树-面试题
Posted nogos
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了树-面试题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
面试题
树的遍历
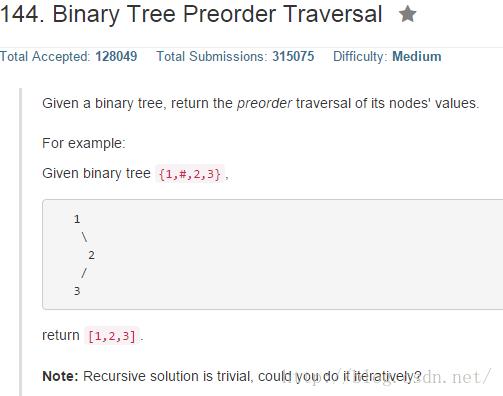
分析
根据前序遍历访问的顺序,优先访问根结点,然后再分别访问左孩子和右孩子。即对于任一结点,其可看做是根结点,因此可以直接访问,访问完之后,若其左孩子不为空,按相同规则访问它的左子树;当访问完其左子树后,再访问它的右子树。因此其处理过程如下:
对于任一结点P:
1)访问结点P,并将结点P入栈;
2)判断结点P的左孩子是否为空,若为空,则取栈顶结点并进行出栈操作,并将栈顶结点的右孩子置为当前的结点P;若不为空,则将P的左孩子置为当前的结点P;
3)直到P为NULL并且栈为空则遍历结束。
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> list=new LinkedList<Integer>();
if(root==null) return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)
list.add(p.val);
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
p=stack.pop();
p=p.right;
return list;

分析
根据中序遍历的顺序,对于任一结点,优先访问其左孩子,而左孩子结点又可以看做一根结点,然后继续访问其左孩子结点,直到遇到左孩子结点为空的结点才进行访问,然后按相同的规则访问其右子树。因此其处理过程如下:
对于任一结点P,
1)若其左孩子不为空,则将P入栈并将P的左孩子置为当前的P,然后对当前结点P再进行相同的处理;
2)若其左孩子为空,则取栈顶元素并进行出栈操作,访问该栈顶结点,然后将当前的P置为栈顶结点的右孩子;
3)直到P为NULL并且栈为空则遍历结束
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> list=new LinkedList<Integer>();
if(root==null) return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
p=stack.pop();
list.add(p.val);
p=p.right;
return list;

分析
后序遍历的非递归实现是三种遍历方式中最难的一种。因为在后序遍历中,要保证左孩子和右孩子都已被访问后才能访问根结点,这就为流程的控制带来了难题。
第一种思路:对于任一结点P,将其入栈,然后沿其左子树一直往下搜索,直到搜索到没有左孩子的结点,此时该结点出现在栈顶,但是此时不能将其出栈并访问,因此其右孩子还未被访问。所以接下来按照相同的规则对其右子树进行相同的处理,当访问完其右孩子时,该结点又出现在栈顶,此时可以将其出栈并访问,这样才能保证了正确的访问顺序。可以看出,在这个过程中,右子数不为空的结点都会两次出现在栈顶,只有在第二次出现在栈顶时,才能访问它。因此需要利用哈希表来标识该结点是否是第一次出现在栈顶。
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> list=new LinkedList<Integer>();
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>();
if(root==null) return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
p=stack.peek();
if(p.right!=null)
if(visit.get(p)==null)
visit.put(p, true);
//第一次处理右子树
p=p.right;
else
list.add(p.val);
stack.pop();
p=null;
else
list.add(p.val);
stack.pop();
p=null;
return list;
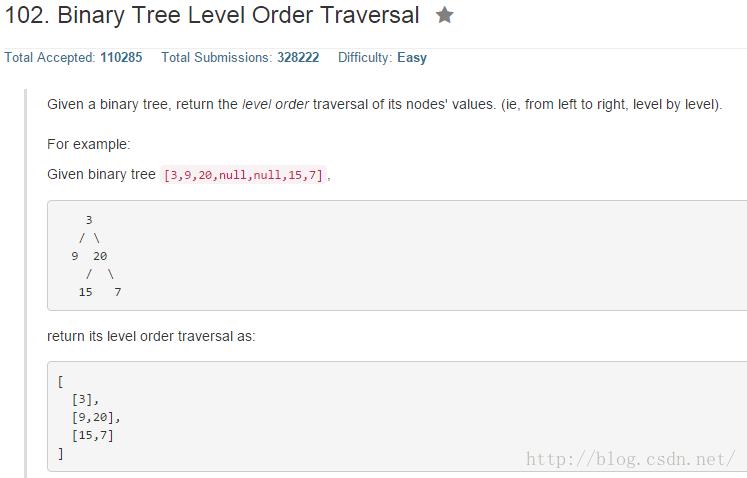
分析
数的层次遍历,即广度优先遍历,利用队列实现。
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root)
List<List<Integer>> levels=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null)return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> nextQueue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(!queue.isEmpty())
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)nextQueue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)nextQueue.add(node.right);
queue=nextQueue;
levels.add(list);
return levels;
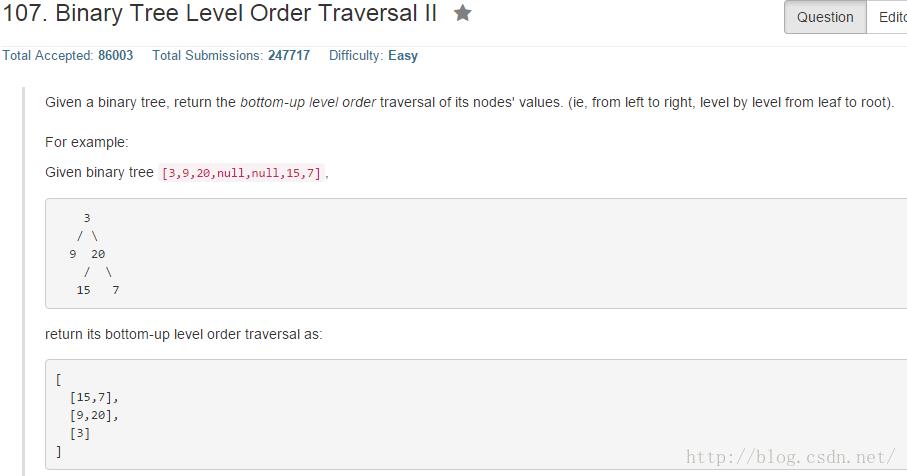
分析
只需将上题结果逆序即可。
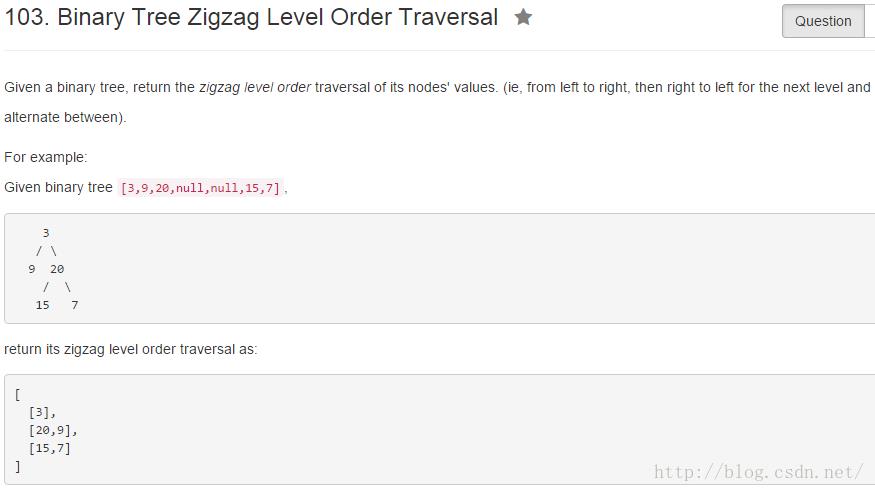
分析
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root)
List<List<Integer>> levels=new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null) return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
int mark=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> nextqueue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(!queue.isEmpty())
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)nextqueue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)nextqueue.add(node.right);
queue=nextqueue;
if(mark==1)
Collections.reverse(list);
mark=(mark+1)%2;
levels.add(list);
return levels;
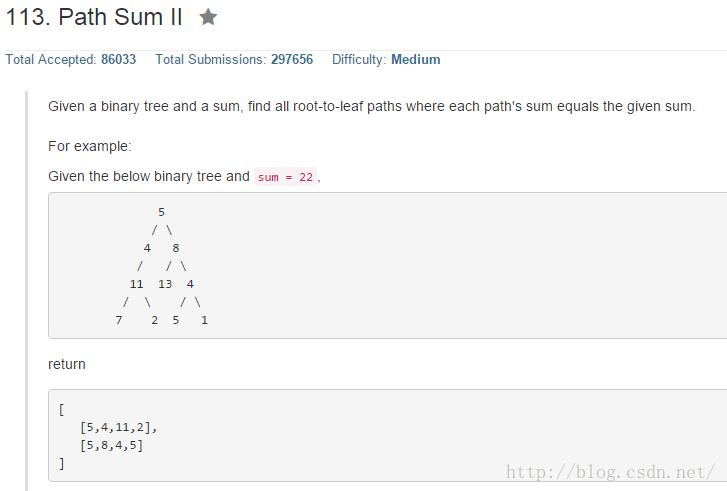
分析
采用后序遍历,栈中的元素即为路径。
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum)
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null) return res;
Map<TreeNode,Boolean> visit=new HashMap<TreeNode,Boolean>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
int nowSum=0;
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)
stack.push(p);
nowSum+=p.val;
p=p.left;
p=stack.peek();
if(p.left==null&&p.right==null&&sum==nowSum)
List<Integer> r=new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(Object i:stack.toArray())
r.add((Integer)((ListNode)i).val);
res.add(r);
if(p.right!=null)
if(visit.get(p)==null)
visit.put(p, true);
//第一次处理右子树
p=p.right;
else
nowSum-=p.val;
stack.pop();
p=null;
else
nowSum-=p.val;
stack.pop();
p=null;
return res;
树的构建

public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder)
int n=preorder.length;
if(n==0)return null;
return doBuildTree(preorder,0,n-1,inorder,0,n-1);
public TreeNode doBuildTree(int[] preorder,int s1,int e1, int[] inorder,int s2,int e2)
if(e1<s1)return null;
int rootindex = 0;
for(int i=s2;i<=e2;i++)
if(inorder[i]==preorder[s1])
rootindex=i;
break;
int leftCount=rootindex-s2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[s1]);
root.left=doBuildTree(preorder,s1+1,s1+leftCount,inorder,s2,rootindex-1);
root.right=doBuildTree(preorder,s1+leftCount+1,e1,inorder,rootindex+1,e2);
return root;

public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder)
int n=inorder.length;
if(n==0)return null;
return doBuildTree(inorder,0,n-1,postorder,0,n-1);
public TreeNode doBuildTree(int[] inorder,int s1,int e1, int[] postorder,int s2,int e2)
if(e1<s1)return null;
int rootindex = 0;
for(int i=s1;i<=e1;i++)
if(inorder[i]==postorder[e2])
rootindex=i;
break;
int leftCount=rootindex-s1;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[e2]);
root.left=doBuildTree(inorder,s1,rootindex-1,postorder,s2,s2+leftCount-1);
root.right=doBuildTree(inorder,rootindex+1,e1,postorder,s2+leftCount,e2-1);
return root;
二分查找树
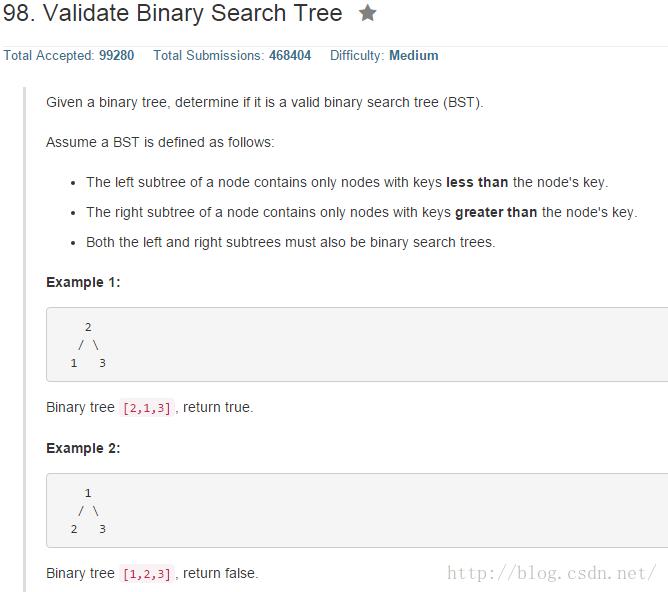
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root)
//二叉查找树的中序遍历为递增的
if(root==null)return true;
List<Integer> list=new LinkedList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
p=stack.pop();
list.add(p.val);
if(list.size()>=2&&list.get(list.size()-1)<=list.get(list.size()-2))
return false;
if(p.right!=null)//处理右子树
p=p.right;
else//处理上一层
p=null;
return true;

public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums)
int n=nums.length;
if(n==0)return null;
return doSortedArrayToBST(nums,0,n-1);
public TreeNode doSortedArrayToBST(int[] nums,int start,int end)
if(end<start)return null;
int mid=(start+end)/2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=doSortedArrayToBST(nums,start,mid-1);
root.right=doSortedArrayToBST(nums,mid+1,end);
return root;
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head)
if(head==null)return null;
int length=listLength(head);
return doSortedListToBST(head,length);
public TreeNode doSortedListToBST(ListNode head,int length)
if(length<=0) return null;
ListNode midListNode=midListNode(head,length);
int leftlength=listLength(head,midListNode);
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(midListNode.val);
root.left=doSortedListToBST(head,leftlength);
root.right=doSortedListToBST(midListNode.next,length-1-leftlength);
return root;
public ListNode midListNode(ListNode head,int length)
int mid=length/2;
int mark=length%2==0?1:0;
ListNode p=head;
while(mid-->mark)
p=p.next;
return p;
public int listLength(ListNode head,ListNode mid)
int length=0;
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=mid)
length++;
p=p.next;
return length;
public int listLength(ListNode head)
int length=0;
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=null)
length++;
p=p.next;
return length;
二叉树递归
public int minDepth(TreeNode root)
if(root==null)return 0;
return doMinDepth(root);
public int doMinDepth(TreeNode root)
if(root==null) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return 1;
int leftDepth=doMinDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth=doMinDepth(root.right);
return 1+Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root)
if(root==null)return 0;
return doMaxDepth(root);
public int doMaxDepth(TreeNode root)
if(root==null) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return 1;
int leftDepth=doMaxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth=doMaxDepth(root.right);
return 1+Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
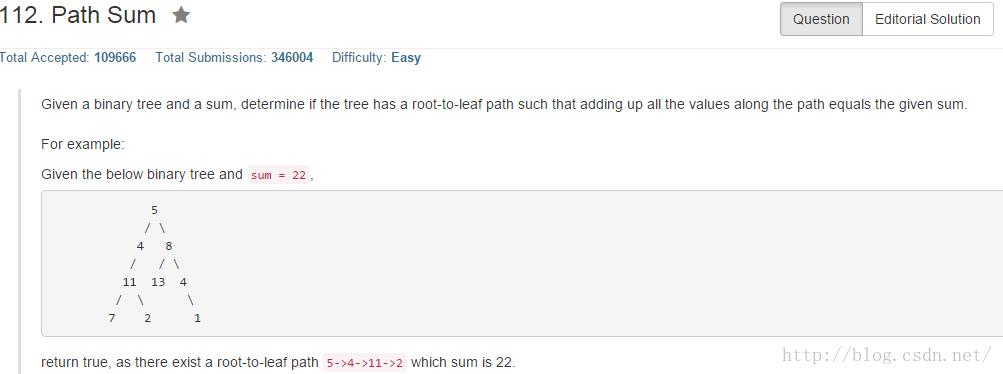
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum)
if(root==null) return false;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null&&sum==root.val)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left,sum-root.val)||hasPathSum(root.right,sum-root.val);
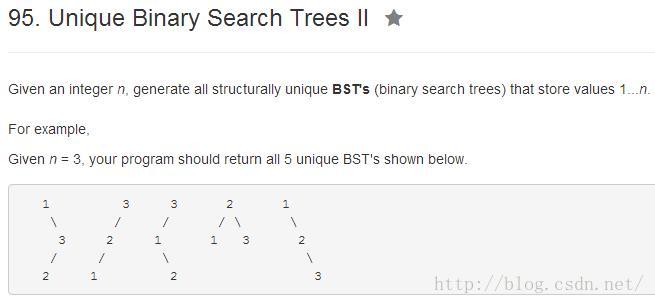
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n)
if(n==0)
return new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
return buildTree(1,n);
public List<TreeNode> buildTree(int start,int end)
List<TreeNode> res=new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
if(start>end)
res.add(null);
return res;
for(int top=start;top<=end;top++)
List<TreeNode> leftTrees=buildTree(start,top-1);
List<TreeNode> rightTrees=buildTree(top+1,end);
for(TreeNode leftTree:leftTrees)
for(TreeNode rightTree:rightTrees)
TreeNode topNode=new TreeNode(top);
topNode.left=leftTree;
topNode.right=rightTree;
res.add(topNode);
return res;
以上是关于树-面试题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章