线程池基本原理详解答
Posted super码王
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了线程池基本原理详解答相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
线程池优点
- 降低系统资源消耗。通过重用已存在的线程,降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
- 提高系统响应速度。当有任务到达时,通过复用已存在的线程,无需等待新线程的创建便能立即执行。
- 方便线程并发数的管控。因为线程若是无限制的创建,可能会导致内存占用过多而产生OOM,并且会造成cpu过度切换,cpu切换线程是有时间成本的,例如需要保持当前执行线程的现场,并恢复要执行线程的现场。
- 提供额外更强大的功能。延时定时线程池。
线程池源码类
-
ThreadPoolExecutor
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, // 核心线程数,常驻人员
int maximumPoolSize, // 最大线程数 》核心线程数,常驻人员+临时工
long keepAliveTime, // 保活时间
TimeUnit unit, // 保活时间单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, // 任务队列
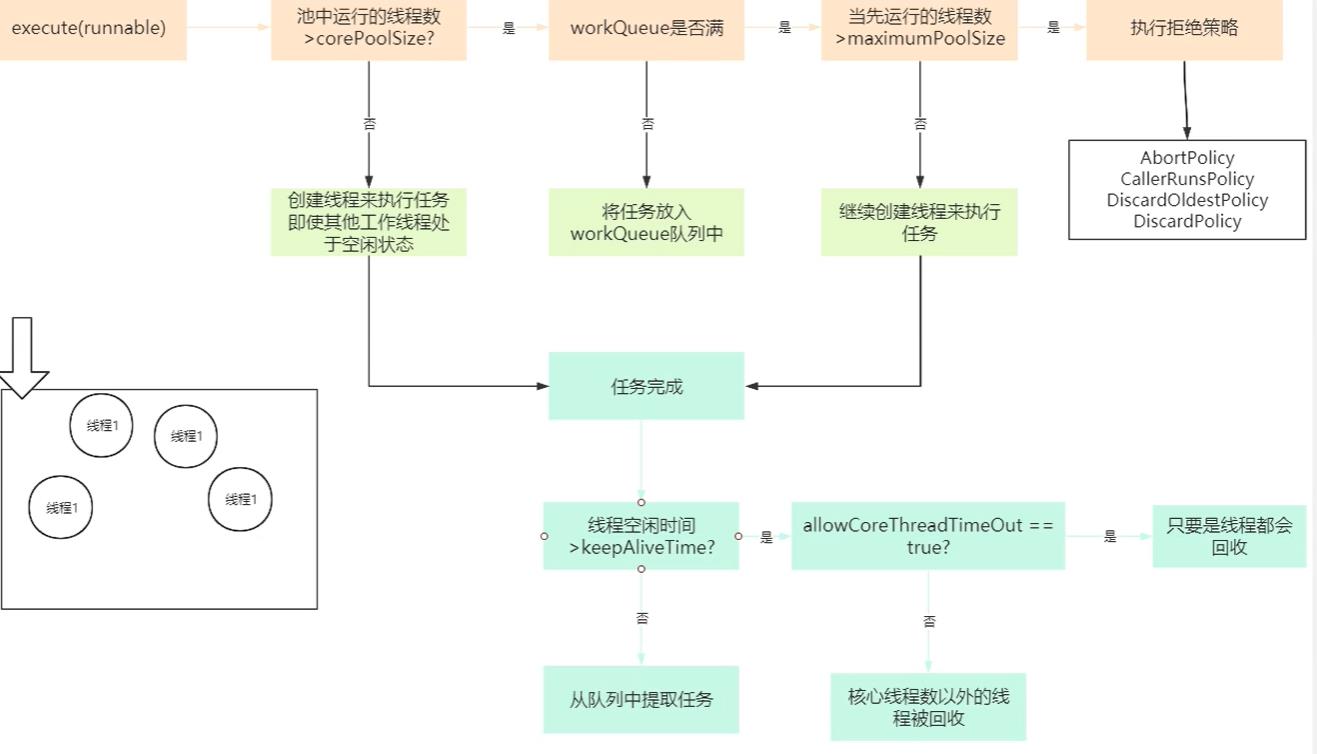
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) // 拒绝策略线程池执行流程
线程池使用代码示例
package com.wust.yq;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class test01
public static void main(String[] args)
LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3);
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 6, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue);
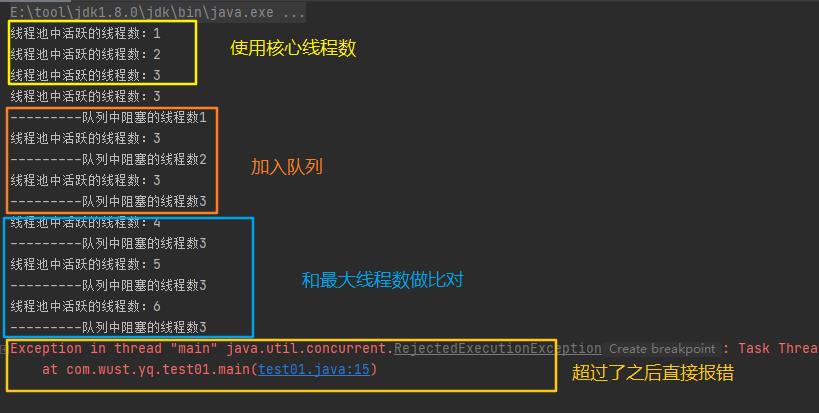
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
MyTestThread t = new MyTestThread();
t.setName(i + "hehe");
threadPool.execute(t);
System.out.println("线程池中活跃的线程数:" + threadPool.getPoolSize());
if (queue.size() > 0)
System.out.println("---------队列中阻塞的线程数" + queue.size());
threadPool.shutdown();
static class MyTestThread extends Thread
@Override
public void run()
try
Thread.sleep(3000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
运行效果截图
拒绝策略类
- AbortPolicv:默认策略,直接抛出异常
- CallerRunsPolicy: 掉线程池中的线程执行
- DiscardOldestPolicy: 抛弃最近的线程正执行的任务,然后执行需要执行的任务
- DiscardPolicy: 直接抛弃,不做处理
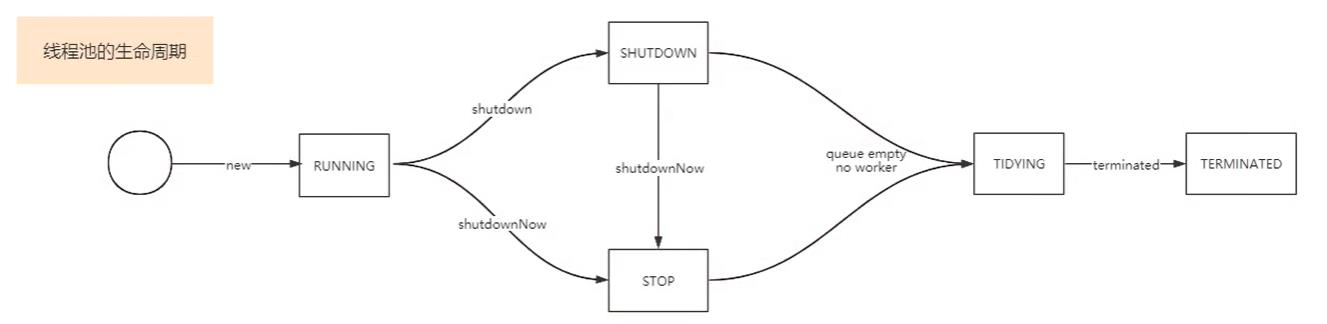
线程池的生命周期
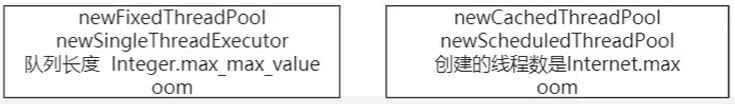
线程池类型(不建议使用)

以上是关于线程池基本原理详解答的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章