对一串字符进行huffman编码并解码
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了对一串字符进行huffman编码并解码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
输入一段字符,用huffman编码对其进行编码,然后对其进行解码 倾家荡产求程序,不需要对文件解码那么复杂的,求一简单程序,作业题!
参考技术A #include <stdlib.h>#include <iostream.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define OVERFLOW -1
typedef struct
char letter;
int weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
HTNode,*HuffmanTree;
typedef char * *HuffmanCode;
void Select(HuffmanTree &HT,int i,int &s1,int &s2)
/*选择森林中,根结点的权值最小和次小的两个树,
*将其根结点的下标号记入s1和s2中
*/
int j, k;
for(k = 1; k < i; k++)
if(HT[k].parent != NULL)
continue;
s1 = k;/*init the number*/
break;
for(j = 1; j < i; j++)
if(HT[j].parent != NULL)
continue;
if(HT[j].weight < HT[s1].weight)
s1 = j;
for(k = 1; k <= i; k++)
if(HT[k].parent != NULL || k == s1)
continue;
s2 = k;
break;
for(j = 1; j < i; j++)
if(HT[j].parent != NULL)
continue;
if(HT[j].weight <= HT[s2].weight && j != s1)
s2 = j;
void HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree &HT,HuffmanCode &HC,char *zi,int *w,int n)
HuffmanTree p;
int m,i,s1,s2,f,c;
int Istart = 1;
char *cd;
if(n <= 1)
return;
m = 2*n-1;
if(!(HT=(HuffmanTree)malloc((m+1)*sizeof(HTNode))))
exit(OVERFLOW);
for(p=HT+1,i=1;i<=n;++i,++zi,++p,++w)
/*生成独立的森林*/
p->parent = NULL;
p->letter = *zi;
p->lchild = NULL;
p->rchild = NULL;
p->weight = *w;
for(;i<=m;++i,++p)
(*p).weight=0;
(*p).parent=0;
(*p).lchild=0;
(*p).rchild=0;
for(i=n+1;i<=m;++i)
Select(HT,i-1,s1,s2);
HT[s1].parent=i;
HT[s2].parent=i;
HT[i].lchild=s1;
HT[i].rchild=s2;
HT[i].weight=HT[s1].weight+HT[s2].weight;
HC=(HuffmanCode)malloc((n+1)*sizeof(char *));
cd=(char*)malloc(n*sizeof(char));/*临时的code存储*/
cd[n-1]='\0';
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
Istart = n - 1;
/*按已生成的哈夫曼树,得到各个字符的哈夫曼编码
*/
for(c = i, f = HT[i].parent; f != 0; c = f, f = HT[f].parent)
if(HT[f].lchild == c)
cd[--Istart] = '0';
else
cd[--Istart] = '1';
HC[i] = (char *)malloc((n - Istart) * sizeof(char));
strcpy(HC[i], &cd[Istart]);
free(cd);
void main()
HuffmanTree HT;
HuffmanCode HC;
int i,j,yu;
char zi[9]='A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H';
int w[100];
char z;
char c[100];
z='A';
cout<<endl;
for(i=0;i<=7;i++)
cout<<"please input the weight for "<<z<<":";
cin>>w[i];
z++;
HuffmanCoding(HT,HC,zi,w,8);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"char weight huffmancode "<<endl;
for(i=1;i<=8;i++)
cout<<HT[i].letter<<" "<<HT[i].weight<<" "<<HC[i]<<endl;
cout<<"please input the text:";
cin>>c;
cout<<"The code is:";
for(i=0; i < strlen(c); i++)
/*根据字符的哈夫曼编码,将输入的文本(变量c表示的)翻译成电码。
*/
cout<<HC[(c[i] - 'A' + 1)];
cout<<endl;
cout<<"Enter the code:";
cin>>c;
j=strlen(c);
yu=15;
i=1;
cout<<"The text is:";
while(i <= j)
while(HT[yu].lchild != 0)/*因为是完全二叉树*/
if(c[i-1] == '0')
/*用哈夫曼树,将输入的电码(变量c表示的)翻译成文本,
说明:变量名c在程序中
*/
yu = HT[yu].lchild;
i++;
continue;
if(c[i-1]== '1')
yu=HT[yu].rchild;
i++;
continue;
/*显示由部分电码译码得到的字符,并准备对后面的电码进行译码*/
cout<<HT[yu].letter;
yu = 15;
cout<<endl;
本回答被提问者和网友采纳 参考技术B #include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
const MAXSIZE=100;
typedef struct Huffmantree
char cname;
int weight,mark;
struct Huffmantree *parent,*lchild,*rchild,*next;
Hftree,*linktree;
linktree tidy_string(char ch[])
int i=0;
linktree tree,ptr,beforeptr,node;
tree=(linktree)malloc(sizeof(Hftree));
if(!tree)
return NULL;
tree->next=NULL;
for(i=0;ch[i]!='\0'&&ch[i]!='\n';i++)
ptr=tree;
beforeptr=tree;
node=(linktree)malloc(sizeof(Hftree));
if(!node)
return NULL;
node->parent=NULL;
node->lchild=NULL;
node->rchild=NULL;
node->next=NULL;
node->mark=0;
node->cname=ch[i];
node->weight=1;
if(tree->next==NULL)
tree->next=node;
else
ptr=tree->next;
while(ptr&&ptr->cname!=node->cname)
ptr=ptr->next;
beforeptr=beforeptr->next;
if(ptr&&ptr->cname==node->cname)
ptr->weight+=1;
free(node);
else
node->next=beforeptr->next;
beforeptr->next=node;
return tree;
linktree squent_node(linktree tree)
linktree head,ph,pt,beforeph;
head=(linktree)malloc(sizeof(Hftree));
if(!head)
return NULL;
head->next=NULL;
ph=head;
beforeph=head;
while(tree->next)
pt=tree->next;
tree->next=pt->next;
pt->next=NULL;
ph=head->next;
beforeph=head;
if(head->next==NULL)
head->next=pt;
else
while(ph&&ph->weight<pt->weight)
ph=ph->next;
beforeph=beforeph->next;
pt->next=beforeph->next;
beforeph->next=pt;
free(tree);
return head;
linktree createHtree(linktree tree)
linktree p,q,newnode,beforep;
for(p=tree->next,q=p->next;p!=NULL&&q!=NULL;p=tree->next,q=p->next)
tree->next=q->next;
q->next=NULL;
p->next=NULL;
newnode=(linktree)malloc(sizeof(Hftree));
if(!newnode)
return NULL;
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->mark=0;
newnode->lchild=p;
newnode->rchild=q;
p->parent=newnode;
q->parent=newnode;
newnode->weight=p->weight+q->weight;
p=tree->next;
beforep=tree;
if(p!=NULL&&p->weight>=newnode->weight)
newnode->next=beforep->next;
beforep->next=newnode;
else
while(p!=NULL&&p->weight<newnode->weight)
p=p->next;
beforep=beforep->next;
newnode->next=beforep->next;
beforep->next=newnode;
return (tree->next);
void Huffman_Coding(linktree tree)
int index=0;
char *code;
linktree ptr=tree;
code=(char*)malloc(10*sizeof(char));
printf("字符以及它的相应权数 : 哈夫曼编码:\n\n");
if(ptr==NULL)
printf("哈夫曼树是空的!\n");
exit(0);
else
while(ptr->lchild&&ptr->rchild&&ptr->mark==0)
while(ptr->lchild&&ptr->lchild->mark==0)
code[index++]='0';
ptr=ptr->lchild;
if(!ptr->lchild&&!ptr->rchild)
ptr->mark=1;
code[index]='\0';
printf("\tw[%c]=%d\t\t\t",ptr->cname,ptr->weight);
for(index=0;code[index]!='\0';index++)
printf("%c",code[index]);
printf("\n");
ptr=tree;
index=0;
if(ptr->rchild&&ptr->rchild->mark==0)
ptr=ptr->rchild;
code[index++]='1';
if(!ptr->lchild&&!ptr->rchild)
ptr->mark=1;
code[index++]='\0';
printf("\tw[%c]=%d\t\t\t",ptr->cname,ptr->weight);
for(index=0;code[index]!='\0';index++)
printf("%c",code[index]);
printf("\n");
ptr=tree;
index=0;
if(ptr->lchild->mark==1&&ptr->rchild->mark==1)
ptr->mark=1;
ptr=tree;
index=0;
printf("\n");
free(code);
void Huffamn_Decoding(linktree tree,char code[])
int i=0,j=0;
char *char0_1;
linktree ptr=tree;
char0_1=(char*)malloc(10*sizeof(char));
cout<<"哈夫曼编码 相应的字符\n\n";
for(j=0,ptr=tree;code[i]!='\0'&&ptr->lchild&&ptr->rchild;j=0,ptr=tree)
for(j=0;code[i]!='\0'&&ptr->lchild&&ptr->rchild;j++,i++)
if(code[i]=='0')
ptr=ptr->lchild;
char0_1[j]='0';
if(code[i]=='1')
ptr=ptr->rchild;
char0_1[j]='1';
if(!ptr->lchild&&!ptr->rchild)
char0_1[j]='\0';
for(j=0;char0_1[j]!='\0';j++)
cout<<char0_1[j];
printf("\t\t%c\n",ptr->cname);
if(code[i]=='\0'&&ptr->lchild&&ptr->rchild)
char0_1[j]='\0';
cout<<" 没有与最后几个字符的0,1序列:"<<char0_1<<"相匹配的字符!"<<endl;
return;
free(char0_1);
void deletenode(linktree tree)
linktree ptr=tree;
if(ptr)
deletenode(ptr->lchild);
deletenode(ptr->rchild);
free(ptr);
int main()
char string[MAXSIZE],code[MAXSIZE];
linktree temp,ht,htree,ptr=NULL;
cout<<"编码:请输入要当前字符串:"<<endl;
cin>>string;
cout<<endl;
temp=tidy_string(string);
ht=squent_node(temp);
htree=createHtree(ht);
Huffman_Coding(htree);
cout<<"解码: 请输入要解码的0,1序列:"<<endl;
cin>>code;
cout<<endl;
Huffamn_Decoding(htree,code);
deletenode(htree);
return 0;
Huffman树及其编解码
Huffman树——编解码
介绍:
??Huffman树可以根据输入的字符串中某个字符出现的次数来给某个字符设定一个权值,然后可以根据权值的大小给一个给定的字符串编码,或者对一串编码进行解码,可以用于数据压缩或者解压缩,和对字符的编解码。
??可是Huffman树的优点在哪?
??1、就在于它对出现次数大的字符(即权值大的字符)的编码比出现少的字符编码短,也就是说出现次数越多,编码越短,保证了对数据的压缩。
??2、保证编的码不会出现互相涵括,也就是不会出现二义性,比如a的编码是00100,b的编码是001,而c的编码是00,,这样的话,对于00100就可能是a,也可能是bc,而Huffman树编码方式不会出现这种问题。
如何实现
??实现Huffman树的编解码需要三种数据类型,一个是优先级队列,用来保存树的结点,二是树,用来解码,三是表,用来当作码表编码。下面我们先一一介绍一下三种数据结构:
1、优先级队列
??优先级队列里存放的是一个一个的树的结点,根据树结点中存放的字符的权值来确定其优先级,权重越小,优先级越小,放的位置越靠前。也就是说第一个结点存放的优先级最小,权值最小。
数据类型
//优先级队列,struct TNode表示树的结点,在后面介绍
typedef struct QNode
struct TNode* val; //树的结点,其实也就是数据域
int priority; //优先级
struct QNode* next; //指针域
*Node;
typedef struct Queue
int size; //队列大小
struct QNode* front; //队列头指针
queue;2、树
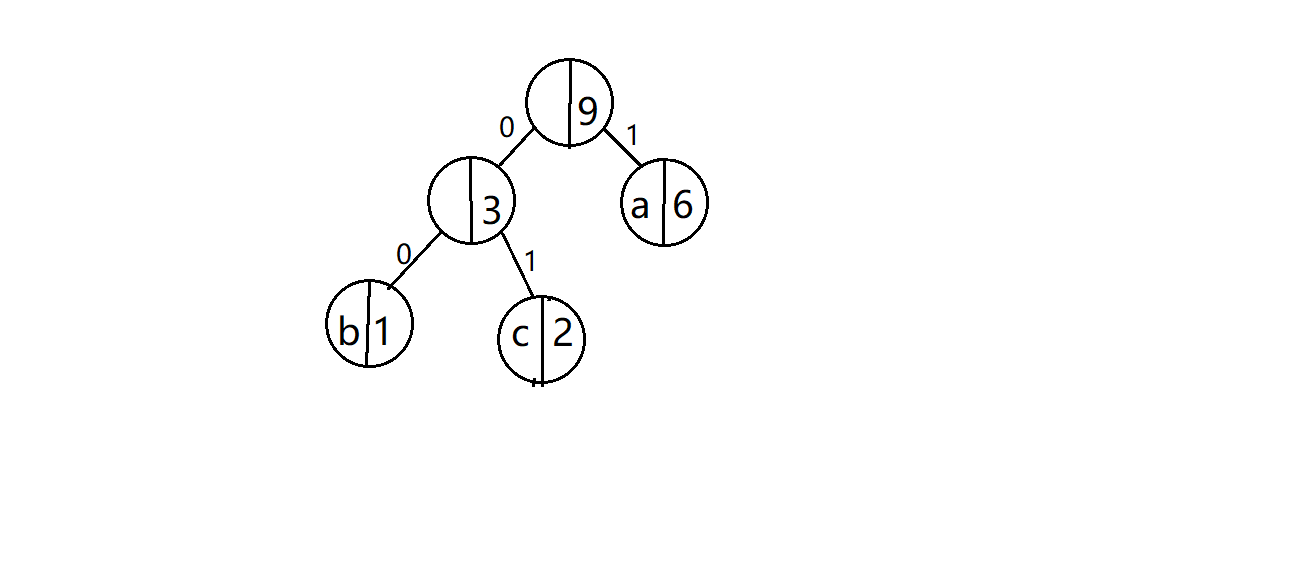
??树里面存放的是字符,以及指向自己的左右孩子结点的指针。比如下图,虽然下图中看起来书中存放了该字符的优先级,但其实可以不加,感觉比较繁琐,所以我取了,但是为了理解方便起见,我在图上标注了出来。
数据类型
//树
typedef struct TNode
char data; //字符值
struct TNode* left; //左孩子
struct TNode* right; //右孩子
*Tree;3、表
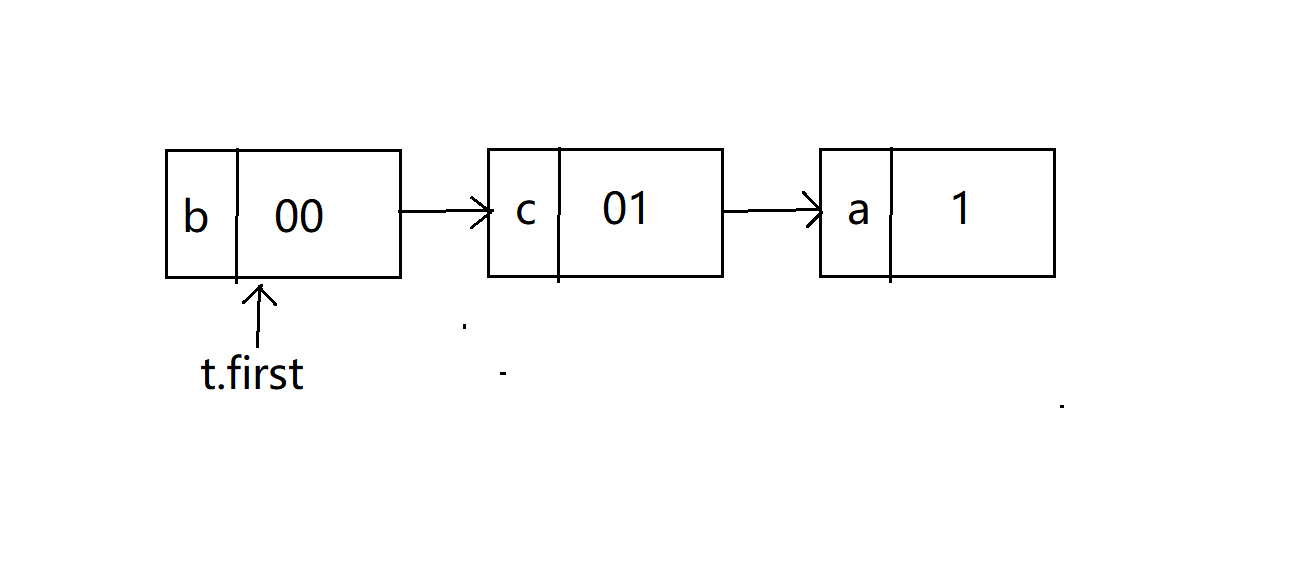
??这个表其实就是一张编码表,里面存放了字符和该字符的编码,用于编码的时候查看。
数据类型
//表
typedef struct BNode
char code[256]; //编码
char symbol; //字符
struct BNode* next; //指向下一个
*bNode;
typedef struct Table
struct BNode* first; //表头
struct BNode* last; //表尾
*table;思路
??为了简单起见我们讲述的时候就先将权值设置为用户输入而不是根据出现频率统计,因为我们作业也刚好是用户输入,文章最后我会贴出根据出现频率统计的代码,有兴趣可以看看。因为用到了很多数据类型所以可能写到一半会觉得有点晕,所以我们开始之前先理一下思路:
先设定a,b,c三个数据,它们的权值分别为6,1,2
??1、首先要根据用户输入的每个字符的权值,创建出一个一个的树结点,然后将其按照优先级的大小存入优先级队列中,按从小到大的顺序,具体实现我会在后面贴。
??2、根据优先级队列中存放的树的结点构建起一棵树。
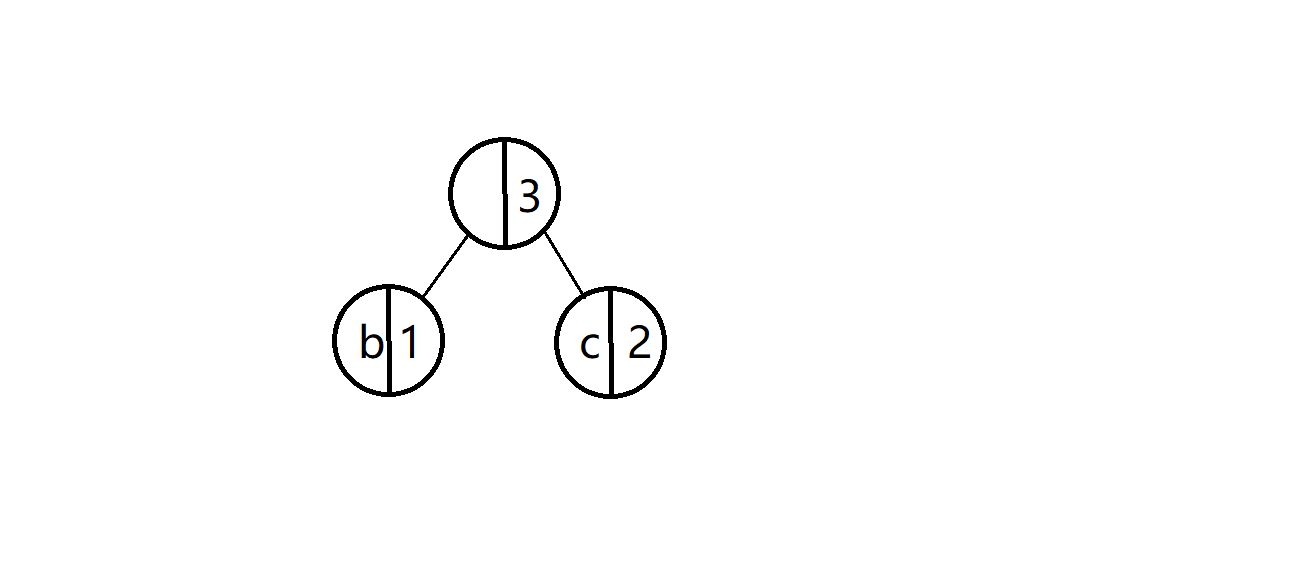
??先出队前两个结点,然后创建一个新的树的结点,新的树的结点的权值就等于出队的两个结点的权值之和,但其没有字符域,也就是说它不是一个真正的树的结点,我们称其为假树结点,对应称为真树结点。
??让出队的两个真树结点作为新得到的假树结点的左右孩子,优先级小的真树结点(也就是先出队的真树结点)作为左孩子,另一个为右孩子。
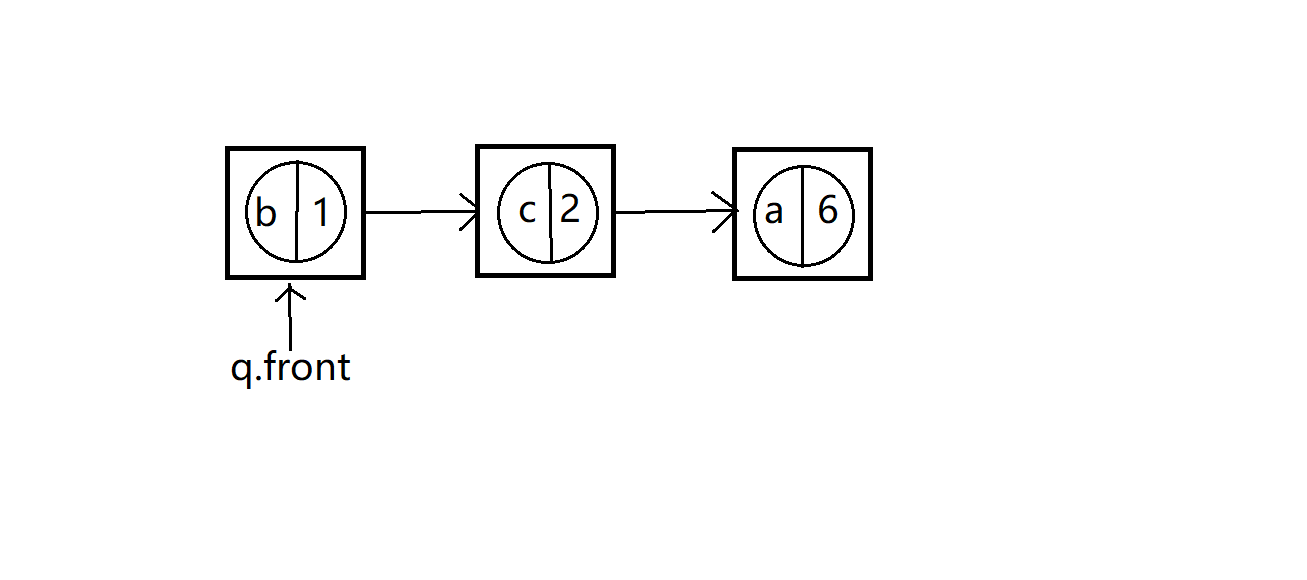
出队后
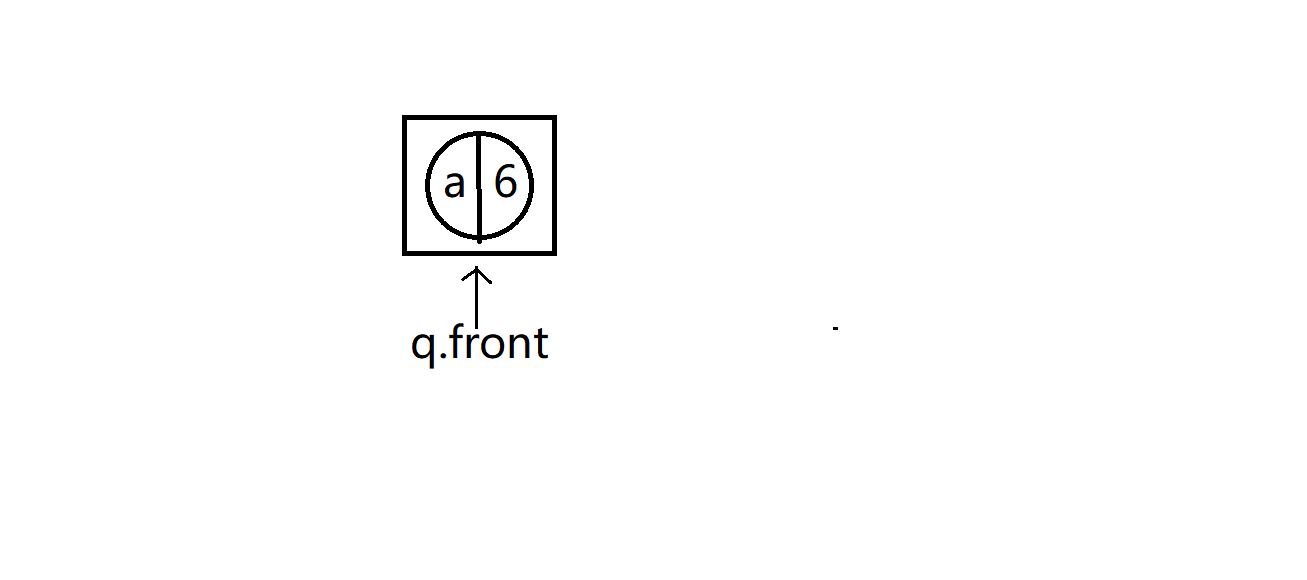
b和c为真树结点,最上面权值为3的为假树结点
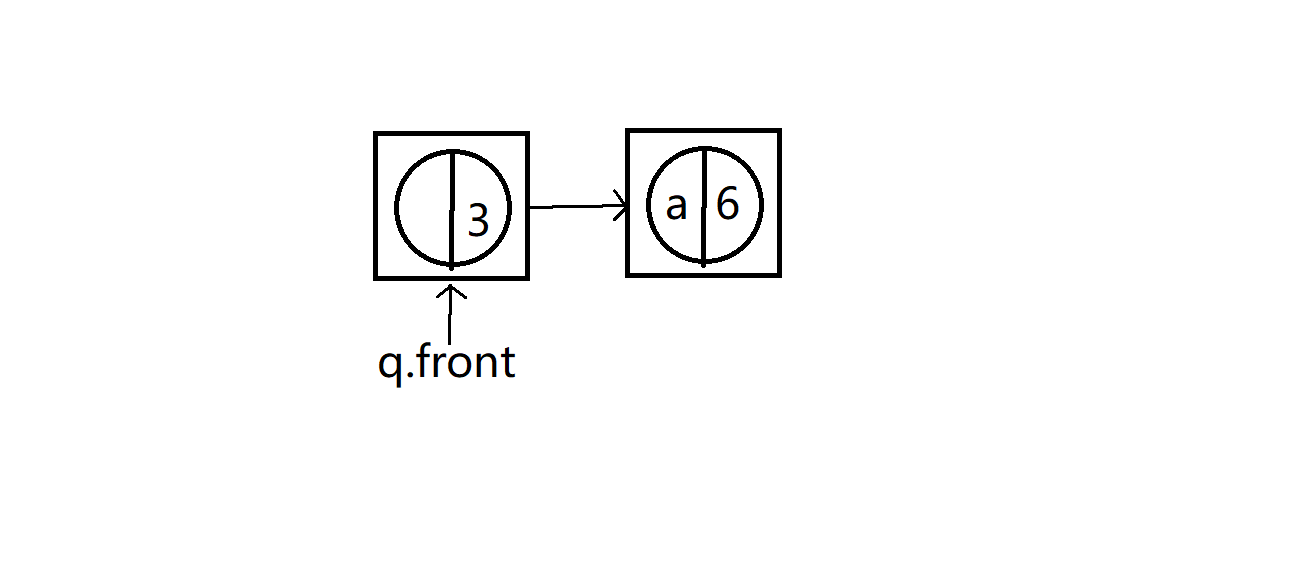
??最后将新创建的假树结点又入队,继续循环操作,直到队列只剩一个结点,那个结点就是假树结点,最后也要作为Huffman树的根节点root。
新的假树结点入队后
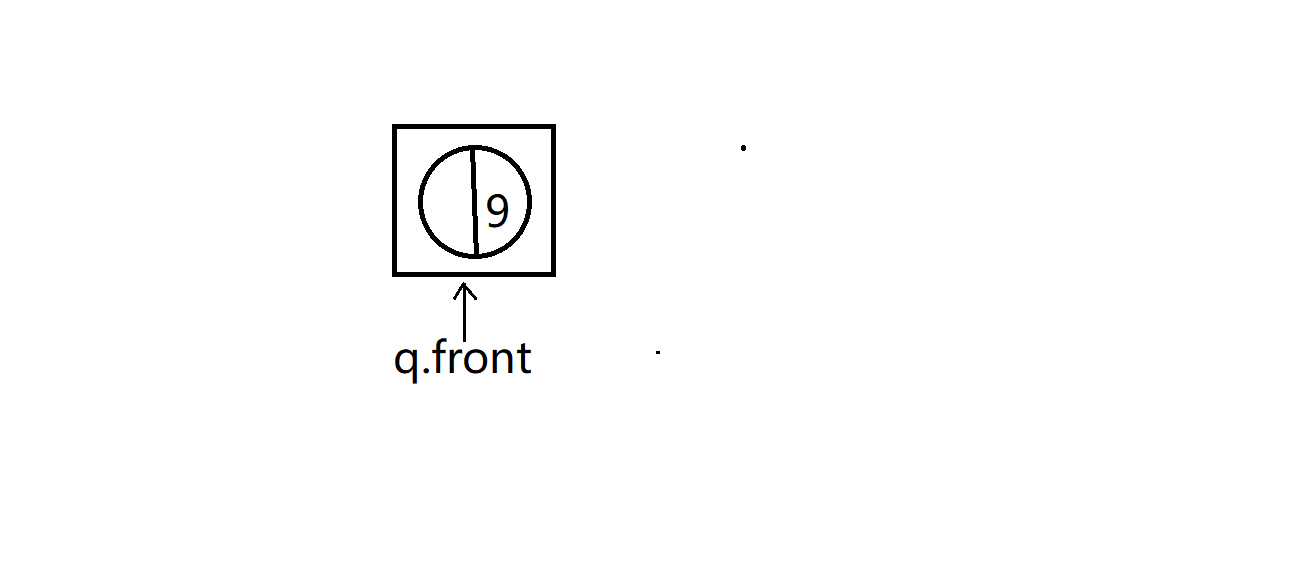
到最后就是下面这样
队列只剩最后一个假树结点,而且作为所构建Huffman树的根节点root

??3、遍历整棵树建起一张码表,通过观察我们发现,真正有意义的真树结点其实都是叶子节点,所以我们在遍历的时候将所有的叶子节点的编码和字符存入表中即可。
??我们规定遍历树建立表的时候,往左孩子访问一层给码值加0,往右就加1。比如刚刚介绍树的时候贴的那张图,b是00,c是01,a是1。
下面是建立起来的码表

构建Huffman树和创建编码表的实现过程
??看完思路之后再看实现过程,我们先看创建队列时候的一系列操作:
??因为为了方便我用了部分C++语法,所以分配内存会是用new,释放内存就是delete,就和C语言里malloc和free是一个作用,其他的都一样。
?队列的初始化:
queue Init_queue()
queue q;
q.size = 0;
q.front = new struct QNode;
if (!q.front)
printf("分配失败!\n");
exit(1);
q.front->next = NULL;
return q;
?队列的插入:
//插入,根据优先级
bool EnQueue(queue& q, Tree avl, int weight)
Node newp = new struct QNode;
newp->val = avl;
newp->priority = weight;
if (q.size == 0 || q.front == NULL) //空表
newp->next = NULL;
q.front = newp;
q.size = 1;
return true;
else //中间位置,需要迭代
if (weight <= q.front->priority) //比第一个都小
newp->next = q.front;
q.front = newp;
q.size++;
return true;
else //中间位置
Node beforp = q.front;
while (beforp->next != NULL)
if (weight <= beforp->next->priority)
newp->next = beforp->next;
beforp->next = newp;
q.size++;
return true;
else
beforp = beforp->next;
//需要插在队列最后
if (beforp->next == NULL)
newp->next = NULL;
beforp->next = newp;
q.size++;
return true;
return true;
创建一个队列:
需要用户输入每个字符和对应的优先级
//创建队列
queue Create_Queue()
queue q = Init_queue();
while (1)
char symbol;
int weight;
cin >> symbol >> weight; //C++里的输入,输入symnol和weight
if (weight == 0) //如果输入的权值为0,表示输入结束
break;
Tree t = new struct TNode;
t->data = symbol;
t->left = NULL;
t->right = NULL;
EnQueue(q, t, weight);
return q;
弹出队列中优先级最小的结点:
//弹出队列优先级最小的
Tree Dequeue(queue& q)
if (q.front == NULL)
cout << "空队!" << endl;
exit(1);
Node p = q.front;
q.front = p->next;
Tree e = p->val;
q.size--;
delete[] p;
return e;
树的函数,根据优先级队列创建一棵树:
//树的函数
//创建一棵树
Tree Create_Tree(queue& q)
while (q.size != 1)
int priority = q.front->priority + q.front->next->priority;
Tree left = Dequeue(q);
Tree right = Dequeue(q);
Tree newTNode = new struct TNode;
newTNode->left = left;
newTNode->right = right;
EnQueue(q, newTNode, priority);
Tree root = new struct TNode;
root = Dequeue(q);
return root;
表的函数,根据树创建一张表:
//创建一张表
table Create_Table(Tree root)
table t = new struct Table;
t->first = NULL;
t->last = NULL;
char code[256];
int k = 0;
travel(root, t, code, k);
return t;
表的函数,对travel函数的实现:
travel函数表示对树的遍历,从而建立起表,采用表尾插入法
void travel(Tree root, table& t, char code[256], int k)
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
code[k] = '\0';
bNode b = new struct BNode;
b->symbol = root->data;
strcpy(b->code, code);
b->next = NULL;
//尾部插入法
if (t->first == NULL) //空表
t->first = b;
t->last = b;
else
t->last->next = b;
t->last = b;
if (root->left != NULL)
code[k] = '0';
travel(root->left, t, code, k + 1);
if (root->right != NULL)
code[k] = '1';
travel(root->right, t, code, k + 1);
编解码
??至此,Huffman树以及编码表已经构建完毕,现在就来实现编解码的函数来检验上述的Huffman树。
编码:
需要传入编码表来进行编码
void EnCode(table t, char* str)
cout << "EnCodeing............./" << endl;
int len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
bNode p = t->first;
while (p != NULL)
if (p->symbol == str[i])
cout << p->code;
break;
p = p->next;
cout << endl;
解码:
需要传入Huffman树来进行编码
void DeCode(Tree root, char* str)
cout << "DeCode............./" << endl;
Tree p = root;
int len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (p->left == NULL && p->right == NULL)
cout << p->data;
p = root;
if (str[i] == '0')
p = p->left;
if (str[i] == '1')
p = p->right;
if (str[i] != '0' && str[i] != '1')
cout << "The Input String Is Not Encoded correctly !" << endl;
return;
if (p->left == NULL && p->right == NULL)
cout << p->data;
cout << endl;
测试数据
int main()
queue q = Create_Queue();
Tree root = Create_Tree(q);
table t = Create_Table(root);
char str[256];
cout << "请输入要编码的字符:" << endl;
cin >> str;
EnCode(t, str);
cout << "请输入要解码的码值:" << endl;
char str1[256];
cin >> str1;
DeCode(root, str1);
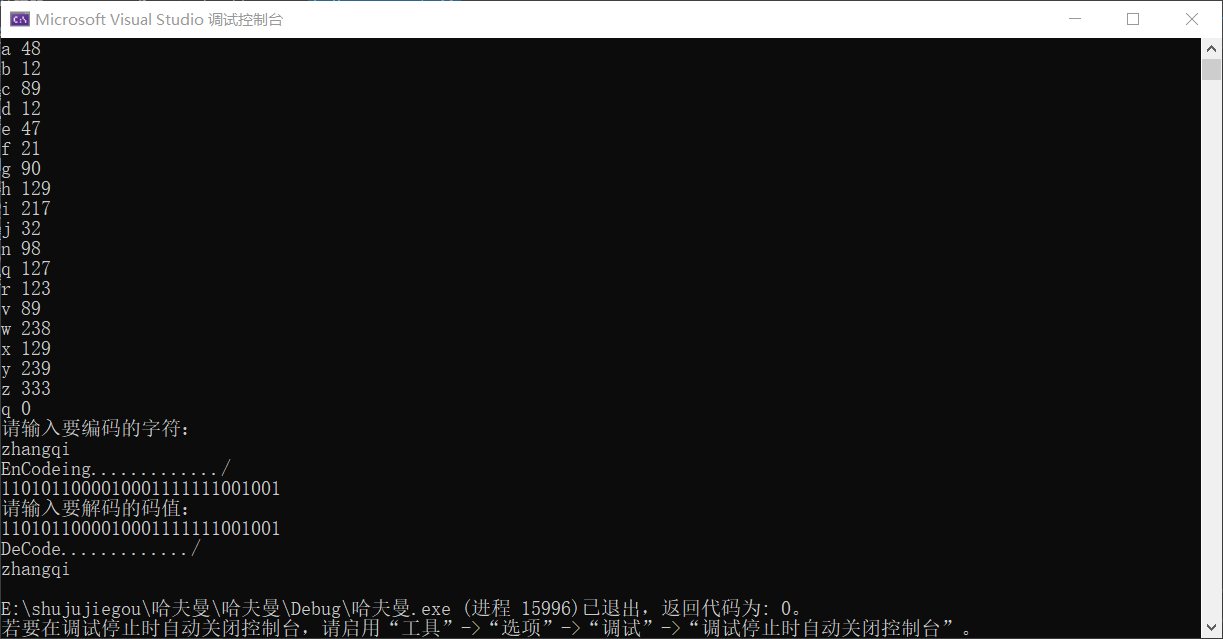
附上截图:
以上是关于对一串字符进行huffman编码并解码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章