java缓存redis缓存guava缓存java中实现缓存的几种方式
Posted Ez4Sterben
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java缓存redis缓存guava缓存java中实现缓存的几种方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、通过HashMap实现缓存
这种方式可以简单实现本地缓存,但是实际开发中不推荐使用,下面我们来实现一下这种方式。
首先创建一个管理缓存的类
public class LocalCache
public static HashMap<String,String> cache = new HashMap<>();
static
String name = 1 + "-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
LocalCache.cache.put(String.valueOf(1),name);
System.out.println("id为"+1+"的数据添加到了缓存");
这个类中有一个静态代码块,静态代码块会在类加载时就执行,我们可以在这里完成对缓存的初始化,决定缓存内一开始就有哪些数据
另外我们还可以把这个类交给spring来管理
@Component
public class LocalCache
public static HashMap<String,String> cache = new HashMap<>();
static
String name = 1 + "-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
LocalCache.cache.put(String.valueOf(1),name);
System.out.println("id为"+1+"的数据添加到了缓存");
@PostConstruct
public void init()
String name = 2 + "-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
LocalCache.cache.put(String.valueOf(2),name);
System.out.println("id为"+2+"的数据添加到了缓存");
在把类交给spring管理后,在方法上加入@PostConstruct可以使这个方法默认执行
随后我们编写一个接口来测试缓存
@RequestMapping("test")
public String test(Long id)
String name = LocalCache.cache.get(String.valueOf(id));
if (name != null)
System.out.println("缓存中存在,查询缓存");
System.out.println(name);
return name;
System.out.println("缓存中不存在,查询数据库");
name = id + "-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println(name);
LocalCache.cache.put(String.valueOf(id),name);
return name;
启动项目
我们可以看到这两个初始化都被执行了,然后我们调用接口查询id为1与id为2的数据
再查询id为3的两次
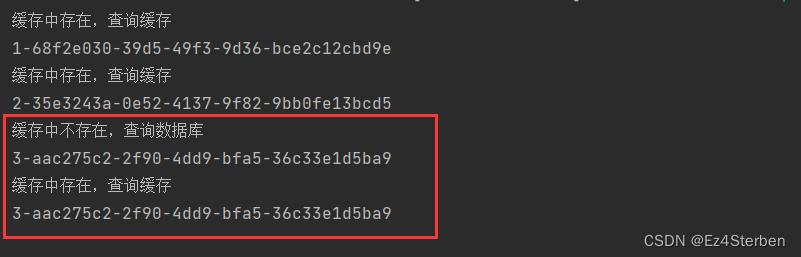
可以看到我们是先生成了一次UUID存入hashmap,第二次查询时hashmap中存在了,直接从hashmap中获得数据,如此一来我们就实现了hashmap形式的本地缓存
二、通过guava local cache实现
guava cache介绍
-
Guava是Google提供的一套Java工具包,而Guava Cache是一套非常完善的本地缓存机制(JVM缓存)。
-
Guava cache的设计来源于CurrentHashMap,可以按照多种策略来清理存储在其中的缓存值且保持很高的并发读写性能。
实际使用
首先导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>23.0</version>
</dependency>
编写配置文件,这里我们创建一个五秒钟过期时间的缓存方便测试
import com.google.common.cache.Cache;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Component
public class GuavaLocalCache
private Cache<String,String> fiveSecondCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
//设置缓存初始大小,应该合理设置,后续会扩容
.initialCapacity(10)
//最大值
.maximumSize(100)
//并发数设置
.concurrencyLevel(5)
//缓存过期时间,写入后5秒钟过期
.expireAfterWrite(5,TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//统计缓存命中率
.recordStats()
.build();
public Cache<String, String> getFiveSecondCache()
return fiveSecondCache;
public void setFiveSecondCache(Cache<String, String> fiveSecondCache)
this.fiveSecondCache = fiveSecondCache;
下面我们对guava cache进行简单的使用,并尝试其中的命中率统计等功能
@Autowired
private GuavaLocalCache guavaLocalCache;
@RequestMapping("guavaTest")
public String guavaTest(Long id)
// 获取缓存
Cache<String, String> fiveSecondCache = guavaLocalCache.getFiveSecondCache();
// 从缓存中获取对象
String nameCache = fiveSecondCache.getIfPresent(String.valueOf(id));
// 缓存中存在
if (nameCache != null)
System.out.println("缓存命中:" + nameCache + ","+ getCacheStats(fiveSecondCache));
return nameCache;
//将数据存入缓存
System.out.println("缓存未命中,"+ getCacheStats(fiveSecondCache));
nameCache = id + "-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
fiveSecondCache.put(String.valueOf(id),nameCache);
return nameCache;
public String getCacheStats(Cache<String, String> cache)
CacheStats stats = cache.stats();
return "缓存命中率:"+stats.hitRate()+"被清除缓存数:"+stats.evictionCount();
首先访问一次id为1的数据,等5秒后再访问一次,然后立刻访问第三次

可以看到缓存未命中两次,其中缓存过期被删除了一次,随后在5秒内立刻访问缓存命中,缓存命中率,被清除缓存数均正确,测试完成
guava cache还有许多没有测试到的功能以及各种淘汰策略和机制,各位可以尝试深入了解。
使用redis实现缓存
redis简介
Redis 是C语言开发的一个开源高性能键值对的内存数据库,可以用来做数据库、缓存、消息中间件等场景,是一种NoSQL(not-only sql,非关系型数据库)的数据库
具体使用
redis的安装以及基本使用欢迎参考我的这两篇博客
redis的简介,Linux安装redis以及jedis的使用
redis中的数据类型以及操作
下面我们介绍在springboot项目中的使用
springboot中有redis的starter我们直接引用即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
在spring配置文件中加入如下设置,这里用的是properties形式的文件,host是部署redis的服务器ip,port是端口号,password是密码,如果没有设置密码不填即可
spring.redis.host=
spring.redis.port=
spring.redis.password=
同样我们编写接口测试
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/redisTest")
public String redisCacheTest(Long id)
String name = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(String.valueOf(id));
if (name != null)
System.out.println("缓存中存在,查询缓存");
System.out.println(name);
return name;
System.out.println("缓存中不存在,查询数据库");
name = id + "-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println(name);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(String.valueOf(id),name);
return name;
同样的,我们查询两次id为1和id为2的数据
随后我们在redis中查看
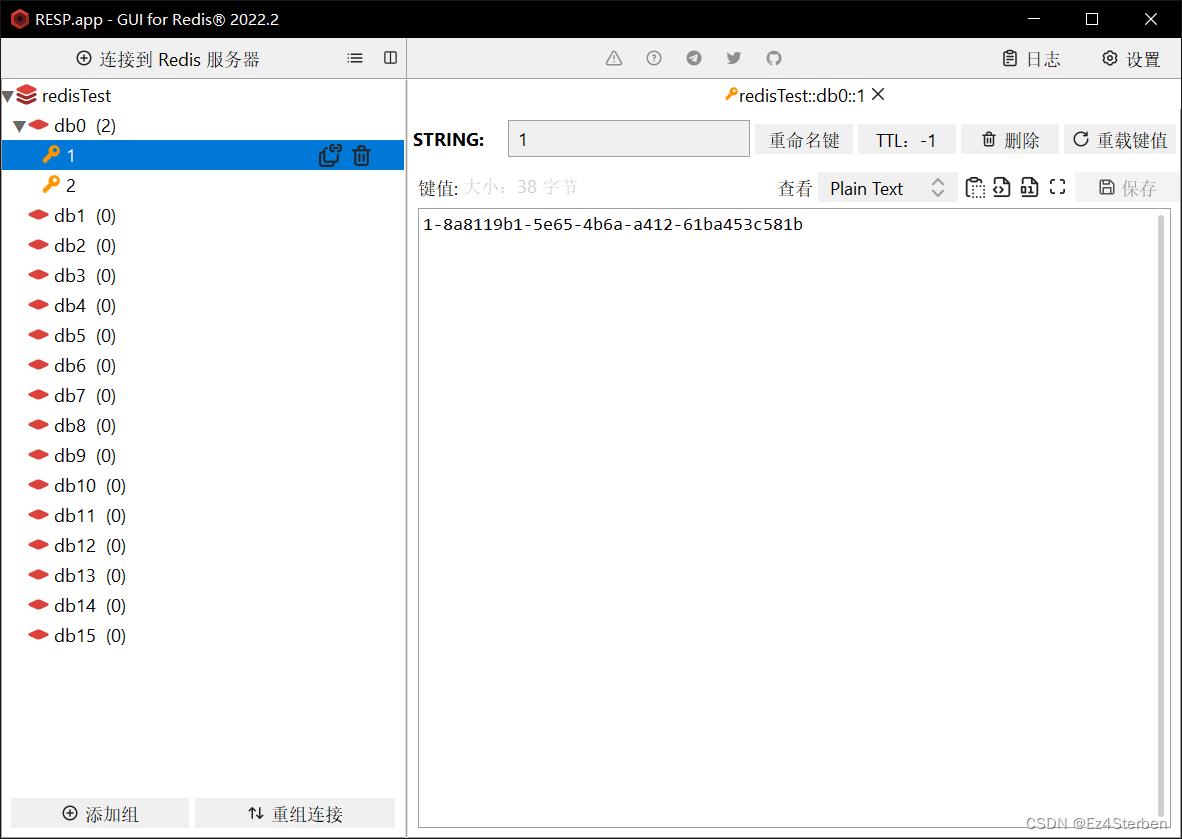
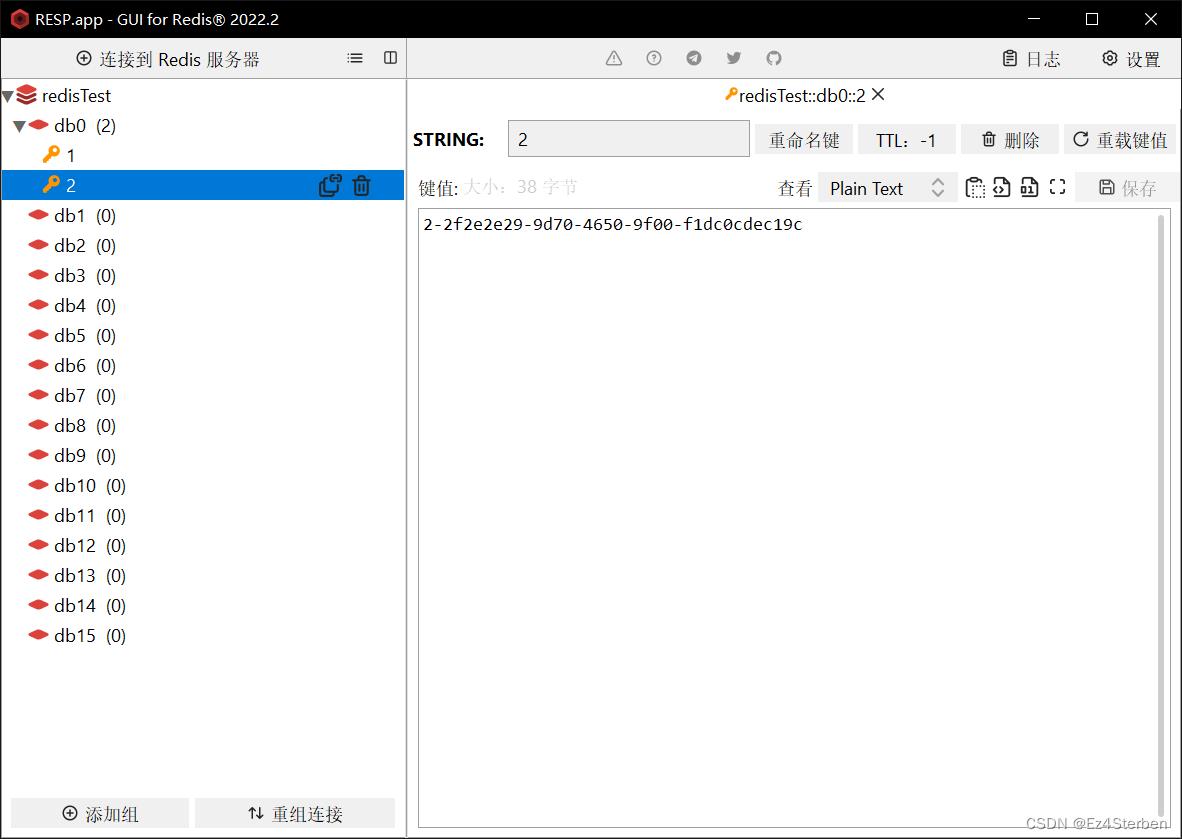
可以看到我们确实的把数据存入redis中作为缓存进行读写了
Java内存缓存-通过Google Guava创建缓存
谷歌Guava缓存Guava介绍
Guava是Google guava中的一个内存缓存模块,用于将数据缓存到JVM内存中。实际项目开发中经常将一些公共或者常用的数据缓存起来方便快速访问。
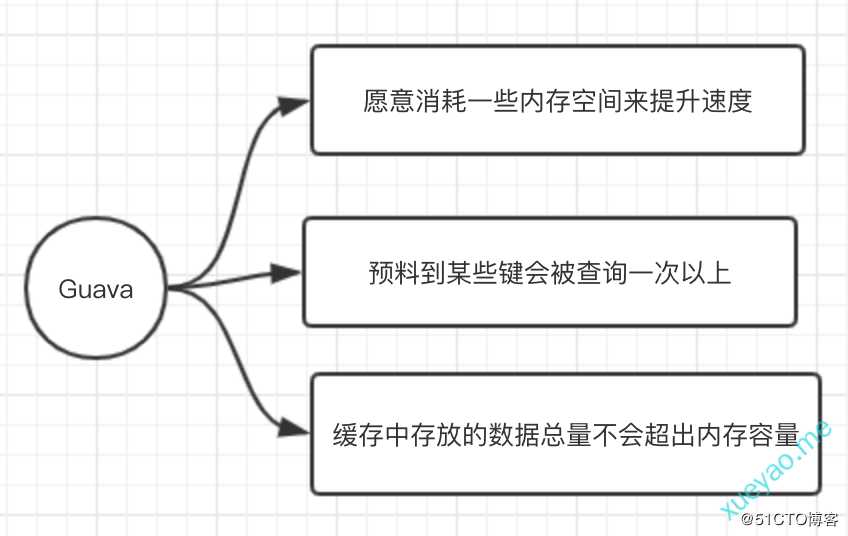
Guava Cache是单个应用运行时的本地缓存。它不把数据存放到文件或外部服务器。如果不符合需求,可以选择Memcached、Redis等工具。
小案例
pom.xml添加guava依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>me.xueyao.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>java-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.cache</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>27.0.1-jre</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>GuavaCacheDemo.java 代码如下:
package me.xueyao.cache.java.guava;
import com.google.common.cache.*;
import me.xueyao.cache.java.pojo.User;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author simon
* https://github.com/google/guava
*/
public class GuavaCacheDemo
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException
//缓存接口这里是LoadingCache,LoadingCache在缓存项不存在时可以自动加载缓存
LoadingCache<String, User> userCache
//CacheBuilder的构造函数是私有的,只能通过其静态方法newBuilder()来获得CacheBuilder的实例
= CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
//设置并发级别为8,并发级别是指可以同时写缓存的线程数
.concurrencyLevel(8)
//设置写缓存后8秒钟过期
.expireAfterWrite(8, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//设置写缓存后1秒钟刷新
.refreshAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
//设置缓存容器的初始容量为5
.initialCapacity(5)
//设置缓存最大容量为100,超过100之后就会按照LRU最近虽少使用算法来移除缓存项
.maximumSize(100)
//设置要统计缓存的命中率
.recordStats()
//设置缓存的移除通知
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<Object, Object>()
@Override
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Object, Object> notification)
System.out.println(notification.getKey() + " 被移除了,原因: " + notification.getCause());
)
//build方法中可以指定CacheLoader,在缓存不存在时通过CacheLoader的实现自动加载缓存
.build(
new CacheLoader<String, User>()
@Override
public User load(String key) throws Exception
System.out.println("缓存没有时,从数据库加载" + key);
return new User("tony" + key, key);
);
// 第一次读取
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
User user = userCache.get("uid" + i);
System.out.println(user);
// 第二次读取
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
User user = userCache.get("uid" + i);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("cache stats:");
//最后打印缓存的命中率等 情况
System.out.println(userCache.stats().toString());
User.java 代码如下:
package me.xueyao.cache.java.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
-
@author simon
*/
public class User implements Serializable
private String userName;
private String userId;public User(String userName, String userId)
this.userName = userName;
this.userId = userId;public String getUserId()
return userId;public void setUserId(String userId)
this.userId = userId;public String getUserName()
return userName;@Override
public String toString()
return userId + " --- " + userName;
运行后的结果如下:
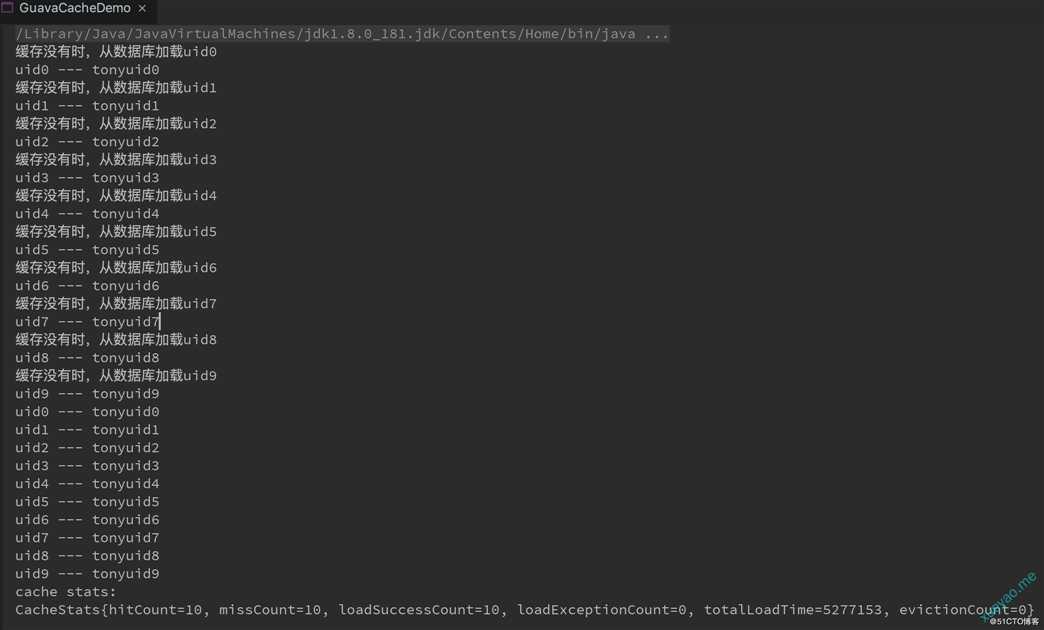
第一次循环时缓存中没有数据,构建了缓存,第二次直接命中缓存。如果程序需要单机内存缓存,可以用该方式构建缓存。
以上是关于java缓存redis缓存guava缓存java中实现缓存的几种方式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章