1.20_Flink的Window全面解析Keyed WindowsWindow AssignersTumbling,Sliding,Session,Global,Window Function
Posted to.to
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了1.20_Flink的Window全面解析Keyed WindowsWindow AssignersTumbling,Sliding,Session,Global,Window Function相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.20.透过窗口看无限数据流----Flink的Window全面解析
1.20.1.Quick Start
1.20.1.1.是什么?
1.20.1.2.如何用?
1.20.1.2.1.Keyed Windows
1.20.1.2.2.Non-Keyed Windows
1.20.1.2.3.简写window操作
1.20.2.Window Assigners
1.20.2.1.分类
1.20.2.2.使用介绍
1.20.2.2.1.Tumbling Windows
1.20.2.2.2.Sliding Windows
1.20.2.2.3.Session Windows
1.20.2.2.4.Global Windows
1.20.3.Window Functions
1.20.3.1.分类
1.20.3.2.使用介绍
1.20.3.2.1.ReduceFunction
1.20.3.2.2.AggregateFunction
1.20.3.2.3.FoldFunction
1.20.3.2.4.ProcessWindowFunction
1.20.3.2.5.增量聚合函数和ProcessWindowFunction整合
1.20.3.2.6.AggregateFunction与ProcessWindowFunction组合
1.20.4.window 生命周期解读
1.20.4.1.生命周期图解
1.20.4.2.分配器(Window Assigners)
1.20.4.3.触发器(Triggers)
1.20.4.4.清除器(Evictors)
1.20.透过窗口看无限数据流----Flink的Window全面解析
以下转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/jmx-bigdata/p/13708868.html
窗口是流式计算中非常常用的算子之一,通过窗口可以将无限流切分成有限流,然后在每个窗口之上使用计算函数,可以实现非常灵活的操作。Flink提供了丰富的窗口操作,除此之外,用户还可以根据自己的处理场景自定义窗口。通过本文,你可以了解到:
窗口的基本概念和简单使用
内置Window Assigners的分类、源码及使用
Window Function的分类及使用
窗口的组成部分及生命周期源码解读
完整的窗口使用Demo案例
1.20.1.Quick Start
1.20.1.1.是什么?
Window(窗口)是处理无界流的核心算子,Window可以将数据流分为固定大小的"桶(buckets)"(即通过按照固定时间或长度将数据流切分成不同的窗口),在每一个窗口上,用户可以使用一些计算函数对窗口内的数据进行处理,从而得到一定时间范围内的统计结果。比如统计每隔5分钟输出最近一小时内点击量最多的前N个商品,这样就可以使用一个小时的时间窗口将数据限定在固定时间范围内,然后可以对该范围内的有界数据执行聚合处理。
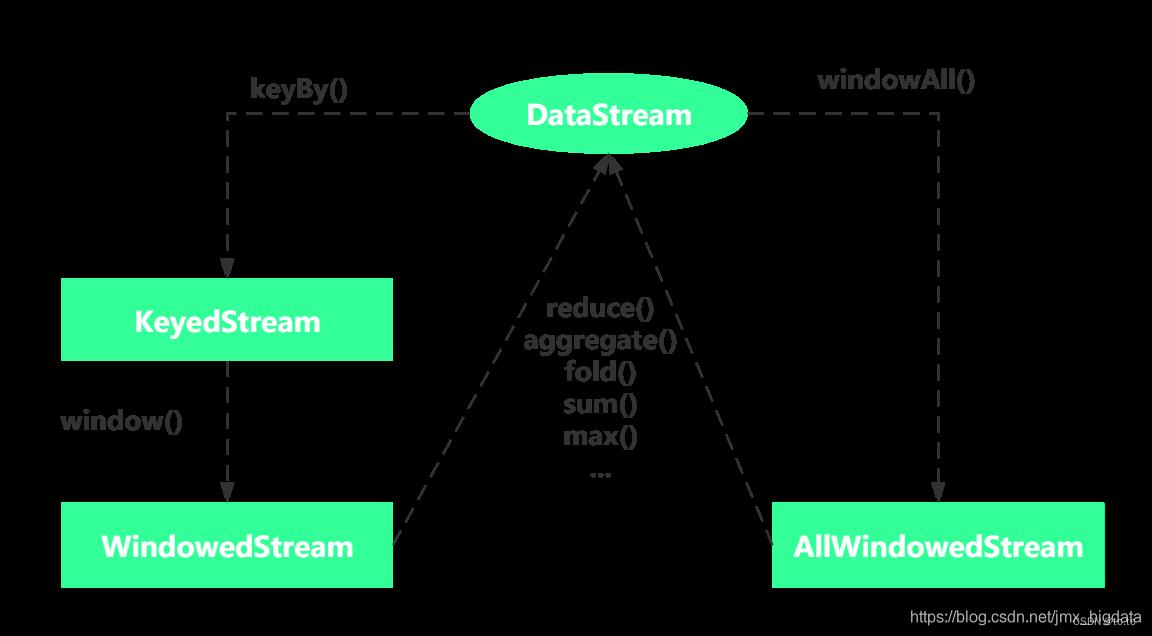
根据作用的数据流(DataStream、KeyedStream),Window可以分为两种:Keyed Windows与Non-Keyed Windows。其中Keyed Windows是在KeyedStream上使用window(…)操作,产生一个WindowedStream。Non-Keyed Windows是在DataStream上使用windowAll(…)操作,产生一个AllWindowedStream。具体的转换关系如下图所示。注意:一般不推荐使用AllWindowedStream,因为在普通流上进行窗口操作,会将所有分区的流都汇集到单个的Task中,即并行度为1,从而会影响性能。
1.20.1.2.如何用?
上面我们介绍了什么是窗口,那么该如何使用窗口呢?具体如下面的代码片段:
1.20.1.2.1.Keyed Windows
stream
.keyBy(...) // keyedStream上使用window
.window(...) // 必选: 指定窗口分配器( window assigner)
[.trigger(...)] // 可选: 指定触发器(trigger),如果不指定,则使用默认值
[.evictor(...)] // 可选: 指定清除器(evictor),如果不指定,则没有
[.allowedLateness(...)] // 可选: 指定是否延迟处理数据,如果不指定,默认使用0
[.sideOutputLateData(...)] // 可选: 配置side output,如果不指定,则没有
.reduce/aggregate/fold/apply() // 必选: 指定窗口计算函数
[.getSideOutput(...)] // 可选: 从side output中获取数据
1.20.1.2.2.Non-Keyed Windows
Stream
.windowAll(...) // 必选: 指定窗口分配器( window assigner)
[.trigger(...)] // 可选: 指定触发器(trigger),如果不指定,则使用默认值
[.evictor(...)] // 可选: 指定清除器(evictor),如果不指定,则没有
[.allowedLateness(...)] // 可选: 指定是否延迟处理数据,如果不指定,默认使用0
[.sideOutputLateData(...)] // 可选: 配置side output,如果不指定,则没有
.reduce/aggregate/fold/apply() // 必选: 指定窗口计算函数
[.getSideOutput(...)] // 可选: 从side output中获取数据
1.20.1.2.3.简写window操作
上面的代码片段中,要在keyedStream上使用window(…)或者在DataStream上使用windowAll(…),需要传入一个window assigner的参数,关于window assigner下文会进行详细解释。如下面代码片段:
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
// Keyed Windows
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
stream
.keyBy(id)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5))) // 5S的滚动窗口
.reduce(MyReduceFunction)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
// Non-Keyed Windows
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
stream
.windowAll(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5))) // 5S的滚动窗口
.reduce(MyReduceFunction)
上面的代码可以简写为:
// ---------------------------------------------------------------
// Keyed Windows
// --------------------------------------------------------------
stream.
.keyBy(id)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5)) //5S的滚动窗口
.reduce(MyReduceFunction)
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// Non-Keyed Windows
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
stream
.timeWindowAll(Time.seconds(5)) // 5S的滚动窗口
.reduce(MyReduceFunction)
关于上面的简写,以KeyedStream为例,对于看一下具体的KeyedStream源码片段,可以看出底层调用的还是非简写时的代码。关于timeWindowAll()的代码也是一样的,可以参考DataStream源码,这里不再赘述。
//会根据用户的使用的时间类型,调用不同的内置window Assigner
public WindowedStream<T, KEY, TimeWindow> timeWindow(Time size)
if (environment.getStreamTimeCharacteristic() == TimeCharacteristic.ProcessingTime)
return window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(size));
else
return window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(size));
1.20.2.Window Assigners
1.20.2.1.分类
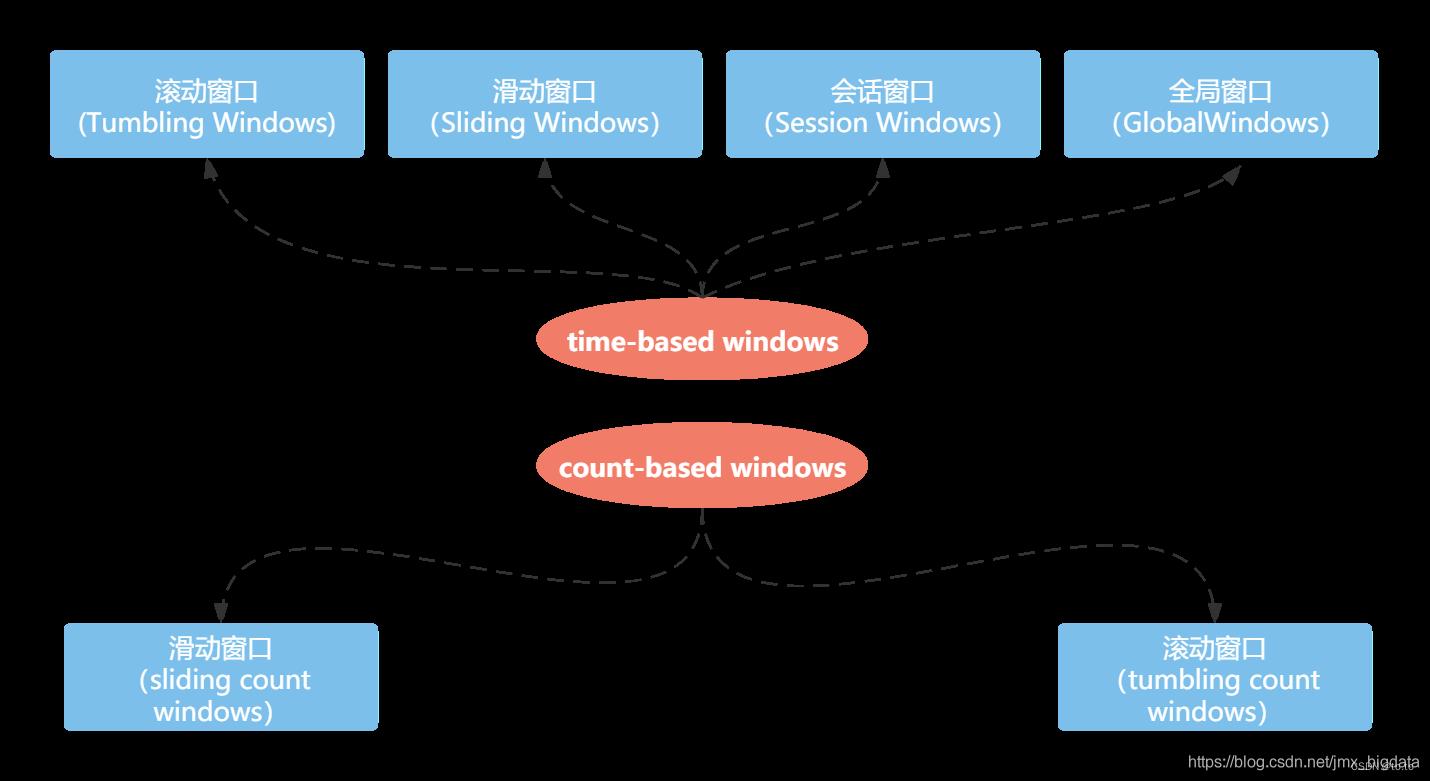
WindowAssigner负责将输入的数据分配到一个或多个窗口,Flink内置了许多WindowAssigner,这些WindowAssigner可以满足大部分的使用场景。比如tumbling windows, sliding windows, session windows , global windows。如果这些内置的WindowAssigner不能满足你的需求,可以通过继承WindowAssigner类实现自定义的WindowAssigner。
上面的WindowAssigner是基于时间的(time-based windows),除此之外,Flink还提供了基于数量的窗口(count-based windows),即根据窗口的元素数量定义窗口大小,这种情况下,如果数据存在乱序,将导致窗口计算结果不确定。本文重点介绍基于时间的窗口使用,由于篇幅有限,关于基于数量的窗口将不做讨论。
1.20.2.2.使用介绍
下面将会对Flink内置的四种基于时间的window assigner,进行一一分析。
1.20.2.2.1.Tumbling Windows
图解
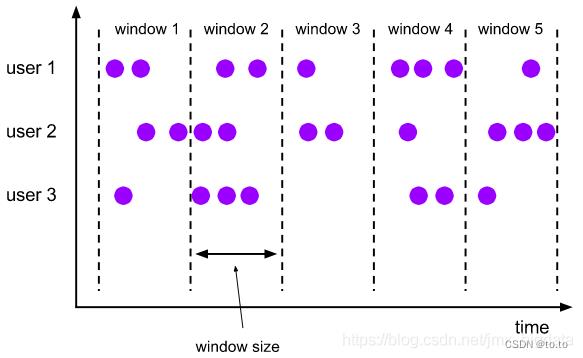
Tumbling Windows(滚动窗口)是将数据分配到确定的窗口中,根据固定时间或大小进行切分,每个窗口有固定的大小且窗口之间不存在重叠(如下图所示)。这种比较简单,适用于按照周期统计某一指标的场景。
关于时间的选择,可以使用Event Time或者Processing Time,分别对应的window assigner为:TumblingEventTimeWindows、TumblingProcessingTimeWindows。用户可以使用window assigner的of(size)方法指定时间间隔,其中时间单位可以是Time.milliseconds(x)、Time.seconds(x)或Time.minutes(x)等。
使用
// 使用EventTime
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10)))
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
// 使用processing-time
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10)))
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
1.20.2.2.2.Sliding Windows
图解
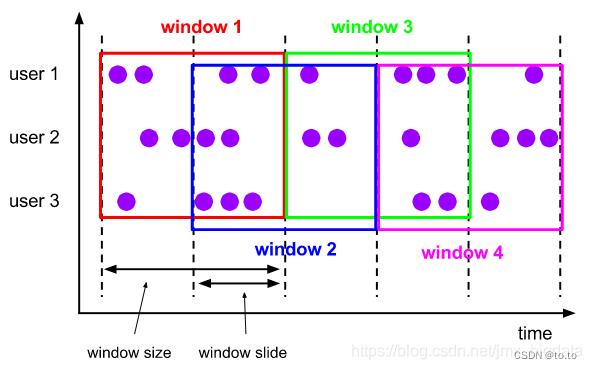
Sliding Windows(滑动窗口)在滚动窗口之上加了一个滑动窗口的时间,这种类型的窗口是会存在窗口重叠的(如下图所示)。滚动窗口是按照窗口固定的时间大小向前滚动,而滑动窗口是根据设定的滑动时间向前滑动。窗口之间的重叠部分的大小取决于窗口大小与滑动的时间大小,当滑动时间小于窗口时间大小时便会出现重叠。当滑动时间大于窗口时间大小时,会出现窗口不连续的情况,导致数据可能不属于任何一个窗口。当两者相等时,其功能就和滚动窗口相同了。滑动窗口的使用场景是:用户根据设定的统计周期来计算指定窗口时间大小的指标,比如每隔5分钟输出最近一小时内点击量最多的前 N 个商品。
关于时间的选择,可以使用Event Time或者Processing Time,分别对应的window assigner为:SlidingEventTimeWindows、SlidingProcessingTimeWindows。用户可以使用window assigner的of(size)方法指定时间间隔,其中时间单位可以是Time.milliseconds(x)、Time.seconds(x)或Time.minutes(x)等。
使用
// 使用EventTime
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5)))
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
// 使用processing-time
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window(SlidingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5)))
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
1.20.2.2.3.Session Windows
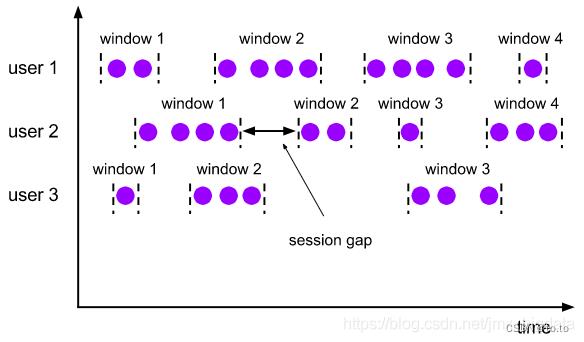
图解
Session Windows(会话窗口)主要是将某段时间内活跃度较高的数据聚合成一个窗口进行计算,窗口的触发的条件是Session Gap,是指在规定的时间内如果没有数据活跃接入,则认为窗口结束,然后触发窗口计算结果。需要注意的是如果数据一直不间断地进入窗口,也会导致窗口始终不触发的情况。与滑动窗口、滚动窗口不同的是,Session Windows不需要有固定窗口大小(window size)和滑动时间(slide time),只需要定义session gap,来规定不活跃数据的时间上限即可。如下图所示。Session Windows窗口类型比较适合非连续型数据处理或周期性产生数据的场景,根据用户在线上某段时间内的活跃度对用户行为数据进行统计。
关于时间的选择,可以使用Event Time或者Processing Time,分别对应的window assigner为:EventTimeSessionWindows和ProcessTimeSessionWindows。用户可以使用window assigner的withGap()方法指定时间间隔,其中时间单位可以是Time.milliseconds(x)、Time.seconds(x)或Time.minutes(x)等。
使用
// 使用EventTime
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window((EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(15)))
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
// 使用processing-time
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window(ProcessingTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(15)))
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
注意:由于session window的开始时间与结束时间取决于接收的数据。windowassigner不会立即分配所有的元素到正确的窗口,SessionWindow会为每个接收的元素初始化一个以该元素的时间戳为开始时间的窗口,使用session gap作为窗口大小,然后再合并重叠部分的窗口。所以, session window 操作需要指定用于合并的 Trigger 和 Window Function,比如ReduceFunction, AggregateFunction, or ProcessWindowFunction。
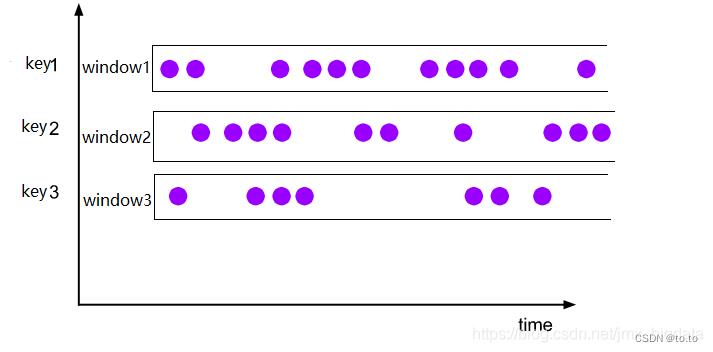
1.20.2.2.4.Global Windows
图解
Global Windows(全局窗口)将所有相同的key的数据分配到单个窗口中计算结果,窗口没有起始和结束时间,窗口需要借助于Triger来触发计算,如果不对Global Windows指定Triger,窗口是不会触发计算的。因此,使用Global Windows需要非常慎重,用户需要非常明确自己在整个窗口中统计出的结果是什么,并指定对应的触发器,同时还需要有指定相应的数据清理机制,否则数据将一直留在内存中。
使用
datastream
.keyBy(id)
.window(GlobalWindows.create())
.process(new MyProcessFunction())
1.20.3.Window Functions
1.20.3.1.分类
Flink提供了两大类窗口函数,分别为增量聚合函数和全量窗口函数。其中增量聚合函数的性能要比全量窗口函数高,因为增量聚合窗口是基于中间结果状态计算最终结果的,即窗口中只维护一个中间结果状态,不要缓存所有的窗口数据。相反,对于全量窗口函数而言,需要对所以进入该窗口的数据进行缓存,等到窗口触发时才会遍历窗口内所有数据,进行结果计算。如果窗口数据量比较大或者窗口时间较长,就会耗费很多的资源缓存数据,从而导致性能下降。
增量聚合函数
包括:ReduceFunction、AggregateFunction和FoldFunction
全量窗口函数
包括:ProcessWindowFunction
1.20.3.2.使用介绍
1.20.3.2.1.ReduceFunction
输入两个相同类型的数据元素按照指定的计算方法进行聚合,然后输出类型相同的一个结果元素。要求输入元素的数据类型与输出元素的数据类型必须一致。实现的效果是使用上一次的结果值与当前值进行聚合。具体使用案例如下:
package com.toto.demo.test;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple3;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.AscendingTimestampExtractor;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners.TumblingEventTimeWindows;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
public class ReduceFunctionExample
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment().setParallelism(1);
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
// 模拟数据
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<Long, Integer, Long>> input = env.fromElements(
Tuple3.of(1L, 10, 1588491228L),
Tuple3.of(1L, 15, 1588491229L),
Tuple3.of(1L, 20, 1588491238L),
Tuple3.of(1L, 25, 1588491248L),
Tuple3.of(2L, 10, 1588491258L),
Tuple3.of(2L, 30, 1588491268L),
Tuple3.of(2L, 20, 1588491278L))
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor<Tuple3<Long, Integer, Long>>()
@Override
public long extractAscendingTimestamp(Tuple3<Long, Integer, Long> element)
return element.f2 * 1000;
);
input.map(new MapFunction<Tuple3<Long,Integer,Long>, Tuple2<Long,Integer>>()
@Override
public Tuple2<Long, Integer> map(Tuple3<Long, Integer, Long> value) throws Exception
// 根据第一个元素分组,求第二个元素的累计和
return Tuple2.of(value.f0, value.f1);
)
.keyBy(0)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10)))
.reduce(new ReduceFunction<Tuple2<Long, Integer>>()
@Override
public Tuple2<Long, Integer> reduce(Tuple2<Long, Integer> value1, Tuple2<Long, Integer> value2) throws Exception
// 根据第一个元素分组,求第二个元素的累计和
return Tuple2.of(value1.f0, value1.f1 + value2.f1);
).print();
env.execute("ReduceFunctionExample");
1.20.3.2.2.AggregateFunction
与ReduceFunction相似,AggregateFunction也是基于中间状态计算结果的增量计算函数,相比ReduceFunction,AggregateFunction在窗口计算上更加灵活,但是实现稍微复杂,需要实现AggregateFunction接口,重写四个方法。其最大的优势就是中间结果的数据类型和最终的结果类型不依赖于输入的数据类型。关于AggregateFunction的源码,如下所示:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.flink.api.common.functions;
import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* <h1>Example: Average and Weighted Average</h1>
*
* <pre>@code
* // the accumulator, which holds the state of the in-flight aggregate
* public class AverageAccumulator
* long count;
* long sum;
*
*
* // implementation of an aggregation function for an 'average'
* public class Average implements AggregateFunction<Integer, AverageAccumulator, Double>
*
* public AverageAccumulator createAccumulator()
* return new AverageAccumulator();
*
*
* public AverageAccumulator merge(AverageAccumulator a, AverageAccumulator b)
* a.count += b.count;
* a.sum += b.sum;
* return a;
*
*
* public AverageAccumulator add(Integer value, AverageAccumulator acc)
* acc.sum += value;
* acc.count++;
* return acc;
*
*
* public Double getResult(AverageAccumulator acc)
* return acc.sum / (double) acc.count;
*
*
*
* // implementation of a weighted average
* // this reuses the same accumulator type as the aggregate function for 'average'
* public class WeightedAverage implements AggregateFunction<Datum, AverageAccumulator, Double>
*
* public AverageAccumulator createAccumulator()
* return new AverageAccumulator();
*
*
* public AverageAccumulator merge(AverageAccumulator a, AverageAccumulator b)
* a.count += b.count;
* a.sum += b.sum;
* return a;
*
*
* public AverageAccumulator add(Datum value, AverageAccumulator acc)
* acc.count += value.getWeight();
* acc.sum += value.getValue();
* return acc;
*
*
* public Double getResult(AverageAccumulator acc)
* return acc.sum / (double) acc.count;
*
*
* </pre>
*
* @param <IN> The type of the values that are aggregated (input values)
* @param <ACC> The type of the accumulator (intermediate aggregate state).
* @param <OUT> The type of the aggregated result
*/
@PublicEvolving
public interface AggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT> extends Function, Serializable
/**
* 创建一个新的累加器
* Creates a new accumulator, starting a new aggregate.
*
* <p>The new accumulator is typically meaningless unless a value is added
* via @link #add(Object, Object).
*
* <p>The accumulator is the state of a running aggregation. When a program has multiple
* aggregates in progress (such as per key and window), the state (per key and window)
* is the size of the accumulator.
*
* @return A new accumulator, corresponding to an empty aggregate.
*/
ACC createAccumulator();
/**
* 将新的数据与累加器进行聚合,返回一个新的累加器
* Adds the given input value to the given accumulator, returning the
* new accumulator value.
*
* <p>For efficiency, the input accumulator may be modified and returned.
*
* @param value The value to add
* @param accumulator The accumulator to add the value to
*
* @return The accumulator with the updated state
*/
ACC add(IN value, ACC accumulator);
/**
* 从累加器中计算最终结果并返回
* Gets the result of the aggregation from the accumulator.
*
* @param accumulator The accumulator of the aggregation
* @return The final aggregation result.
*/
OUT getResult(ACC accumulator);
/**
* 合并两个累加器并返回结果
* Merges two accumulators, returning an accumulator with the merged state.
*
* <p>This function may reuse any of the given accumulators as the target for the merge
* and return that. The assumption is that the given accumulators will not be used any
* more after having been passed to this function.
*
* @param a An accumulator to merge
* @param b Another accumulator to merge
*
* @return The accumulator with the merged state
*/
ACC merge(ACC a, ACC b);
具体使用代码案例:
package com.toto.demo.test;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple3;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.以上是关于1.20_Flink的Window全面解析Keyed WindowsWindow AssignersTumbling,Sliding,Session,Global,Window Function的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章