Kotlin协程源码分析-7 Context左向链表
Posted 不会写代码的丝丽
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kotlin协程源码分析-7 Context左向链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
-
上下文基本概念:
上下文可以理解为当前环境存储各类有用信息,再简单说就是存储数据的一个集合。 -
集合:
存放相同数据结构的一个容器,而容器的实现有很多种,链表类型,数组类型,树类型。
而在Kotlin中Context作为容器的实现采用一个链表的方式,而这个链表实现方式和我们所认知的有少许的不同。
首先来看Context声明
/**
* 协程上下文对象。上下文就是个容器,这里采用了左向链表的实现
*/
public interface CoroutineContext
/**
* 传入一个key对象返回对应数据
*/
public operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E?
/**
* 传入一个初始化的数值 [initial],[initial]其实就是CoroutineContext类型。然后遍历this的链表元素[Element],然后返回一个新的上下文
*
*/
public fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R
/**
* 将[传入的context]内容拼接当前[this的链表内容] 然后返回一个新的上下文,新的上下文包含
* 插入的新元素(不可变来实现线程安全,[this的链表内容]原有的链表元素还在)。[传入的context]的内容如果和[this的链表内容]有重复那么去除[this的链表内容]重复内容
*/
public operator fun plus(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext =
//传入的元素是空那么必要拼接直接返回
if (context === EmptyCoroutineContext) this else // fast path -- avoid lambda creation
//[this的链表内容]作为acc参数启动fold参数,然后遍历[传入的context]所有元素
context.fold(this) acc, element ->
//element元素是[传入的context]中存储的个对象
//minusKey函数用于去除某个上下文链表中一个元素,然后返回一个新的上下文,这里不会改变原来element这个对象的链表(不可变的线程安全模式)
val removed = acc.minusKey(element.key)
//EmptyCoroutineContext 返回时表示链表没有任何元素
if (removed === EmptyCoroutineContext) element else
//获取一个拦截器对象,由于拦截器对象太常用了,所以这里是做优化,把拦截器放在链表末尾
//链表放末尾容易更快速取得。如果当前element是ContinuationInterceptor对象话,这里一定返回null(上一步就去除了重复类)
val interceptor = removed[ContinuationInterceptor]
//如果拦截器对象为空的话,直接拼接CombinedContext对象中。CombinedContext对象可以视为一个节点对象
if (interceptor == null) CombinedContext(removed, element) else
//拦截器不为空,在[传入的context]去除它,返回一个不包含的它的上下文
val left = removed.minusKey(ContinuationInterceptor)
//为了严谨起见在判断一次left是不是为空(minusKey和get函数有可能子类实现机制不统一导致问题,如果根据规范判空可以省略)
if (left === EmptyCoroutineContext) CombinedContext(element, interceptor) else
//链表放最后
CombinedContext(CombinedContext(left, element), interceptor)
/**
*返回一个去除链表中key的对象的上下文。
*/
public fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext
/**
* Key 标识接口
*/
public interface Key<E : Element>
/**
* 上下文链表中元素标识接口
*/
public interface Element : CoroutineContext
/**
* 这个元素对应的键
*/
public val key: Key<*>
/**
*
*/
public override operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E? =
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
if (this.key == key) this as E else null
/**
* 进行累加的高阶函数。由于element对象不是一个集合对象,所以这里不会递归,只会执行一次 operation
*/
public override fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R =
operation(initial, this)
/**
* 如果当前key相等那么返回EmptyCoroutineContext。这个函数寓意就是用来去除key
*/
public override fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext =
if (this.key == key) EmptyCoroutineContext else this
链表节点对象CombinedContext,CombinedContext可以理解为上下文中每个节点,而元素存储属性element,上一个节点用属性left引用
由于都是简单的数据结构我这里不在做注释
// this class is not exposed, but is hidden inside implementations
// this is a left-biased list, so that `plus` works naturally
@SinceKotlin("1.3")
internal class CombinedContext(
private val left: CoroutineContext,
private val element: Element
) : CoroutineContext, Serializable
override fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E?
var cur = this
while (true)
cur.element[key]?.let return it
val next = cur.left
if (next is CombinedContext)
cur = next
else
return next[key]
public override fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R =
operation(left.fold(initial, operation), element)
public override fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext
element[key]?.let return left
val newLeft = left.minusKey(key)
return when
newLeft === left -> this
newLeft === EmptyCoroutineContext -> element
else -> CombinedContext(newLeft, element)
private fun size(): Int
var cur = this
var size = 2
while (true)
cur = cur.left as? CombinedContext ?: return size
size++
private fun contains(element: Element): Boolean =
get(element.key) == element
private fun containsAll(context: CombinedContext): Boolean
var cur = context
while (true)
if (!contains(cur.element)) return false
val next = cur.left
if (next is CombinedContext)
cur = next
else
return contains(next as Element)
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean =
this === other || other is CombinedContext && other.size() == size() && other.containsAll(this)
override fun hashCode(): Int = left.hashCode() + element.hashCode()
override fun toString(): String =
"[" + fold("") acc, element ->
if (acc.isEmpty()) element.toString() else "$acc, $element"
+ "]"
private fun writeReplace(): Any
val n = size()
val elements = arrayOfNulls<CoroutineContext>(n)
var index = 0
fold(Unit) _, element -> elements[index++] = element
check(index == n)
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
return Serialized(elements as Array<CoroutineContext>)
private class Serialized(val elements: Array<CoroutineContext>) : Serializable
companion object
private const val serialVersionUID: Long = 0L
private fun readResolve(): Any = elements.fold(EmptyCoroutineContext, CoroutineContext::plus)
来个个案例吧:
public class My4CoroutineName(
val name: String
) : AbstractCoroutineContextElement(My4CoroutineName)
public companion object Key : CoroutineContext.Key<My4CoroutineName>
override fun toString(): String = "CoroutineName($name)"
public class My5CoroutineName(
val name: String
) : AbstractCoroutineContextElement(My5CoroutineName)
public companion object Key : CoroutineContext.Key<My5CoroutineName>
override fun toString(): String = "CoroutineName($name)"
public class My3CoroutineName(
val name: String
) : AbstractCoroutineContextElement(My3CoroutineName)
public companion object Key : CoroutineContext.Key<My3CoroutineName>
override fun toString(): String = "CoroutineName($name)"
fun studyContext()
val my3CoroutineName = My3CoroutineName("hello")
val my4CoroutineName = My4CoroutineName("world")
val my5CoroutineName = My5CoroutineName("world")
val newElement = my3CoroutineName + my4CoroutineName + my5CoroutineName
println("<top>.studyContext")
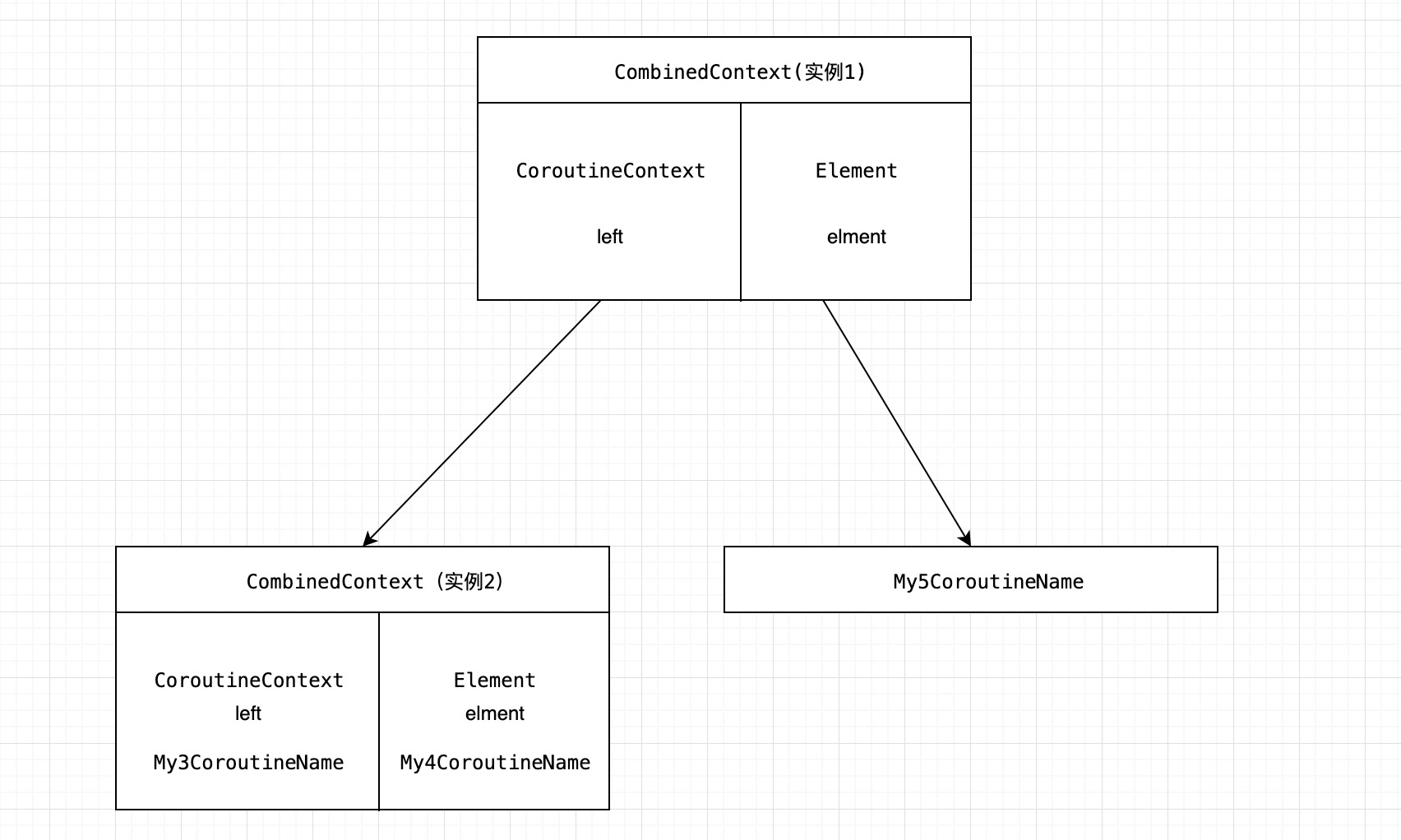
看下删除操作吧:
fun studyContext()
val my3CoroutineName = My3CoroutineName("hello")
val my4CoroutineName = My4CoroutineName("world")
val my5CoroutineName = My5CoroutineName("world")
val newElement = my3CoroutineName + my4CoroutineName + my5CoroutineName
val minusKey = newElement.minusKey(My3CoroutineName)
println("<top>.studyContext")

这里做下总结:
Kotlin采用不可变的链表保证了线程的安全(每次改动链表内容都是在一个新的上下文中操作),且使用+操作符的时候显得更加自然。
以上是关于Kotlin协程源码分析-7 Context左向链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章