 16:31:18.039 INFO [danny-codebase,,,,,main] com.code.io.blog.NIONonBlockingServer - receive connection from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53060
2022-07-30 16:33:12.919 INFO [danny-codebase,,,,,main] com.code.io.blog.NIONonBlockingServer - receive message from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53004 message:hello
2022-07-30 16:33:18.940 INFO [danny-codebase,,,,,main] com.code.io.blog.NIONonBlockingServer - receive message from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53032 message:hello
2022-07-30 16:33:19.942 INFO [danny-codebase,,,,,main] com.code.io.blog.NIONonBlockingServer - receive message from client. client:/127.0.0.1:53060 message:hello
NIO非阻塞模式这种用法跟 《Java网络编程——BIO(Blocking IO)》 中说的BIO多线程处理请求的方式类似,让服务端可以同时处理多个客户端请求,即使某一个客户端的读/写事件未就绪也不会阻塞线程(比如上面服务端执行serverSocketChannel.accept()时如果没有客户端连接不会阻塞而是会返回null;执行channel.read(byteBuffer)时如果读不到数据不会阻塞而是会返回0),而是会继续处理其他客户端的请求。
需要注意的是,这里的非阻塞,是指serverSocketChannel执行accept()、socketChannel执行read()时是非阻塞的(会立刻返回结果)。但是在客户端有就绪事件,处理客户端的请求时,比如服务端接收客户端连接请求的过程、服务端读取数据(数据拷贝)的过程,是阻塞的。
IO多路复用模式
看完NIO非阻塞模式的使用方法你是不是就觉得万无一失了?No!这种方式也有一个很大的缺点就是,当一直没有客户端事件就绪时,服务端线程就会一直循环,白白占用了CPU资源,所以上面代码中为了减小CPU消耗,在每次处理完所有Channel的就绪事件后,会调用Thread.sleep(1000);让服务端线程休息1秒再执行。那有没有什么方法可以在没有客户端事件就绪时,服务端线程等待,当有了请求再继续工作呢?
有,那就是IO多路复用模式,相对于上面的非阻塞模式,IO多路复用模式主要是引入了Selector选择器,且需要把Channel设置为非阻塞模式(默认是阻塞的)。
在 《Java网络编程——NIO(Non-Blocking IO)组件》 中说到,Selector可以作为一个观察者,可以把已知的Channel(无论是服务端用来监听客户端连接的ServerSocketChannel,还是服务端和客户端用来读写数据的SocketChannel)及其感兴趣的事件(READ、WRITE、CONNECT、ACCEPT)包装成一个SelectionKey,注册到Selector上,Selector就会监听这些Channel注册的事件(监听的时候如果没有事件就绪,Selector所在线程会被阻塞),一旦有事件就绪,就会返回这些事件的列表,继而服务端线程可以依次处理这些事件。
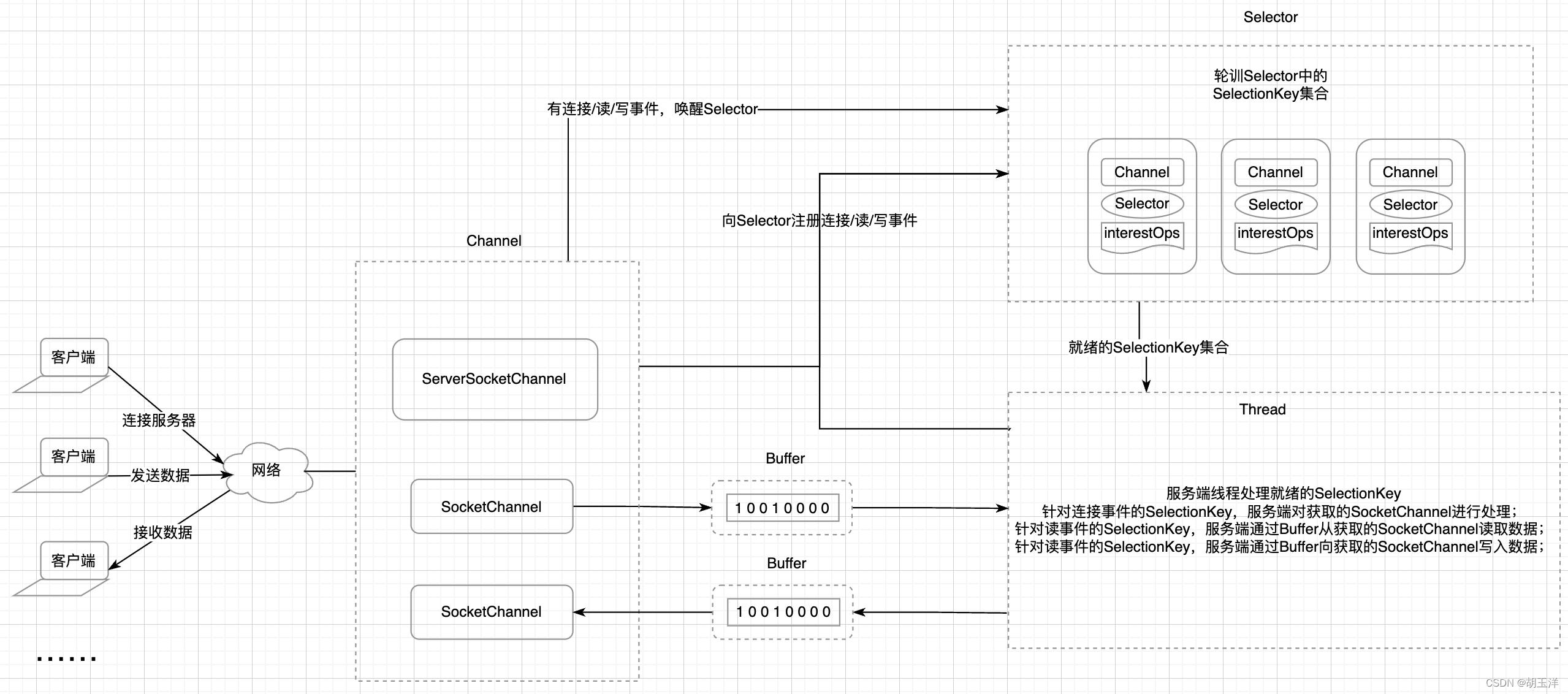
服务端例子如下:
@Slf4j
public class NioselectorServer
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080), 50);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
SelectionKey serverSocketKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true)
// 从Selector中获取事件(客户端连接、客户端发送数据……),如果没有事件发生,会阻塞
int count = selector.select();
log.info("select event count:" + count);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
// 有客户端请求建立连接
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable())
handleAccept(selectionKey);
// 有客户端发送数据
else if (selectionKey.isWritable())
handleRead(selectionKey);
// select 在事件发生后,就会将相关的 key 放入 Selector 中的 selectedKeys 集合,但不会在处理完后从 selectedKeys 集合中移除,需要我们自己手动删除
iterator.remove();
private static void handleAccept(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (Objects.nonNull(socketChannel))
log.info("receive connection from client. client:", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 设置客户端Channel为非阻塞模式,否则在执行socketChannel.read()时会阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
Selector selector = selectionKey.selector();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
private static void handleRead(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
int length = socketChannel.read(readBuffer);
if (length > 0)
log.info("receive message from client. client: message:", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()
, new String(readBuffer.array(), 0, length, "UTF-8"));
else if (length == -1)
// 客户端正常断开(socketChannel.close())时,在服务端也会产生读事件,且读到的数据长度为-1
socketChannel.close();
return;
SelectionKey表示一对Selector和Channel的关系,从SelectionKey中可以获得已经准备好数据的Channel。
SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT —— 针对服务端,接收连接就绪事件,表示服务器监听到了客户连接
SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT —— 针对客户端,连接就绪事件,表示客户与服务器的连接已经建立就绪
SelectionKey.OP_READ —— 读就绪事件,表示通道中已经有了可读的数据,可以执行读操作
SelectionKey.OP_WRITE —— 写就绪事件,表示已经可以向通道写数据了(通道目前可以用于写操作)
- 以Debug模式启动服务端,初始化完ServerSocketChannel后,手动设置了ServerSocketChannel的阻塞模式为非阻塞,并且为ServerSocketChannel在Selector上注册了一个ACCEPT事件,当有客户端向服务端请求连接时会触发该事件。当执行到
int count = selector.select();时,服务端阻塞,等待客户端连接 - 以Debug模式运行一个客户端A,当执行完
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080));时,服务端selector.select()方法返回了就绪的IO事件数量为1(就是客户端A的请求连接事件) - 当服务端接收到客户端A的连接后,把客户端连接——SocketChannel设置为非阻塞,并且在Selector实例上注册一个读事件,这时客户端连接SocketChannel会对读事件感兴趣,当这个客户端发送数据时,会唤醒Selector。当服务端下一次循环再次执行到
int count = selector.select();时,会再次阻塞,等待客户端的IO事件 - 客户端A继续执行完
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);后,服务端selector.select()方法返回了就绪的IO事件数量为1(就是客户端A的写数据事件) - 当服务端在读取客户端A的数据时(下次执行
selector.select()之前),同时启动客户端B、客户端C(或者再多开几个线程,否则可能模拟不出来),等服务端下次执行selector.select()时,返回的就绪的IO事件数量可能有多个,然后可以根据selectionKey.isAcceptable()、selectionKey.isReadable()、selectionKey.isWritable()来分别处理对应的事件。
但是,如果客户端连接或读写时间过长,也只能一个一个处理。NIO只是把BIO中等待的时间(比如socket.getInputStream().read())充分利用,为在多核CPU机器上的运行提高了效率,可以用多线程+NIO的IO多路复用模式来处理。
转载请注明出处——胡玉洋 《Java网络编程——NIO的阻塞IO模式、非阻塞IO模式、IO多路复用模式的使用》
以上是关于Java网络编程——NIO的阻塞IO模式非阻塞IO模式IO多路复用模式的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章