BulletproofsSigma protocolHalo2等ZK方案小结
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了BulletproofsSigma protocolHalo2等ZK方案小结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
当前的ZK构建方案有:
- 1)Bulletproofs
- 2)Sigma protocol(+ Fiat-Shamir)
- 3)Halo2
- 4)Plonky2
- 5)MPC-in-the-head proof(MPCith)
2. Bulletproofs
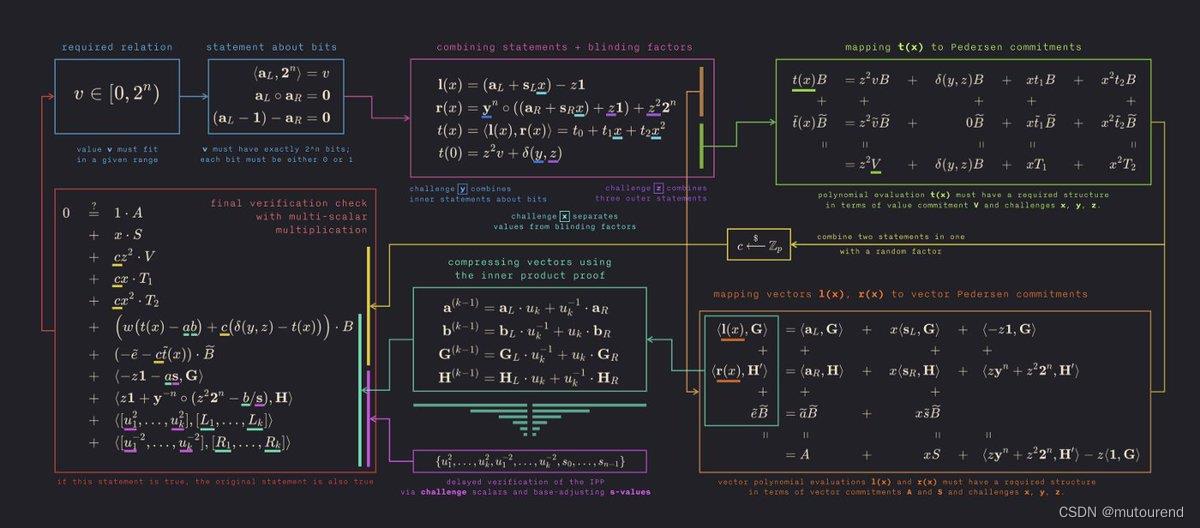
Bulletproofs的特点为:
- 1)无需trusted setup的short NIZK
- 2)基于Pedersen commitment构建
- 3)支持proof aggregation
- 4)Prover time为: O ( N ⋅ log ( N ) ) O(N\\cdot \\log(N)) O(N⋅log(N)),约30秒
- 5)Verifier time为: O ( N ) O(N) O(N),约1秒
- 6)proof size为: O ( log ( N ) ) O(\\log(N)) O(log(N)),约1.3KB
- 7)基于的安全假设为:discrete log
Bulletproofs适用的场景为:
- 1)range proofs(仅需约600字节)
- 2)inner product proofs
- 3)MPC协议中的intermediary checks
- 4)aggregated and distributed (with many private inputs) proofs
Bulletproofs不适合的场景有:
- 1)需在链上验证的复杂任意statement
目前Bulletproofs方案已用于:
- 1)比特币的隐私交易:ELEMENTS Confidential Transactions
- 2)Monero:Monero Becomes Bulletproof
- 3)Stellar Shielded Tx(Cloak):Cloak隐私资产协议
当前Bulletproofs开源库有:
- 1)https://github.com/dalek-cryptography/bulletproofs(Rust)
- 2)https://github.com/adjoint-io/bulletproofs(Haskell)
- 3)https://github.com/bbuenz/BulletProofLib(Java)
Bulletproofs相关学习资源有:
- 1)Stanford Bulletproofs
- 2)论文作者Benedikt Bünz Bulletproofs视频
- 3)Building on Bulletproofs
3. Sigma Protocol(+ Fiat-Shamir)
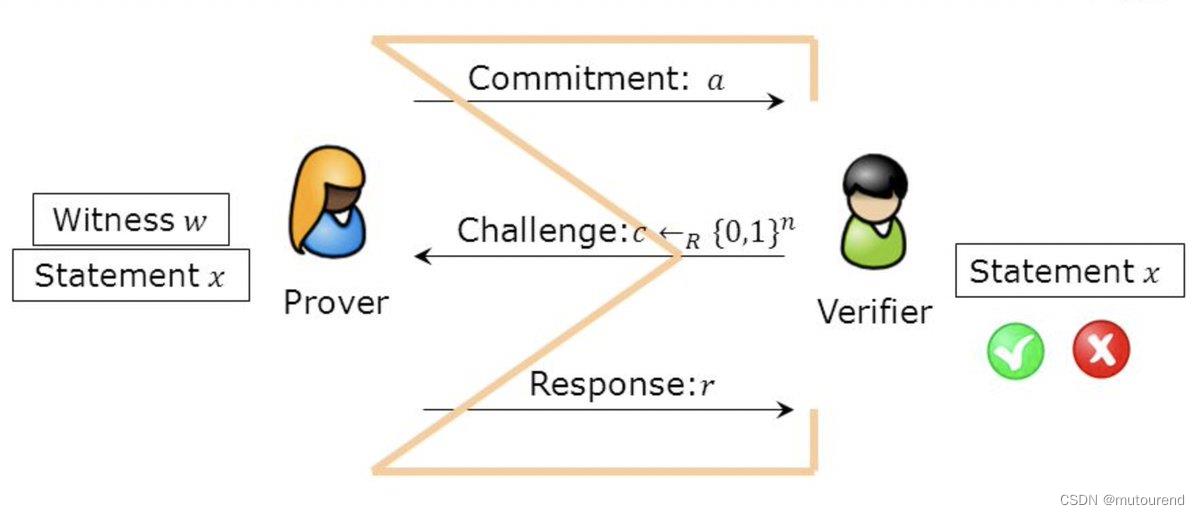
Sigma Protocol(+ Fiat-Shamir)特点为:
- 1)无需trusted setup的short proof。
- 2)需要constant number(3)of public-key operations。
- 3)可配置组合多个Sigma proofs,类似为A and\\or B、eq(A,B)、all(n,A)。
- 4)基于的安全假设为:discrete log,honest verifier。
Sigma Protocol(+ Fiat-Shamir)适于的场景为:
- 1)discrete log(dlog)proofs
- 2)one-of-many dlogs
- 3)discrete log equality(dleq)
Sigma Protocol(+ Fiat-Shamir)不适合的场景有:
- 1)复杂任意计算。
当前Sigma Protocol已用于:
- 1)Signal (Algebraic MACs for group chats):Technology Preview: Signal Private Group System
- 2)dleq proofs in the adaptor signatures
- 3)verifiable random functions
- 4)ElGamal encryption in the Cryptography for #MeToo
Sigma Protocol相关开源库有:
- 1)https://github.com/LLFourn/secp256kfun/tree/master/sigma_fun(Rust)
- 2)https://pkg.go.dev/go.dedis.ch/kyber/v4/proof(Go)
- 3)https://github.com/cryptobiu/libscapi(C++)
- 4)https://github.com/spring-epfl/zksk(Python)
Sigma Protocol相关学习资料有:
- 1)Zero Knowledge Proofs with Sigma Protocols
- 2)Sigma Protocols and (Non-Interactive) Zero Knowledge
- 3)ZKProof Standardizing Sigma Protocols?
4. Halo2
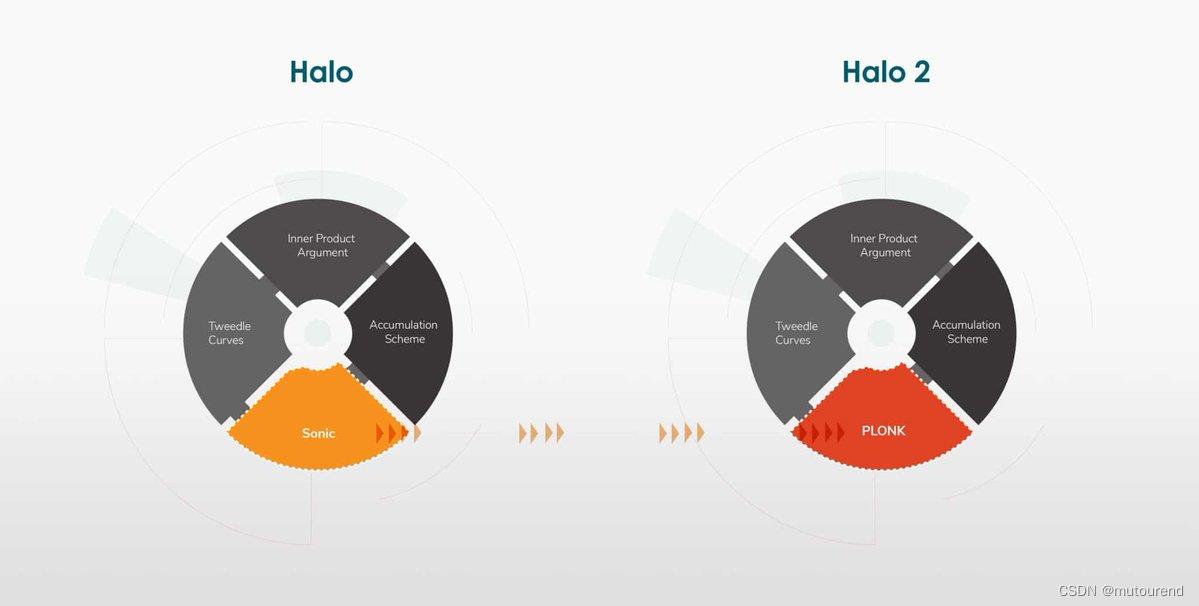
Halo2主要特点为:
- 1)无需trusted setup,将accumulation scheme 与 PLONKish arithmetization高效结合。
- 2)基于IPA commitment scheme。
- 3)繁荣的开发者生态。
- 4)Prover time为: O ( N ∗ log N ) O(N*\\log N) O(N∗logN)。
- 5)Verifier time为: O ( 1 ) > O(1)> O(1)>Groth16。
- 6)Proof size为: O ( log N ) O(\\log N) O(logN)。
- 7)基于的安全假设为:discrete log。
Halo2相关开源库有:
- 1)https://github.com/zcash/halo2:ZCash官方版本,采用IPA承诺机制。
- 2)https://github.com/privacy-scaling-explorations/halo2wrong:将ZCash官方版本中的IPA承诺机制替换为KZG承诺机制。
- 3)https://github.com/Orbis-Tertius/halo2:将ZCash官方版本中的IPA承诺机制替换为FRI承诺机制。(开发中)
- 4)Mina Kimchi proof system:Mina版本,Halo2部分见https://github.com/o1-labs/proof-systems(Rust),递归实现见https://github.com/MinaProtocol/mina/tree/develop/src/lib/pickles(OCaml)。
Halo2适于的场景有:
- 1)任意可验证计算
- 2)递归proof composition
- 3)基于lookup-based Sinsemilla function的circuit-optimized hashing
Halo2不适于的场景为:
- 1)除非替换使用KZG版本的Halo2,否则在以太坊上验证开销大。
当前ZCash官方版本暂未支持递归,目前递归可用的有:
- 1)Scroll团队KZG版本的https://github.com/scroll-tech/halo2-snark-aggregator
- 2)Orbis Labs团队正在使用Tiny-RAM架构构建其accumulation scheme:https://github.com/Orbis-Tertius/tiny-ram-halo2
目前Halo2已用于:
- 1)ZCash shielded protocol(Orchard):Bringing Halo 2 to Zcash
- 2)Scroll zkEVM:Scroll zkEVM
- 3)Orbis ZK-Rollup on Cardano:https://github.com/Orbis-Tertius/Orbis
- 4)Dark Fi L1:Dark.fi
Halo2相关学习资料有:
- 1)基本解释:Explaining Halo 2
- 2)doc:Halo2文档
- 3)视频:Zcash: Halo 2 and SNARKs without Trusted Setups
- 4)数学:2021年11月Vitalik博客Halo and more: exploring incremental verification and SNARKs without pairings
- 5)Halo2生态展示:2022年8月视频Halo 2 Community Showcase - Ying Tong at Zcon3
- 6)更多:https://github.com/adria0/awesome-halo2
5. Plonky2

Plonky2主要特点为:
- 1)无需trusted setup,将FRI与PLONK结合。
- 2)针对具有SIMD的处理器进行了优化,并采用了64 byte Goldilocks fields。
- 3)Prover time为: O ( log N ) O(\\log N) O(logN)。
- 4)Verifier time为: O ( log N ) O(\\log N) O(logN)。
- 5)Proof size为: O ( N ∗ log N ) O(N*\\log N) O(N∗logN)。
- 6)基于的安全假设为:collision-resistant hash function。
Plonky2的主要特色在于:
- 1)支持如下选择:
- 1.1)选择fewer rows,意味着fast prover;
- 1.2)选择fewer columns,意味着fast verifier。
- 2)根据https://github.com/Sladuca/sha256-prover-comparison中的对比可知:
- 2.1)Plonky2 STARK is ~38x faster than Halo2, ~64x faster than Groth16 on 3yo MBP。
- 2.2)Plonky2 STARK does 142 hashes/sec on a 2021 MBP with an M1 processor。
- 3)FRI中使用Poseidon sponge和GMIMC作为哈希函数。
Plonky2适于的场景有:
- 1)任意可验证计算。
- 2)递归proof composition。
- 3)使用自定义gate进行电路优化。
Plonky2不适于的场景为:
- 1)受限于其non-native arithmetic,不适于包含椭圆曲线运算的statements。
Plonky2已用于:
Plonky2相关开源库见:
Plonky2相关学习资料见:
6. MPC-in-the-head proof
相关论文有:
- 2021年论文 Formal security analysis of MPC-in-the-head zero-knowledge protocols:开源代码见:https://github.com/Nsidorenco/Decomposition-zk。形式化安全分析,采用eC语言。
所谓MPC是指:
- 1)各方可基于其私有输入进行分布式计算。
- 2)每方都生成一个transcript(its view)。
- 3)关键点在于#1:若MPC的最终结果出错,则在某处存在inconsistent view。
所谓Secret Sharing秘密共享:
- 1)为MPC的一种常用抽象,将某个秘密切分给多方,使得他们需共同协作来使用该秘密。
- 2)关键点在于#2:若仅公开共享的部分秘密,则该秘密仍是未知的。
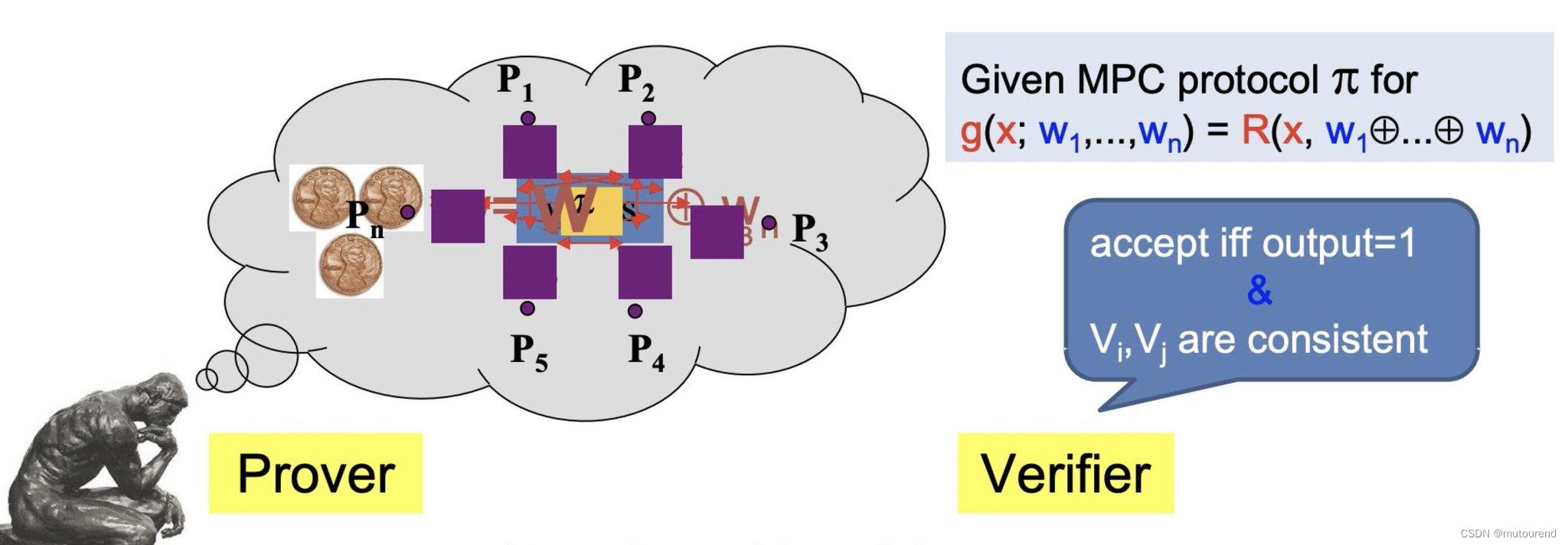
所谓MPC-in-the-head(MPCith)是一个ZK系统:
- 1)Prover会simulate an MPC "in their head"来基于 某private input(已分享给多个虚拟方) 计算任意函数。注意,所simulate的各方会根据其所使用的秘密块来生成a view。
- 2)Verifier会请求公开这些view的一个子集,公开的子集数量不足以恢复出该private input,但是又能从信任发生不一致性的概率很低。若概率不够低,可重复这种交互多次(如约300次)。
- 3)可使用Fiat-Shamir将以上过程实现为非交互式的,并可并行化。
- 4)生成proof所用的底层MPC原语并不重要,仅所生成的views是重要的。从而可将simulated MPC看成是黑盒略过,从而可避免大量开销。
MPCith:
- 1)用于boolean circuits效率很高,不像大多数其它NIZKs仅适于arithmetic circuit。
- 2)可与具有private addresses的RAM进行扩展。从而很容易将verifiable computation circuit编译为任意程序。
MPCith的特点为:
- Prover time为: O ( N ) O(N) O(N)< Groth16。
- Verifier time为: O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。
- Proof size为: O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。
- 加法运算是free的,乘法运算占用大多数开销。
- 进行可验证计算的开销要低很多:为(1/n_reps*n_parties=> 约1/600),要远低于SNARKs的(约1/100万)。
MPCith适于的场景有:
- 1)boolean circuit:
- 1.1)对于不易于转换为arithmetic circuit的复杂程序,如SHA hashes;
- 1.2)机器学习以及设计浮点运算的近似计算,可借助boolean circuit实现逐位运算。
- 2)delegated proving(证明委托):
- 2.1)如需为某statement创建SNARK,但不想自己计算,也不想将witness告知第三方的情况。可创建一个MPCith proof,然后委托方可创建一个新的证明来验证该MPCith proof。
MPCith不适于的场景为:
- 1)任何需要进行链上验证的场景。
目前MPCith已用于:
MPCith相关开源库有:
- 1)https://github.com/trailofbits/reverie/tree/stacked-ikos(Rust):Reverie is an implementation (prover and verifier) of the MPC-in-the-head NIZKPoK。
- 2)https://github.com/cronokirby/boo-hoo(Rust):ZKBoo。
- 3)https://github.com/cronokirby/Rem-Boo(Rust):Fast ZK proofs over boolean circuits with RAM。
MPCith相关学习资料有:
- 1)2022年8月6日episode:MPC In The Head Special
- 2)入门论文:2016年 ZKBoo: Faster Zero-Knowledge for Boolean Circuits
- 3)安全分析:2021年论文 Formal security analysis of MPC-in-the-head zero-knowledge protocols:开源代码见:https://github.com/Nsidorenco/Decomposition-zk。形式化安全分析,采用eC语言。
参考资料
[1] twitter ZK方案之Bulletproofs、Halo2小结
[2] twitter MPC-in-the-head proofs
以上是关于BulletproofsSigma protocolHalo2等ZK方案小结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章