LTE随机接入RACH流程preamble发送
Posted yyl_woniu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LTE随机接入RACH流程preamble发送相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
首先对于TDD与FDD模式,随机接入处理流程一致。参考36.300 10.1.5触发随机接入的场景有如下六种:
1、ue由RRC_IDLE态发起初始接入流程
2、RRC Connection Re-establishment RRC链接重建立过程触发随机接入,便于ue在RRC无线链路建立失败后重新发起随机接入。
3、小区切换Handover发起随机接入
4、RRC_CONNECTED,RRC链接态下行数据到达随机接入(UL上行失步)
5、RRC_CONNECTED,RRC链接态上行数据到达随机接入(UL上行失步或者无可用PUCCH资源用于SR请求)
6、RRC_CONNECTED,RRC链接态,ue需要定位时,TA失步导致随机接入
触发随机接入过程的方式有3种:(1)PDCCH order触发;(2)MAC sublayer触发;(3)上层触发。
由PDCCH order发起的随机接入过程(“initiated by a PDCCH order”)只有在如下场景才会发生:(1)eNodeB要发送下行数据时,发现丢失了UE的上行同步,它会强制UE重新发起随机接入过程以获取正确的时间调整量;(2)UE定位。
这时eNodeB会通过特殊的DCI format 1A 告诉UE需要重新发起随机接入,并告诉UE应该使用的Preamble Index和PRACH Mask Index。(见36.212的5.3.3.1.3节、36.213的Table 8-4)

由MAC sublayer发起随机接入过程的场景有:UE有上行数据要发送,但在任意TTI内都没有可用于发送SR的有效PUCCH资源。此时上行数据传输的流程变为:
(1)UE 发送preamble;
(2)eNodeB回复RAR,RAR携带了UL grant信息;
(3)UE开始发送上行数据。
随机接入处理类型可以分为两种:
1、基于非竞争的随机接入(包括小区切换、 TA失步以及DL下行数据到达导致的随机接入流程)
2、基于竞争的随机接入(6中随机接入中的前5种)
基于竞争的随机接入
处理流程如下:

通过上图,基于竞争的随机接入包括4条交互消息,首先ue向基站enb发起随机接入请求rach requset(RA),基站测检测到RA的msg1消息,会通过mac层给ue回复RAR随机接入请求响应msg2消息,同时完成msg3(RRC connect request)消息所需资源的调度与下发(与msg2一同下发),基站侧在收到msg3消息后,完成竞争接入解决发送msg4(RRC connect request response)消息。
1) Random Access Preamble on RACH in uplink:
rach的作用主要有以下两点:
i) Achieve UP link synchronization between UE and eNB
ii) Obtain the resource for Message 3 (e.g, RRC Connection Request)
DL下行同步,ue通过下行同步消息PSS/SSS已经完成,对每个ue一致。但对于每个ue来说,相对于基站的位置远近不一,如果有上行数据需要发送,在基站测因为上行SC-OFDMA正交需求,需要每个ue发送的上行数据到达基站的时间一致,这样需要ue与基站见取得上行同步(https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42227141/article/details/84886278有相对详细描述)。
步骤一:UE发送preamble
Prach内容(RACH Preamble)
Preamble的主要作用是告诉eNodeB有一个随机接入请求,并使得eNodeB能估计其与UE之间的传输时延,以便eNodeB校准uplink timing并将校准信息通过timing advance command告知UE。
UE要成功发送preamble,需要:(1)选择preamble index;(2)选择用于发送preamble的PRACH资源;(3)确定对应的RA-RNTI;( 4)确定目标接收功率PREAMBLE_RECEIVED_TARGET_POWER。
根据36.211 5.7,random access preamble结构如下:包括Tcp以及Tseq
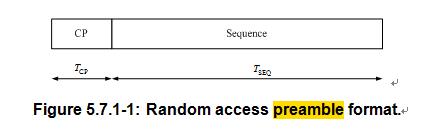

random access preamble生成
随机序列通过零自相关Zadoff-Chu序列生成,生成若干64bit字长的root Zadoff-Chu根序列,ue通过高层配置完成跟序列的选择。(没研究明白,具体生成方式参考36.211 5.7.2)
 where u = physical root sequence index
where u = physical root sequence index

在生成preamble后,会将序列码分成两组group A 、group B,A/B中的preamble划分规则36.321 5.1。
- the groups of Random Access Preambles and the set of available Random Access Preambles in each group:
The preambles that are contained in Random Access Preambles group A and Random Access Preambles group B are calculated from the parameters numberOfRA-Preambles and sizeOfRA-PreamblesGroupA:
If sizeOfRA-PreamblesGroupA is equal to numberOfRA-Preambles then there is no Random Access Preambles group B. The preambles in Random Access Preamble group A are the preambles 0 to sizeOfRA-PreamblesGroupA – 1 and, if it exists, the preambles in Random Access Preamble group B are the preambles sizeOfRA-PreamblesGroupA to numberOfRA-Preambles – 1 from the set of 64 preambles as defined in [36.211 5.7.2].
- if Random Access Preambles group B exists, the thresholds, messagePowerOffsetGroupB and messageSizeGroupA, the configured UE transmitted power of the Serving Cell performing the Random Access Procedure, PCMAX, c [10], and the offset between the preamble and Msg3, deltaPreambleMsg3, that are required for selecting one of the two groups of Random Access Preambles.
对于ue如何从group A 、group B选择preamble。在36.321 5.1中有明确说明
1、在ra-PreambleIndex与ra-PRACH-MaskIndex 明确已近完成配置情况下,使用配置好的参数
2、上述参数没有配置,preamble选择规则如下:
1)if msg3首次传输,在group B存在且Msg3的大小大于messageSizeGroupA,且pathloss小于PCMAX,c – preambleInitialReceivedTargetPower - deltaPreambleMsg3 – messagePowerOffsetGroupB,则选择group B;否则选择group A。
2)msg3 已经传输,使用与首次msg3传输相同的group中的随机preamble。
3)确定了group之后,UE从该group中随机选择一个preamble并将PRACH Mask Index设置为0。
Prach时频域资源
andom access preamble的发送由mac层触发,严格按照协议规定的时频域资源进行。PRACH resources资源位置由SIB2中PRACH配置参数prach-ConfigurationIndex 决定,由prach-ConfigurationIndex 确定的时域信息如下

对于type2类型也即时TDD模式,根据prach-ConfigurationIndex 可以确定Preamble Format ,是指前面的4种格式,使用哪个Prach格式。For frame structure type 2 with PRACH configuration 0, 1, 2, 20, 21, 22, 30, 31, 32, 40, 41, 42, 48, 49, 50, or with PRACH configuration 51, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57 in UL/DL configuration 3, 4, 5, the UE may for handover purposes assume an absolute value of the relative time difference between radio frame in the current cell and the target cell is less than 153600*Ts .

lte中type2类型的preamble发送时频域资源由四元组 确定,
确定,  指定了preamble可以选择在哪些系统帧上发送(0:所有帧;1:偶数帧;2:奇数帧)。
指定了preamble可以选择在哪些系统帧上发送(0:所有帧;1:偶数帧;2:奇数帧)。  指定preamble是位于一个系统帧的前半帧还是后半帧(0:前半帧;1:后半帧)。
指定preamble是位于一个系统帧的前半帧还是后半帧(0:前半帧;1:后半帧)。  指定preamble起始的上行子帧号,该子帧号位于两个连续的downlink-to-uplink switch point之间,且从0开始计数(见图21-5)。format 4是个例外,其 标记为(*)。四元组由rach-ConfigurationIndex 指示,参考36.11 5.7
指定preamble起始的上行子帧号,该子帧号位于两个连续的downlink-to-uplink switch point之间,且从0开始计数(见图21-5)。format 4是个例外,其 标记为(*)。四元组由rach-ConfigurationIndex 指示,参考36.11 5.7


对于TDD而言,preamble在频域上的起始RB是由prach-ConfigIndex和prach-FrequencyOffset确定的。通过prach-ConfigIndex查36.211的Table 5.7.1-4得到 (频域的偏移,单位是6个RB),通过prach-FrequencyOffset可以得到
(频域的偏移,单位是6个RB),通过prach-FrequencyOffset可以得到  ,再通过如下公式,可以得到format 0~3的preamble在频域上的起始RB:
,再通过如下公式,可以得到format 0~3的preamble在频域上的起始RB:

其中 是上行系统rb资源数,为了保证上行单载波的频域资源连续性,PRACH资源通常分布在上行带宽的两端(“高低频位置交错”)。起始位置由
是上行系统rb资源数,为了保证上行单载波的频域资源连续性,PRACH资源通常分布在上行带宽的两端(“高低频位置交错”)。起始位置由 确定,一般紧挨着PUCCH资源的位置。公式中的6表示preamble发送资源需要6个RB块。
确定,一般紧挨着PUCCH资源的位置。公式中的6表示preamble发送资源需要6个RB块。
对于format 4而言,起始RB的计算公式如下:

其中 是系统帧号,
是系统帧号, 是该系统帧内DL到UL转换点的子帧个数,例如TDD1 DSUUDDSUUD 对应的
是该系统帧内DL到UL转换点的子帧个数,例如TDD1 DSUUDDSUUD 对应的 为3。对否??(where
为3。对否??(where  is the number of DL to UL switch points within the radio frame.)
is the number of DL to UL switch points within the radio frame.)
以上是关于LTE随机接入RACH流程preamble发送的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
[4G&5G专题-77]:流程 - 4G LTE 接入网的随机接入流程