RabbitMQ 服务异步通信 -- 入门案例(消息预存机制)SpringAMQP发布订阅模式(FanoutExchangeDirectExchangeTopicExchange)消息转换器
Posted CodeJiao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了RabbitMQ 服务异步通信 -- 入门案例(消息预存机制)SpringAMQP发布订阅模式(FanoutExchangeDirectExchangeTopicExchange)消息转换器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
- 1. 入门案例
- 2. 完成官方Demo中的hello world案例
- 3. SpringAMQP
- 4. 消息转换器
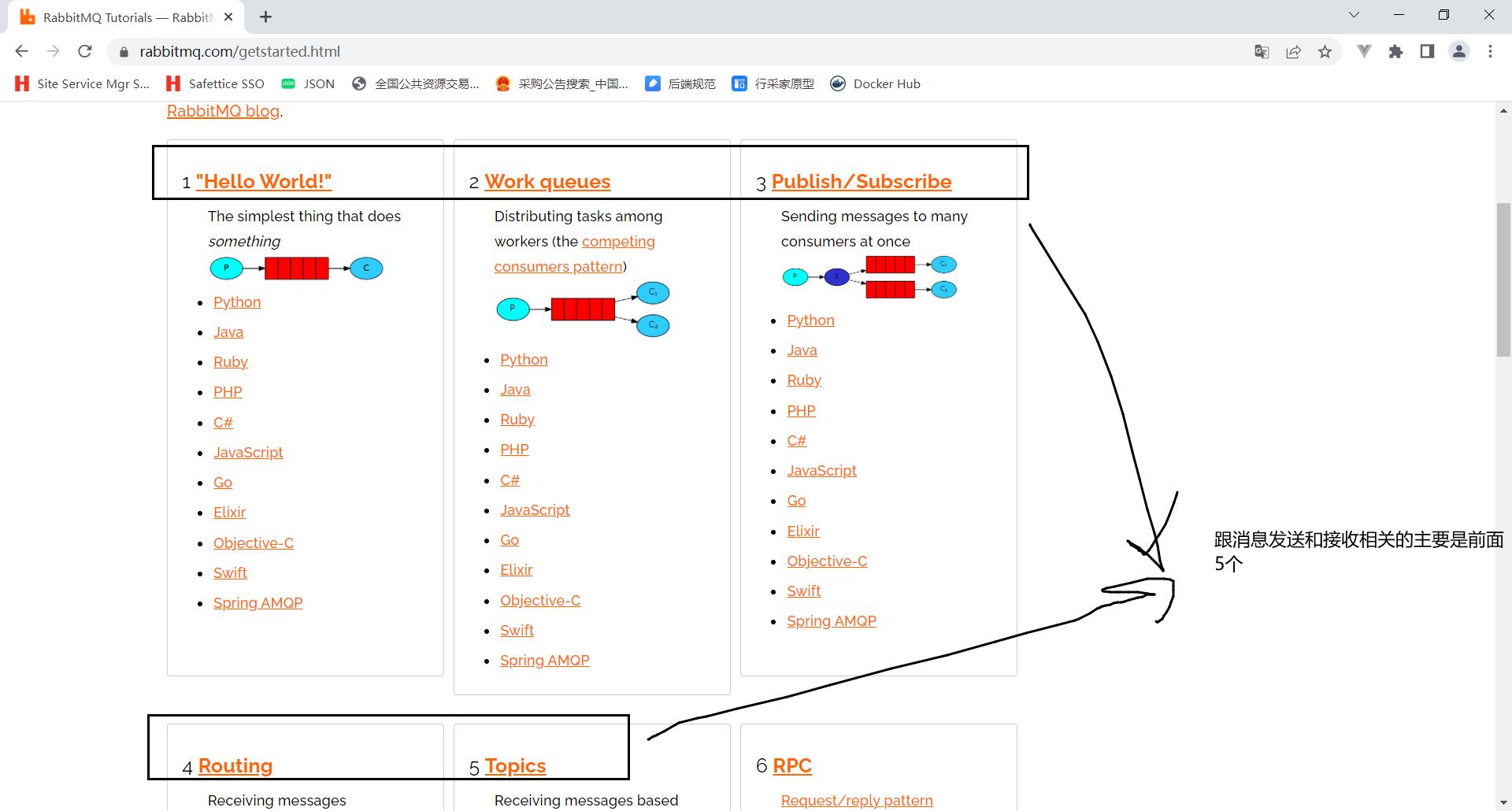
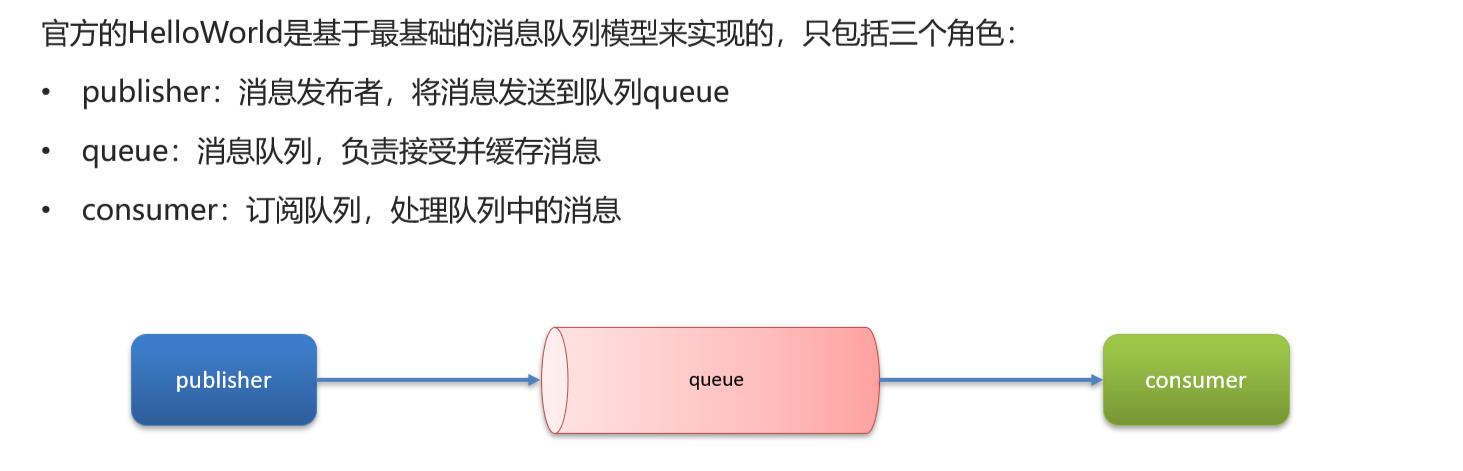
1. 入门案例

2. 完成官方Demo中的hello world案例
2.1 创建1个工程,2个模块
2.1.1 父工程的依赖,子工程不需要导入额外的依赖

<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.1.2 配置子工程的配置文件(内容一样)

logging:
pattern:
dateformat: MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS
2.1.3 编写发布者的test文件

package cn.itcast.mq.helloworld;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class PublisherTest
@Test
public void testSendMessage() throws IOException, TimeoutException
// 1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
// 1.1.设置连接参数,分别是:主机名、端口号、vhost、用户名、密码
factory.setHost("192.168.135.130");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("codejiao");
factory.setPassword("317525");
// 1.2.建立连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
// 2.创建通道Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3.创建队列
String queueName = "simple.queue";
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
// 4.发送消息
String message = "hello, rabbitmq!";
channel.basicPublish("", queueName, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("发送消息成功:【" + message + "】");
// 5.关闭通道和连接
channel.close();
connection.close();
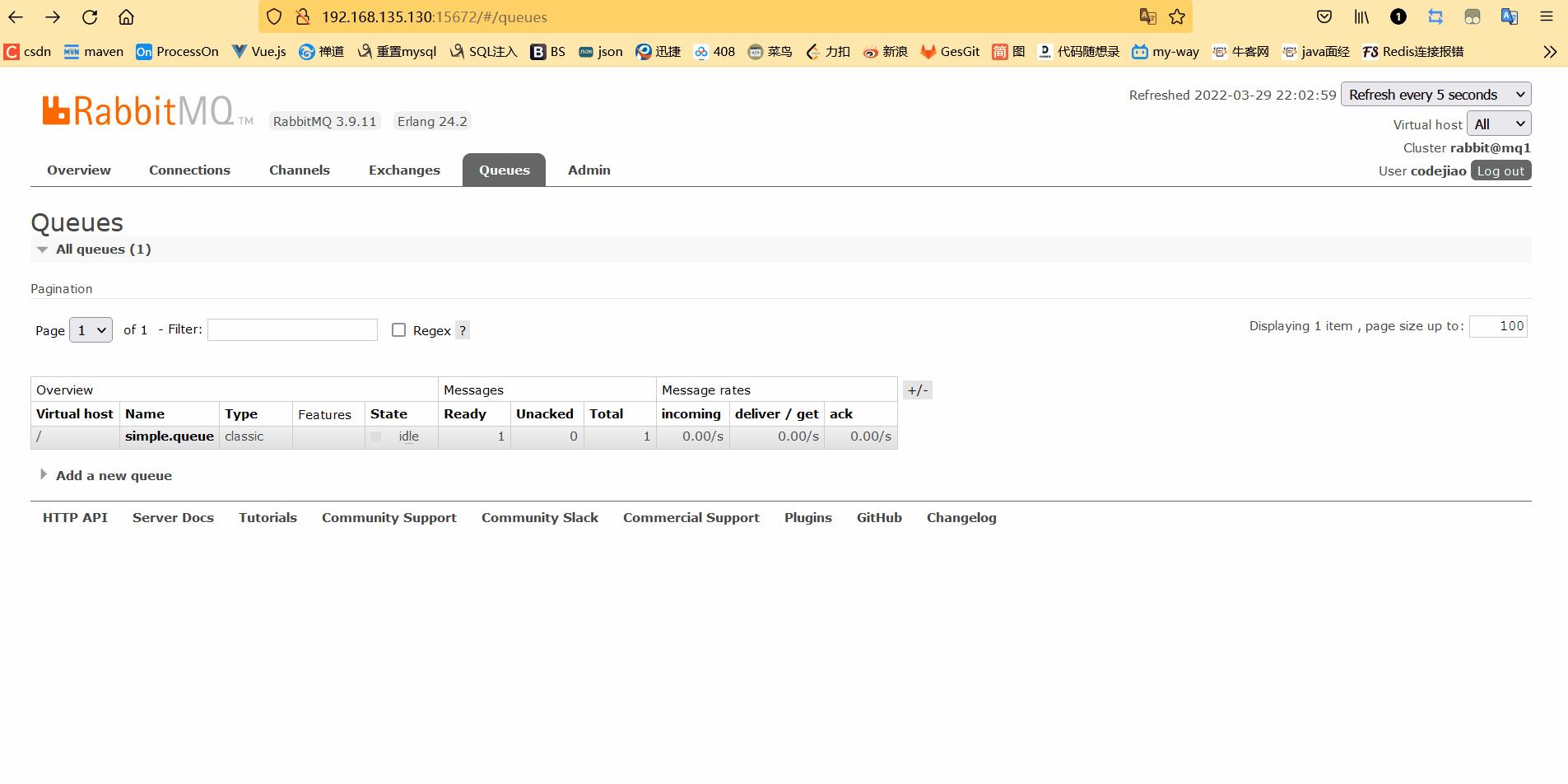
运行结果:


2.1.4 编写消费者的test文件

package cn.itcast.mq.helloworld;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class ConsumerTest
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException
// 1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
// 1.1.设置连接参数,分别是:主机名、端口号、vhost、用户名、密码
factory.setHost("192.168.135.130");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("codejiao");
factory.setPassword("317525");
// 1.2.建立连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
// 2.创建通道Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3.创建队列
String queueName = "simple.queue";
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
// 4.订阅消息
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel)
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException
// 5.处理消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println("接收到消息:【" + message + "】");
);
System.out.println("等待接收消息。。。。");
运行结果:

消息被消费者消费以后,会消失。

2.1.5 基本消息队列工作流程
基本消息队列的消息发送流程:
-
建立
connection -
创建
channel -
利用
channel声明队列 -
利用
channel向队列发送消息
基本消息队列的消息接收流程:
-
建立
connection -
创建
channel -
利用
channel声明队列 -
定义
consumer的消费行为handleDelivery() -
利用
channel将消费者与队列绑定
3. SpringAMQP
3.1 SpringAMQP介绍
SpringAMQP是基于RabbitMQ封装的一套模板,并且还利用SpringBoot对其实现了自动装配,使用起来非常方便。
SpringAMQP提供了三个功能:
- 自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
- 基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
- 封装了
RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
3.2 利用SpringAMQP实现HelloWorld中的基础消息队列功能
在父工程mq-demo中引入依赖
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.2.1.消息发送
首先配置MQ地址,在publisher服务的application.yml中添加配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.135.130 # 主机名
port: 5672 # 端口
virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机
username: codejiao # 用户名
password: 317525 # 密码
然后在publisher服务中编写测试类SpringAmqpTest,并利用RabbitTemplate实现消息发送:
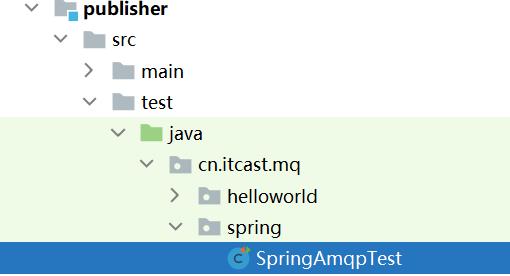
package cn.itcast.mq.spring;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringAmqpTest
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void testSimpleQueue()
// 队列名称
String queueName = "simple.queue";
// 消息
String message = "hello, spring amqp!";
// 发送消息 发送的前提是simple.queue这个队列已经存在, 下面这句话不会创建消息队列
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message);
运行结果:


小结:

3.2.2.消息接收
首先配置MQ地址,在consumer服务的application.yml中添加配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.135.130 # 主机名
port: 5672 # 端口
virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机
username: codejiao # 用户名
password: 317525 # 密码
然后在consumer服务的cn.itcast.mq.listener包中新建一个类SpringRabbitListener,代码如下:

package cn.itcast.mq.listener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener
// 这里可以指定多个队列
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg) throws InterruptedException
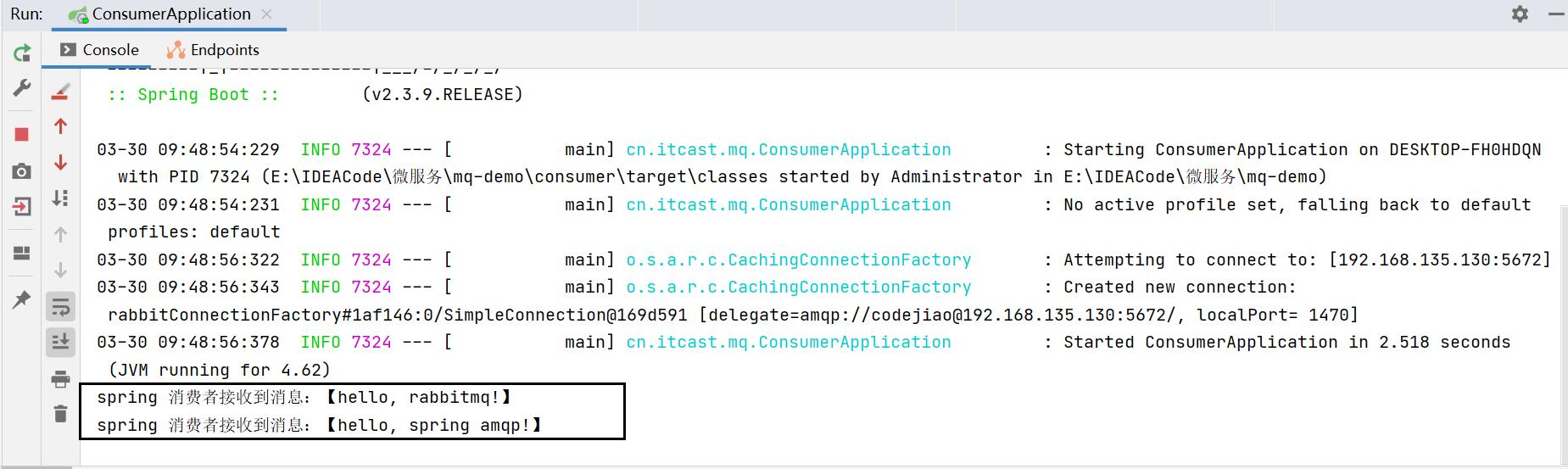
System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息:【" + msg + "】");
运行结果:
3.2.3 小结

3.3.WorkQueue 工作队列
Work queues,也被称为(Task queues),任务模型。简单来说就是让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。
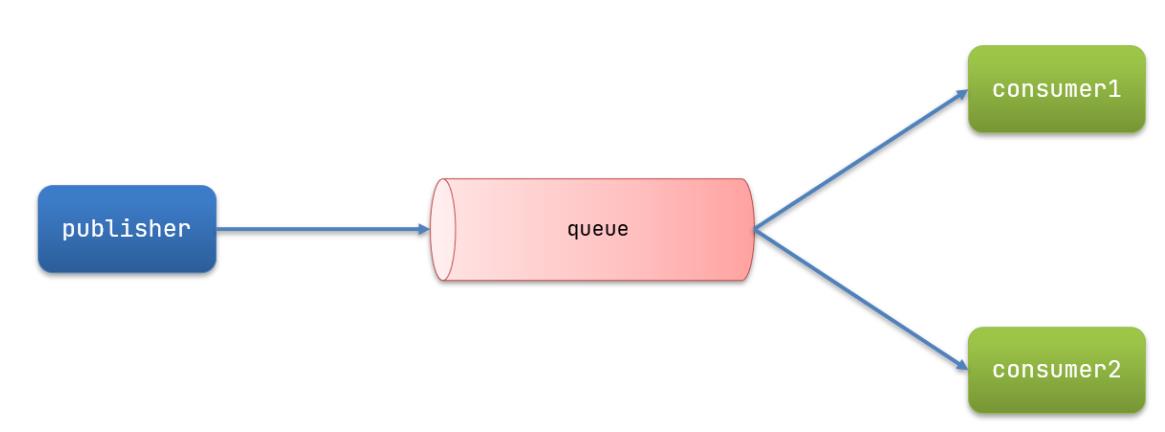
当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。
此时就可以使用work 模型,多个消费者共同处理消息处理,速度就能大大提高了。
3.4 案例:模拟WorkQueue,实现一个队列绑定多个消费者

3.4.1.消息发送
这次我们循环发送,模拟大量消息堆积现象。
在publisher服务中的SpringAmqpTest类中添加一个测试方法:

/**
* workQueue
* 向队列中不停发送消息,模拟消息堆积。
*/
@Test
public void testWorkQueue() throws InterruptedException
// 队列名称
String queueName = "simple.queue";
// 消息
String message = "hello, message_";
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message + i);
// 模拟发布者1s发布50条消息
Thread.sleep(20);
3.4.2.消息接收
要模拟多个消费者绑定同一个队列,我们在consumer服务的SpringRabbitListener中添加2个新的方法:
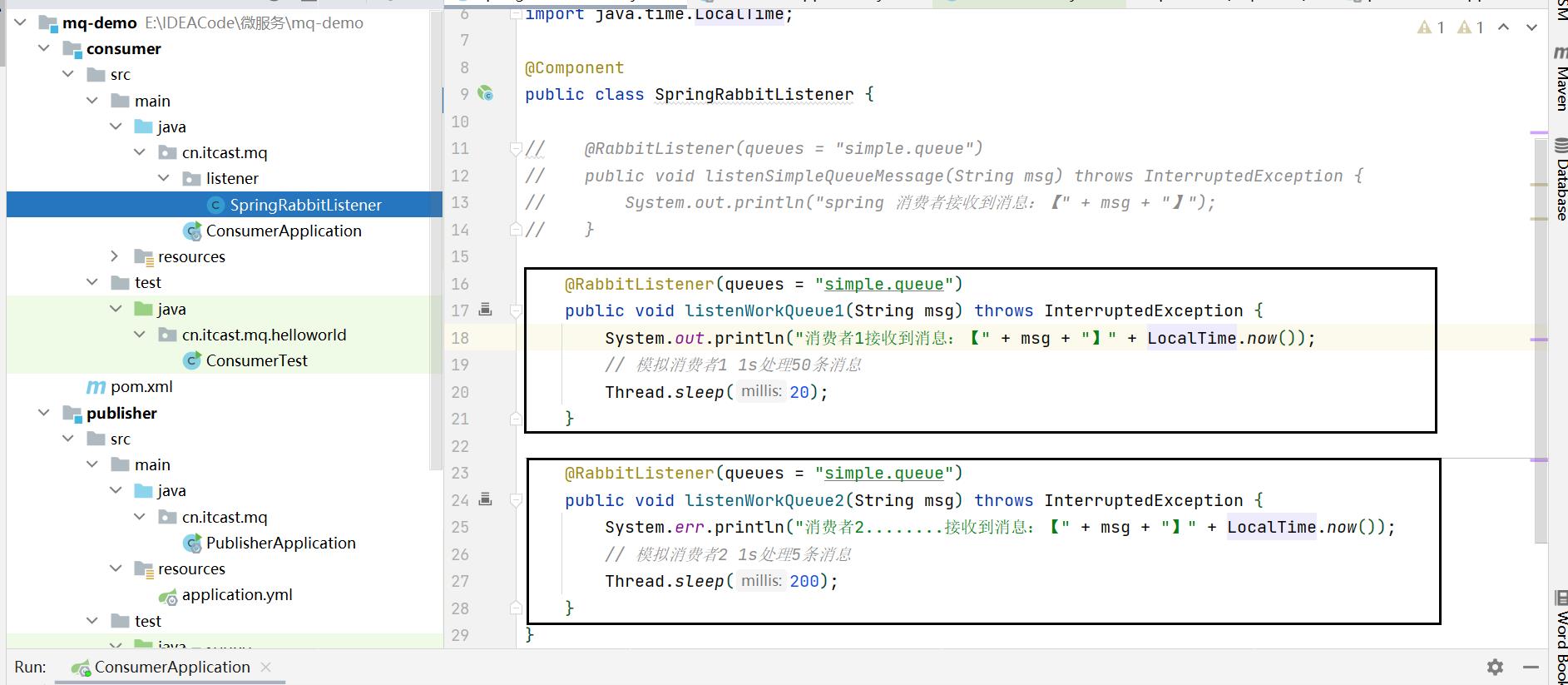
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
// 模拟消费者1 1s处理50条消息
Thread.sleep(20);
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException
System.err.println("消费者2........接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
// 模拟消费者2 1s处理5条消息
Thread.sleep(200);
注意到这个消费者sleep了1000秒,模拟任务耗时。
3.4.3 运行结果(发现消息预取机制)
我们来分析消息处理的结果:我们发现消费者1处理的全是偶数的消息,消费者2处理的全是奇数的消息。本来打算1s处理完发布者发布的50条消息,结果6s才处理完所有的消息。究其原因是因为消息预取机制,给所有的消费者分配了一样多的消息。
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_0】10:11:56.488
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_1】10:11:56.501
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_2】10:11:56.520
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_4】10:11:56.562
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_6】10:11:56.604
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_8】10:11:56.646
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_10】10:11:56.688
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_3】10:11:56.701
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_12】10:11:56.728
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_14】10:11:56.769
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_16】10:11:56.812
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_18】10:11:56.854
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_20】10:11:56.895
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_5】10:11:56.901
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_22】10:11:56.937
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_24】10:11:56.979
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_26】10:11:57.020
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_28】10:11:57.062
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_7】10:11:57.102
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_30】10:11:57.104
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_32】10:11:57.145
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_34】10:11:57.186
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_36】10:11:57.231
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_38】10:11:57.272
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_9】10:11:57.302
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_40】10:11:57.312
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_42】10:11:57.355
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_44】10:11:57.397
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_46】10:11:57.439
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_48】10:11:57.481
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_11】10:11:57.503
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_13】10:11:57.703
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_15】10:11:57.903
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello,以上是关于RabbitMQ 服务异步通信 -- 入门案例(消息预存机制)SpringAMQP发布订阅模式(FanoutExchangeDirectExchangeTopicExchange)消息转换器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章