pytorch Vgg网络模型
Posted 为了维护世界和平_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了pytorch Vgg网络模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Vgg网络
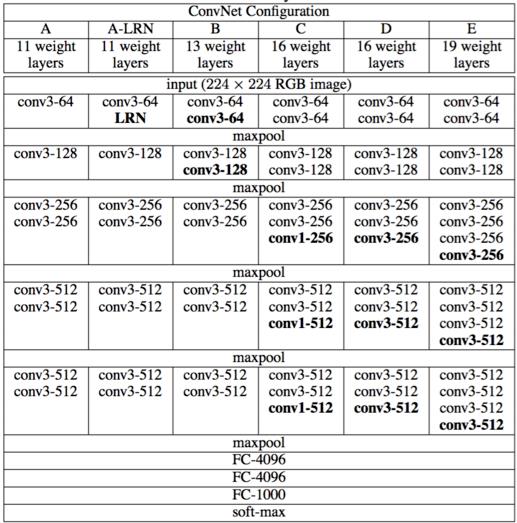
网络亮点
-
通过堆叠多个3x3的卷积核来代替大尺寸卷积核(减少参数)
堆叠两个3x3的卷积核代替一个5x5的卷积核,堆叠三个3x3的卷积核代替7X7卷积核
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# official pretrain weights
model_urls =
'vgg11': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg11-bbd30ac9.pth',
'vgg13': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg13-c768596a.pth',
'vgg16': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg16-397923af.pth',
'vgg19': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth'
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512*7*7, 4096), #512 channel 7x7 图像大小
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224 输入图像
x = self.features(x)
# N x 512 x 7 x 7 展平前
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
# N x 512*7*7 送入分类
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
# nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def make_features(cfg: list):
layers = []
in_channels = 3#RGB 三通道
for v in cfg:
if v == "M":
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)#非关键字参数
#模型深度选择
cfgs =
'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
def vgg(model_name="vgg16", **kwargs):
assert model_name in cfgs, "Warning: model number not in cfgs dict!".format(model_name)
cfg = cfgs[model_name]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), **kwargs)
return model
#网络模型打印
vgg_module = vgg("vgg13")
print(vgg_module)
网络模型打印输出
VGG(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(15): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(16): ReLU(inplace=True)
(17): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(18): ReLU(inplace=True)
(19): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(20): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(21): ReLU(inplace=True)
(22): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(23): ReLU(inplace=True)
(24): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)
)
)
以上是关于pytorch Vgg网络模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章