Elasticsearch:使用 Elasticsearch categorize_text 聚合对日志进行分类
Posted Elastic 中国社区官方博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Elasticsearch:使用 Elasticsearch categorize_text 聚合对日志进行分类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

作为一名前系统管理员,我个人对 categorize_text 对探索日志的意义感到兴奋。 这种新的 Elasticsearch 功能是我希望在那些日子里拥有的东西。 花费大量时间筛选大量日志以找出令人不安的模式。 categorize_text 在查询时将流行的日志模式带到最前沿。 此功能与 Elasticsearch 已经广泛且强大的聚合框架相结合,可缩短获取信息的时间。 探索成山的日志变得更加容易。 在 Kibana 中自动集群日志、计算统计数据和可视化是任何 SRE 或管理员的有力工具。
categorize_text 聚合是如何工作?
categorize_text 从文档 _source 读取文本并使用自定义 tokenizer ml_standard 创建 tokenizer,该 tokenizer 专门为一般机器生成的文本构建。 事实上,异常检测中提供的许多相同选项在 categorize_text 中可用。 分析文本后,将使用 DRAIN 算法的修改版本将 token 聚集在一起。 DRAIN 构建一个 token 树并认为较早的 token 更重要。 我们稍微修改了算法,以允许在构建类别时合并文本中较早的token。 本质上,具有高可变性的 token 被删除,而更一致的 token 形成类别定义。
文本分类示例
以下是 categorize_text 解析以下 nginx 日志行的方式。
"message": "2018/11/26 18:09:45 [error] 8#8: *4781 open() \\"/etc/nginx/html/wan.php\\" failed (2: No such file or directory), client: 154.91.201.90, server: _, request: \\"POST /wan.php HTTP/1.1\\", host: \\"35.246.148.213\\"",
"message": "2018/11/20 17:26:36 [error] 8#8: *3672 open() \\"/etc/nginx/html/pe.php\\" failed (2: No such file or directory), client: 139.159.210.222, server: _, request: \\"POST /pe.php HTTP/1.1\\", host: \\"35.246.148.213\\""使用默认设置,它将成为以下类别:
error open * failed No such file or directory client server request * host公共 token 包含在类别定义中,变量 token(在这种情况下为 url 文件路径)用 * 值省略。
既然我们知道它在高层次上是如何工作的,那么它怎么能被使用呢?
可视化日志类别的示例
让我们研究 categorize_text 聚合的三个用例,它们可以帮助你作为系统管理员:随时间按类别识别问题、显示最常见的错误类别和类别趋势可视化。 以下示例均使用 Kibana Vega 在查询时可视化日志类别。
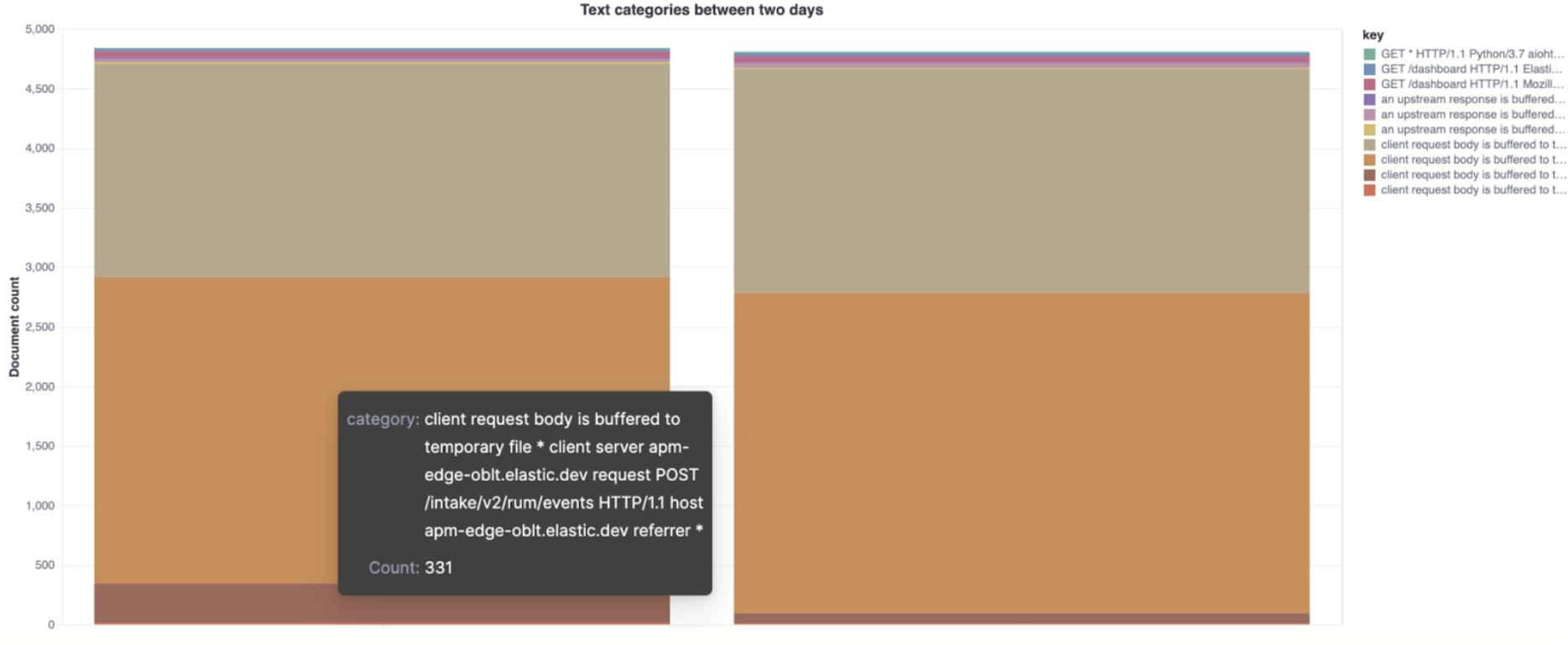
比较不同日期的顶级类别
以下示例显示了两天内 NGINX 错误的不同顶级类别。 在将之前已知的 “好日子” 与系统行为不稳定的日子进行比较时,这很有用。
"$schema": "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json",
"title": "Text categories between two days",
"data":
"url":
"index": "filebeat-*",
"body":
"size": 0,
"query":
"bool":
"filter": [
"term": "event.dataset": "nginx.error",
"bool":
"should": [
"range":
"@timestamp":
"gte": "2021-02-25T00:00:00.000Z",
"lte": "2021-02-25T12:00:00.000Z"
,
"range":
"@timestamp":
"gte": "2021-02-26T00:00:00.000Z",
"lte": "2021-02-26T12:00:00.000Z"
],
"minimum_should_match": 1
]
,
"aggs":
"sample":
"sampler": "shard_size": 5000,
"aggs":
"categories":
"categorize_text":
"field": "message",
"similarity_threshold": 20,
"max_unique_tokens": 20
,
"aggs":
"time_buckets":
"filters":
"filters":
"first":
"range":
"@timestamp":
"gte": "2021-02-25T00:00:00.000Z",
"lte": "2021-02-25T12:00:00.000Z"
,
"second":
"range":
"@timestamp":
"gte": "2021-02-26T00:00:00.000Z",
"lte": "2021-02-26T12:00:00.000Z"
,
"format": "property": "aggregations.sample.categories.buckets"
,
"transform": [
"fold": [
"time_buckets.buckets.first.doc_count",
"time_buckets.buckets.second.doc_count"
],
"as": ["subKey", "subValue"]
],
"mark": "bar",
"encoding":
"x": "field": "subKey", "type": "ordinal", "axis": "title": null,
"y":
"field": "subValue",
"type": "quantitative",
"axis": "title": "Document count"
,
"color": "field": "key",
"tooltip": [
"field": "key", "type": "nominal", "title": "category",
"field": "subValue", "type": "quantitative", "title": "Count"
]
,
"layer": ["mark": "bar", "encoding": "color": "field": "key"]
如果你对如何使用 Vega 来进行可视化还不是很了解的话,请参阅文章 “Kibana:Vega 可视化入门 - 定制自己的可视化图”。
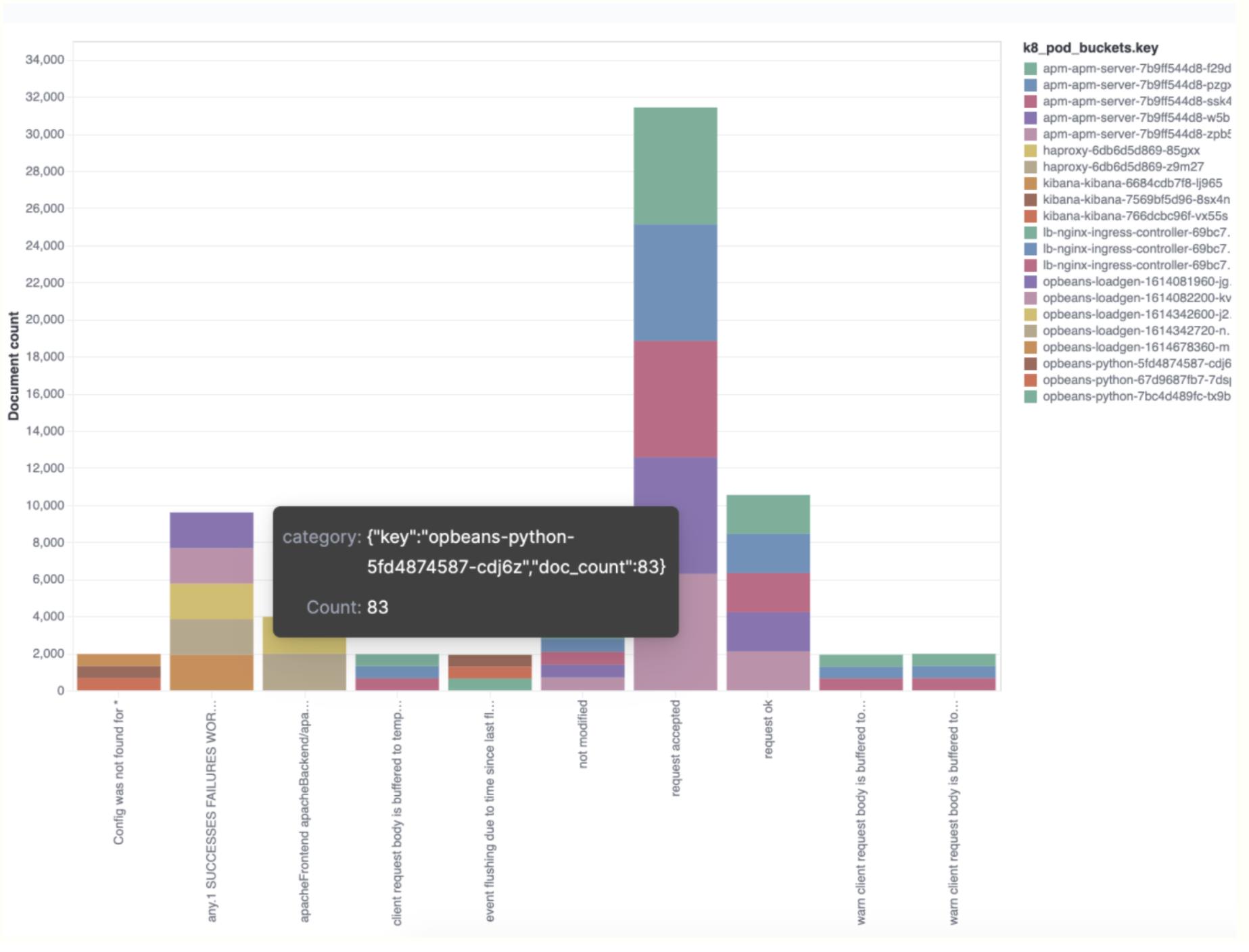
通过术语聚合收集顶级类别
此术语聚合示例显示了每个类别中哪些术语值最普遍。 在这种特殊情况下,
Kubernetes pod 是使用的术语。
"$schema": "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json",
"title": "Event counts from all indexes",
"data":
"url":
"%context%": true,
"%timefield%": "@timestamp",
"index": "filebeat-8.0.0-*",
"body":
"aggs":
"sample":
"sampler": "shard_size": 5000,
"aggs":
"categories":
"categorize_text":
"field": "message",
"similarity_threshold": 20,
"max_unique_tokens": 20
,
"aggs":
"k8_pod":
"terms": "field": "kubernetes.pod.name", "size": 5
,
"size": 0
,
"format": "property": "aggregations.sample.categories.buckets"
,
"transform": [
"flatten": ["k8_pod.buckets"], "as": ["k8_pod_buckets"]
],
"mark": "bar",
"encoding":
"x": "field": "key", "type": "ordinal", "axis": "title": false,
"y":
"field": "doc_count",
"type": "quantitative",
"axis": "title": "Document count"
,
"color": "field": "k8_pod_buckets.key",
"tooltip": [
"field": "k8_pod_buckets",
"type": "nominal",
"title": "category"
,
"field": "k8_pod_buckets.doc_count",
"type": "quantitative",
"title": "Count"
]
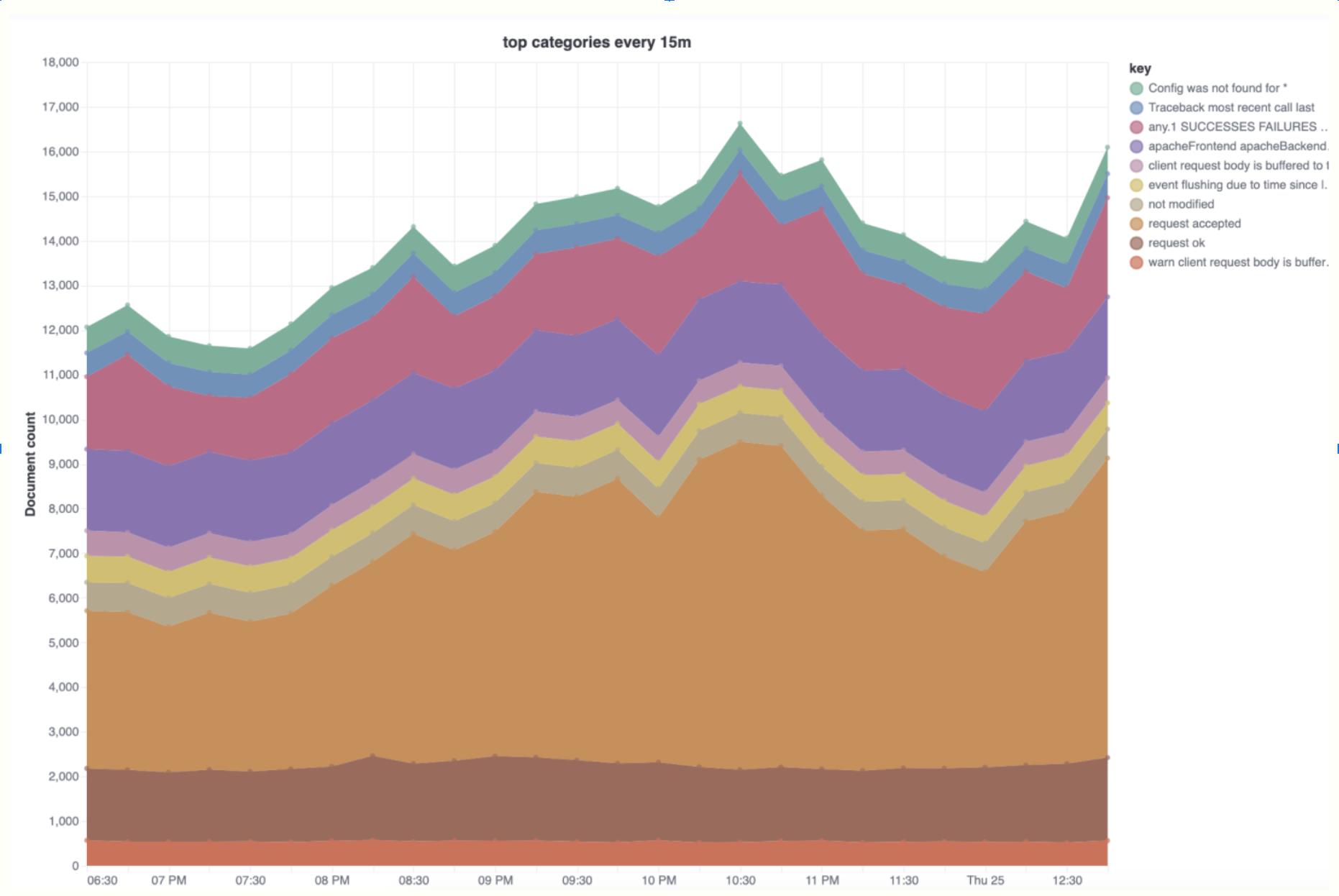
随着时间的推移可视化类别趋势
此分析可用于探索奇怪的日志记录峰值,并帮助确定哪些类别对峰值的贡献最大。
"$schema": "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json",
"title": "top categories every 15m",
"data":
"url":
"%context%": true,
"%timefield%": "@timestamp",
"index": "filebeat-8.0.0-*",
"body":
"aggs":
"categories":
"categorize_text":
"field": "message",
"similarity_threshold": 20,
"max_unique_tokens": 20
,
"aggs":
"time_buckets":
"date_histogram":
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "15m",
"min_doc_count": 1
,
"size": 0
,
"format": "property": "aggregations.categories.buckets"
,
"transform": ["flatten": ["time_buckets.buckets"], "as": ["buckets"]],
"mark": "area",
"encoding":
"tooltip": [
"field": "buckets.key", "type": "temporal", "title": "Date",
"field": "key", "type": "nominal", "title": "Category",
"field": "buckets.doc_count", "type": "quantitative", "title": "Count"
],
"x": "field": "buckets.key", "type": "temporal", "axis": "title": "category",
"y":
"field": "buckets.doc_count",
"type": "quantitative",
"stack": true,
"axis": "title": "Document count"
,
"color": "field": "key", "type": "nominal"
,
"layer": [
"mark": "area",
"mark": "point",
"selection":
"pointhover":
"type": "single",
"on": "mouseover",
"clear": "mouseout",
"empty": "none",
"fields": ["buckets.key", "key"],
"nearest": true
,
"encoding":
"size":
"condition": "selection": "pointhover", "value": 100,
"value": 5
,
"fill": "condition": "selection": "pointhover", "value": "white"
]
试试看
这些示例只是 7.16 技术预览版中发布的 categorize_text 聚合的开始。 对机器生成的文本进行分类和 Elasticsearch 中强大的聚合框架为你提供了大量的日志和数据探索机会。 立即启动 Elastic Cloud 集群并试一试。 我们很想听听你的反馈——在我们的讨论论坛或社区 Slack 频道中加入有关 Elastic 机器学习的对话。
更多阅读:Elasticsearch:使用 categorize text aggregation 来创建更好的警报
以上是关于Elasticsearch:使用 Elasticsearch categorize_text 聚合对日志进行分类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章