Android Jetpack 学习之旅--> Paging 的使用
Posted Kevin-Dev
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Jetpack 学习之旅--> Paging 的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
几乎所有的 android 开发者都会遇到在 RecyclerView 加载大量数据的情况,如果是在数据库请求,需要消耗数据库资源并且需要花费较多的时间,同样的,如果是发送网络请求,则需要消耗带宽和更多的时间,无论处于哪一种情形,对于用户的体验都是糟糕的。
介绍
1. 学习资料
官方文档:Paging
谷歌实验室:官方教程
官方Demo:网络方式,数据库方式
2. 谷歌官方介绍
The Paging Library helps you load and display small chunks of data at a time. Loading partial data on demand reduces usage of network bandwidth and system resources.
3. Paging 架构
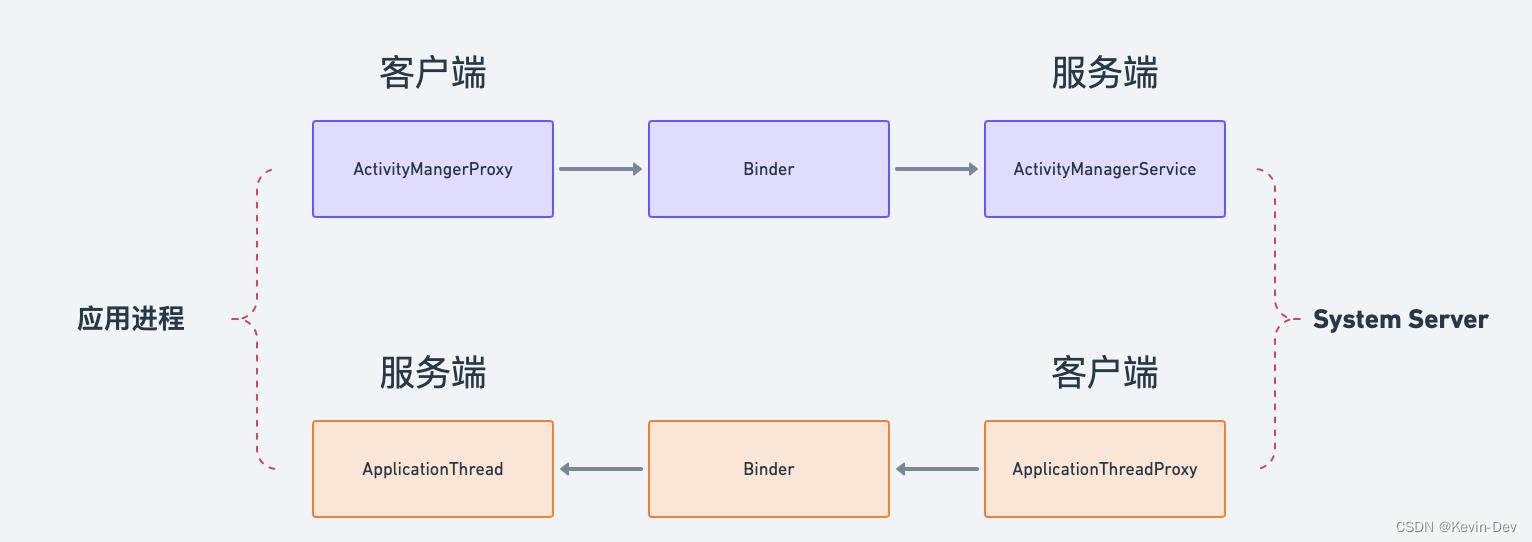
4. 优点
网上的分页解决方法挺多的,与他们相比,Paging 有什么优点呢?
RxJava 2以及Android Jetpack的支持,如LiveData、Room。- 自定义分页策略。
- 异步处理数据。
- 结合
RecyclerView等
实战
1. 效果图
2. 添加依赖
ext.pagingVersion = '2.1.0-alpha01'
dependencies
...
// paging
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:$pagingVersion"
3. 创建数据源
1)非 Room 数据库
如果没有使用 Room 数据库,我们需要自定义实现 DataSource ,通常实现 DataSource 有三种方式,分别继承三种抽象类,它们分别是:
-
PageKeyedDataSource<Key, Value>
分页请求数据的场景 -
ItemKeyedDataSource<Key, Value>
以表的某个列为key,加载其后的N个数据(个人理解以某个字段进行排序,然后分段加载数据) -
PositionalDataSource<T>
当数据源总数特定,根据指定位置请求数据的场景
// 因为代表着不同方式,所以不需要看Dao层
class ShoeRepository private constructor(private val shoeDao: ShoeDao)
/**
* 通过id的范围寻找鞋子
*/
fun getPageShoes(startIndex:Long,endIndex:Long):List<Shoe> = shoeDao.findShoesByIndexRange(startIndex,endIndex)
//... 省略
/**
* 自定义PageKeyedDataSource
* 演示Page库的时候使用
*/
class CustomPageDataSource(private val shoeRepository: ShoeRepository) : PageKeyedDataSource<Int, Shoe>()
private val TAG: String by lazy
this::class.java.simpleName
// 第一次加载的时候调用
override fun loadInitial(params: LoadInitialParams<Int>, callback: LoadInitialCallback<Int, Shoe>)
val startIndex = 0L
val endIndex: Long = 0L + params.requestedLoadSize
val shoes = shoeRepository.getPageShoes(startIndex, endIndex)
callback.onResult(shoes, null, 2)
// 每次分页加载的时候调用
override fun loadAfter(params: LoadParams<Int>, callback: LoadCallback<Int, Shoe>)
Log.e(TAG, "startPage:$params.key,size:$params.requestedLoadSize")
val startPage = params.key
val startIndex = ((startPage - 1) * BaseConstant.SINGLE_PAGE_SIZE).toLong() + 1
val endIndex = startIndex + params.requestedLoadSize - 1
val shoes = shoeRepository.getPageShoes(startIndex, endIndex)
callback.onResult(shoes, params.key + 1)
override fun loadBefore(params: LoadParams<Int>, callback: LoadCallback<Int, Shoe>)
// ... 省略 类似loadAfter
----------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------
/**
* 构建CustomPageDataSource的工厂
*/
class CustomPageDataSourceFactory(val shoeRepository: ShoeRepository):DataSource.Factory<Int,Shoe>()
override fun create(): DataSource<Int, Shoe>
return CustomPageDataSource(shoeRepository)
2)Room 数据库
直接在 Room 的 Dao 层中这样使用:
/**
* 鞋子的方法
*/
@Dao
interface ShoeDao
//... 省略
// 配合LiveData 返回所有的鞋子
@Query("SELECT * FROM shoe")
fun getAllShoesLD(): DataSource.Factory<Int, Shoe>
4. 构建 LiveData
想要获得 LiveData<PagedList> 则需要先创建 LivePagedListBuilder ,LivePagedListBuilder 有设分页数量和配置参数两种构造方法,设置分页数量比较简单,直接查看 Api 就可以使用,我们看看如何配置参数使用:
class ShoeModel constructor(shoeRepository: ShoeRepository) : ViewModel()
// 鞋子集合的观察类
val shoes: LiveData<PagedList<Shoe>> = LivePagedListBuilder<Int, Shoe>(
CustomPageDataSourceFactory(shoeRepository) // DataSourceFactory
, PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(10) // 分页加载的数量
.setEnablePlaceholders(false) // 当item为null是否使用PlaceHolder展示
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(10) // 预加载的数量
.build())
.build()
5. 创建 PagedListAdapter
PagedListAdapter 就是特殊的 RecyclerView 的 RecyclerAdapter,跟 RecyclerAdapter 一样,需要继承并实现其方法,这里使用了 Data Binding:
/**
* 鞋子的适配器 配合Data Binding使用
*/
class ShoeAdapter constructor(val context: Context) :
PagedListAdapter<Shoe, ShoeAdapter.ViewHolder>(ShoeDiffCallback())
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder
return ViewHolder(
RecyclerItemShoeBinding.inflate(
LayoutInflater.from(parent.context)
, parent
, false
)
)
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int)
val shoe = getItem(position)
holder.apply
bind(onCreateListener(shoe!!.id), shoe)
itemView.tag = shoe
/**
* Holder的点击事件
*/
private fun onCreateListener(id: Long): View.OnClickListener
return View.OnClickListener
val intent = Intent(context, DetailActivity::class.java)
intent.putExtra(BaseConstant.DETAIL_SHOE_ID, id)
context.startActivity(intent)
class ViewHolder(private val binding: RecyclerItemShoeBinding) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root)
fun bind(listener: View.OnClickListener, item: Shoe)
binding.apply
this.listener = listener
this.shoe = item
executePendingBindings()
ShoeDiffCallback
class ShoeDiffCallback: DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Shoe>()
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: Shoe, newItem: Shoe): Boolean
return oldItem.id == newItem.id
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: Shoe, newItem: Shoe): Boolean
return oldItem == newItem
6. 监听数据
/**
* 鞋子页面
*/
class ShoeFragment : Fragment()
// ... 省略
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View?
val binding: FragmentShoeBinding = FragmentShoeBinding.inflate(inflater, container, false)
context ?: return binding.root
val adapter = ShoeAdapter(context!!)
binding.recycler.adapter = adapter
onSubscribeUi(adapter)
return binding.root
/**
* 鞋子数据更新的通知
*/
private fun onSubscribeUi(adapter: ShoeAdapter)
viewModel.shoes.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, Observer
if (it != null)
adapter.submitList(it)
)
阅读推荐
小结

以上是关于Android Jetpack 学习之旅--> Paging 的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android Jetpack 学习之旅--> Data Binding 的使用
Android Jetpack学习之旅--> Navigation 的使用
Android Jetpack 学习之旅--> ViewModel & LiveData 的使用
Android Jetpack 学习之旅--> Room 的使用