Spring AOP 切面增强
Posted jiguansheng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring AOP 切面增强相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景
背景:我们在开发过程中,经常需要做些周边功能: 性能统计、日志、事物管理。我们需要考虑如何解耦这些周边功能开发和核心业务开发区分开达到提升代码质量目的。
定义
在AOP思想里面定义
周边功能定义是(性能统计、日志、事务管理),被定义成切面。
核心功能和切面功能单独开发。
然后把核心功能和切面功能编织在一起。
核心概念
在AOP概念里,所有的方法称为连接点。
被AOP应用拦截到的方法称为切点。
我们在切点前后添加一段逻辑代码比如方法前、方法后、方法前后。称为增强/通知。
切面是切点和增强/通知总成
织入: 把切面加入对象,并创建代理对象过程叫做织入。 这个工作是由spring完成的。
切点
每个方法都可以称为连接点。
定义增强/通知代码
@Before 目标方法调用前通知
@AfterReturning 目标方法成功返回后通知
@After 目标方法调用之后通知
@AfterThrowing 目标方法抛出异常后通知
@Around 环绕执行
aop简单示例
定义业务Service
public interface AnswerService
void answerQuestion();
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AnswerServiceImpl implements AnswerService
@Override
public void answerQuestion()
Answer answer = new Answer();
answer.setId(1L)
.setAuthor("jiguansheng")
.setContent("笨笨是好宝宝");
log.info(answer.toString());
定义切面
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class SpringLearnAop
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.springcorelearn.answer..*(..))")
public void definitionPointCut()
@AfterReturning("definitionPointCut()")
public void afterProcess()
log.info("结束了。。。。");
@Before("definitionPointCut()")
public void beforeProcess()
log.info("想到我了");
输出
想到我了
Answer(id=1, content=笨笨是好宝宝, author=jiguansheng)
结束了。。。。
熟悉Spring AOP之前一定要熟悉Spring ApplicationContext启动流程和bean生命周期。
Spring 工作流程
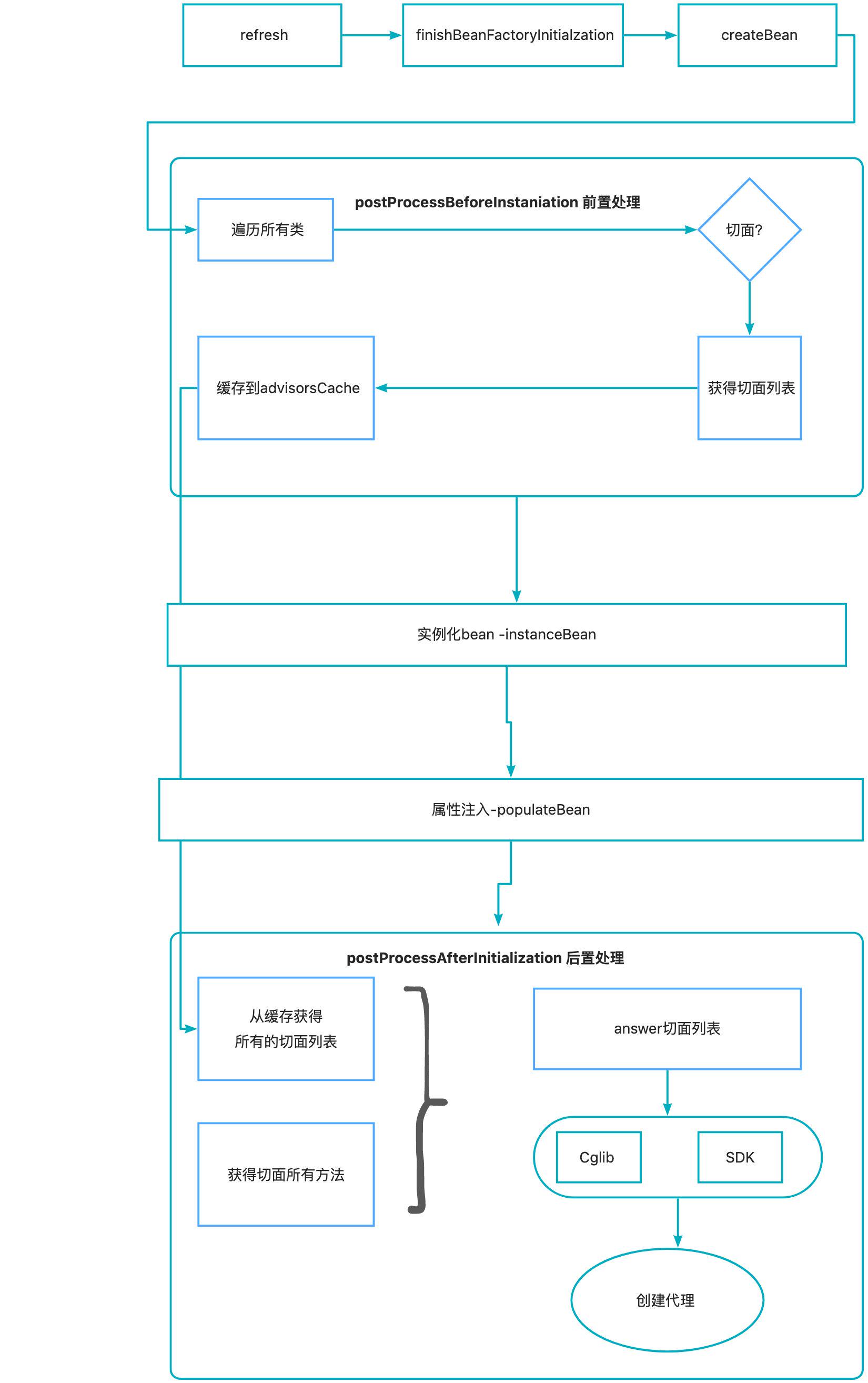
分析
postProcessBeforeInstantiation 实例化前处理
创建AnswerService 前置处理。遍历容器所有的类,查找并遍历所有的切面信息。然后将切面信息保存到缓存中。比如案例中的SpringLearnAop。
postProcessAfterInitializaiton 初始化后处理
获得AnswerService 切面信息: 首先从缓存中拿到切面信息和AnswerService 方法。然后找到所有需要进行AOP的方法。
创建AOP代理对象:视AnswerService是否是接口。是接口采用sdk代理。若不是采用cglib代理。
代码入口
refresh
源码
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
//
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
catch (BeansException ex)
finally
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException
if (logger.isTraceEnabled())
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames)
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit())
if (isFactoryBean(beanName))
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean)
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean)
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
else
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
if (isEagerInit)
getBean(beanName);
else
getBean(beanName);
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames)
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton)
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null)
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
, getAccessControlContext());
else
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
smartInitialize.end();
分析
finishBeanFactoryInitialization 初始化所有关联的非懒加载的单例。
instantiate all remaing (non-lazy-init) singletons
主要调用了preInstantiateSingletons()->beanFactory.getBean,对所有bean实例化操作。
getBean
源码
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton())
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () ->
try
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
catch (BeansException ex)
//
);
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
分析
若bean不存在,调用createBean创建
createBean
源码
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null)
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
// Prepare method overrides.
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
try
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null)
return bean;
分析
resolveBeforeInstantiation
createBean 埋入前置处理器。
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
源码
@Nullable
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware)
Object result = bp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null)
return result;
return null;
而InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 有个类是AnnotationAwareAsepctJAutoProxyCreator 处理。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
源码
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
//....
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName))
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null)
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName))
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
return null;
分析
shouldSkip方法非常重要.由于其等于true。所以还是返回null。
shouldSkip
源码
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
// TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect names
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors)
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&
((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName))
return true;
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
分析
findCandidateAdvisors 非常重要,作用是查询可能的切面信息。
findCandidateAdvisors
源码
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors()
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null)
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
分析
重点是buildAspectJAdvisors方法
buildAspectJAdvisors
源码
/**
* Look for AspectJ-annotated aspect beans in the current bean factory,
* and return to a list of Spring AOP Advisors representing them.
* <p>Creates a Spring Advisor for each AspectJ advice method.
* @return the list of @link org.springframework.aop.Advisor beans
* @see #isEligibleBean
*/
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors()
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null)
synchronized (this)
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null)
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
//1、取出所有的bean名称
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
//2、遍历所有bean
for (String beanName : beanNames)
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName))
continue;
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);
if (beanType == null)
continue;
//3、是否是切面类
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType))
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON)
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
//4、获得切面列表
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName))
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
else
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
else
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
if (aspectNames.isEmpty())
return Collections.emptyList();
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames)
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null)
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
else
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
return advisors;
分析
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors
看方法参数是lb、Object.class 。 获取符合类型的所有bean。类型是Object。说明查询所有的beanName
for (String beanName : beanNames)
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);
this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)
遍历所有的bean,检查其是否是aop切面元数据类。
取出aop切面元数据类的增强通知方法。转化成Advice 类。
存入advisors 集合中。
isAspect
源码
@Override
public boolean isAspect(Class<?> clazz)
return (hasAspectAnnotation(clazz) && !compiledByAjc(clazz));
private boolean hasAspectAnnotation(Class<?> clazz)
return (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(clazz, Aspect.class) != null);
分析
判断类是否是切面元数据配置。是否有Aspect 注解
getAdvisors
源码
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory)
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
//getAdvisorMethod 遍历所有方法
//查找切点定义方法。
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass))
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);
if (advisor != null)
advisors.add(advisor);
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated())
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields())
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null)
advisors.add(advisor);
return advisors;
getAdvisorMethod
源码
// Exclude @Pointcut methods
private static final MethodFilter adviceMethodFilter = ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS
.and(method -> (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null));
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass)
List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, methods::add, adviceMethodFilter);
if (methods.size() > 1)
methods.sort(adviceMethodComparator);
return methods;
分析
取得类所有增强通知的注解(@After @AfterReturning @Before @Around @AfterThrowing),忽略Pointcut注解
getAdvisor
源码
@Override
@Nullable
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName)
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null)
return null;
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
源码
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName)
//。。。。。
if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated())
//省略去懒加载部分配置代码。
else
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
//实例化切面通知
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
instantiateAdvice
源码
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut)
Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
getAdvice
源码
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName)
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null)
return null;
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType())
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
return null;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning()))
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing()))
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null)
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
分析
按增强通知注解走不同逻辑分支,实例化切面信息。
3、 是否是配置类
advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
postProcessAfterInitializaiton 后置处理
源码
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors())
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null)
return result;
result = current;
return result;
AbstractAutoProxyCreator
源码
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName)
if (bean != null)
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean)
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
return bean;
wrapIfNecessary
源码
/**
* Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access
* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey)
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName))
return bean;
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey)))
return bean;
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName))
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY)
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
分析
如源码所见,如果我们对此增强通知,那么我们创建代理。
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
源码
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource)
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty())
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
return advisors.toArray();
分析
findEligibleAdvisors 查询匹配的切面
findEligibleAdvisors
源码
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty())
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
return eligibleAdvisors;
分析
findCandidateAdvisors 查询匹配切面并返回。
findCandidateAdvisor
源码
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors()
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null)
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
分析
aspectJAdvisorBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors 读取前置处理的保存的切面信息。
再回到findEligibleAdvisors。
findAdvisorsThatCanApply
源码
/**
* Search the given candidate Advisors to find all Advisors that
* can apply to the specified bean.
* @param candidateAdvisors the candidate Advisors
* @param beanClass the target's bean class
* @param beanName the target's bean name
* @return the List of applicable Advisors
* @see ProxyCreationContext#getCurrentProxiedBeanName()
*/
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
finally
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply
源码
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz)
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty())
return candidateAdvisors;
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors)
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz))
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
//遍历每一个增强通知
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors)
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor)
// already processed
continue;
//能否应用在answerService上。
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions))
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
return eligibleAdvisors;
分析
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors)
遍历每一个增强通知。
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions))
评估是否能应用在answerService上。
若匹配上返回候选的增强通知。
canApply
源码
/**
* Can the given advisor apply at all on the given class?
* <p>This is an important test as it can be used to optimize out an advisor for a class.
* This version also takes into account introductions (for IntroductionAwareMethodMatchers).
* @param advisor the advisor to check
* @param targetClass class we're testing
* @param hasIntroductions whether the advisor chain for this bean includes
* any introductions
* @return whether the pointcut can apply on any method
*/
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions)
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor)
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor)
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
else
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
/**
* Can the given pointcut apply at all on the given class?
* <p>This is an important test as it can be used to optimize
* out a pointcut for a class.
* @param pc the static or dynamic pointcut to check
* @param targetClass the class to test
* @param hasIntroductions whether the advisor chain
* for this bean includes any introductions
* @return whether the pointcut can apply on any method
*/
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions)
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass))
return false;
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE)
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher)
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass))
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes)
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods)
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass))
return true;
return false;
分析
canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions)
pca.getPointcut() 取出匹配增强器的切点(pointcut)。
tartgetClass 目标类。
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) for (Method method : methods)
取目标类所有的方法和MethodMatcher做决策。是否匹配目标方法。若匹配返回true。
返回 wrapIfNecessary 方法
创建代理
源码
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));createProxy
源码
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource)
//省略若干行代码
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
// Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader
ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader();
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader())
classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader();
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
分析
简单理解就是 实例化ProxyFactory 代理工厂对象并返回代理类。
getProxy
源码
public Object getProxy()
return createAopProxy().getProxy();
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy()
if (!this.active)
activate();
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
DefaultAopProxyFactory.createAopproxy
源码
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() &&
(config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)))
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null)
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(targetClass))
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
else
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
分析
决策目标类是否是个接口。是的使用sdk代理 (jdkDnynamicAopProxy)否则采用ObjenesisCglibAopProxy.
以上是关于Spring AOP 切面增强的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章