C++学习--点滴记录008
Posted 鲁棒最小二乘支持向量机
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++学习--点滴记录008相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
8 结构体
8.1 结构体基本概念
结构体属于用户自定义的数据类型,允许用户存储不同的数据类型
8.2 结构体定义和使用
语法:struct 结构体名 结构体成员列表 ;
通过结构体创建变量的方式有三种:
- struct 结构体名 变量名
- struct 结构体名 变量名 = 成员1值 , 成员2值…
- 定义结构体时顺便创建变量
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
///结构体定义
struct student
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
stu3; //结构体变量创建方式3
void test01()
//结构体变量创建方式1
struct student stu1; //struct 关键字可以省略
stu1.name = "张三";
stu1.age = 18;
cout << "姓名:" << stu1.name << " 年龄:" << stu1.age<< endl;
//结构体变量创建方式2
struct student stu2 = "李四",19 ;
cout << "姓名:" << stu2.name << " 年龄:" << stu2.age<< endl;
stu3.name = "王五";
stu3.age = 18;
cout << "姓名:" << stu3.name << " 年龄:" << stu3.age<< endl;
int main()
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;

总结1:定义结构体时的关键字是struct,不可省略
总结2:创建结构体变量时,关键字struct可以省略
总结3:结构体变量利用操作符 “.” 访问成员
8.3 结构体数组
作用: 将自定义的结构体放入到数组中方便维护
语法: struct 结构体名 数组名[元素个数] = , , ...
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结构体定义
struct student
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
;
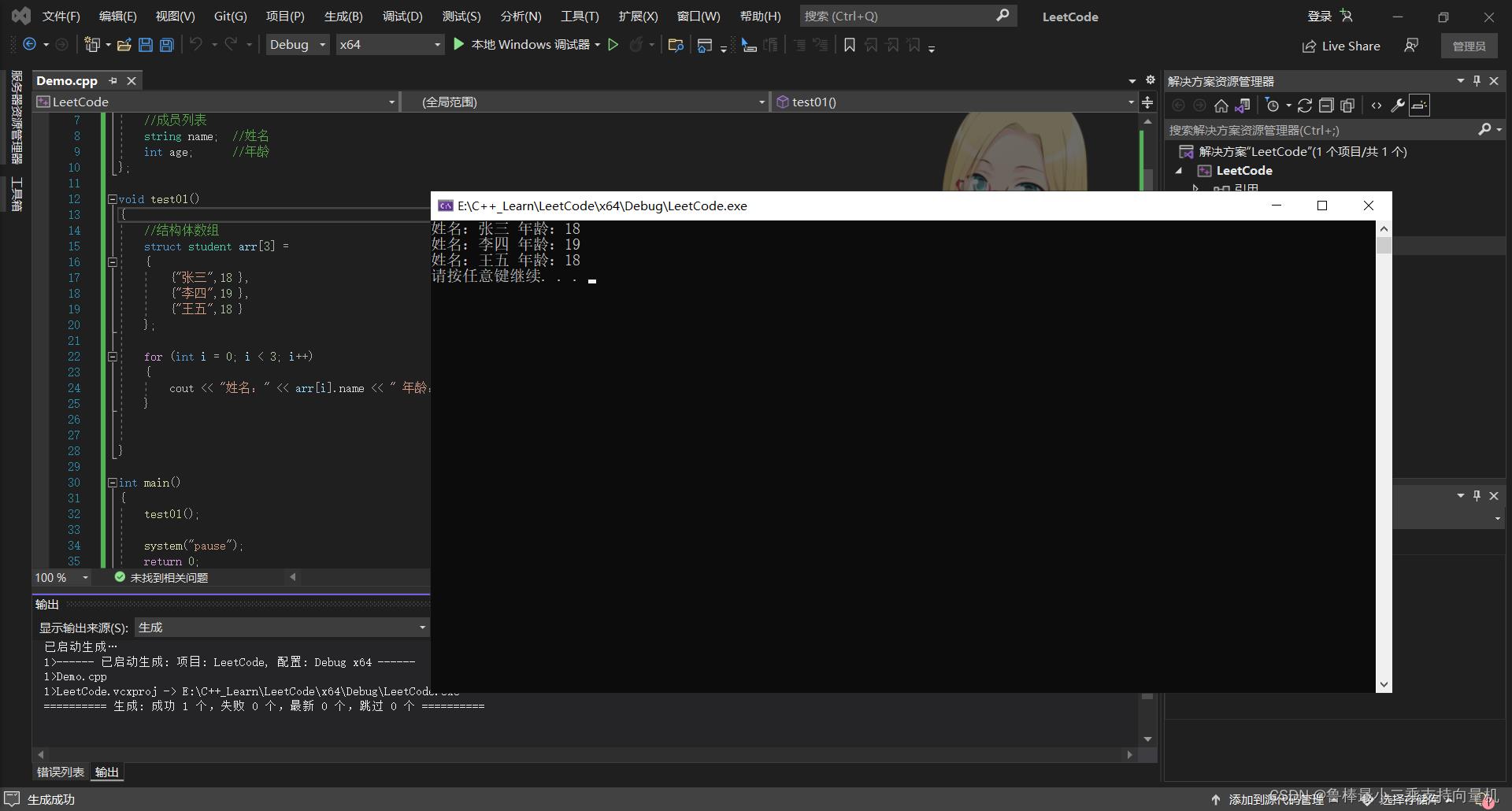
void test01()
//结构体数组
struct student arr[3] =
"张三",18 ,
"李四",19 ,
"王五",18
;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
cout << "姓名:" << arr[i].name << " 年龄:" << arr[i].age<< endl;
int main()
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
8.4 结构体指针
作用: 通过指针访问结构体中的成员
- 利用操作符
->可以通过结构体指针访问结构体属性
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结构体定义
struct student
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
;
void test01()
struct student stu = "张三",18 ;
struct student* p = &stu;
p->age = 20; //指针通过 -> 操作符可以访问成员
cout << "姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << endl;
int main()
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
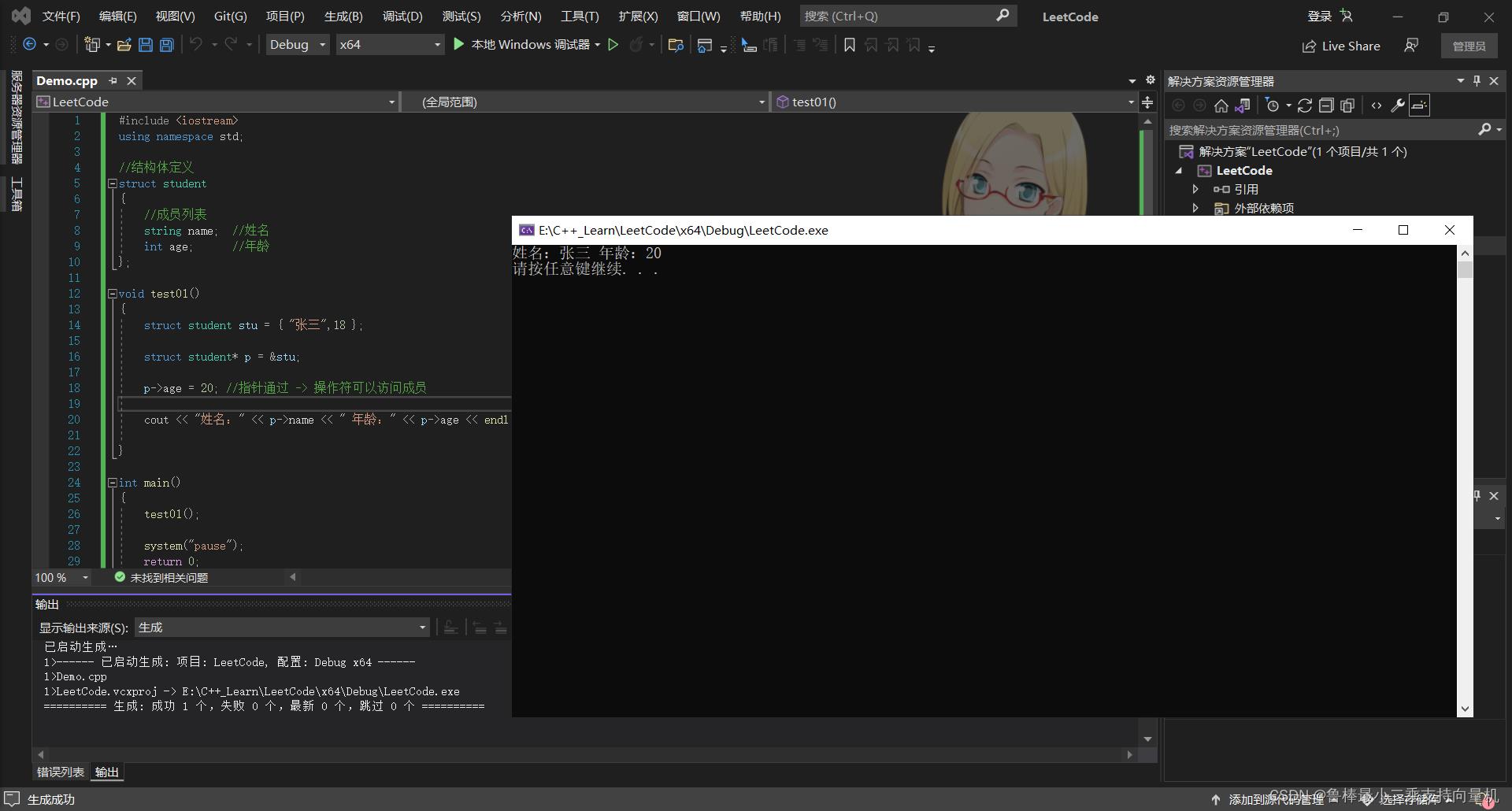
总结:结构体指针可以通过 -> 操作符 来访问结构体中的成员
8.5 结构体嵌套结构体
作用: 结构体中的成员可以是另一个结构体
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//学生结构体定义
struct student
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
int score; //分数
;
//教师结构体定义
struct teacher
//成员列表
int id; //编号
string name; //教师姓名
int age; //教师年龄
struct student stu; //子结构体 学生
;
void test01()
struct teacher t1;
t1.id = 10000;
t1.name = "王老师";
t1.age = 40;
t1.stu.name = "张三";
t1.stu.age = 18;
t1.stu.score = 100;
cout << "教师 编号: " << t1.id << " 姓名: " << t1.name << " 年龄: " << t1.age << endl;
cout << "学生 姓名: " << t1.stu.name << " 年龄:" << t1.stu.age << " 分数: " << t1.stu.score << endl;
int main()
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;

8.6 结构体做函数参数
作用: 将结构体作为参数向函数中传递
传递方式有两种:
- 值传递
- 地址传递
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct student
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
;
//值传递
void printStudent(student stu)
stu.age = 28;
cout << "子函数中 姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << endl;
//地址传递
void printStudent2(student* stu)
stu->age = 28;
cout << "子函数中 姓名:" << stu->name << " 年龄: " << stu->age << endl;
void test01()
student stu = "张三",18 ;
//值传递
printStudent(stu);
cout << "主函数中 姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << endl;
cout << endl;
//地址传递
printStudent2(&stu);
cout << "主函数中 姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << endl;
int main()
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
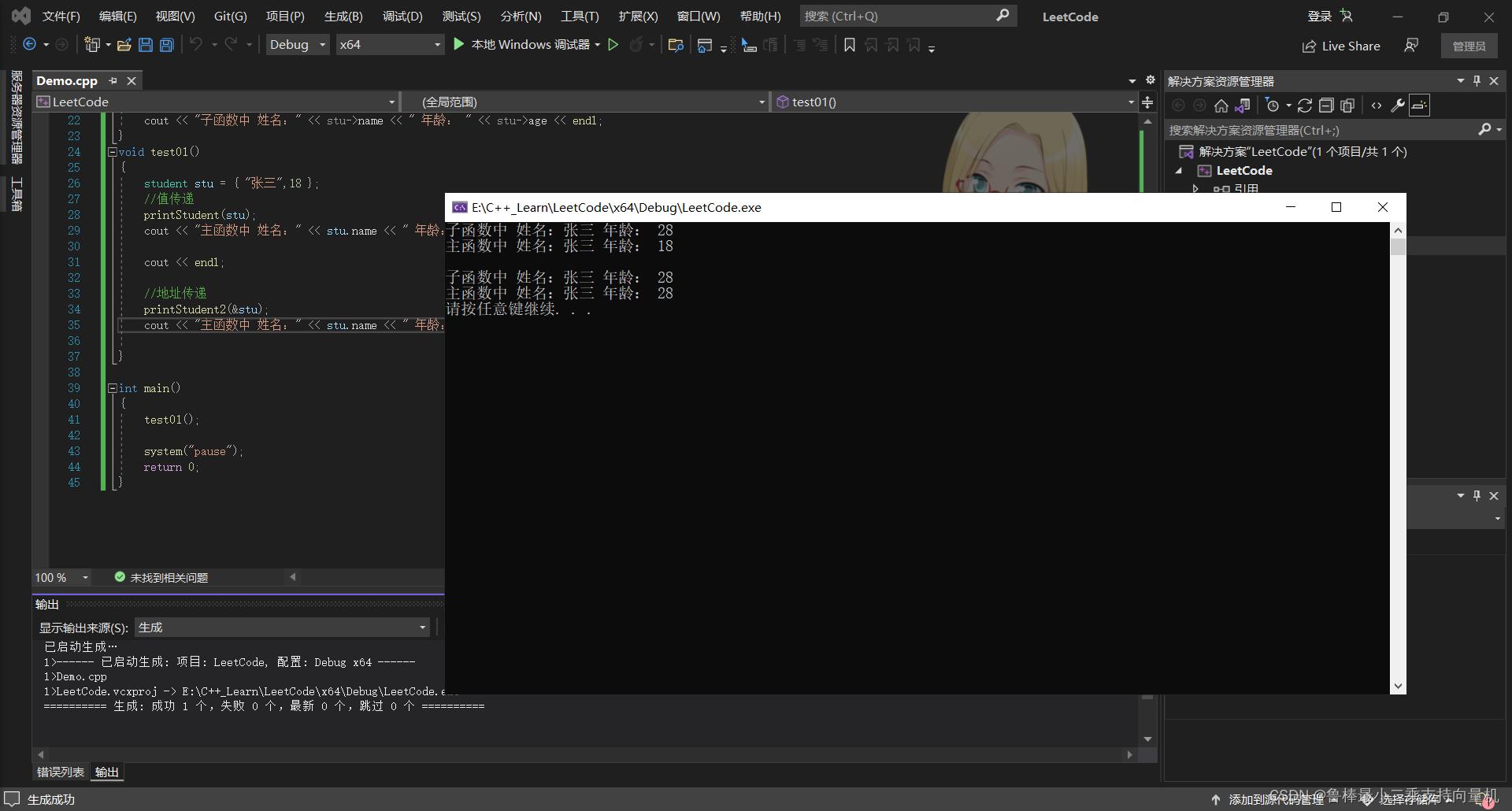
总结:如果不想修改主函数中的数据,用值传递,反之用地址传递
8.7 结构体中 const使用场景
作用: 用const来防止误操作
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct student
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
;
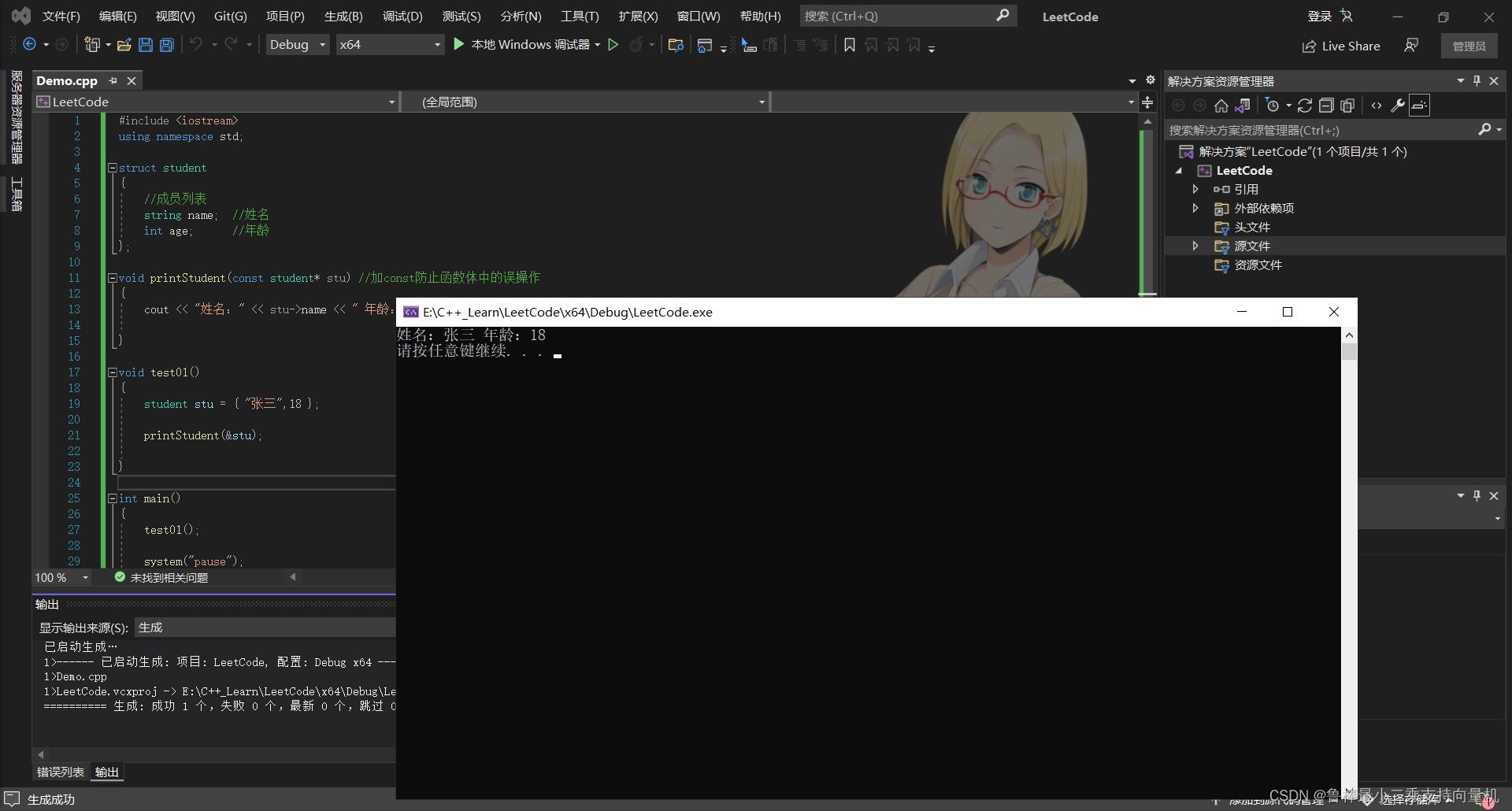
void printStudent(const student* stu) //加const防止函数体中的误操作
cout << "姓名:" << stu->name << " 年龄:" << stu->age << endl;
void test01()
student stu = "张三",18 ;
printStudent(&stu);
int main()
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
希望本文对大家有帮助,上文若有不妥之处,欢迎指正
分享决定高度,学习拉开差距
以上是关于C++学习--点滴记录008的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章