深入理解Java虚拟机——方法调用(静态分派调用)
Posted 小志的博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深入理解Java虚拟机——方法调用(静态分派调用)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、静态分派调用
1.1、方法静态分派调用演示
-
示例代码
/** * @description: 静态分派调用示例 * @author: xz */ public class Test3 static class Parent static class Child1 extends Parent static class Child2 extends Parent public void hello(Parent parent) System.out.println("hello parent"); public void hello(Child1 child1) System.out.println("hello child1"); public void hello(Child2 child2) System.out.println("hello child2"); public static void main(String[] args) Parent p1 = new Child1(); Parent p2 = new Child2(); Test3 test3 = new Test3(); test3.hello(p1); test3.hello(p2); -
输出结果
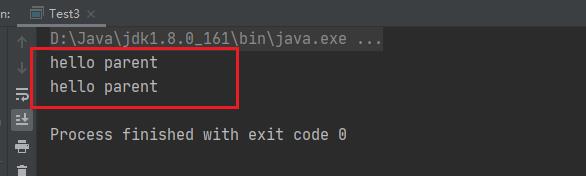
-
总结
由输出结果可知,执行的是参数类型为Parent 的重载。
1.2、静态类型和实例类型
1.2.1、静态类型
- 上面的代码中的“Parent”称为变量的静态类型(Static Type),或者叫做外观类型(Apparent Type)。
1.2.2、实例类型
- 上面的代码中的“Child1”称为变量的实例类型(Actual Type)。
1.2.2、静态类型和实例类型的区别
-
静态类型的变化仅仅在使用时发生,变量本身的静态类型不会改变,并且最终的静态类型是在编译期可知的。
-
实际类型变化的结果再运行期才可确定,编译器在编译程序的时候并不知道一个对象的实际类型是什么。
-
例如下面的代码:
/**实际类型变化*/ Parent p1 = new Child1(); p1 =new Child2();/**静态类型变化*/ test3.hello((Child1)p1); test3.hello((Child1)p2);
1.3、静态分派调用的概述
- 所有依赖静态类型来定位方法自行版本的分派动作称为静态分派。静态分派的典型应用是方法重载。
- 静态分派发生在编译阶段,因此确定静态分派的动作实际上不是由虚拟机来执行的。
以上是关于深入理解Java虚拟机——方法调用(静态分派调用)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章