React Native 源码分析——Native View创建流程
Posted 薛瑄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了React Native 源码分析——Native View创建流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、React Native 源码分析(一)—— 启动流程
2、React Native 源码分析(二)—— 通信机制
3、React Native 源码分析(三)—— Native View创建流程
4、React Native 源码分析(四)—— 任务调度
5、React Native 源码分析(五)—— 事件分发
前两篇分析了,React Native 的启动和 通信机制,这篇来分析一下,在收到React 的通信数据字符串后,是如何在原生创建对应的View,React标签设置的View的属性,如何被原生View解析,为什么在自定义View调用requestLayout没有作用呢?
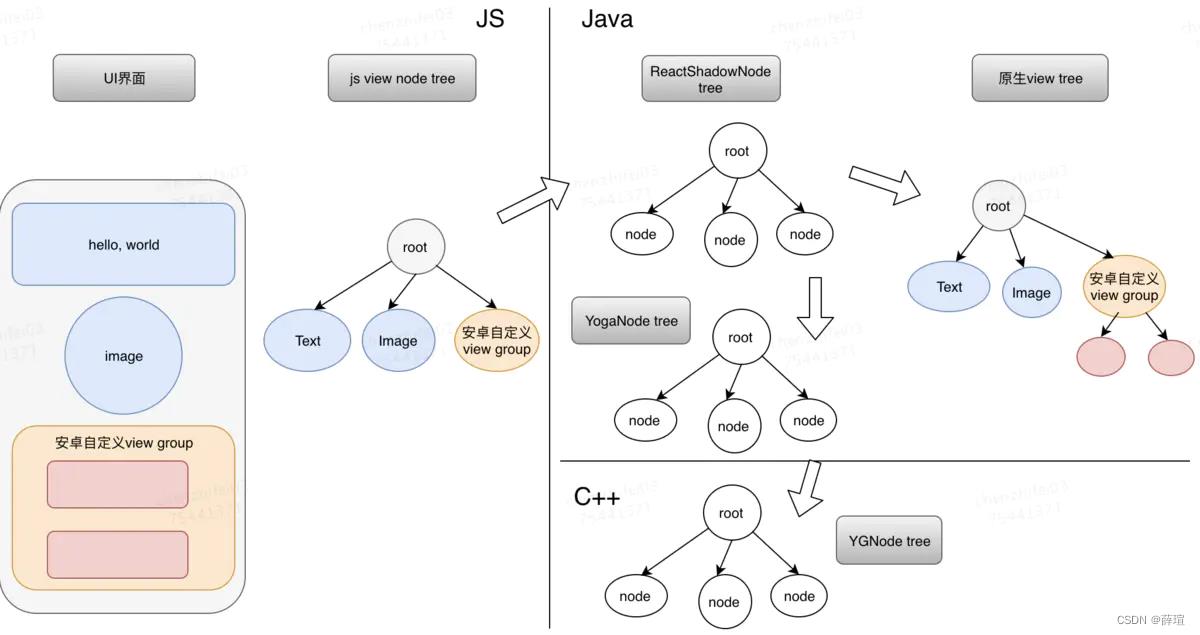
熟悉React 源码的小伙伴们应该知道,React对Component 最终解析为字符串,来提供给ReactNative 使用。在React 中是调用 UIManagerModule中提供的@ReactMethod 一系列方法,来实现在android创建View。下面先来看下ReactNative中UI相关的类图、各类的功能。然后我们从Android接收到这些字符串开始分析源码。
图一(来源)

图二(来源)

在开始分析源码前,先来看下,从React 传递过来的数据是什么样的,如下图,在桥通信中,是根据methodId找到对应的mMethod(这里是UIManager.createView),后续根据 [3,"RCTRawText",31,"text":"Press onChange"] 来创建View

下面我们就从上图断点堆栈中的UIManagerModule 开始分析
源码分析
1、UIManagerModule# createView
@ReactMethod
public void createView(int tag, String className, int rootViewTag, ReadableMap props)
mUIImplementation.createView(tag, className, rootViewTag, props);
UIManagerModule 中函数的具体实现都是交给UIImplementation处理的,下面来看看在UIImplementation中处理
2、UIImplementation# createView
/** Invoked by React to create a new node with a given tag, class name and properties. */
public void createView(int tag, String className, int rootViewTag, ReadableMap props)
if (!mViewOperationsEnabled)
return;
synchronized (uiImplementationThreadLock)
//首先创建ShadowNode,它用来表示React中一个对应的node,之后根据这个ShadowNode去创建对应的View
ReactShadowNode cssNode = createShadowNode(className);
ReactShadowNode rootNode = mShadowNodeRegistry.getNode(rootViewTag);
//设置node的tag ,它的值是在React中生成的,
cssNode.setReactTag(tag); // Thread safety needed here
cssNode.setViewClassName(className);
cssNode.setRootTag(rootNode.getReactTag());
cssNode.setThemedContext(rootNode.getThemedContext());
mShadowNodeRegistry.addNode(cssNode);
//根据React中该node设置的属性,来更新对应的ReactShadowNode
ReactStylesDiffMap styles = null;
if (props != null)
styles = new ReactStylesDiffMap(props);
//这里最终是调用了ReactShadowNode,@ReactProp注解方法的函数,把styles设置到ReactShadowNode的成员变量中的
cssNode.updateProperties(styles);
handleCreateView(cssNode, rootViewTag, styles);
下面介绍一下 该段代码的重要点,:
ReactShadowNode
ReactShadowNode 代表一个React nodes,可以理解为Android层对React层view的表示,它存在的主要目的是 :
- 为了View的measure、layout。ReactNative的中原生View的measure、layout 是由Yoga这个库来实现的,而不是使用原生的measure、layout 。
- 可以自定义属性,在React node中使用,例如 <Text/> 对应的ShadowNode,@ReactProp 定义了text属性,如下:
public class ReactRawTextShadowNode extends ReactShadowNodeImpl
@VisibleForTesting public static final String PROP_TEXT = "text";
private @Nullable String mText = null;
public ReactRawTextShadowNode()
@ReactProp(name = PROP_TEXT)
public void setText(@Nullable String text)
mText = text;
markUpdated();
public @Nullable String getText()
return mText;
@Override
public boolean isVirtual()
return true;
@Override
public String toString()
return getViewClass() + " [text: " + mText + "]";
ReactShadowNode、 YogaNode(java)、YogaNode(C++)是一一对应的,ReactNative 对View的测量、布局,是在Yoga框架中进行的,后面calculateRootLayout函数中会介绍
ReactTag
ReactTag是在React中创建的,单数表示 默认UI框架 ,双数表示Fabric框架的node。两种ReactNative架构的对比,可以参考React Native 源码分析(一)—— 启动流程
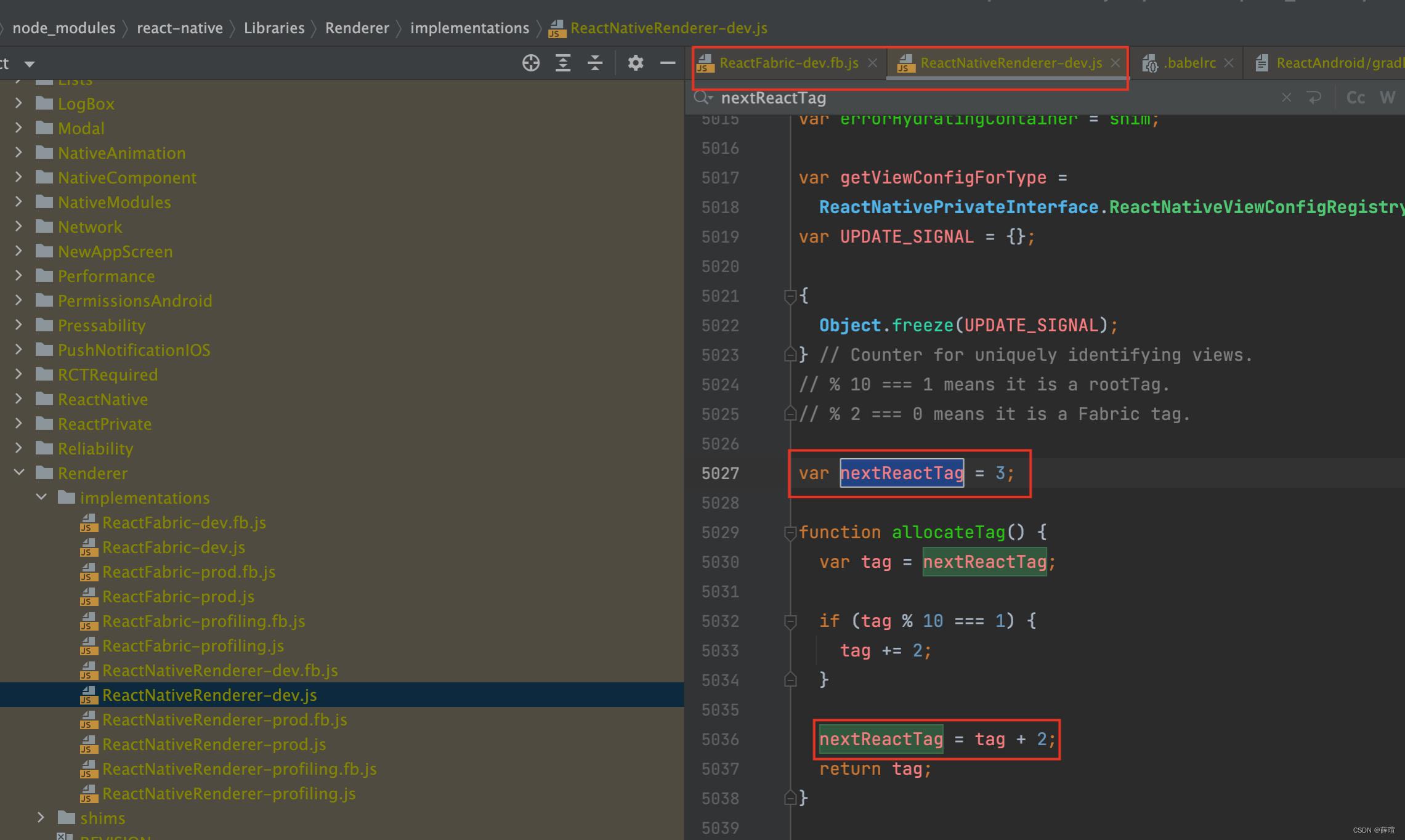
在ReactFabric-dev.js 中的nextReactTag = 2
在点击事件中,也会用到ReactTag 用于区分新旧UI框架,如下图:

React Native 0.64.2 针对异常Unable to find JSIModule for class UIManager,怎么定位这个错误,顺着点击事件去找,在上面这个红框的位置断点,等待错误uiManagerType的出现,为什么会错误,是因为自定义view 中子view的tag,没有按照ReactTag的分配规则
cssNode.updateProperties(styles);
ReactShadowNodeImpl 中的 updateProperties,会调用到ViewManagerPropertyUpdater.updateProps,如下
public static <T extends ReactShadowNode> void updateProps(T node, ReactStylesDiffMap props)
//查找ShadowNodeSetter,该接口有setProperty和getProperties 两个方法
ShadowNodeSetter<T> setter = findNodeSetter(node.getClass());
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Object>> iterator = props.mBackingMap.getEntryIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = iterator.next();
//设置属性值到ReactShadowNode中
setter.setProperty(node, entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
上面的实现比较抽象,具体ShadowNodeSetter的实现是什么,来看下面的代码
private static <T extends ReactShadowNode> ShadowNodeSetter<T> findNodeSetter(
Class<? extends ReactShadowNode> nodeClass)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//在缓存中查找
ShadowNodeSetter<T> setter = (ShadowNodeSetter<T>) SHADOW_NODE_SETTER_MAP.get(nodeClass);
if (setter == null)
//查找是否有 Class.forName(clsName + "$$PropsSetter"); 的类,如果没有提供就使用FallbackShadowNodeSetter
//我们在自定义ReactShadowNode时,也可以写个内部类PropsSetter,来实现属性赋值的操作
setter = findGeneratedSetter(nodeClass);
if (setter == null)
setter = new FallbackShadowNodeSetter<>(nodeClass);
SHADOW_NODE_SETTER_MAP.put(nodeClass, setter);
return setter;
如果没有提供PropsSetter,那么都会使用默认的FallbackShadowNodeSetter,下面来看看
private FallbackShadowNodeSetter(Class<? extends ReactShadowNode> shadowNodeClass)
//它会根据ReactShadowNode,把其中使用@ReactProp 注解的方法提取出来,用注解属性name的值 进行区分
mPropSetters =
ViewManagersPropertyCache.getNativePropSettersForShadowNodeClass(shadowNodeClass);
@Override
public void setProperty(ReactShadowNode node, String name, Object value)
//获取注解属性name的值 对应的函数,函数时以Method 的形式存储在类PropSetter中
ViewManagersPropertyCache.PropSetter setter = mPropSetters.get(name);
if (setter != null)
//通过反射,在对象node上调用函数,传值为value,这样就相当于是调用了ReactShadowNode中@ReactProp 注解的方法
setter.updateShadowNodeProp(node, value);
到此ReactShadowNode 就已经创建、赋值完成了,继续往下分析handleCreateView
3、UIImplementation# handleCreateView
protected void handleCreateView(
ReactShadowNode cssNode, int rootViewTag, @Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap styles)
//是否是一个虚拟的node,就是没有对应的native view。
// 那么有个疑问,没有对应的native view,那它的内容如何显示出来呢?
if (!cssNode.isVirtual())
mNativeViewHierarchyOptimizer.handleCreateView(cssNode, cssNode.getThemedContext(), styles);
通过图一,可以清楚看到,UIImplementation中的函数,都交给了NativeViewHierarchyOptimizer,对View 的层级进行优化
4、NativeViewHierarchyOptimizer# handleCreateView
/** Handles a createView call. May or may not actually create a native view. */
public void handleCreateView(
ReactShadowNode node,
ThemedReactContext themedContext,
@Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap initialProps)
//判断这个View 是否是一个纯容器view,它自身没有任何需要绘制的,只是为了包裹其他view
boolean isLayoutOnly =
node.getViewClass().equals(com.facebook.react.uimanager.ViewProps.VIEW_CLASS_NAME)
&& isLayoutOnlyAndCollapsable(initialProps);
node.setIsLayoutOnly(isLayoutOnly);
if (node.getNativeKind() != NativeKind.NONE)
//向队列中添加一个创建view的任务
mUIViewOperationQueue.enqueueCreateView(
themedContext, node.getReactTag(), node.getViewClass(), initialProps);
5、UIViewOperationQueue# enqueueCreateView
public void enqueueCreateView(
ThemedReactContext themedContext,
int viewReactTag,
String viewClassName,
@Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap initialProps)
synchronized (mNonBatchedOperationsLock)
mCreateViewCount++;
//添加到mNonBatchedOperations ArrayDeque
mNonBatchedOperations.addLast(
new CreateViewOperation(themedContext, viewReactTag, viewClassName, initialProps));
代码5.2
private final class CreateViewOperation extends ViewOperation
private final ThemedReactContext mThemedContext;
private final String mClassName;
private final @Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap mInitialProps;
public CreateViewOperation(
ThemedReactContext themedContext,
int tag,
String className,
@Nullable ReactStylesDiffMap initialProps)
super(tag);
mThemedContext = themedContext;
mClassName = className;
mInitialProps = initialProps;
Systrace.startAsyncFlow(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_VIEW, "createView", mTag);
@Override
public void execute()
//执行队列的任务时,会执行这里
Systrace.endAsyncFlow(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_VIEW, "createView", mTag);
mNativeViewHierarchyManager.createView(mThemedContext, mTag, mClassName, mInitialProps);
创建view的操作,被添加到mNonBatchedOperations后,在js->java 一批通信结束后,会调用这些操作,下面来看看
6、onBatchComplete
通过前两篇文章,我们知道,js->java 的回调是 CatalystInstanceImpl 中的静态内部类BridgeCallback,onBatchComplete调用过程如下
BridgeCallback#onBatchComplete -> NativeModuleRegistry#onBatchComplete -> UIManagerModule#onBatchComplete
UIManagerModule#onBatchComplete
为了省篇幅,就不贴代码了,执行 UIManagerModule中的onBatchComplete ,如果设置listener,就调用。最后调用到mUIImplementation.dispatchViewUpdates(batchId);
UIImplementation#onBatchComplete
/** Invoked at the end of the transaction to commit any updates to the node hierarchy. */
public void dispatchViewUpdates(int batchId)
...
final long commitStartTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
try
//更新Root及其子View 的大小、位置。子View的更新是添加到队列中的,代码7分析
updateViewHierarchy();
//在上个函数更新View的时候,会mTagsWithLayoutVisited.put(tag, true); 防止相同的更新被添加到队列。添加队列完成后,就清除mTagsWithLayoutVisited
mNativeViewHierarchyOptimizer.onBatchComplete();
//从队列中取出任务,添加到新线程中,等ReactChoreographer执行回调mDispatchUIFrameCallback时,会触发新线程中的任务,代码8分析
mOperationsQueue.dispatchViewUpdates(batchId, commitStartTime, mLastCalculateLayoutTime);
finally
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
7、UIImplementation #updateViewHierarchy
protected void updateViewHierarchy()
try
for (int i = 0; i < mShadowNodeRegistry.getRootNodeCount(); i++)
int tag = mShadowNodeRegistry.getRootTag(i);
ReactShadowNode cssRoot = mShadowNodeRegistry.getNode(tag);
//root view 的widthSpec、heightSpec 是 在ReactRootView中通过uiManager.updateRootLayoutSpecs设置的
if (cssRoot.getWidthMeasureSpec() != null && cssRoot.getHeightMeasureSpec() != null)
try
//递归通知所有cssNode 即将开始calculateLayout
notifyOnBeforeLayoutRecursive(cssRoot);
finally
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
//计算root view 的位置,通过YogaNative 来计算的
calculateRootLayout(cssRoot);
try
//递归更新子View,其中如果hasNewLayout()为true,就把更新子View的任务加入到队列UIViewOperationQueue
//然后设置标志位mHasNewLayout = false,后面在访问相同cssNode的 hasNewLayout()就是false
applyUpdatesRecursive(cssRoot, 0f, 0f);
finally
Systrace.endSection(Systrace.TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
...
...
下面分析一下其中的 calculateRootLayout和applyUpdatesRecursive
calculateRootLayout
calculateRootLayout(cssRoot);的调用过程如下:
ReactShadowNode 和 YogaNode是一一对应的
ReactShadowNode的实现是ReactShadowNodeImpl,YogaNode的实现有YogaNodeJNIBase
代码7.2
calculateRootLayout(cssRoot); //cssRoot 是根ReactShadowNode
-> ReactShadowNode# calculateLayout
-> YogaNodeJNIBase# calculateLayout(width, height); //广度优先遍历YogaNode节点
->YogaNative.jni_YGNodeCalculateLayoutJNI(mNativePointer, width, height, nativePointers, nodes);
//下面调用到C++,源码路径ReactAndroid/src/main/jni/first-party/yogajni/jni/YGJNIVanilla.cpp
->jni_YGNodeCalculateLayoutJNI
->YGNodeCalculateLayoutWithContext
->YGLayoutNodeInternal //这里会先从缓存中,取数据,如果没有就进行计算
->YGNodelayoutImpl // 这里就是RN 的 flexbox layout 算法的实现,
可以通过ReactShadowNode#setMeasureFunction() 来向YogaNode设置一个测量函数,在Yoga框架中 对UI进行计算时,就可以调用到我们自定义的Measure函数
举个例子:
ReactTextViewManager 中创建
public ReactTextShadowNode createShadowNodeInstance()
return new ReactTextShadowNode();
ReactTextShadowNode 的是继承ReactBaseTextShadowNode
构造函数会调用initMeasureFunction->setMeasureFunction,后者的实现是在ReactBaseTextShadowNode
@Override
public void setMeasureFunction(YogaMeasureFunction measureFunction)
mYogaNode.setMeasureFunction(measureFunction);
mYogaNode对应的类是 YogaNodeJNIBase
public void setMeasureFunction(YogaMeasureFunction measureFunction)
//最终还是在java中调用自定义的measure
mMeasureFunction = measureFunction;
//告诉YogaNative 有自定义的measure
YogaNative.jni_YGNodeSetHasMeasureFuncJNI(mNativePointer, measureFunction != null);
jni_YGNodeSetHasMeasureFuncJNI 调用到C++ src/main/jni/first-party/yogajni/jni/YGJNIVanilla.cpp
static void jni_YGNodeSetHasMeasureFuncJNI(
JNIEnv* env,
jobject obj,
jlong nativePointer,
jboolean hasMeasureFunc)
//调用到node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/yoga/yoga/YGNode.cpp 的setMeasureFunc
_jlong2YGNodeRef(nativePointer)
->setMeasureFunc(hasMeasureFunc ? YGJNIMeasureFunc : nullptr);
在YGNode.cpp 中,是把函数YGJNIMeasureFunc 设置到了measure_ 的YGMeasureFunc类型变量 noContext 中了,YGJNIMeasureFunc在下面会介绍到。
接着代码7.2 看看,在YGNodelayoutImpl 算法中,是如何调用到设置的measureFunction
->YGNodelayoutImpl
//hasMeasureFunc 就是判断measure_.noContext 是否为空
-> if (node->hasMeasureFunc())
YGNodeWithMeasureFuncSetMeasuredDimensions
-> const YGSize measuredSize = node->measure(
innerWidth,
widthMeasureMode,
innerHeight,
heightMeasureMode,
layoutContext);
//进入类 node_modules/react-native/ReactCommon/yoga/yoga/YGNode.cpp,见下图7.1
-> YGSize YGNode::measure(
float width,
YGMeasureMode widthMode,
float height,
YGMeasureMode heightMode,
void* layoutContext)
return facebook::yoga::detail::getBooleanData(flags, measureUsesContext_)
? measure_.withContext(
this, width, widthMode, height, heightMode, layoutContext)
: measure_.noContext(this, width, widthMode, height, heightMode);
//进入类 ReactAndroid/src/main/jni/first-party/yogajni/jni/YGJNIVanilla.cpp 中的YGJNIMeasureFunc,
//是在jni_YGNodeSetHasMeasureFuncJNI中设置的
//调用到java YogaNodeJNIBase 的measure函数,因为objectClass是YogaNodeJNIBase的对象
//见下图7.2
-> static const jmethodID methodId = facebook::yoga::vanillajni::getMethodId(
env, objectClass.get(), "measure", "(FIFI)J");
下图7.1

下图7.2

// Implementation Note: Why this method needs to stay final
//
// We cache the jmethodid for this method in Yoga code. This means that even if a subclass
// were to override measure, we'd still call this implementation from layout code since the
// overriding method will have a different jmethodid. This is final to prevent that mistake.
@DoNotStrip
public final long measure(float width, int widthMode, float height, int heightMode)
if (!isMeasureDefined())
throw new RuntimeException("Measure function isn't defined!");
//这里就调用到了自定义的measure
return mMeasureFunction.measure(
this,
width,
YogaMeasureMode.fromInt(widthMode),
height,
YogaMeasureMode.fromInt(heightMode));
最终每个YogaNode 测量、布局完的结果,会保存到YogaNodeJNIBase的 arr 数组中
applyUpdatesRecursive(cssRoot, 0f, 0f);的调用过程如下:
UIImplementation#applyUpdatesRecursive()
-> 以上是关于React Native 源码分析——Native View创建流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章