ARMv8 ARM64 架构 整体介绍
Posted __pop_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ARMv8 ARM64 架构 整体介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这里整理一些 arm64(aarch64是armv8下面的一个工作状态,一般我们将其称为arm64?)
在这里不考虑 aarch32
这里的主要内容是 手册 arm ARM
arm ARM
// cpu mmu 相关
// 内存模型相关
// 编程模型相关
还有其他的内容,可以参考以下架构手册
coresight
// 调试模型相关
gic
// 异常模型相关
smmu
// dma mmu 相关
generic timer
amba
// 内存模型相关 : cache一致性(ACE总线)
文章目录
市场
SOC
移动端(手机)市场
高通,三星,苹果,MTK,华为
服务器市场
ARMv8的通用化
架构
架构版本
架构有哪些
armv8-a, armv8.1-a, armv8.2-a
armv8.3-a, armv8.4-a, armv8.5-a
armv8.6-a, armv8.7-a //没有 armv8.8-a了
// 往下是 armv9.0-a,armv9.1-a,armv9.2-a (2022-2-10 15:57:38)
没有具体的register指示当前的CPU实现的是Armv8.x .
但有register(ID_AA64* 寄存器)可以指示当前的CPU实现了Armv8.x所支持的功能。
ID_AA64AFR0/1_EL1
ID_AA64DFR0/1_EL1
ID_AA64ISAR0/1_EL1
ID_AA64MMFR0/1/2_EL1
ID_AA64PFR0/1_EL1
比如,ID_AA64MMFR2_EL1.AT表示Armv8.4-A是否支持宽松的对齐要求。
编程模型
执行状态(Execution state)
armv7有两种执行状态,arm和thumb。
//cpsr 的 T
// 0:arm
// 1:thumb
// 应该reset 是 arm 状态
// 异常时,cpsr 中的 T 被置位 0 , 也就是 进入arm state
armv8有两种执行状态(Execution state),aarch32和aarch64
// PSTATE 的 nRW
// 0:aarch64
// 1:aarch32
// On reset into an Exception level that is using AArch64.
// On taking an exception to an Exception level that is using AArch64.
aarch64指令
// 学习怎么看指令集
1.运算
算术运算
整数/浮点/向量
逻辑运算
2.分支(程序流控制/跳转)
3.访存
4.系统控制
异常处理
原子操作
fence
系统寄存器访问
aarch64寄存器
通用寄存器(31个)// D1.6.1 The general purpose registers, R0-R30 P2277
X0 - X30 // P99 B1.2.1 Registers in AArch64 state
SIMD&FP registers(32个+2)
V0 - V31
FPCR, FPSR // Two SIMD and floating-point control and status registers
PC寄存器
PC
状态寄存器(1个) // D1.7 Process state, PSTATE P2284
PSTATE
特殊寄存器(27个)// C5.2 Special-purpose registers P347
• CurrentEL, that holds PSTATE.EL, and that software can read to determine the current Exception level.
• DAIF, that holds the current PSTATE.D, A, I, F interrupt mask bits.
• DIT, that holds the PSTATE.DIT bit.
• ELR_EL1, that holds the address to return to for an exception return from EL1.
• ELR_EL2, that holds the address to return to for an exception return from EL2.
• ELR_EL3, that holds the address to return to for an exception return from EL3.
• FPCR, that provides control of floating-point operation.
• FPSR, that provides floating-point status information.
• NZCV, that holds the PSTATE.N, Z, C, V condition flags.
• PAN, that holds the PSTATE.PAN state bit.
• SP_EL0, that holds the stack pointer for EL0.
• SP_EL1, that holds the stack pointer for EL1.
• SP_EL2, that holds the stack pointer for EL2.
• SP_EL3, that holds the stack pointer for EL3.
• SPSel, that holds PSTATE.SP, that at EL1 or higher selects the current SP.
• SPSR_abt, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch32 Abort mode.
• SPSR_EL1, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch64 EL1.
• SPSR_EL2, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch64 EL2.
• SPSR_EL3, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch64 EL3.
• SPSR_fiq, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch32 FIQ mode.
• SPSR_irq, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch32 IRQ mode.
• SPSR_und, that holds process state on taking an exception to AArch32 Undefined mode.
• SSBS, that holds the PSTATE.SSBS bit.
• TCO, that holds the PSTATE.TCO bit.
• UAO, that holds the PSTATE.UAO bit.
• DLR_EL0, that holds the address to return to for a return from Debug state.
• DSPSR_EL0, that holds process state on entry to Debug state
系统寄存器(7类) // D13 P2817
1.通用系统控制寄存器
2.调试寄存器
3.性能监控寄存器
4.活动监控寄存器
5.统计扩展寄存器
6.RAS寄存器
7.通用定时寄存器
// 特殊寄存器中的几个寄存器和 系统寄存器全部用 MSR 和 MRS 指令访问
ARMv8与ARMv7的区别
ARMv7 与 ARMv8 的关系,相当于
ARMv8 包括 AARCH32 和 AARCH64
其中 AARCH32 完全兼容 ARMv7 , 可以认为 AARCH32 就是 ARMv7
其中 AARCH64 和 AARCH32(即ARMv7) 完全不同,是完全不同的两套指令集
| 类别 | ARMv7 | ARMv8 |
|---|---|---|
| 工作状态 | ATM&THUMB | AARCH32&AARCH64 |
| 指令集 | A32&T32 | A32&T32&A64 |
| 调用标准 | ATPCS/AAPCS/AAPCS32 | AAPCS64 |
| 指令位数 | 32 | 32 |
| 寄存器位数 | 32 | 64 |
| 通用寄存器个数 | 16 | 32 |
| 特权级 | PL0(app)/1(os)/2(hyp)&SecurePL1 | EL0(app)/1(os)/2(hyp)/3(trust) |
| 异常入口 | 8个(其中一个无效) | 16个(4类,每类4个入口) |
| 物理内存寻址空间 | <4G | 远远大于4G |
| 虚拟内存地址空间 | 4G | 远远大于4G |
| MMU支持页面大小 | 最大16KB | 4KB/16KB/64KB |
| 虚拟地址空间有效位 | 32 | 39/42/48 |
| 数据宽度(byte) | 8/16/32 | 8/16/32/64/128 |
| 是否向前兼容 | AARCH32兼容ARMv7 | AARCH64与AARCH32完全不同 |
EL0 (可以访问)(视角下)的指令及寄存器
在EL0执行会生成UNDEFINED异常(异常后ESR_EL1.ISS为0),不建议执行
ERET
ERETAA, ERETAB
HVC
LDGM
SMC
STGM
STZGM
在 EL0 执行会生成异常,有相应用途
UDF
SVC
BRK
DCPS1
在 EL0 执行会进入debug mode,有相应用途
HLT
其他 在手册中的 aarch64指令 都可以执行
1. 可能会产生 EL 切换,但不一定产生
2. 在EL0下都可被正常执行
// 在访问权限被禁用的情况下,从EL0对系统寄存器的任何访问都会导致指令表现为未定义。
// Any access from EL0 to a System register with the access right disabled causes the instruction to behave as UNDEFINED .
Registers in AArch64 state
X0-X30
SP_EL0
PC
V0-V31
FPCR, FPSR
NZCV
System registers // 后缀为_EL0的寄存器
Cache ID registers
Debug registers
Performance Monitors registers
Activity Monitors registers
Thread ID registers
Timer registers
ABI
FP&NEON指令集
异常模型
-
irq & fiq : 异步中断(无同步中断)
device -> GIC -> armv8 cpu
armv8 cpu
register : asm volatile("msr daifclr, #0x03");
GIC
register : GICD->ISENABLER[M] = (0x1 << N);
device
register :
TIMER3->CURRENT_VALUE0 = 0x0FFFFFF;
TIMER3->LOAD_COUNT0 = 0x0FFFFFF;
TIMER3->CONTROL_REG = 0x05; //auto reload & enable the timer
RK3399 实例:
https://github.com/hceng/RK3399/tree/master/hardware/3_irq/code
- sync : 同步异常
- error : 异步异常
内存模型
MMU
cache
内存三大问题
目前(2022-6-24 13:59:48) 浅显的将 除MMU外的内存问题 分为三大类问题 // 极有可能更新为N类问题
1. 缓存一致性
硬件实现体现在
MESI/SCU
ACE/CCI(CHI/CCN)
软件实现体现在
共享属性page.SH[1:0]
// 在软件上看来会影响
1.缓存到哪一个cache域
2.cache维护指令的时候会广播到哪一个cache域
3.内存屏障指令 的 广播域
cache维护指令和PoU/PoC // 在软件上看来会影响cache维护操作的域
2. 原子性
软件体现在
原子指令
3. memory order(内存一致性)
硬件体现在
TODO
// ARMv8-A-Programmer-Guide.pdf P191
//The ARMv8 architecture employs a weakly-ordered model of memory.
软件体现在
MAIR , page.AttrIndx[2:0] // 在软件上看来 会 区分 Device 和 Normal
1. Device 根据 GRE 分类
2. Normal 由于 有cache 分类,根据 page.SH[1:0] 分类
内存屏障指令(内存屏障指令的参数 会用到 page.SH[1:0])
缓存一致性
原子性
memory order(狭义的内存一致性)
debug模型
External Debug
- debug1 : External Debug : 基于JTAG的 芯片DEBUG 文章整理
Self-hosted Debug
- debug2 : AArch64 Self-hosted Debug : [自调试]
Trace & profiling
boot 模型
虚拟化模型
虚拟化代码跑在 EL2 , 这套代码可由 linux提供
安全模型
安全代码跑在 EL3 , 这套代码是独立的,不由linux提供
其他模型
开发工具
gcc toolchain & gdb
不同供应商的汇编工具 具有不同的语法.
通常助记符和汇编指令是相同的,但汇编伪指令,定义,标号和只是语法有可能有差别
汇编工具有两类
1.ARM汇编器armasm
2.gnu汇编器(主流)
gcc 的选项
-march=rv32ima
// Specify the name of the target architecture and, optionally, one or more feature modifiers.
// 对于armv8 , 可填入 armv8-a, armv8.1-a, armv8.2-a, armv8.3-a, armv8.4-a, armv8.5-a
// 对于armv7 , 可填入 armv7-a+vfpv4
// 对于riscv , 可填入 RV32IMAFDC
// 表示要生成哪一类 汇编指令
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「__pop_」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u011011827/article/details/121375243
qemu
开发环境
软件开发
裸机(baremetal)开发
1.EL1 boot -> EL0 APP
2.EL0 APP --syscall--> EL1 --eret--> EL0 APP
3.external debug
4.printf on uart
RTOS
ARMv8 一般不跑RTOS
linux
arm64-linux 镜像
-
以arm32为例,arm64类似.各个镜像执行结果
arm64-linux boot 符号
boot时的内存管理
debug
boot
架构相关代码
其他
微架构
// ARM SOC 战略 :
从 Big.LITTLE 到 三簇(大中小)
Big.LITTLE:
ARMv7 : 4个A15和4个A7
2011年,ARM公司正式宣布了ARM v8指令集
2012年,推出了Cortex-A57,A53架构
2015年,推出了Cortex-A72,A55
A75,A55
A77,A55
A78,A55
三簇 :
Exynos 9820 : 双 Exynos M4 大核+双 A75 中核+四 A55 小核架构的三簇结构
骁龙8150 : 大中小架构,不过是“1+3+4”
麒麟980 :
麒麟9000: 采用1+3+4三簇8核心
资料
Big.LITTLE
https://www.donews.com/article/detail/4660/29172.html
三簇:
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1617524988948811428&wfr=spider&for=pc
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1616580085082056451&wfr=spider&for=pc
- [流水线
- [多发射
ref手册内容
DDI0487E_armv8_A_architecture_reference_manual.pdf
A.Armv8 Architecture Introduction and Overview
B.The AArch64 Application Level Architecture
EL0 上的软件运行视角的架构
Programmers’ Model ---
Memory Model ---
C.The AArch64 Instruction Set
EL0/1/2/3 跑的指令
D.The AArch64 System Level Architecture
EL1/2/3 上的软件运行视角的架构
Programmers’ Model ---
Memory Model ---
Virtual Memory System Architecture &&&
Exception Model &&&
debug Model &&&
Self-hosted Debug
Self-hosted Trace
H.External Debug
安全模型 : 无
虚拟化模型 : 无
E.The AArch32 Application Level Architecture
F.The AArch32 Instruction Sets
G.The AArch32 System Level Architecture
H.External Debug
I.Memory-mapped Components of the Armv8 Architecture
J.Architectural Pseudocode
K.Appendixes
指令速查卡
// ARMv8-A : A64 A32 T32
// ARMv7-A : A32 T32 A16
// ARMv7-R : A32 T32 A16
// ARMv7-M : T32
// aarch64(A64) reference card
// arm32(A32) reference card
// thumb2(T32) reference card (https://wenku.baidu.com/view/9011deddce2f0066f533221c.html)
// thumb(A16) reference card
// RISC-V-Reader-Chinese-v2p1.pdf
// 64-ia-32-architectures-software-developer-vol-1-manual.pdf
// 64-ia-32-architectures-software-developer-system-programming-manual-325384.pdf
// 64-ia-32-architectures-software-developer-instruction-set-reference-manual-325383.pdf
基础篇.ARM架构介绍
ARM架构介绍(1)
本章主要介绍ARM架构通用知识,不仅仅包括ARMv7\\ARMv8/ARMv9
1.ARM体系结构介绍
ARM公司主要向客户提供处理器IP。ARM体系结构是一种硬件规范,主要用来约定指令集、芯片内部体系结构等。以指令集为例,ARM体系结构并没规定每一条指令在硬件IP中如何实现,只是约定了每条指令的格式、行为规范、参数等。
为了降低客户基于ARM体系结构开发处理器(processor 或 core)的难度,ARM公司通常在发布新版本的体系结构之后,根据不同的应用需求开发出兼容该体系结构的处理器(processor 或 core)IP,然后授权给客户。客户获得ARM设计的处理器IP后,基于其定制和设计自己的SOC。
以ARMv8体系结构为例,ARM公司先后开发出Cortex-A53、Cortex-A55、Cortex-A72、Cortex-A73等多款处理器IP。
ARM架构为 processor 或 core的设计提供了基础,通常我们可以将processor 或 core称为Processing Element(PE)。
2.ARM授权模式
ARM公司一般有两种授权方式:
- 体系结构授权。客户可以根据这个规范自行设计与之兼容的处理器。
- 处理器IP授权。ARM公司根据某个版本的体系结构来设计处理器,然后把处理器的设计方案授权给客户。
市面上的大部分芯片都是直接采用ARM处理器IP,少部分大厂如高通、TI他们基于ARM 公版IP进行二次开发,而像苹果这样的大佬甚至自己基于ARM架构规范实现自己的处理器IP。
3.架构和微架构
3.1 什么是架构(处理器领域)
其实前面已经有所介绍。在这里,主要指的是处理器的功能规范。 架构指定处理器的行为方式,例如它有什么指令以及指令做什么,而不包括如何做。
架构视为硬件和软件之间的规则。 该架构描述了软件可以依赖硬件提供哪些功能。 一些功能是可选的,我们将在稍后的微架构部分讨论。
架构可能会规定:

3.2 什么是微架构
架构(Architecture)不会告诉您处理器是如何构建和工作的。 处理器的构建和设计被称为微架构。 微架构( micro-architecture)规定了处理器应该如何工作,我们上述提到的”ARM公司根据某个版本的体系结构来设计处理器IP“ 就是微架构,如Cortex-A53 和Cortex-A72 都是基于Armv8-A 架构实现的微架构。
微架构通常包括:
- 几级Cache和Cache Size大小等。
- 几级流水线。
- 每条指令执行的周期。
- 其他可选供能。
例如,Cortex-A53 和 Cortex-A72 都是 Armv8-A 架构的实现。 这意味着它们具有相同的架构,但它们具有非常不同的微架构,如下图所示
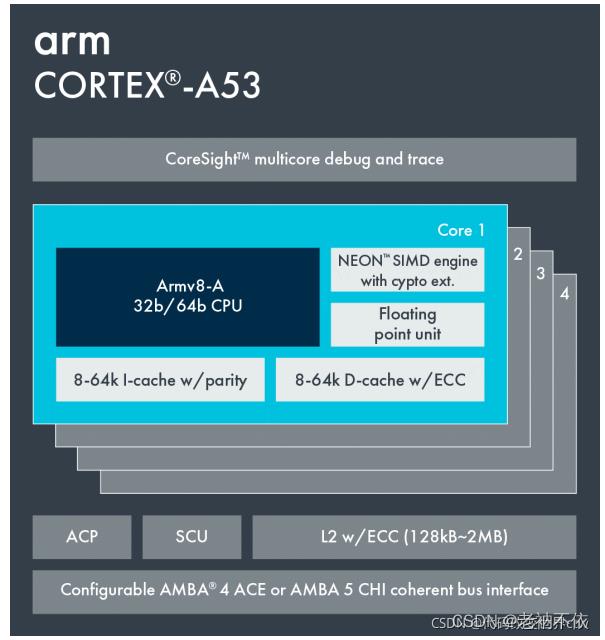

4.Arm 架构和微架构的发展
4.1 Timeline

4.2 产品演进
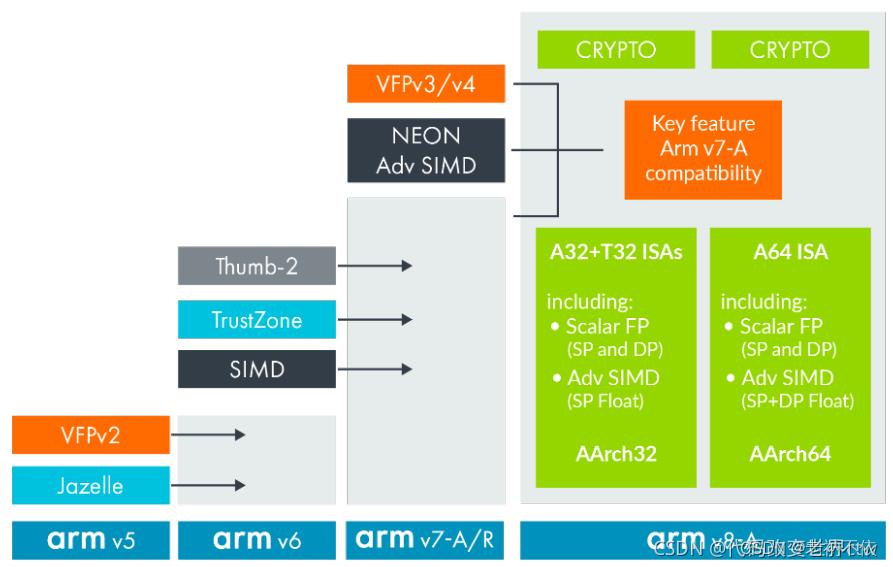
Arm 架构是最著名的 Arm 规范,但它并不是唯一的规范。现代片上系统 (SoC) 除了Core之外的其他IP同样也遵循一些其他ARM规范。 下图提供了一些示例:

- Generic Interrupt Controller
- System Memory Management Unit (SMMU or IOMMU)
- Generic Timer
- Server Base System Architecture and Trusted Base System Architecture
- Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture(AMBA)
4.3 ARM产品分类
ARM11芯片之后,也就是从ARMv7架构开始,ARM IP微架构的命名方式有所改变。
新的处理器家族,改以Cortex命名,ARM微架构根据应用场景分为三个系列,分别是Cortex-A,Cortex-R,Cortex-M。

Cortex-A系列(A:Application)
面向性能密集型系统的应用处理器内核。主要针对日益增长的消费娱乐和无线产品设计,用于具有高计算要求、运行丰富操作系统及提供交互媒体和图形体验的应用领域,如智能手机、平板电脑、汽车娱乐系统、数字电视,智能本、电子阅读器、家用网络、家用网关和其他各种产品。。
Cortex-R系列 (R:Real-time)
面向实时应用的高性能内核。主要针对需要运行实时操作的系统应用,面向如汽车制动系统、动力传动解决方案、大容量存储控制器等深层嵌入式实时应用。
Cortex-M系列(M:Microcontroller)
面向各类嵌入式应用的微控制器内核。该系列面向微控制器领域,主要针对成本和功耗敏感的应用,如智能测量、人机接口设备、汽车和工业控制系统、家用电器、消费性产品和医疗器械等。
Cortex-SC系列(SC:SecurCore)
其实,除了上述三大系列之外,还有一个主打安全的Cortex-SC系列(SC:SecurCore),主要用于政府安全芯片。
5. Arm 架构文档
- Arm Architecture Reference Manual (Arm ARMs) - 架构类的文档, 一般就看这个
- Arm Cortex processor has a Technical Reference Manual (TRM) - arm core的文档, 基本不用看
- Arm Cortex processor also has a Configuration or Integration Manual (CIM) - 可能是给ASIC看的
例如你要学习 Cortex-A75 processor,可以去查看以下文档:

以上是关于ARMv8 ARM64 架构 整体介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章