使用AOP+反射实现Excel数据的读取
Posted 浅殇忆流年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用AOP+反射实现Excel数据的读取相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
如果我们遇到把excel表格中的数据导入到数据库,首先我们要做的是:将excel中的数据先读取出来。
因此,今天就给大家分享一个读取Excel表格数据的代码示例:
为了演示方便,首先我们创建一个Spring Boot项目;具体创建过程这里不再详细介绍;
示例代码主要使用了Apache下的poi的jar包及API;因此,我们需要在pom.xml文件中导入以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.13</version>
</dependency>
主要代码:
ExcelUtils.java
import com.example.springbatch.xxkfz.annotation.ExcelField;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @author xxkfz
* Excel工具类
*/
@Slf4j
public class ExcelUtils
private HSSFWorkbook workbook;
public ExcelUtils(String fileDir)
File file = new File(fileDir);
try
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(new FileInputStream(file));
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 读取Excel数据
*
* @param sheetName
* @param object
* @return
*/
public List readFromExcelData(String sheetName, Object object)
List result = new ArrayList();
// 获取该对象的class对象
Class class_ = object.getClass();
// 获得该类的所有属性
Field[] fields = class_.getDeclaredFields();
// 读取excel数据 获得指定的excel表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheet(sheetName);
// 获取表格的总行数
int rowCount = sheet.getLastRowNum() + 1; // 需要加一
if (rowCount < 1)
return result;
// 获取表头的列数
int columnCount = sheet.getRow(0).getLastCellNum();
// 读取表头信息,确定需要用的方法名---set方法
// 用于存储方法名
String[] methodNames = new String[columnCount]; // 表头列数即为需要的set方法个数
// 用于存储属性类型
String[] fieldTypes = new String[columnCount];
// 获得表头行对象
HSSFRow titleRow = sheet.getRow(0);
// 遍历表头列
for (int columnIndex = 0; columnIndex < columnCount; columnIndex++)
// 取出某一列的列名
String colName = titleRow.getCell(columnIndex).toString();
/*
// 将列名的首字母字母转化为大写
String UColName = Character.toUpperCase(colName.charAt(0)) + colName.substring(1, colName.length());
// set方法名存到methodNames
methodNames[columnIndex] = "set" + UColName;
*/
//
String fieldName = fields[columnIndex].getName();
String UpperFieldName = Character.toUpperCase(fieldName.charAt(0)) + fieldName.substring(1, fieldName.length());
methodNames[columnIndex] = "set" + UpperFieldName;
// 遍历属性数组
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++)
// 获取属性上的注解name值
String name = fields[i].getAnnotation(ExcelField.class).name();
// 属性与表头相等
if (Objects.nonNull(name) && colName.equals(name))
// 将属性类型放到数组中
fieldTypes[columnIndex] = fields[i].getType().getName();
// 逐行读取数据 从1开始 忽略表头
for (int rowIndex = 1; rowIndex < rowCount; rowIndex++)
// 获得行对象
HSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(rowIndex);
if (row != null)
Object obj = null;
// 实例化该泛型类的对象一个对象
try
obj = class_.newInstance();
catch (Exception e1)
e1.printStackTrace();
// 获得本行中各单元格中的数据
for (int columnIndex = 0; columnIndex < columnCount; columnIndex++)
String data = row.getCell(columnIndex).toString();
// 获取要调用方法的方法名
String methodName = methodNames[columnIndex];
obj = this.valueConvert(fieldTypes[columnIndex], methodName, class_, obj, data);
result.add(obj);
return result;
/**
* @param fieldType 字段类型
* @param methodName 方法名
* @param class_
* @param data
* @return
*/
private Object valueConvert(String fieldType, String methodName, Class class_, Object obj, String data)
Method method = null;
if (Objects.isNull(fieldType) || Objects.isNull(methodName) || Objects.isNull(class_) || Objects.isNull(obj))
return obj;
try
switch (fieldType)
case "java.lang.String":
method = class_.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, String.class);
method.invoke(obj, data); // 执行该方法
break;
case "java.lang.Integer":
method = class_.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, Integer.class);
Integer value = Integer.valueOf(data);
method.invoke(obj, value); // 执行该方法
break;
case "java.lang.Boolean":
method = class_.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, Boolean.class);
Boolean booleanValue = Boolean.getBoolean(data);
method.invoke(obj, booleanValue); // 执行该方法
break;
case "java.lang.Double":
method = class_.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, Double.class);
double doubleValue = Double.parseDouble(data);
method.invoke(obj, doubleValue); // 执行该方法
break;
case "java.math.BigDecimal":
method = class_.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, BigDecimal.class);
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(data);
method.invoke(obj, bigDecimal); // 执行该方法
break;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
return obj;
ExcelField.java
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @author xxkfz
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.TYPE) //注解放置的目标位置,METHOD是可注解在方法级别上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解在哪个阶段执行
@Documented
public @interface ExcelField
String name() default "";
实体类 ExcelFileField.java
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class ExcelFileField
@ExcelField(name = "id")
private String id;
@ExcelField(name = "code")
private String code;
@ExcelField(name = "type")
private String type;
@ExcelField(name = "version")
private String version;
函数测试
@Test
void readExcel()
ExcelUtils utils = new ExcelUtils("E:/test.xls");
ExcelFileField interfaceField = new ExcelFileField();
List list = utils.readFromExcelData("sheet1", interfaceField);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
ExcelFileField item = (ExcelFileField) list.get(i);
System.out.println(item.toString());
Excel表格数据
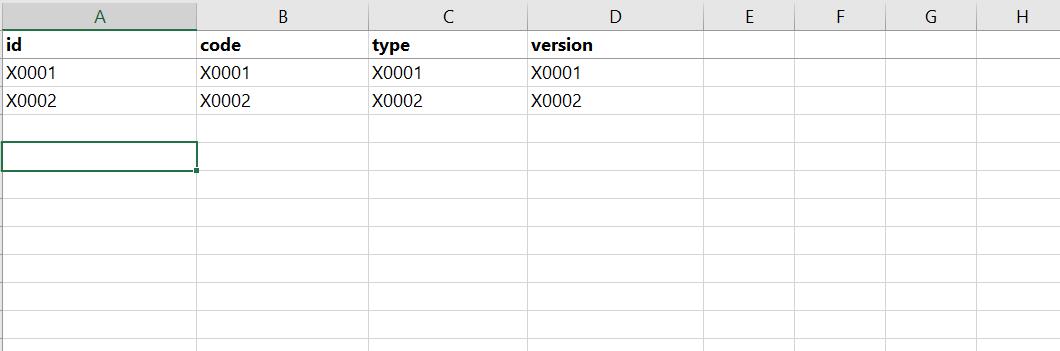
测试结果:
ExcelFileField(id=X0001, code=X0001, type=X0001, version=X0001)
ExcelFileField(id=X0002, code=X0002, type=X0002, version=X0002)
Process finished with exit code 0
本篇文章到这里就基本结束了,如果这篇文章对你有帮助,希望大家能留下你的点赞、 关注、 分享、 留言❤️❤️❤️
以上是关于使用AOP+反射实现Excel数据的读取的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章