linux中有名管道与匿名管道的实现
Posted 西邮菜
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了linux中有名管道与匿名管道的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、匿名管道
多用于父进程与子进程之间的通信,用到的频率很高,挺重要的。定义一个大小为2的数组、使用pipe函数将其变为匿名管道的两端,fd[0]:代表读端、fd[1]:代表写端。子进程和父进程根据功能分别关闭读或写端。当然是使用read和write函数来对管道的数据进行读写,下面这个函数的功能就是父进程给子进程传输hello world,子进程读后把字符串发送到标准输出上。如下图可以看到结果是正确的。使用完都关掉、养成好习惯。
int pipe(int filedes[2]);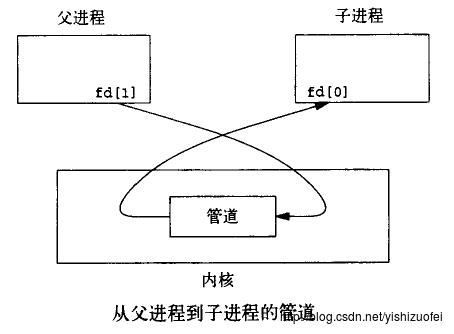
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define LINEBUF 1024
int main()
int fd[2];
char line[LINEBUF];
pid_t pid;
int len;
if(pipe(fd)<0)
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
pid=fork();
if(pid<0)
perror("fork");
exit(0);
else if(pid>0)
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1],"hello wweforld\\n",15);
close(fd[1]);
if(wait(NULL)==-1)
perror("wait");
exit(0);
else
close(fd[1]);
len=read(fd[0],line,LINEBUF);
write(1,line,len);
close(fd[0]);
exit(0);
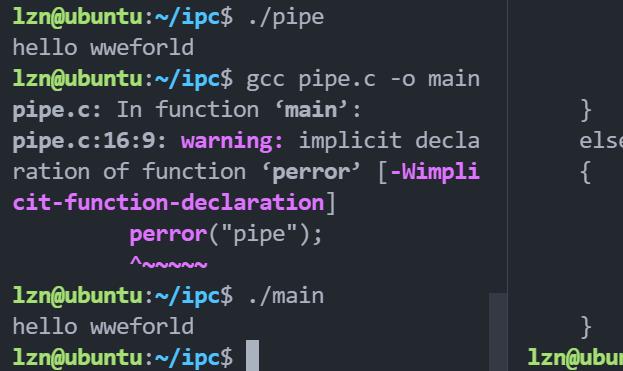
二、有名管道
有名管道也叫命名管道,与匿名管道的不同之处就是命名管道可以实现无亲缘关系的进程之间通信。在文件系统目录中存在一个管道文件,这个文件仅仅是文件系统中的标示,并不在磁盘上占据空间。在使用时,在内存上开辟空间,作为两个进程数据交互的通道。使用mkfifo()函数创建一个命名管道,之后编写程序可以利用read、write等函数使用它。
读端:使用open函数时mode采用O_RDONLY。
写端:使用open函数时mode采用O_WRONLY。
int mkfifo(const char *filename,mode_t mode);写端:利用main的参数来确定传输信息。
#include<unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define MYINFO "./pip"
#define MAX_BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
int main(int argc,char** argv)
int fd;
int len;
char buff[MAX_BUFFER_SIZE];
sscanf(argv[1],"%s",buff);
fd=open(MYINFO,O_WRONLY);
if(fd==-1)
exit(1);
len=write(fd,buff,MAX_BUFFER_SIZE);
if(len<=0)
exit(1);
printf("write %s to fifo\\n",buff);
close(fd);
exit(0);
读端:相当于服务器,只要写端写入就读出,所以写成了while循环。
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define MYINFO "./pip"
#define MAX_BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
int main(int argc,int** argv)
int fd;
char buf[MAX_BUFFER_SIZE];
int len;
fd=open(MYINFO,O_RDONLY);
if(fd==-1)
printf("open file error\\n");
exit(1);
while(1)
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)) ;
len=read(fd,buf,MAX_BUFFER_SIZE);
if(len>0)
printf("read from buf:%s\\n",buf);
printf("\\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
 此时写端写入数据,但读端未开启。下来开启读端。
此时写端写入数据,但读端未开启。下来开启读端。
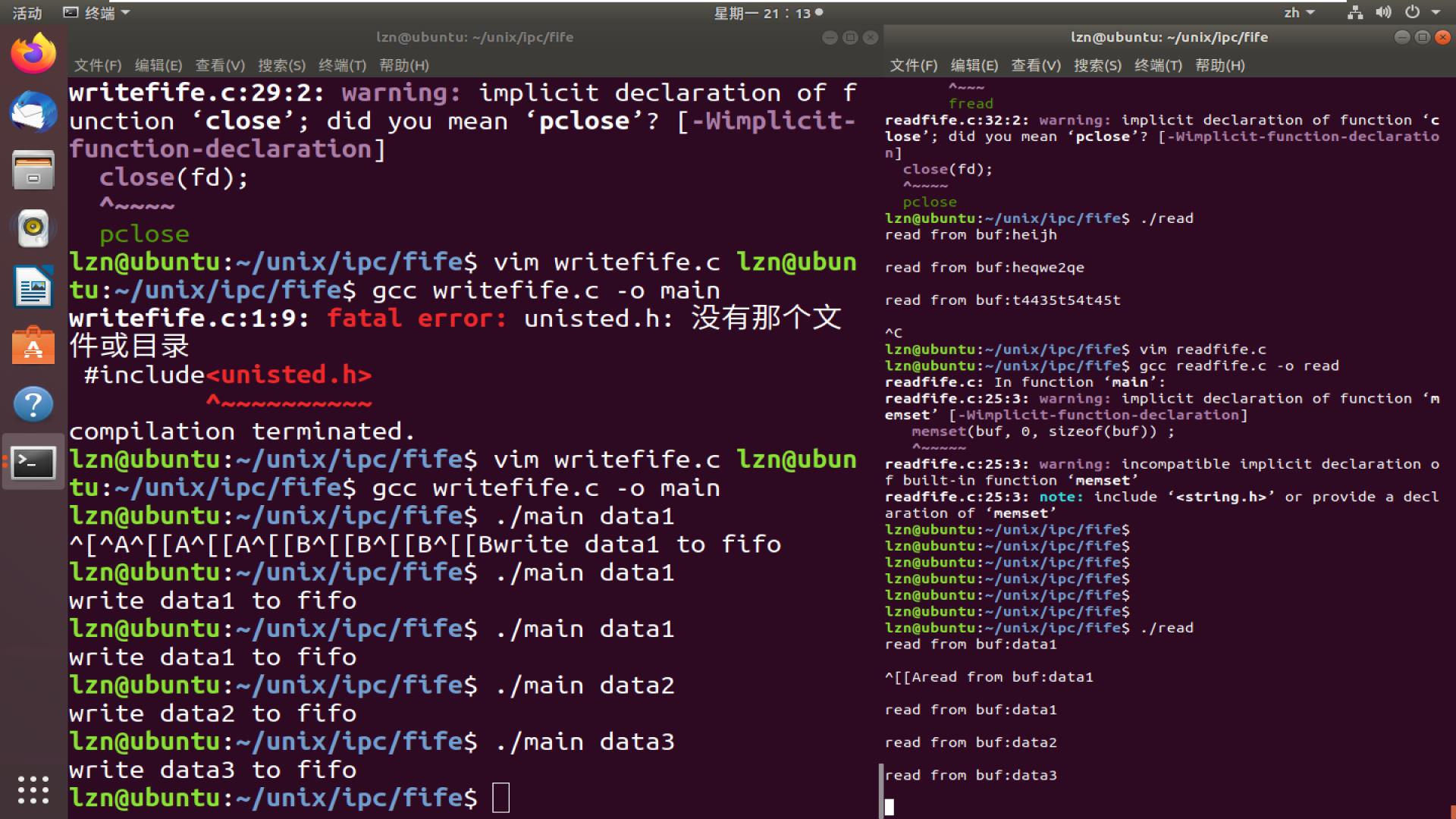
可以看到正常的执行。 读的时候要注意printf的行缓冲,不输出的办法就是printf后加\\n,或者使用fflush函数解决。
以上是关于linux中有名管道与匿名管道的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章