Golang下sync.Mutex专题
Posted 刘贤松handler
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Golang下sync.Mutex专题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景:
Go语言包中的 sync 包提供了两种锁类型:sync.Mutex 和 sync.RWMutex。
Mutex 是最简单的一种锁类型,同时也比较暴力,当一个 goroutine 获得了 Mutex 后,其他 goroutine 就只能乖乖等到这个 goroutine 释放该 Mutex。
RWMutex 相对友好些,是经典的单写多读模型。在读锁占用的情况下,会阻止写,但不阻止读,也就是多个 goroutine 可同时获取读锁(调用 RLock() 方法;而写锁(调用 Lock() 方法)会阻止任何其他 goroutine(无论读和写)进来,整个锁相当于由该 goroutine 独占。从 RWMutex 的实现看,RWMutex 类型其实组合了
引文:Go语言互斥锁(sync.Mutex)和读写互斥锁(sync.RWMutex)
Mutex使用示例
package core
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"sync"
"github.com/fatih/color"
)
const (
FATAL = 5
ERROR = 4
WARN = 3
IMPORTANT = 2
INFO = 1
DEBUG = 0
)
var LogColors = map[int]*color.Color
FATAL: color.New(color.FgRed).Add(color.Bold),
ERROR: color.New(color.FgRed),
WARN: color.New(color.FgYellow),
IMPORTANT: color.New(color.Bold),
DEBUG: color.New(color.FgCyan).Add(color.Faint),
type Logger struct
sync.Mutex
debug bool
silent bool
func (l *Logger) SetSilent(s bool)
l.silent = s
func (l *Logger) SetDebug(d bool)
l.debug = d
func (l *Logger) Log(level int, format string, args ...interface)
l.Lock()
defer l.Unlock()
if level == DEBUG && !l.debug
return
else if level < ERROR && l.silent
return
if c, ok := LogColors[level]; ok
c.Printf(format, args...)
else
fmt.Printf(format, args...)
if level == FATAL
os.Exit(1)
func (l *Logger) Fatal(format string, args ...interface)
l.Log(FATAL, format, args...)
func (l *Logger) Error(format string, args ...interface)
l.Log(ERROR, format, args...)
func (l *Logger) Warn(format string, args ...interface)
l.Log(WARN, format, args...)
func (l *Logger) Important(format string, args ...interface)
l.Log(IMPORTANT, format, args...)
func (l *Logger) Info(format string, args ...interface)
l.Log(INFO, format, args...)
func (l *Logger) Debug(format string, args ...interface)
l.Log(DEBUG, format, args...)
Mutex有两种操作模式:
- 正常模式(非公平模式)
阻塞等待的goroutine保存在FIFO的队列中,唤醒的goroutine不直接拥有锁,需要与新来的goroutine竞争获取锁。因为新来的goroutine很多已经占有了CPU,所以唤醒的goroutine在竞争中很容易输;但如果一个goroutine获取锁失败超过1ms,则会将Mutex切换为饥饿模式。
- 饥饿模式(公平模式)
这种模式下,直接将等待队列队头goroutine解锁goroutine;新来的gorountine也不会尝试获得锁,而是直接插入到等待队列队尾。
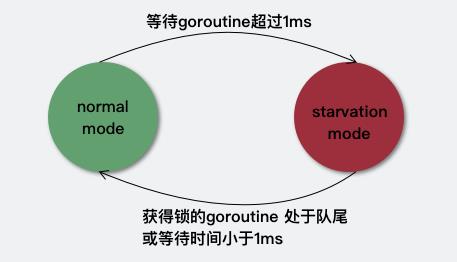
如果一个goroutine获得了锁,并且他在等待队列队尾 或者 他等待小于1ms,则会将Mutex的模式切换回正常模式。正常模式有更好的性能,新来的goroutine通过几次竞争可以直接获取到锁,尽管当前仍有等待的goroutine。而饥饿模式则是对正常模式的补充,防止等待队列中的goroutine永远没有机会获取锁。
以上是关于Golang下sync.Mutex专题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章