WDK学习笔记_docker容器客户端_fabric-go-sdk
Posted 原来如此-
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了WDK学习笔记_docker容器客户端_fabric-go-sdk相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
摘要
本周在上周搭建的区块链网络及智能合约基础上进行了开发,成功的解决了上周在客户端容器上无法实例化链码的问题,并在客户端容器上实现了调用链码的操作,但客户端容器是在linux系统的命令行上进行操作的,不方便进行应用开发。于是学习了fabric-go-sdk,并用其创建了资源管理客户端、通道管理客户端,用这两个客户端实现了将节点加入通道、在节点上安装链码、实例化链码的操作。但在调用链码时遇到了问题:

目前在解决该问题中,解决该问题后,就可马上写好基于区块链的后端服务器了。(由于区块链资源较少,大多数参考资料版本也不完全一样,需要花时间摸索,所以这周就只学了区块链)
一、智能合约在区块链上的部署步骤
- 按照配置文件启动区块链网络的各个节点。(若需要在命令行与区块链进行交互,还需要启动客户端容器,也可使用fabric-go-sdk代替客户端容器与区块链忘记交互);
- 创建通道文件;
- 将各个节点加入通道,在同一通道下的成员,共享同一个账本;
- 在需要执行交易及背书的节点上安装链码;
- 初始化链码;
- 调用链码。
二、用docker容器创建的客户端在命令行上与区块链网络进行交互
2.1 容器内创建通道
peer channel create -o orderer.trace.com:7050 --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/trace.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.trace.com-cert.pem -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/channel.tx
2.2 加入通道
peer channel join -b mychannel.block
2.3 安装链码
:
peer chaincode install -n testcc -v 1.0 -p github.com/chaincode/go
2.4 初始化链码
peer chaincode instantiate -o orderer.trace.com:7050 --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/trace.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.trace.com-cert.pem -C mychannel -n testcc -l golang -v 1.0 -c '"Args":["init","a","100","b","200"]' -P "AND ('OrgGenerateMSP.member')"
2.5 调用链码
-
发送交易
tls: false
peer chaincode invoke -o orderer.example.com:7050 --tls false --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/trace.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.trace.com-cert.pem -C mychannel -n testcc -c '"Args":["invoke","a","b","10"]'tls: true
peer chaincode invoke -o orderer.trace.com:7050 --tls true --cafile /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/trace.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.trace.com-cert.pem -C mychannel -n testcc -c '"Args":["invoke","a","b","10"]' -
查询
peer chaincode query -o orderer.trace.com:7050 /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/ordererOrganizations/trace.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.trace.com-cert.pem -C mychannel -n mycc -c '"Args":["query","a"]'
三、fabric-go-sdk与区块链网络交互
fabric-go-sdk是用来创建客户端,与区块链网络进行交互的。
3.1 步骤
- 编写config.yaml配置文件;
- 创建fabric-sdk实例;
- 创建资源管理客户端,对一系列客户端进行管理,如:创建通道,加入通道,安装链码,实例化链码等;
- 创建通道客户端,用来执行调用链码等操作。
3.2 config.yaml配置文件
在该文件中,主要写明白:
- 每个客户端的信息,如:所属组织,密钥和证书文件;
- fabric网络的结构信息,如orderer组织证书、节点等; 并不需要所有fabric网络的信息,只需要当前client进行通信的那部分网络的配置信息。
# file:config.yaml
name: "trace-network"
#
# Schema version of the content. Used by the SDK to apply the corresponding parsing rules.
#
version: 1.0.0
#
# The client section used by GO SDK.
#
client:
# Which organization does this application instance belong to? The value must be the name of an org
# defined under "organizations"
organization: OrgGenerate
logging:
level: info
# Root of the MSP directories with keys and certs.
cryptoconfig:
path: /root/trace/crypto-config
# Some SDKs support pluggable KV stores, the properties under "credentialStore"
# are implementation specific
credentialStore:
path: /tmp/trace-store
# [Optional]. Specific to the CryptoSuite implementation used by GO SDK. Software-based implementations
# requiring a key store. PKCS#11 based implementations does not.
cryptoStore:
path: /tmp/trace-msp
# BCCSP config for the client. Used by GO SDK.
BCCSP:
security:
enabled: true
default:
provider: "SW"
hashAlgorithm: "SHA2"
softVerify: true
level: 256
tlsCerts:
# [Optional]. Use system certificate pool when connecting to peers, orderers (for negotiating TLS) Default: false
systemCertPool: false
# [Optional]. Client key and cert for TLS handshake with peers and orderers
client:
key:
path: /root/trace/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/generate.trace.com/users/User1@generate.trace.com/tls/client.key
cert:
path: /root/trace/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/generate.trace.com/users/User1@generate.trace.com/tls/client.crt
#
# [Optional]. But most apps would have this section so that channel objects can be constructed
# based on the content below. If an app is creating channels, then it likely will not need this
# section.
#
channels:
# name of the channel
mychannel:
# Required. list of orderers designated by the application to use for transactions on this
# channel. This list can be a result of access control ("org1" can only access "ordererA"), or
# operational decisions to share loads from applications among the orderers. The values must
# be "names" of orgs defined under "organizations/peers"
# deprecated: not recommended, to override any orderer configuration items, entity matchers should be used.
# orderers:
# - orderer.kevin.kongyixueyuan.com
# Required. list of peers from participating orgs
peers:
peer0.generate.trace.com:
# [Optional]. will this peer be sent transaction proposals for endorsement? The peer must
# have the chaincode installed. The app can also use this property to decide which peers
# to send the chaincode install request. Default: true
endorsingPeer: true
# [Optional]. will this peer be sent query proposals? The peer must have the chaincode
# installed. The app can also use this property to decide which peers to send the
# chaincode install request. Default: true
chaincodeQuery: true
# [Optional]. will this peer be sent query proposals that do not require chaincodes, like
# queryBlock(), queryTransaction(), etc. Default: true
ledgerQuery: true
# [Optional]. will this peer be the target of the SDK's listener registration? All peers can
# produce events but the app typically only needs to connect to one to listen to events.
# Default: true
eventSource: true
peer1.generate.trace.com:
endorsingPeer: true
chaincodeQuery: true
ledgerQuery: true
eventSource: true
policies:
#[Optional] options for retrieving channel configuration blocks
queryChannelConfig:
#[Optional] min number of success responses (from targets/peers)
minResponses: 1
#[Optional] channel config will be retrieved for these number of random targets
maxTargets: 1
#[Optional] retry options for query config block
retryOpts:
#[Optional] number of retry attempts
attempts: 5
#[Optional] the back off interval for the first retry attempt
initialBackoff: 500ms
#[Optional] the maximum back off interval for any retry attempt
maxBackoff: 5s
#[Optional] he factor by which the initial back off period is exponentially incremented
backoffFactor: 2.0
#[Optional] options for retrieving discovery info
discovery:
#[Optional] discovery info will be retrieved for these number of random targets
maxTargets: 2
#[Optional] retry options for retrieving discovery info
retryOpts:
#[Optional] number of retry attempts
attempts: 4
#[Optional] the back off interval for the first retry attempt
initialBackoff: 500ms
#[Optional] the maximum back off interval for any retry attempt
maxBackoff: 5s
#[Optional] he factor by which the initial back off period is exponentially incremented
backoffFactor: 2.0
#[Optional] options for the event service
eventService:
# [Optional] resolverStrategy specifies the peer resolver strategy to use when connecting to a peer
# Possible values: [PreferOrg (default), MinBlockHeight, Balanced]
#
# PreferOrg:
# Determines which peers are suitable based on block height lag threshold, although will prefer the peers in the
# current org (as long as their block height is above a configured threshold). If none of the peers from the current org
# are suitable then a peer from another org is chosen.
# MinBlockHeight:
# Chooses the best peer according to a block height lag threshold. The maximum block height of all peers is
# determined and the peers whose block heights are under the maximum height but above a provided "lag" threshold are load
# balanced. The other peers are not considered.
# Balanced:
# Chooses peers using the configured balancer.
resolverStrategy: PreferOrg
# [Optional] balancer is the balancer to use when choosing a peer to connect to
# Possible values: [Random (default), RoundRobin]
balancer: Random
# [Optional] blockHeightLagThreshold sets the block height lag threshold. This value is used for choosing a peer
# to connect to. If a peer is lagging behind the most up-to-date peer by more than the given number of
# blocks then it will be excluded from selection.
# If set to 0 then only the most up-to-date peers are considered.
# If set to -1 then all peers (regardless of block height) are considered for selection.
# Default: 5
blockHeightLagThreshold: 5
# [Optional] reconnectBlockHeightLagThreshold - if >0 then the event client will disconnect from the peer if the peer's
# block height falls behind the specified number of blocks and will reconnect to a better performing peer.
# If set to 0 then this feature is disabled.
# Default: 10
# NOTES:
# - peerMonitorPeriod must be >0 to enable this feature
# - Setting this value too low may cause the event client to disconnect/reconnect too frequently, thereby
# affecting performance.
reconnectBlockHeightLagThreshold: 10
# [Optional] peerMonitorPeriod is the period in which the connected peer is monitored to see if
# the event client should disconnect from it and reconnect to another peer.
# Default: 0 (disabled)
peerMonitorPeriod: 5s
#
# list of participating organizations in this network
#
organizations:
OrgGenerate:
mspid: OrgGenerateMSP
cryptoPath: peerOrganizations/generate.trace.com/users/username@generate.trace.com/msp
peers:
- peer0.generate.trace.com
- peer1.generate.trace.com
# [Optional]. Certificate Authorities issue certificates for identification purposes in a Fabric based
# network. Typically certificates provisioning is done in a separate process outside of the
# runtime network. Fabric-CA is a special certificate authority that provides a REST APIs for
# dynamic certificate management (enroll, revoke, re-enroll). The following section is only for
# Fabric-CA servers.
certificateAuthorities:
- ca.generate.trace.com
- tlsca.generate.trace.com
#
# List of orderers to send transaction and channel create/update requests to. For the time
# being only one orderer is needed. If more than one is defined, which one get used by the
# SDK is implementation specific. Consult each SDK's documentation for its handling of orderers.
#
orderers:
orderer.trace.com:
url: localhost:7050
# these are standard properties defined by the gRPC library
# they will be passed in as-is to gRPC client constructor
grpcOptions:
ssl-target-name-override: orderer.trace.com
# These parameters should be set in coordination with the keepalive policy on the server,
# as incompatible settings can result in closing of connection.
# When duration of the 'keep-alive-time' is set to 0 or less the keep alive client parameters are disabled
keep-alive-time: 0s
keep-alive-timeout: 20s
keep-alive-permit: false
fail-fast: false
# allow-insecure will be taken into consideration if address has no protocol defined, if true then grpc or else grpcs
allow-insecure: false
tlsCACerts:
# Certificate location absolute path
path: /root/trace/crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/trace.com/tlsca/tlsca.trace.com-cert.pem
#
# List of peers to send various requests to, including endorsement, query
# and event listener registration.
#
peers:
peer0.generate.trace.com:
# this URL is used to send endorsement and query requests
url: localhost:7051
# eventUrl is only needed when using eventhub (default is delivery service)
eventUrl: localhost:7053
grpcOptions:
ssl-target-name-override: peer0.generate.trace.com
# These parameters should be set in coordination with the keepalive policy on the server,
# as incompatible settings can result in closing of connection.
# When duration of the 'keep-alive-time' is set to 0 or less the keep alive client parameters are disabled
keep-alive-time: 0s
keep-alive-timeout: 20s
keep-alive-permit: false
fail-fast: false
# allow-insecure will be taken into consideration if address has no protocol defined, if true then grpc or else grpcs
allow-insecure: false
tlsCACerts:
# Certificate location absolute path
path: /root/trace/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/generate.trace.com/tlsca/tlsca.generate.trace.com-cert.pem
peer1.generate.trace.com:
# this URL is used to send endorsement and query requests
url: localhost:8051
# eventUrl is only needed when using eventhub (default is delivery service)
eventUrl: localhost:8053
grpcOptions:
# ssl-target-name-override: peer1.generate.trace.com
# These parameters should be set in coordination with the keepalive policy on the server,
# as incompatible settings can result in closing of connection.
# When duration of the 'keep-alive-time' is set to 0 or less the keep alive client parameters are disabled
keep-alive-time: 0s
keep-alive-timeout: 20s
keep-alive-permit: false
fail-fast: false
# allow-insecure will be taken into consideration if address has no protocol defined, if true then grpc or else grpcs
allow-insecure: false
tlsCACerts:
# Certificate location absolute path
path: /root/trace/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/generate.trace.com/tlsca/tlsca.generate.trace.com-cert.pem
#
# Fabric-CA is a special kind of Certificate Authority provided by Hyperledger Fabric which allows
# certificate management to be done via REST APIs. Application may choose to use a standard
# Certificate Authority instead of Fabric-CA, in which case this section would not be specified.
#
certificateAuthorities:
ca.generate.trace.com:
url: http://localhost:7054
tlsCACerts:
# Certificate location absolute path
path: /root/trace/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/generate.trace.com/ca/ca.generate.trace.com-cert.pem
# Fabric-CA supports dynamic user enrollment via REST APIs. A "root" user, a.k.a registrar, is
# needed to enroll and invoke new users.
registrar:
enrollId: admin
enrollSecret: adminpw
# [Optional] The optional name of the CA.
caName: ca.generate.trace.com
entityMatchers:
peer:
- pattern: (\\w*)peer0.generate.trace.com(\\w*)
urlSubstitutionExp: localhost:7051
eventUrlSubstitutionExp: localhost:7053
sslTargetOverrideUrlSubstitutionExp: peer0.generate.trace.com
mappedHost: peer0.generate.trace.com
- pattern: (\\w*)peer1.generate.trace.com(\\w*)
urlSubstitutionExp: localhost:8051
eventUrlSubstitutionExp: localhost:8053
sslTargetOverrideUrlSubstitutionExp: peer1.generate.trace.com
mappedHost: peer1.generate.trace.com
orderer:
- pattern: (\\w*)orderer.trace.com(\\w*)
urlSubstitutionExp: localhost:7050
sslTargetOverrideUrlSubstitutionExp: orderer.trace.com
mappedHost: orderer.trace.com
certificateAuthorities:
- pattern: (\\w*)ca.generate.trace.com(\\w*)
urlSubstitutionExp: http://localhost:7054
mappedHost: ca.geberate.trace.com
3.2 实例化go sdk函数
输入config.yaml配置文件地址,返回实例化后的sdk。
该函数主要是使用fabric-go-sdk中的fabsdk.New(config.FromFile(configFile))其中configFilePath就是config.yaml的文件路径。
// 输入config.yaml配置文件地址,返回实例化后的sdk。
func SetupSDK(configFilePath string) (*fabsdk.FabricSDK, error)
sdk, err := fabsdkWDK学习笔记第四周_区块链总体简述
摘要
区块链是一个单向链式存储结构,区块中存储了前一个区块的hash值,交易数据等,区块间通过区块中存储的“前一个区块的hash值”连接,当链中某个区块数据被删除或者修改,其hash值改变,随后区块无法再通过之前的hash值与之连接,区块链就会断掉。所以区块链中的数据是可以做到不可篡改,永久追溯的。比特币根据这一思路,将所有区块链分布式存储在各个节点中,并在其基础上引如了工作量证明机智和共识协议,工作量证明机制使得篡改数据要大量算力消耗大量成本,共识机制使得攻击者算力只有大于诚信节点算力时,才可能攻击成功。两者结合使得其中存储数据是非常安全可靠的。但比特币由于其脚本语言的限制,不具备图灵完整性,在其上面扩展有一定局限性。于是发展出了以太坊,以太坊的采用的脚本语言具有图灵完整性,在设计时就将其作为一个开发平台,开发者可以在此基础上创建任意的基于共识的、可扩展的、标准化的、特性完备的、易于开发的和协同的应用。同时以太坊改善了工作量证明机制,降低了算力对挖矿的影响,防止大矿池导致的中心化。但是在比特币和以太坊中,存储的数据人人都可查询,数据没有隐私,不适合企业开发,为了解决该问题,出现了超级账本,超级账本引入了联盟链的概念,不属于联盟链的成员无法访问链中的数据或者访问数据有限,从而保证了数据的隐私性,为了降低维护成本,取消了挖矿机制(工作量证明机制),用背书策略和改善的共识协议产生新块。
一、区块链简述
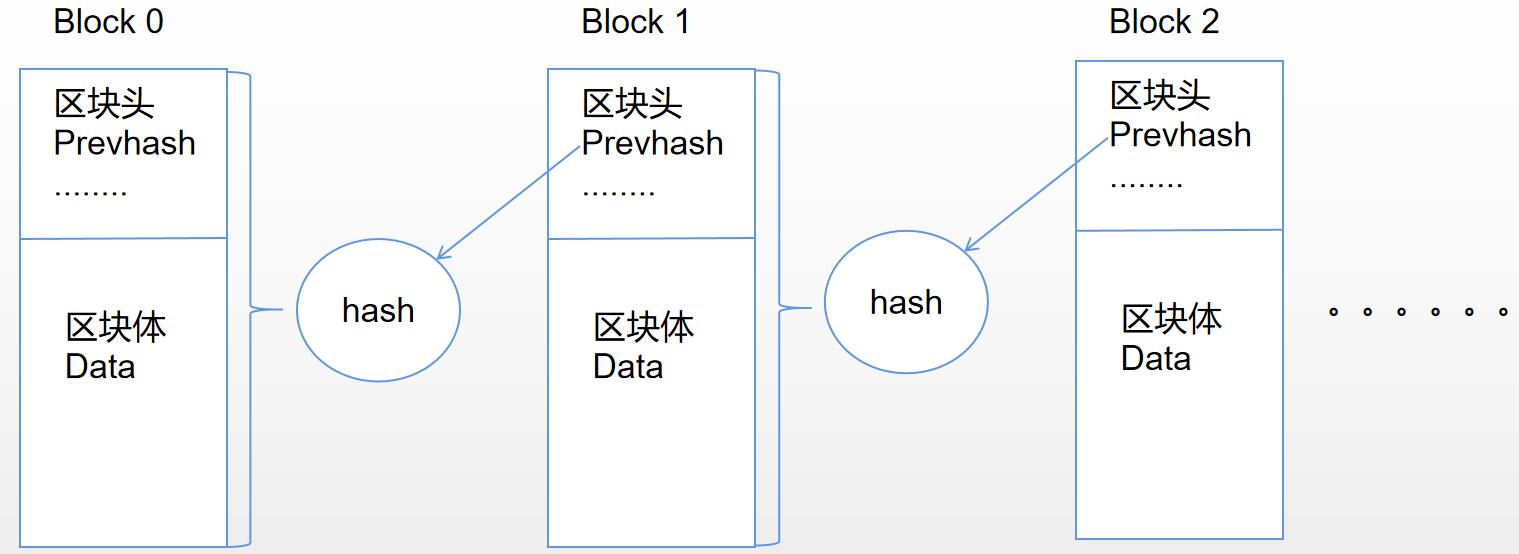
如下图,区块链是一个链式的存储结构,区块链是由区块首尾相连形成的单向链式结构,区块是链式存储结构中的最小单元,其中第一个区块称为创始区块。区块又分为区块头和区块体,其中:
- 区块头记录了区块头版本号(Version)、上一个区块的Hash值(PrevHash)、该区块所有交易数据的Hash值(MerkleRoot)、该区块生成的时间(Timestamp)等。
- 区块体中存储着交易数据。
二、比特币简述
2.1 比特币的安全性
比特币是通过区块链技术实现的电子现金系统,它是完全去中心化的,就算交易信道和交易节点不可信的情况下,仍能保证交易的安全性。这是怎么做的的呢?
我们知道在区块链中,若其中某个区块中数据被篡改,那么该区块hash值就会发生变化,就无法通过hash值和下一个区块相连,区块链就会断掉。所以我们可能会以此觉得区块链中的数据是不可篡改的,但是这并不是真正的不可篡改,因为攻击者可以更新后面所有区块中的“上一个区块的Hash值(PrevHash)”使得区块链再次连接起来,为了解决这个问题,中本聪引入了工作量证明机制与共识机制:
- 工作量证明机制:在区块头中加入一个工作量证明机制的可变数(nonce),每生成一个新区块时,要求其hash值要满足特定要求(难度与全网当前算力有关),如要求其hash值以“0000”开头,通过暴力穷举nonce使得新区块的hash值满足要求。
- 共识机制:最先找到该nonce的节点就成为该区块的记账人,它需要将它找到的可变数广播给其他节点,当有一半以上的节点确认其没问题,它才可在区块链上创建该区块,其他节点也跟随它在自己的链上创建该区块(在比特币系统中每个节点都有一条完整的区块链)。
于是,若某个攻击者要篡改区块链中间某个区块的数据,它需要将该区块及后面所有区块的工作量全做一遍,该代价是巨大的,在没有巨大算力突破下也是不可能的。为了防止被攻击,中本聪还引入了奖励机制,在创建新区块时,最先找到nonce值的记账人可以获得50比特币的奖励(奖励从2008年起每四年减少一半),这就使得维护区块链的收益远远大于攻击区块链的收益,实现了真正点对点的安全。可以发现,和传统的数据库相比,区块链存储数据的效率很低(大约10分钟一次),但其正是用数据的存储效率换来了数据的安全。
2.2 带工作量证明的区块链实践
用python简单实现带工作量证明的区块链:
import time
import hashlib
class Proofofwork: #工作量证明函数
def __init__(self, block):
self.block = block
def mine(self):
i = 0
prefix = "00000"
while True:
random = str(i)
obj = hashlib.sha256()
obj.update(self.block.data.encode('utf-8'))
obj.update(random.encode('utf-8'))
digest = obj.hexdigest()
if digest.startswith(prefix):
return random,digest
i += 1
class Block:
def __init__(self, data, pre_hash):
self.pre_hash = pre_hash
self.data = data
self.time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M_%S", time.localtime())
self.random = 0
@property
def hash(self):
# obj = hashlib.sha256()
# obj.update(self.data.encode('utf-8'))
# obj.update(self.random.encode('utf-8'))
proof = Proofofwork(self)
self.random, digest = proof.mine()
return digest
# def gethash(data):
# obj = hashlib.sha256()
# obj.update(str(data).encode('utf-8'))
# return obj.hexdigest()
def orblock(data): #初始块的创建
# block = Block(data, pre_hash="")
# proof = Proofofwork(block)
return Block(data, pre_hash="")
class add_block: #新增块的函数
def __init__(self):
self.block = [orblock("Number one Bloce")]
def add(self, data):
pre_block = self.block[ len(self.block)-1 ]
new_block = Block(data, pre_block.hash)
self.block.append(new_block)
return new_block
bc = add_block()
while True:
for n,i in enumerate(bc.block):
print(n)
print("pre_hash:{0}".format(bc.block[n].pre_hash))
print("data: {}".format(bc.block[n].data))
print("hash: {}".format(bc.block[n].hash))
print("time: {}".format(bc.block[n].time))
if(bc.block[n].pre_hash and bc.block[n].pre_hash != bc.block[n-1].hash):
print("InValid Block")
# print("\\n i.hash:{}".format(i.pre_hash))
# print("上一个的hash:{} \\n".format(bc.block[n-1].hash))
else:
print("Valid Block")
print("\\n")
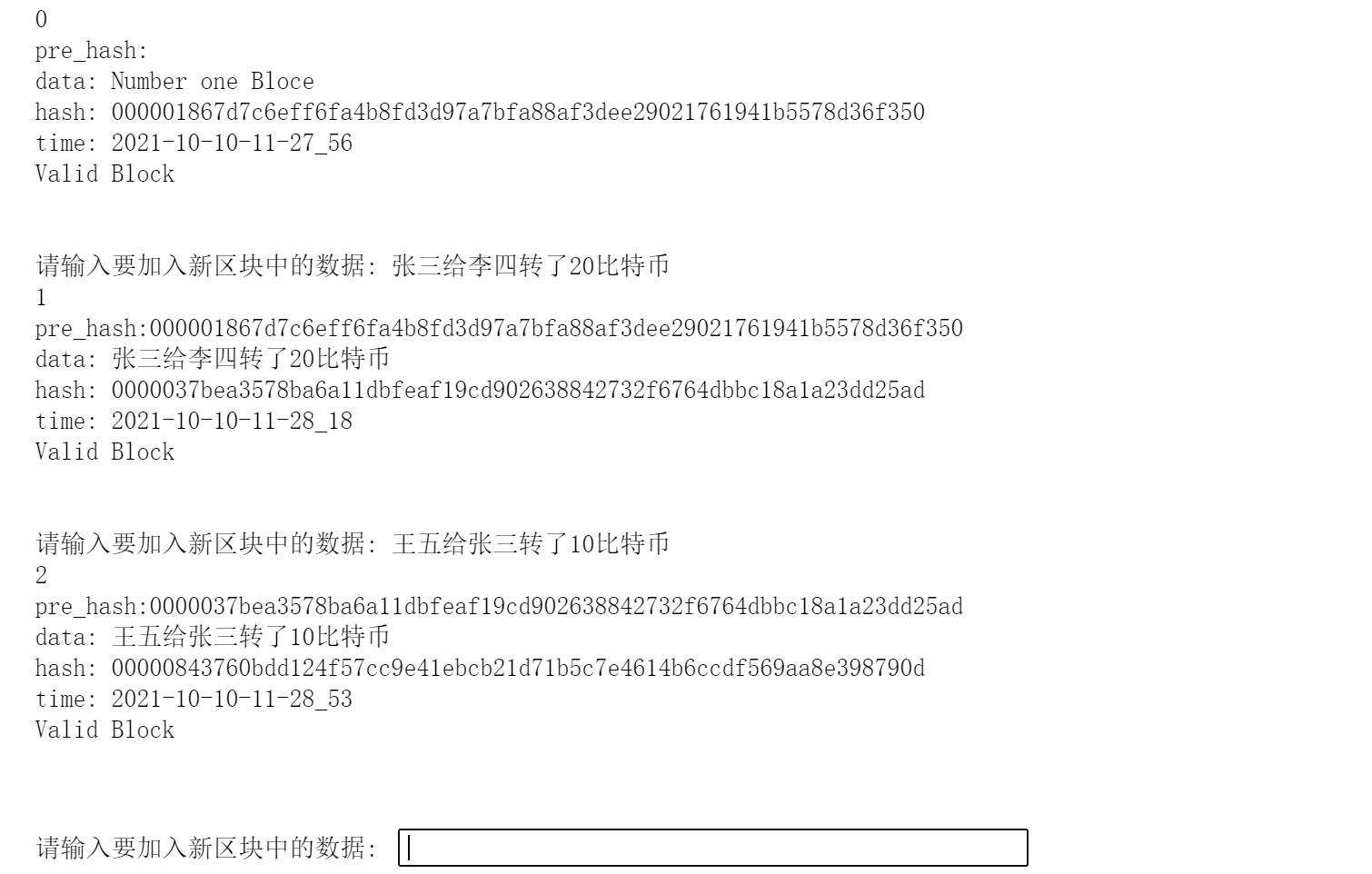
bc.add(input("请输入要加入新区块中的数据: "))
输出结果:
三、以太坊简述
比特币使用了一套基于堆栈的脚本语言,这语言虽然具有一定灵活性,使得像多重签名这样的功能得以实现,然而却不足以构建更高级的应用。
为了解决比特币扩展性不足的问题,创建了以太坊。以太坊不单单是电子货币交易系统,它是一个平台,提供各种模块来让用户搭建应用,开发者可以在此基础上创建任意的基于共识的、可扩展的、标准化的、特性完备的、易于开发的和协同的应用。因为以太坊内部数据是以区块链方式存储的,所以我们创建的系统中的数据也是不可篡改,可追溯的。与比特币相比:
- 以太坊平台对底层区块链进行了封装,让区块链开发着可以直面上层应用进行开发,大大降低了开发难度。
- 以太坊采用的是账户模型,不再使用UTXO,每笔交易只有一个输入,一个输出,一个签名。
- 以太坊采用改进POW,避免了能耗问题。
- 引入了图灵完备的智能合约开发语言。
智能合约是在区块链上保存的代码,一旦保存不可撤销不可更改。智能合约部署成功后会返回一个地址,可以通过该地址访问智能合约。
四、超级账本简述
比特币和以太坊都是公链,所有人都可参与,所有人都可查阅,数据是公开透明的,数据的隐私得不到保证。超级账本就是为了解决该问题的。
超级账本是针对企业级用户进行开发的,它引入了联盟链的概念,不在许可中的用户无法访问链中的区块从而保证了数据的隐私性,为了提高数据的存储效率,它取消了交易量证明机制,采用了背书策略改善了共识系统,创建新区块不需要消耗大量算力,降低了维护成本。
总结
区块链中数据可以通过工作量证明机制,共识协议,数据分布式存储等方法,使其变的基本上不可篡改,且可永久追溯。在某些应用领域具有天然的优势。若想要做数据安全性高的系统开发,我们可在以太坊和超级账本的平台上进行开发,但在以坊公网中,部署智能合约及发送交易时需要支付一定以太币(目前约2万一枚)作为工资给矿工,成本高。所以最好的是用超级账本进行开发,其成本低,参与成员越多,通道越多,安全性越高。
参考
以上是关于WDK学习笔记_docker容器客户端_fabric-go-sdk的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章