Spring 源码学习系列BeanNameAware#setBeanName 方法的调用时机
Posted 明明如月学长
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring 源码学习系列BeanNameAware#setBeanName 方法的调用时机相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、背景
前一节我们研究了 《ApplicationContextAware 方法的调用时机》 ,对 IOC 容器最核心的方法 refresh 有了初步的了解。

这节,我们将借助 BeanNameAware 方法的调用时机对 Bean 的初始化进一步学习。
二、分析
2.1 代码示例
实现 BeanNameAware接口:
package org.example.aware.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class NameAwaredTestBean implements BeanNameAware
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name)
System.out.println("beanName:" + name);
编写配置:
package org.example.aware.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example.aware.bean")
public class AwareConfiguration
执行:
package org.example.aware;
import org.example.aware.bean.NameAwaredTestBean;
import org.example.aware.config.AwareConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class AwareApplication
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AwareConfiguration.class);
NameAwaredTestBean atBean = ctx.getBean(NameAwaredTestBean.class);
System.out.println(atBean);
2.2 由外到内
先猜想后验证法
按照“国际惯例” 我们先进行猜测:BeanNameAware 应该比前文的 ApplicationContextAware 的时机更早,因为在 setBeanName 里我们可以修改 bean 的名称,而 ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext 里面很可能会用到 bean 的名称来构造策略 Map。
接下来我们进行验证。按照“老传统” 在 setBeanName 方法上断点。
发现调用来自:
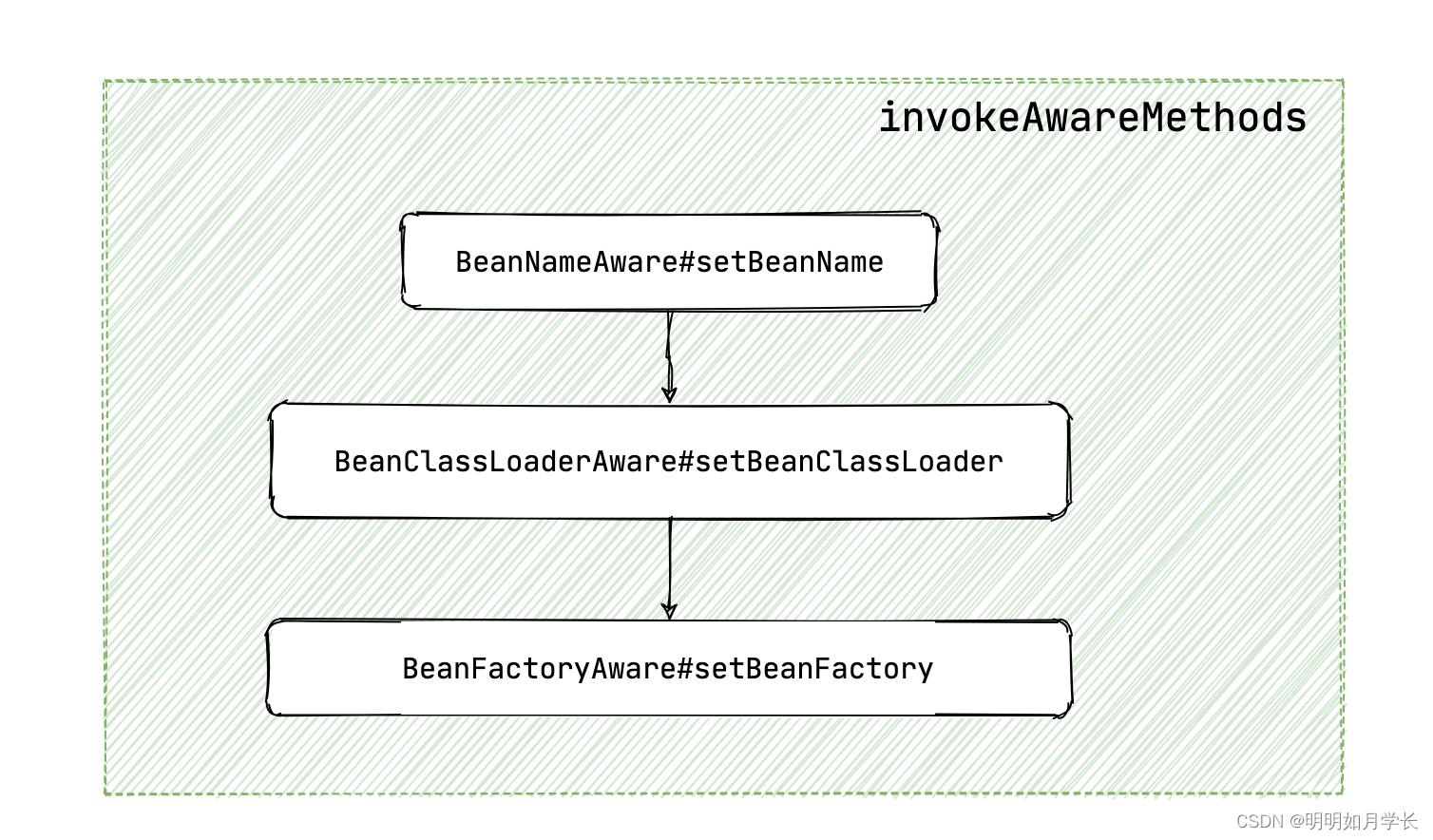
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean)
if (bean instanceof Aware)
//1 设置 BeanName
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware)
// 调用来自这里
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
//2 设置 BeanClassLoader
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware)
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null)
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
//3 设置 BeanFactory
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware)
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
从这里我们可以看出 BeanClassLoaderAware#setBeanClassLoader 和 BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory 都在 invokeAwareMethods 方法里一起调用。
再上追溯一层:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
/**
* Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
* as well as init methods and bean post processors.
* 初始化给定的 Bean 实例,应用 init 方法和 bean 后置处理器
* <p>Called from @link #createBean for traditionally defined beans,
* and from @link #initializeBean for existing bean instances.
* 调用来自 createBean
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be @code null, if given an existing bean instance)
* @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
* @see #invokeInitMethods
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
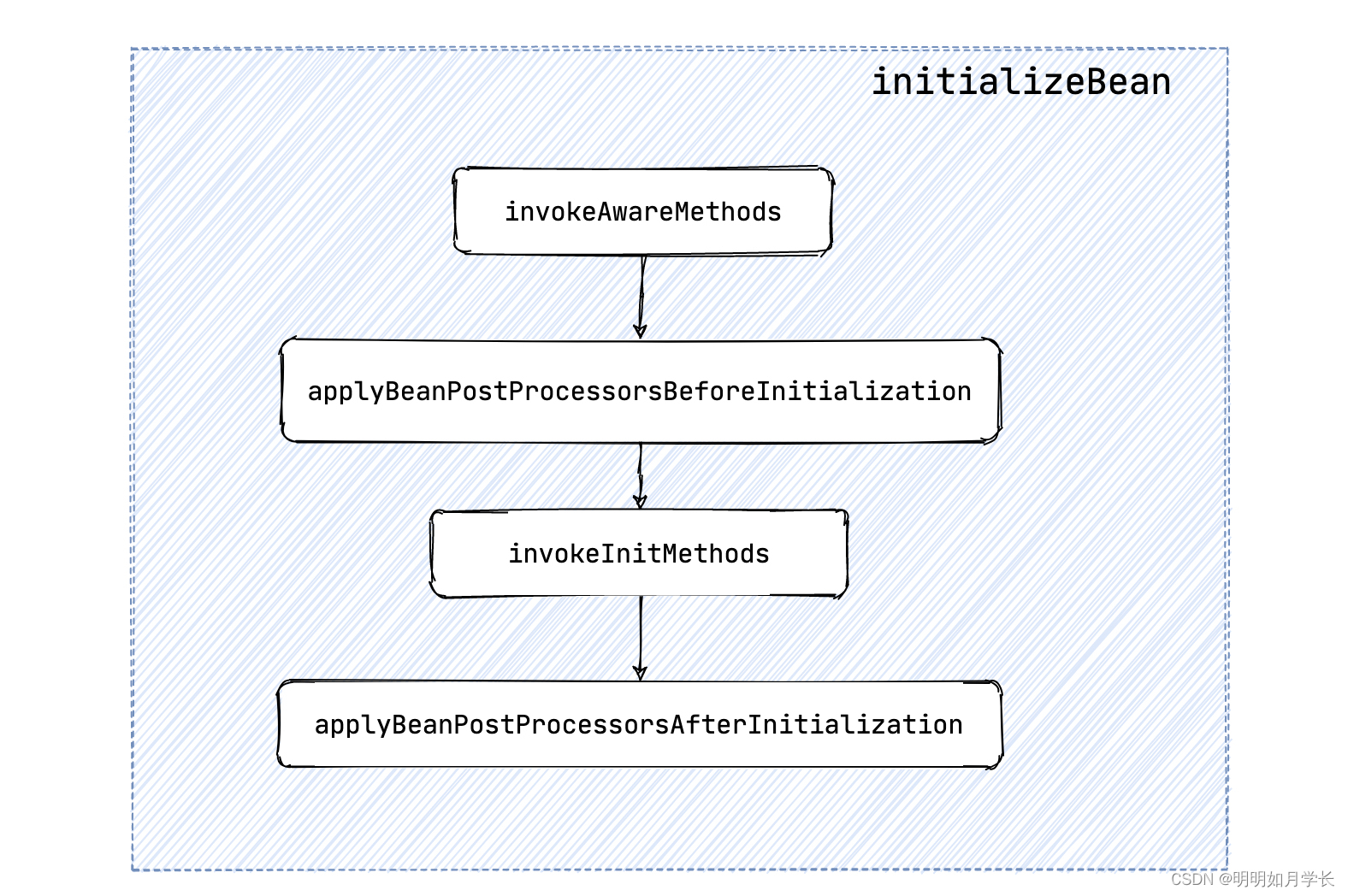
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
, getAccessControlContext());
else
//【重要】执行到这里
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic())
// 执行 BeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
try
// 执行 Init 方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
catch (Throwable ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic())
// 执行 BeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
return wrappedBean;
主要流程:
其中 invokeInitMethods 方法的源码如下:
/**
* Give a bean a chance to react now all its properties are set,
* and a chance to know about its owning bean factory (this object).
* This means checking whether the bean implements InitializingBean or defines
* a custom init method, and invoking the necessary callback(s) if it does.
* 检查当前 bean 是否实现了 InitializingBean 接口或者定义了 init 方法,如果有则执行调用
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the merged bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be @code null, if given an existing bean instance)
* @throws Throwable if thrown by init methods or by the invocation process
* @see #invokeCustomInitMethod
*/
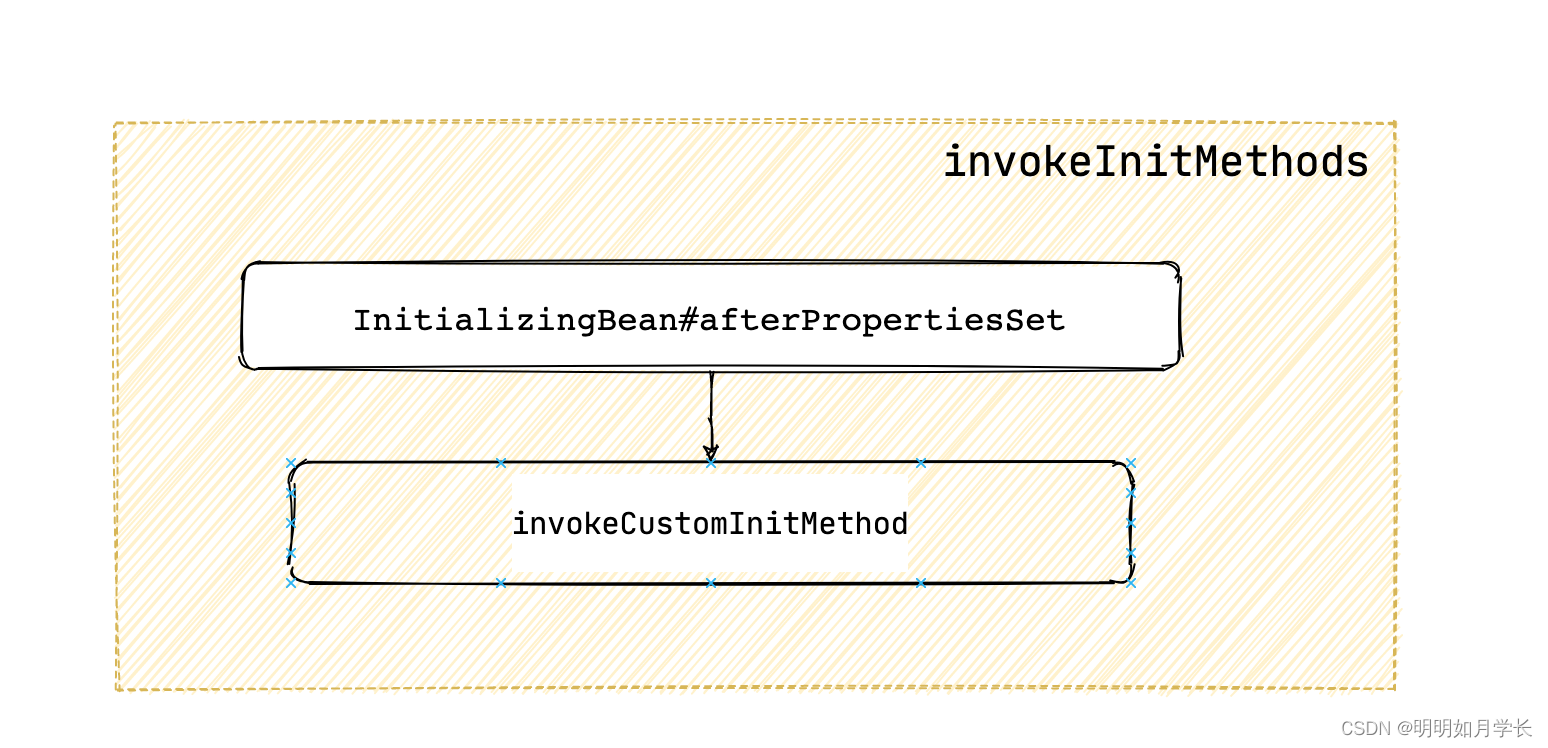
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable
// 检查是否实现了 InitializingBean 接口
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet")))
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
try
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
, getAccessControlContext());
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae)
throw pae.getException();
else
// 调用 InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet 方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class)
// 获取 init 方法名 并执行调用
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName))
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
可以看到这里先执行 InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet 然后再执行自定义 init 方法。
再往上追溯和前一篇文章非常类似。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking @code postProcessBeforeInstantiation callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException
// Instantiate the bean.
// 实例化 bean
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton())
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
if (instanceWrapper == null)
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class)
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock)
if (!mbd.postProcessed)
try
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
catch (Throwable ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure)
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () ->
// 构造 早期暴漏的 bean 引用,来解决循环依赖问题
getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
// 初始化 bean 实例.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 【重要】 执行到这里( bean 初始化)
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
catch (Throwable ex)
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName()))
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
else
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
// 省略部分代码
// Register bean as disposable.
try
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex)
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
return exposedObject;
再往上层回溯到 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton 这里:
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name,
* creating and registering a new one if none registered yet.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the ObjectFactory to lazily create the singleton
* with, if necessary
* @return the registered singleton object
*/
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory)
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects)
// 先通过 bean 名称从单例 bean 缓存中获取 bean 实例
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 如果没有执行创建
if (singletonObject == null)
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction)
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
// 执行单例bean 创建的前置逻辑
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions)
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try
//【重要】执行到这里
// 创建单例 bean
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
catch (IllegalStateException ex)
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null)
throw ex;
catch (BeanCreationException ex)
if (recordSuppressedExceptions)
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions)
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
throw ex;
finally
if (recordSuppressedExceptions)
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
// 执行单例bean 创建的后置逻辑
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
// 如果是新创建的单例 Bean ,则添加到 beanName 到 单例 bean 的缓存中
if (newSingleton)
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
return singletonObject;
再往上一层:
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException
// 省略部分代码
//1 如果是单例,创建单例 bean
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton())
// 底层
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () ->
try
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
catch (BeansException ex)
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
);
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
// 2 prototype
else if (mbd.isPrototype())
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
// 由于是 prototype -> 每次都新建一个实例
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
finally
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
// 省略部分代码
return (T) bean;
再往上追溯:
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class))
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.