Spring 学习系列Bean 的生命周期之初始化与销毁
Posted 明明如月学长
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring 学习系列Bean 的生命周期之初始化与销毁相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、背景
本文将结合一个简单案例,学习 Bean 生命周期中的初始化和销毁阶段的具体内容。

二、案例
Bean 的定义
package org.example.lifecycle.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class SomeBean implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean
private Integer value;
public SomeBean()
System.out.println("构造方法");
public void setValue(Integer value)
System.out.println("setValue:" + value);
this.value = value;
public void open()
System.out.println("init-method - 执行 ...");
public void close()
System.out.println("destroy-method - 执行 ...");
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct()
System.out.println("@PostConstruct - 执行 ...");
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy()
System.out.println("@PreDestroy - 执行 ...");
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet()
System.out.println("InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet");
@Override
public void destroy()
System.out.println("DisposableBean#destroy");
如果想要 @PostConstruct、@PreDestroy 生效,可以使用@Component 注解,代替 xml 的方式。
配置信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="org.example.lifecycle.bean.SomeBean"
init-method="open" destroy-method="close">
<property name="value" value="1"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试代码
package org.example.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class LifecycleApplication
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println("准备初始化IOC容器。。。");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lifecycle/bean-initmethod.xml");
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(LifeCycleConfiguration.class);
System.out.println("IOC容器初始化完成。。。");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("准备销毁IOC容器。。。");
ctx.close();
System.out.println("IOC容器销毁完成。。。");
执行结果:
准备初始化IOC容器。。。
构造方法
setValue:1
InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
init-method - 执行 …
IOC容器初始化完成。。。准备销毁IOC容器。。。
DisposableBean#destroy
destroy-method - 执行 …
IOC容器销毁完成。。。
图示:
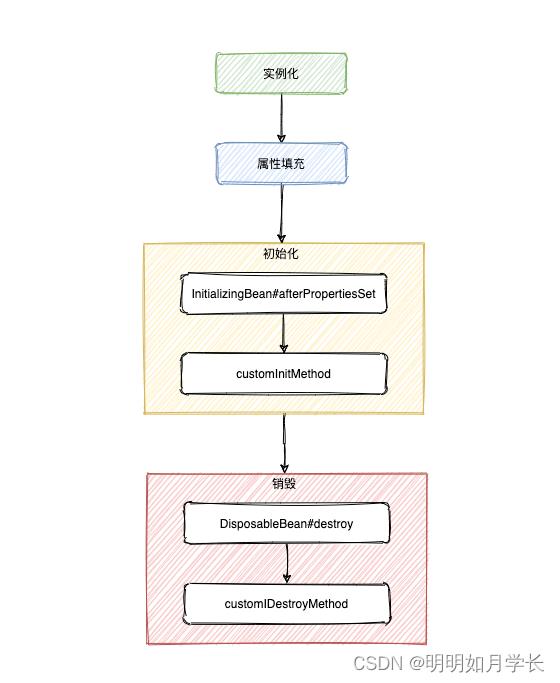
三、分析
先猜想后验证:实例化、属性填充、初始化、销毁。具体是实现接口的初始化方法先执行还是自定义的初始化方法先执行需要看代码。
我们采用断掉调试法来分析学习,对每个方法打上断点,进行调试。
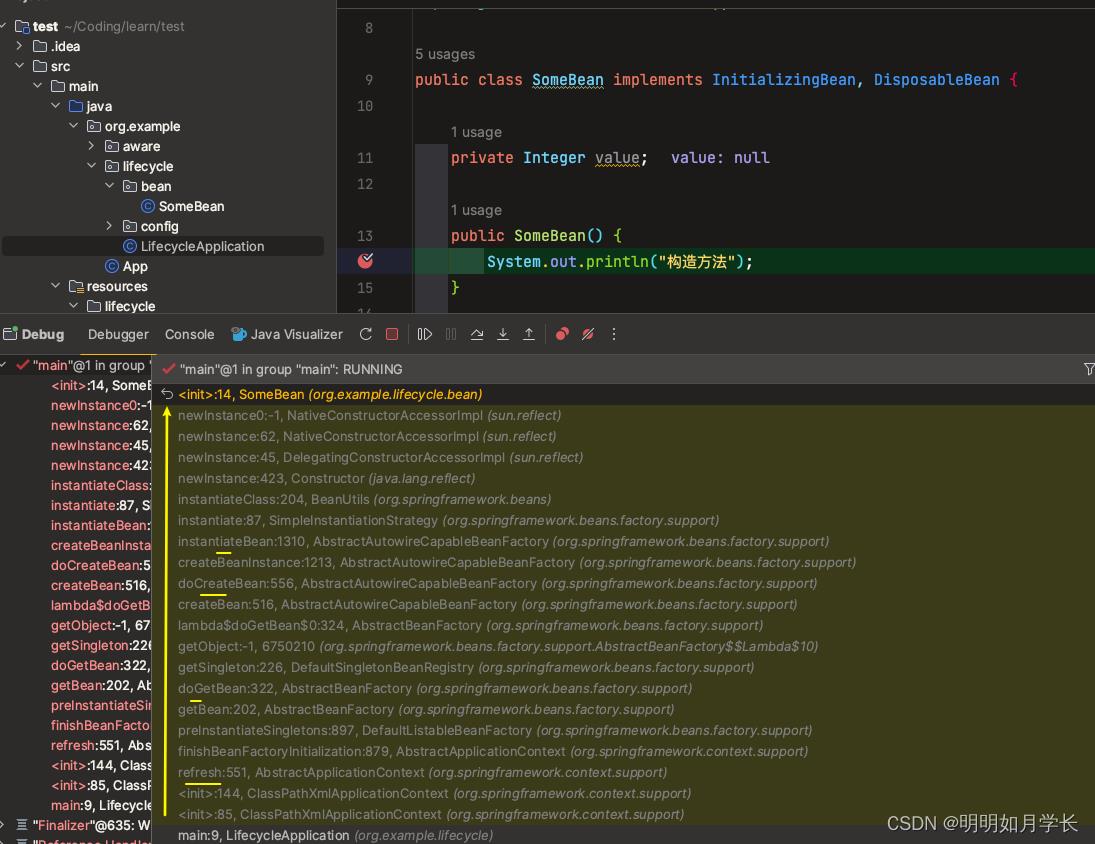
【1】执行到构造方法
【2】执行到 setValue 方法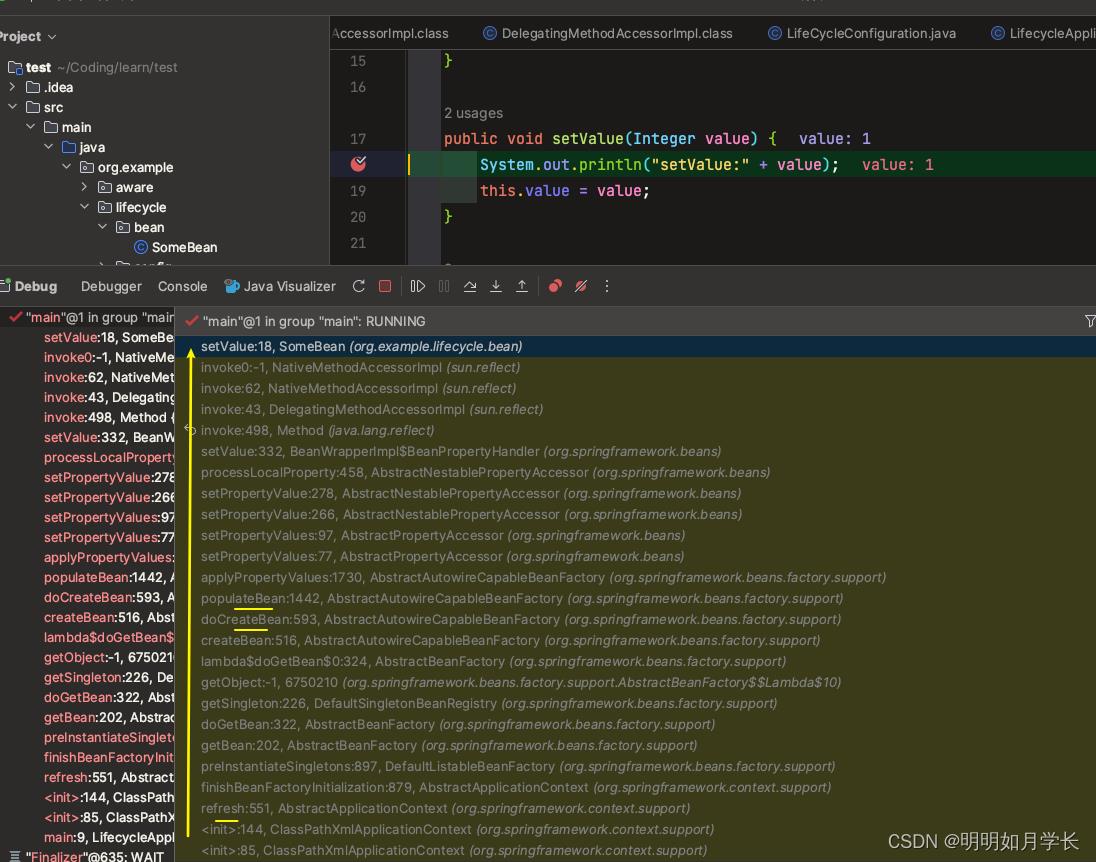
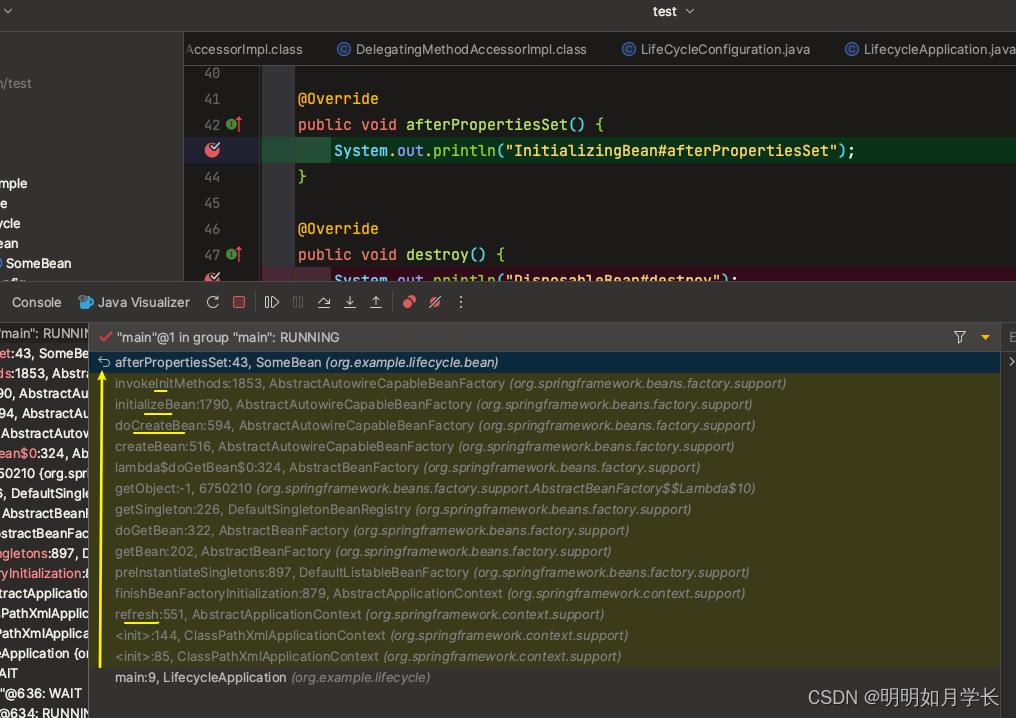
【3】执行到 InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet 方法
【4】执行到 init-method

核心方法 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//1 初始化前的准备
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//2 获取 BeanFactory,加载所有 bean 的定义信息(未实例化)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 3 BeanFactory 的预处理配置
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 4. 准备 BeanFactory 完成后进行的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 5. 执行 BeanFactory 创建后的后置处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 6. 注册 Bean 的后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 7. 初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 8. 初始化事件派发器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 9. 子类的多态 onRefresh
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 10. 监听器检查和注册
registerListeners();
// ------- BeanFactory已创建完成 --------
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 11. 初始化所有剩下的单例Bean(非懒加载的)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 12. 完成容器的创建工作(发布相应的事件)
finishRefresh();
catch (BeansException ex)
if (logger.isWarnEnabled())
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 销毁已经创建的单例避免浪费资源
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
// 重置 active 标记
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
// 异常抛给调用方
throw ex;
finally
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
//13 清理缓存
resetCommonCaches();
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//1 初始化前的准备
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//2 获取 BeanFactory,加载所有 bean 的定义信息(未实例化)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 3 BeanFactory 的预处理配置
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 4. 准备 BeanFactory 完成后进行的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 5. 执行 BeanFactory 创建后的后置处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 6. 注册 Bean 的后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 7. 初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 8. 初始化事件派发器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 9. 子类的多态 onRefresh
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 10. 监听器检查和注册
registerListeners();
// ------- BeanFactory已创建完成 --------
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 11. 初始化所有剩下的单例Bean(非懒加载的)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 12. 完成容器的创建工作(发布相应的事件)
finishRefresh();
catch (BeansException ex)
if (logger.isWarnEnabled())
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 销毁已经创建的单例避免浪费资源
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
// 重置 active 标记
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
// 异常抛给调用方
throw ex;
finally
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
//13 清理缓存
resetCommonCaches();
【1】实例化、【2】属性填充、【3】afterPropertiesSet、【4】自定义 init 方法 都在 步骤 11 。
核心方法:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton())
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
if (instanceWrapper == null)
//【1】 实例化:执行构造方法
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class)
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock)
if (!mbd.postProcessed)
try
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
catch (Throwable ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure)
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try
//【2】属性填充:执行到 setValue
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//【3】初始化 Bean: 执行到 InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
catch (Throwable ex)
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName()))
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
else
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
if (earlySingletonExposure)
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null)
if (exposedObject == bean)
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName))
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans)
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean))
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty())
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
// Register bean as disposable.
try
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
return exposedObject;
核心方法 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
, getAccessControlContext());
else
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic())
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
try
// 步骤【3】和【4】
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
catch (Throwable ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic())
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
return wrappedBean;
核心方法 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet")))
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
try
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
, getAccessControlContext());
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae)
throw以上是关于Spring 学习系列Bean 的生命周期之初始化与销毁的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章