强化学习PPO算法
Posted 喜欢库里的强化小白
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了强化学习PPO算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
强化学习PPO算法
最近再改一个代码,需要改成PPO方式的,由于之前没有接触过此类算法,因此进行了简单学习,论文没有看的很详细,重点看了实现部分,这里只做简单记录。
这里附上论文链接,需要的可以详细看一下。
Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithms.
一、PPO算法
PPO算法本质上是一个On-Policy的算法,它可以对采样到的样本进行多次利用,在一定程度上解决样本利用率低的问题,收到较好的效果。论文里有两种实现方式,一种是结合KL的penalty的,另一种是clip裁断的方法。大部分都是采用的后者,本文记录的也主要是后者的实现。
二、伪代码
在网上找了一下伪代码,大概两类,前者是Open AI的,比较精炼,后者是Deepmind的,写的比较详细,在这里同时附上.
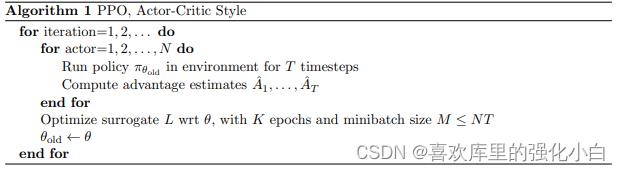
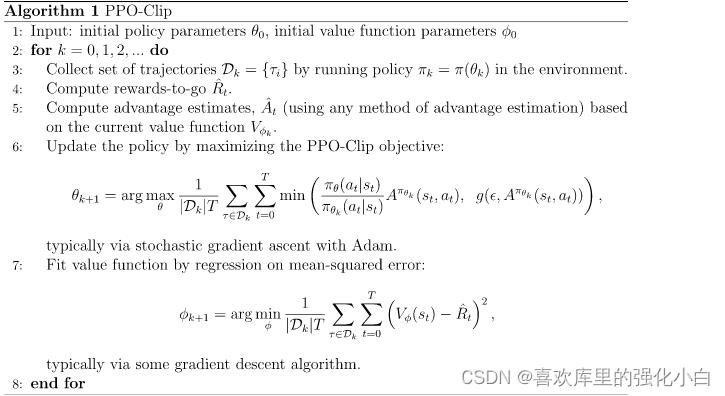
三、相关的简单理论
1.ratio
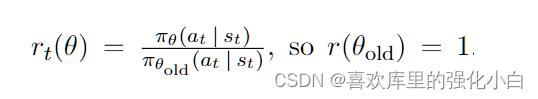
这里的比例ratio,是两种策略下动作的概率比,而在程序实现中,用的是对动作分布取对数,而后使用e指数相减的方法,具体实现如下所示:
action_logprobs = dist.log_prob(action)
ratios = torch.exp(logprobs - old_logprobs.detach())
2.裁断
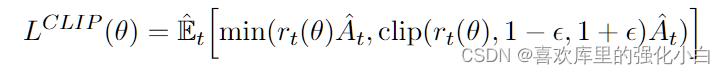
其中,裁断对应的部分如下图所示:
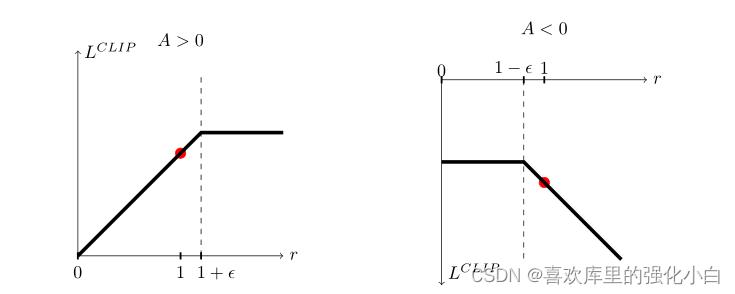
上述公式代表的含义如下:
clip公式含义.

这里我是这样理解的:
(1)如果A>0,说明现阶段的(st,at)相对较好,那么我们希望该二元组出现的概率越高越好,即ratio中的分子越大越好,但是分母分子不能差太多,因此需要加一个上限;
(2)如果A<0,说明现阶段的(st,at)相对较差,那么我们希望该二元组出现的概率越低越好,即ratio中的分子越小越好,但是分母分子不能差太多,因此需要加一个下限.
3.Advantage的计算
论文里计算At的方式如下,在一些情况下可以令lamda为1;还有一种更常用的计算方式是VAE,这里不进行描述.。
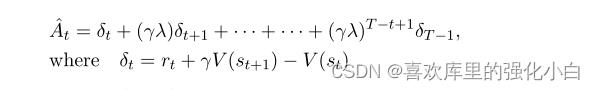
对应的代码块如下:
def update(self, memory):
# Monte Carlo estimate of rewards:
rewards = []
discounted_reward = 0
for reward, is_terminal in zip(reversed(memory.rewards), reversed(memory.is_terminals)):
if is_terminal:
discounted_reward = 0
discounted_reward = reward + (self.gamma * discounted_reward)
rewards.insert(0, discounted_reward)
4.loss的计算
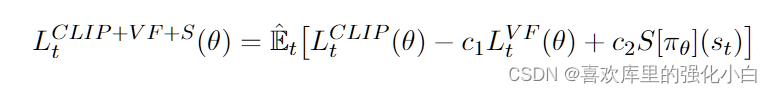
这里的第一项,对应裁断项,需要计算ratio和Advantage,之后进行裁断;
这里的第二项,对应的为对应的值的均方误差;
这里的第三项,为交叉熵
程序的实现如下所示:
surr1 = ratios * advantages
surr2 = torch.clamp(ratios, 1 - self.eps_clip, 1 + self.eps_clip) * advantages
loss = -torch.min(surr1, surr2) + 0.5 * self.MseLoss(state_values, rewards) - 0.01 * dist_entropy
四、算法实现
这里算法的实现参考了一位博主
PPO代码.
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*-coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/6/18 15:53
# @Author : Wang xiangyu
# @File : PPO.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.distributions import MultivariateNormal
import gym
import numpy as np
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
class Memory:
def __init__(self):
self.actions = []
self.states = []
self.logprobs = []
self.rewards = []
self.is_terminals = []
def clear_memory(self):
# del语句作用在变量上,而不是数据对象上。删除的是变量,而不是数据。
del self.actions[:]
del self.states[:]
del self.logprobs[:]
del self.rewards[:]
del self.is_terminals[:]
class ActorCritic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, action_std):
super(ActorCritic, self).__init__()
# action mean range -1 to 1
self.actor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim, 64),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(64, 32),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(32, action_dim),
nn.Tanh()
)
# critic
self.critic = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim, 64),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(64, 32),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(32, 1)
)
# 方差
self.action_var = torch.full((action_dim,), action_std * action_std).to(device)
def forward(self):
# 手动设置异常
raise NotImplementedError
def act(self, state, memory):
action_mean = self.actor(state)
cov_mat = torch.diag(self.action_var).to(device)
dist = MultivariateNormal(action_mean, cov_mat)
action = dist.sample()
action_logprob = dist.log_prob(action)
memory.states.append(state)
memory.actions.append(action)
memory.logprobs.append(action_logprob)
return action.detach()
def evaluate(self, state, action):
action_mean = self.actor(state)
action_var = self.action_var.expand_as(action_mean)
# torch.diag_embed(input, offset=0, dim1=-2, dim2=-1) → Tensor
# Creates a tensor whose diagonals of certain 2D planes (specified by dim1 and dim2) are filled by input
cov_mat = torch.diag_embed(action_var).to(device)
# 生成一个多元高斯分布矩阵
dist = MultivariateNormal(action_mean, cov_mat)
# 我们的目的是要用这个随机的去逼近真正的选择动作action的高斯分布
action_logprobs = dist.log_prob(action)
# log_prob 是action在前面那个正太分布的概率的log ,我们相信action是对的 ,
# 那么我们要求的正态分布曲线中点应该在action这里,所以最大化正太分布的概率的log, 改变mu,sigma得出一条中心点更加在a的正太分布。
dist_entropy = dist.entropy()
state_value = self.critic(state)
return action_logprobs, torch.squeeze(state_value), dist_entropy
class PPO:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, action_std, lr, betas, gamma, K_epochs, eps_clip):
self.lr = lr
self.betas = betas
self.gamma = gamma
self.eps_clip = eps_clip
self.K_epochs = K_epochs
self.policy = ActorCritic(state_dim, action_dim, action_std).to(device)
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.policy.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=betas)
self.policy_old = ActorCritic(state_dim, action_dim, action_std).to(device)
self.policy_old.load_state_dict(self.policy.state_dict())
self.MseLoss = nn.MSELoss()
def select_action(self, state, memory):
state = torch.FloatTensor(state.reshape(1, -1)).to(device)
return self.policy_old.act(state, memory).cpu().data.numpy().flatten()
def update(self, memory):
# Monte Carlo estimate of rewards:
rewards = []
discounted_reward = 0
for reward, is_terminal in zip(reversed(memory.rewards), reversed(memory.is_terminals)):
if is_terminal:
discounted_reward = 0
discounted_reward = reward + (self.gamma * discounted_reward)
rewards.insert(0, discounted_reward)
# Normalizing the rewards:
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).to(device)
rewards = (rewards - rewards.mean()) / (rewards.std() + 1e-5)
# convert list to tensor
# 使用stack可以保留两个信息:[1. 序列] 和 [2. 张量矩阵] 信息,属于【扩张再拼接】的函数;
old_states = torch.squeeze(torch.stack(memory.states).to(device), 1).detach()
old_actions = torch.squeeze(torch.stack(memory.actions).to(device), 1).detach()
old_logprobs = torch.squeeze(torch.stack(memory.logprobs), 1).to(device).detach()
#这里即可以对样本进行多次利用,提高利用率
# Optimize policy for K epochs:
for _ in range(self.K_epochs):
# Evaluating old actions and values :
logprobs, state_values, dist_entropy = self.policy.evaluate(old_states, old_actions)
# Finding the ratio (pi_theta / pi_theta__old):
ratios = torch.exp(logprobs - old_logprobs.detach())
# Finding Surrogate Loss:
advantages = rewards - state_values.detach()
surr1 = ratios * advantages
surr2 = torch.clamp(ratios, 1 - self.eps_clip, 1 + self.eps_clip) * advantages
loss = -torch.min(surr1, surr2) + 0.5 * self.MseLoss(state_values, rewards) - 0.01 * dist_entropy
# take gradient step
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.mean().backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# Copy new weights into old policy:
self.policy_old.load_state_dict(self.policy.state_dict())
def main():
############## Hyperparameters ##############
env_name = "Pendulum-v1"
render = False
solved_reward = 300 # stop training if avg_reward > solved_reward
log_interval = 20 # print avg reward in the interval
max_episodes = 10000 # max training episodes
max_timesteps = 1500 # max timesteps in one episode
update_timestep = 4000 # update policy every n timesteps
action_std = 0.5 # constant std for action distribution (Multivariate Normal)
K_epochs = 80 # update policy for K epochs
eps_clip = 0.2 # clip parameter for PPO
gamma = 0.99 # discount factor
lr = 0.0003 # parameters for Adam optimizer
betas = (0.9, 0.999)
#############################################
# creating environment
env = gym.make(env_name)
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.shape[0]
memory = Memory()
ppo = PPO(state_dim, action_dim, action_std, lr, betas, gamma, K_epochs, eps_clip)
print(lr, betas)
# logging variables
running_reward = 0
avg_length = 0
time_step = 0
# training loop
for i_episode in range(1, max_episodes + 1):
state = env.reset()
for t in range(max_timesteps):
time_step += 1
# Running policy_old:
action = ppo.select_action(state, memory)
state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# Saving reward and is_terminals:
memory.rewards.append(reward)
memory.is_terminals.append(done)
# update if its time
if time_step % update_timestep == 0:
ppo.update(memory)
memory.clear_memory()
time_step = 0
running_reward += reward
if render:
env.render()
if done:
break
avg_length += t+1
# stop training if avg_reward > solved_reward
if running_reward > (log_interval * solved_reward):
print("########## Solved! ##########")
torch.save(ppo.policy.state_dict(), './PPO_continuous_solved_.pth'.format(env_name))
break
# save every 500 episodes
if i_episode % 500 == 0:
torch.save(ppo.policy.state_dict(), './PPO_continuous_.pth'.format(env_name))
# logging
if i_episode % log_interval == 0:
avg_length = int(avg_length / log_interval)
running_reward = int((running_reward / log_interval))
print('Episode \\t Avg length: \\t Avg reward: '.format(i_episode, avg_length, running_reward))
running_reward = 0
avg_length = 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
五、效果
可以看到经过一段时间的训练,奖励有了一定升高.
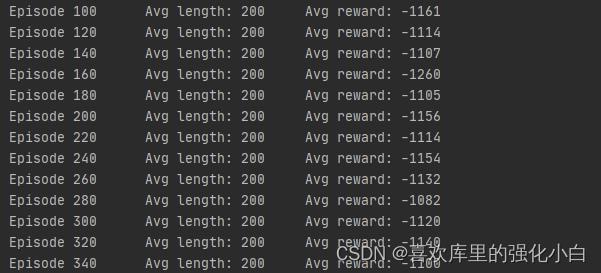
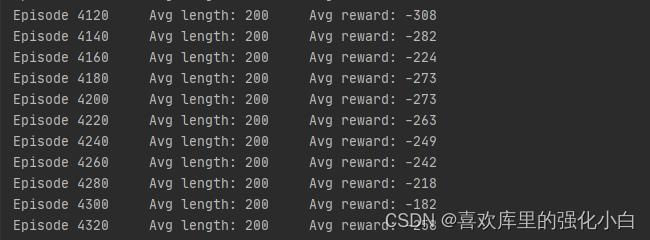
六、感悟
感悟是对改的项目的总结,和本文没有什么关系。
这次改的项目参考了PPO的代码,架子基本也是搭好的,所以改起来也没有想象的那么困难。但应该是我第一次改代码,之前只是看代码,从来没有尝试改过那么多,可以感觉到看代码和改代码这两个能力间差的真的很多,写代码就更困难了emm,可以说经过这一次,可以更好的看到和别人的差距,不过对自己也有很大提高。在以后的学习中,还是需要多看多写,逐步提高。
以上是关于强化学习PPO算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章