6个非常实用的 Python 代码块,适合收藏~
Posted Python学习与数据挖掘
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了6个非常实用的 Python 代码块,适合收藏~相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
大家好,今天分享几个平时我会用到的 Python 代码块,每个都小而精,喜欢记得关注、点赞、收藏。
1,批量修改文件名
日常工作中,可能会有这样的需求:把一个文件夹下所有 jpg 图片转化为 png ;假设文件夹下只有4、5 张,手动修改的话是没问题,但如果数量达到上百张,就有点让人头疼,这个代码块正是用来解决此类问题的
import os
def batch_rename(work_dir, old_ext, new_ext):
# files = os.listdir(work_dir)
for filename in os.listdir(work_dir):
# Get the file extension
split_file = os.path.splitext(filename)
# Unpack tuple element
root_name, file_ext = split_file
# Start of the logic to check the file extensions, if old_ext = file_ext
if old_ext == file_ext:
# Returns changed name of the file with new extention
newfile = root_name + new_ext
# Write the files
os.rename(
os.path.join(work_dir, filename),
os.path.join(work_dir, newfile)
)
print("rename is done!")
print(os.listdir(work_dir))
2 ,返回文件夹下所有指定文件名
有时我们需要统计一下当前文件夹下中包含全部的 png 文件或者说含有 png 图片数量,此功能常用于文件检索;标准库 os 虽然有一些很强大的函数,但没有一个能满足我们这个需求,那么我想下面的这个代码块或许能帮到你!
def get_filename(path,filetype): # 输入路径、文件类型 例如'.csv'
name = []
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path):
for i in files:
if filetype+' ' in i+' ': # 这里后面不加一个字母可能会出问题,加上一个(不一定是空格)可以解决99.99%的情况
name.append(i)
return name # 输出由有后缀的文件名组成的列表
3,文件夹不存在时自动创建
这个功能在日常开发办公中会经常用到,主要用到了 os 模块的两个函数
-
os.path.exists(path)判断文件夹是否存在; -
os.makedirs(path)创建文件夹
import os # Import the OS module
MESSAGE = 'The directory already exists.'
TESTDIR = 'testdir'
try:
home = os.path.expanduser("~")
print(home) # Print the location
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(home, TESTDIR)): # os.path.join() for making a full path safely
os.makedirs(os.path.join(home, TESTDIR)) # If not create the directory, inside their home directory
else:
print(MESSAGE)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
4,打印当前运行环境
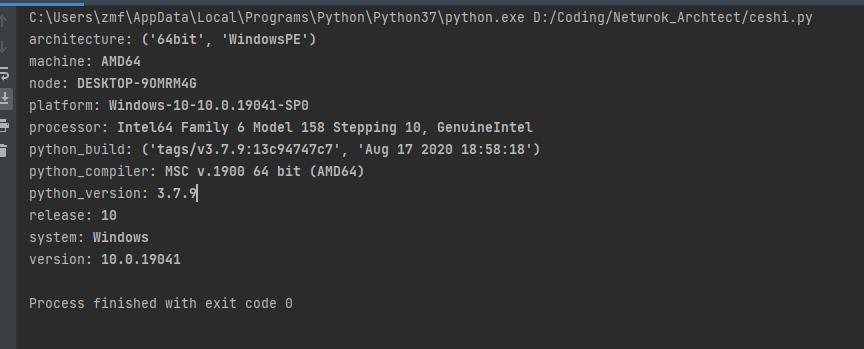
如果你想利用 Python 脚本快速查看当前电脑的系统(Linux、Windows)、架构(32位还是 64 位)、处理器、Python 版本及运行环境等信息,下面这个代码块能够帮到你
import platform as pl
profile = [
'architecture',
'machine',
'node',
'platform',
'processor',
'python_build',
'python_compiler',
'python_version',
'release',
'system',
'version',
]
class bcolors:
HEADER = '\\033[95m'
OKBLUE = '\\033[94m'
OKGREEN = '\\033[92m'
WARNING = '\\033[93m'
FAIL = '\\033[91m'
ENDC = '\\033[0m'
BOLD = '\\033[1m'
UNDERLINE = '\\033[4m'
for key in profile:
if hasattr(pl, key):
print(key + bcolors.BOLD + ": " + str(getattr(pl, key)()) + bcolors.ENDC)
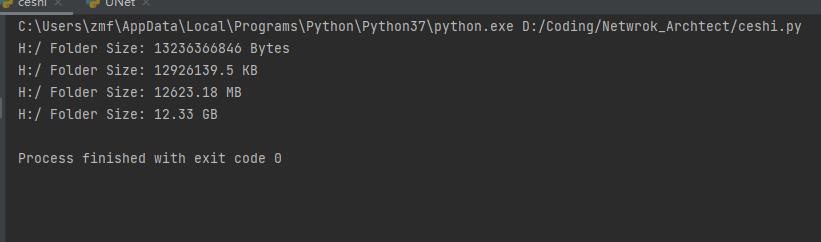
5,获取指定文件夹下内存大小
日常工作中这个模块我们可能用不到,查看文件大小的话用代码跑还不如直接鼠标右键查看该文件的属性信息;但是,对于以后开发工作中,可以将此功能镶嵌到开发的软件中,作为一个 监控文件夹内存大小 的功能存在
import os
import sys # Load the library module and the sys module for the argument vector'''
try:
directory = "H:/" # Set the variable directory to be the argument supplied by user.
except IndexError:
sys.exit("Must provide an argument.")
dir_size = 0 # Set the size to 0
fsizedicr = 'Bytes': 1,
'KB': float(1) / 1024,
'MB': float(1) / (1024 * 1024),
'GB': float(1) / (1024 * 1024 * 1024)
for (path, dirs, files) in os.walk(
directory):
for file in files: # Get all the files
filename = os.path.join(path, file)
dir_size += os.path.getsize(filename) # Add the size of each file in the root dir to get the total size.
fsizeList = [str(round(fsizedicr[key] * dir_size, 2)) + " " + key for key in fsizedicr] # List of units
if dir_size == 0:
print("File Empty") # Sanity check to eliminate corner-case of empty file.
else:
for units in sorted(fsizeList)[::-1]: # Reverse sort list of units so smallest magnitude units print first.
print(" Folder Size: ".format(directory)+ units)
6, 定时关机或重启
os 中 system 函数可通过设定一些参数,实现开关机包含定时命令;另外声明一下,此代码块仅供科普,如果正在用电脑的话请勿尝试,,,
import os
from os import system
# 关机
# os.system("shutdown -s -t 60 ")
# 重启
system("shutdown -r -t 100")
小结
以上是本篇文章的全部内容了,希望这 几个代码块能够对你以后日常工作有所帮助,觉得文章内容不错的话请记得点个赞,也算是对我的鼓励,
推荐文章
技术交流
欢迎转载、收藏、有所收获点赞支持一下!

目前开通了技术交流群,群友已超过2000人,添加时最好的备注方式为:来源+兴趣方向,方便找到志同道合的朋友
- 方式①、发送如下图片至微信,长按识别,后台回复:加群;
- 方式②、添加微信号:dkl88191,备注:来自CSDN
- 方式③、微信搜索公众号:Python学习与数据挖掘,后台回复:加群

 阅读世界,共赴山海
阅读世界,共赴山海
 423全民读书节,邀你共读
423全民读书节,邀你共读
以上是关于6个非常实用的 Python 代码块,适合收藏~的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章