总结-模型评价指标的定义(基于CatBoost文档)
Posted oliveQ
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了总结-模型评价指标的定义(基于CatBoost文档)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Objectives and metrics-CatBoost Tutorial
- 损失函数、代价函数和目标函数的区别
- 回归问题
- 多元回归问题
- 分类问题
- 多分类问题
- 多标签分类
- 排序问题
- 自定义损失函数loss_function的说明
损失函数、代价函数和目标函数的区别
本部分参考自——机器学习中的目标函数、损失函数、代价函数有什么区别?
The loss function computes the error for a single training example;
the cost function is the average of the loss funcitons of the entire training set.
— — Andrew NG
- 损失函数(Loss Function )是定义在单个样本上的,算的是一个样本的误差。
- 代价函数(Cost Function )是定义在整个训练集上的,是所有样本误差的平均,也就是损失函数的平均。(也被称作经验风险)
- 目标函数(Object Function)定义为:最终需要优化的函数。等于经验风险+结构风险(也就是代价函数 + 正则化项)。代价函数最小化,降低经验风险,正则化项最小化降低。
源自CatBoost Tutorial的Objectives and metrics
回归问题
for regressor use RMSE, MultiRMSE, SurvivalAft,
MAE, Quantile, LogLinQuantile, Poisson,
MAPE, Lq or custom objective object
可以优化的目标函数
MAE

MAPE

Poisson
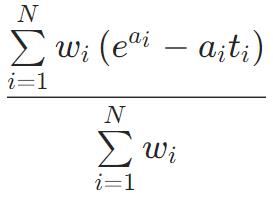
Quantile(α=0.5)=MAE

图像处理应用中,经常会用到quantile分位数损失函数,这个函数的作用是求数列或矩阵的分位数。在给定预测变量的某些值时,估计因变量的条件“分位数”。Quantile Loss实际上只是MAE的扩展形式(当分位数是第50个百分位时,Quantile Loss退化为MAE)。
RMSE
默认的函数:均方根误差
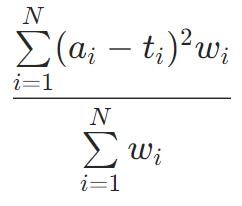
RMSEWithUncertainty
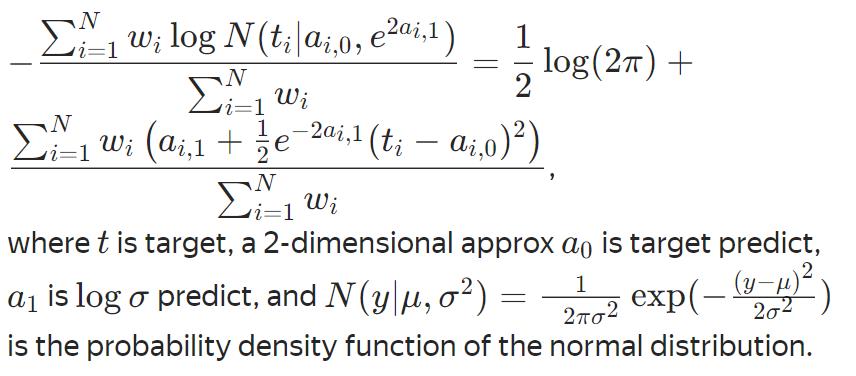
LogLinQuantile(α=0.5)
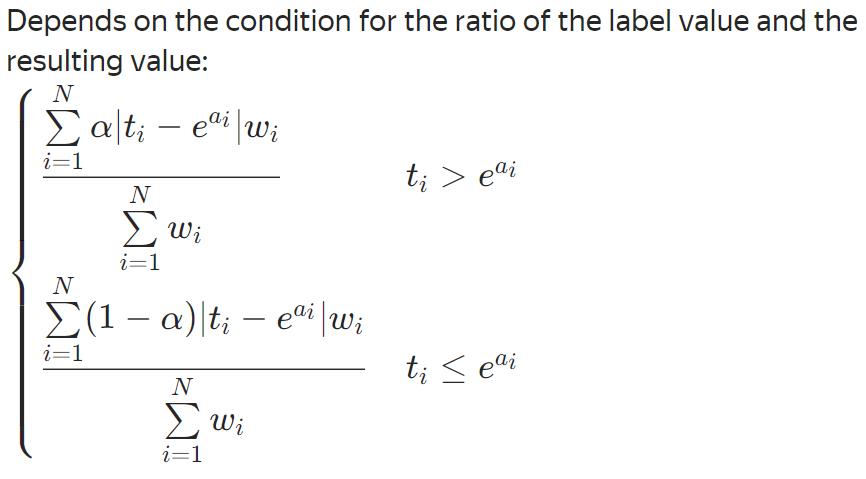
Lq

Huber

超参数δ(delta)控制:误差降到多小时变为二次误差。当Huber损失在[0−δ,0+δ] 之间时,等价为MSE,而在[−∞,δ]和[ δ , + ∞ ] 时为MAE。Huber损失结合了MSE和MAE的优点,对异常点更加鲁棒。
Expectile(α=0.5)

Tweedie
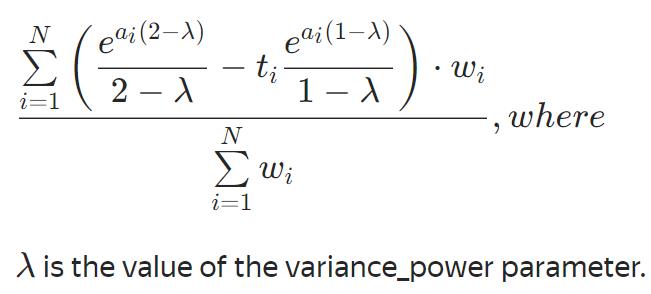
不可优化的评估函数
FairLoss

NumErrors

SMAPE

R2

MSLE

MedianAbsoluteError

多元回归问题
可以优化
MultiRMSE
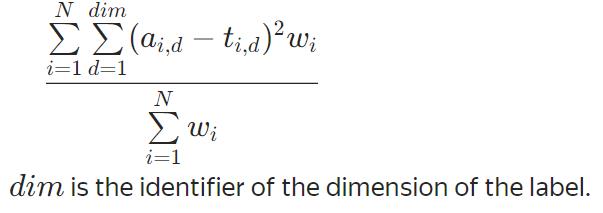
分类问题
可以优化
Logloss
二分类常用的对数损失函数

CrossEntropy
多分类问题中,交叉熵损失函数用来评估【当前训练得到的概率分布】与【真实分布】的差异情况,减少交叉熵损失就是在提高模型的预测准确率。

不能优化
Precision
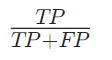
Recall

F
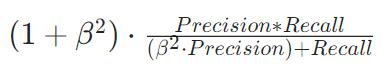
F1

BalancedAccuracy

BalancedErrorRate

MCC
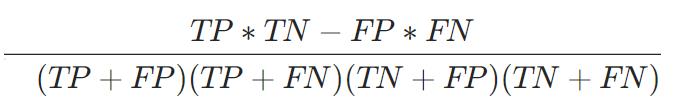
Accuracy

CtrFactor

AUC
Classic

Ranking

QueryAUC
Classic type

Ranking type

NormalizedGini=2AUC -1
BrierScore
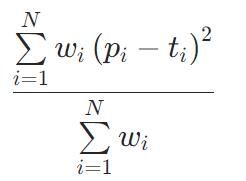
HingeLoss
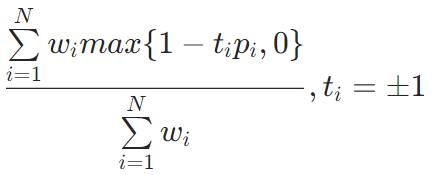
HammingLoss

ZeroOneLoss=1−Accuracy
Kappa

LogLikelihoodOfPrediction

多分类问题
可以优化
MultiClass
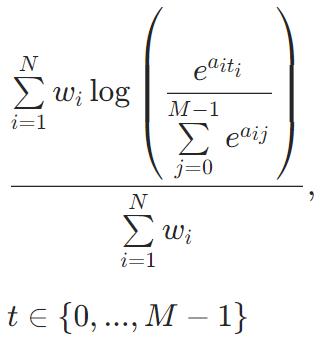
MultiClassOneVsAll

不能优化
Precision、Recall、F、F1
同二分类
TotalF1
取决于平均参数的值
Weighted

Macro
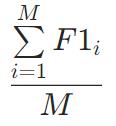
Micro
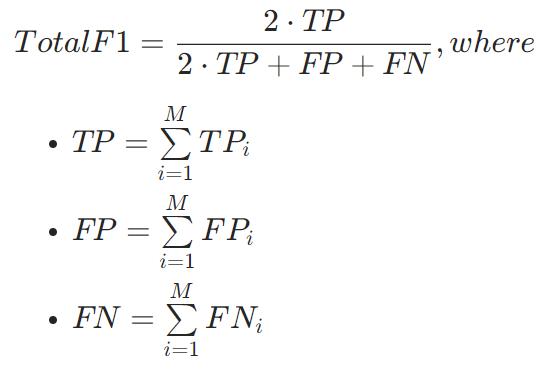
MCC
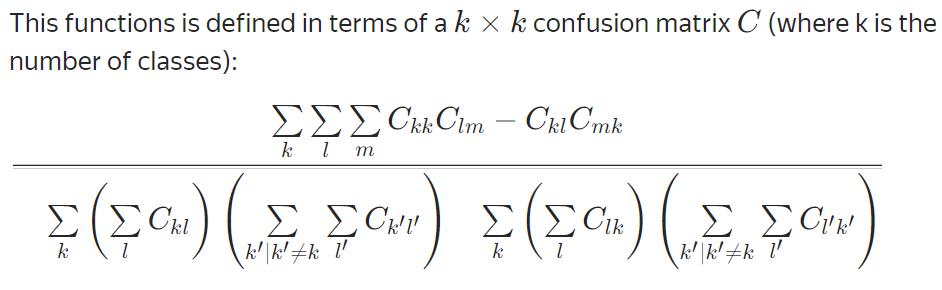
Accuracy
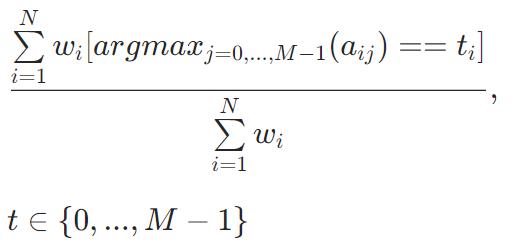
HammingLoss
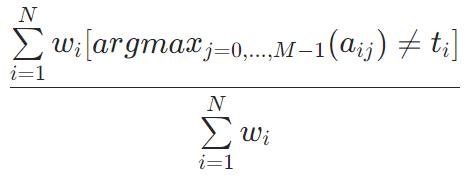
ZeroOneLoss=1−Accuracy
Kappa

Kappa系数是一种衡量分类精度的指标,
将Kappa系数作为2个分类器的差异性度量准则时,其取值范围为κ≤1
κ=1时表示分类结果完全相同,不具有差异性;
κ=0时表示分类结果相同,是偶然产生的,具有差异性;
κ<0表示分类器分类结果具有很大差异性.
κ值愈小,表征2个分类器的差异性愈大.
AUC
根据二进制分类计算原则,对编号为 0 到 M-1 的每个类 k 分别计算该值。 k 类的对象被认为是正的,而所有其他的都被认为是负的。

多标签分类
可以优化
MultiLogloss
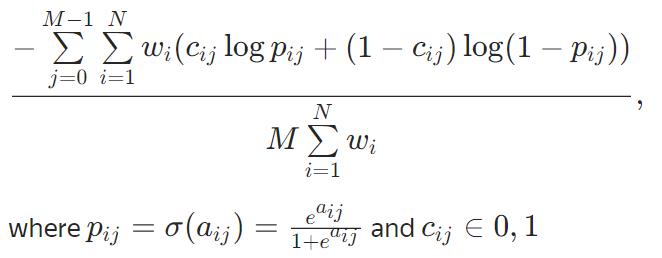
MultiCrossEntropy

不能优化
Precision、Recall、F、F1
同二分类
Accuracy
该公式取决于 type 参数的值
Classic

PerClass

HammingLoss

排序问题
Pairwise metrics
来自同一组的两个成员,必有输(n)赢(p),max_pairs是每组中生成对的最大数量。如果没有给出对则生效,因此不重复生成。
PairLogit、PairLogitPairwise(可优化)
与 PairLogit 相比,PairLogitPairwise可能会在大型数据集上提供更准确的结果,但计算速度要慢得多。
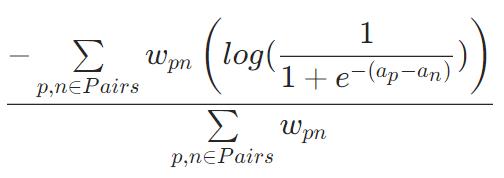
PairAccuracy(不可优化)

Groupwise metrics
YetiRankPairwise(可优化)
与 YetiRank 相比,此指标在大数据集上提供更准确的结果,但速度明显较慢。

YetiRank(可优化)
与 YetiRankPairwise 相比,该指标在大数据集上给出的结果不太准确,但速度明显更快。

StochasticFilter(可优化)
直接优化为预先定义的对象顺序计算的 FilteredDCG 指标,用于过滤固定排名下的对象。因此,FilteredDCG 度量可用于优化。


StochasticRank(可优化)
直接优化所选指标。所选指标的值将写入输出数据
有关详细信息,请参阅论文 StochasticRank:无标度离散函数的全局优化。
【Common parameters】num_estimations=1,mu=0,metric如下
【top】-1。这是组中用于计算排名指标的顶级样本数。顶部样本要么是具有最大近似值的样本,要么是具有最低目标值的样本(如果近似值相同)。
DCG
【type】Base, Exp.指标计算原则
【denominator】LogPosition, Position.指标分母类型
NDCG
【type】Base, Exp.指标计算原则
【denominator】LogPosition, Position.指标分母类型
PFound
【decay】0.85
QueryCrossEntropy(可优化, α=0.95)

QueryRMSE(可优化)

QuerySoftMax(可优化)

PFound(不可优化)

NDCG(不可优化)

DCG、FilteredDCG、AverageGain(不可优化)

PrecisionAt(不可优化)
RecallAt(不可优化)

MAP(不可优化):对象按预测相关性的降序排序
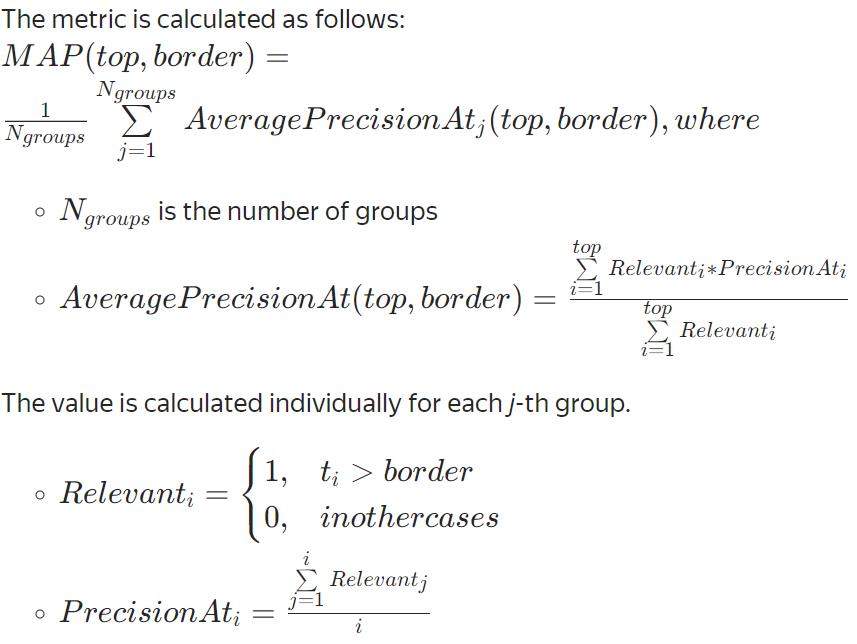
ERR(不可优化)
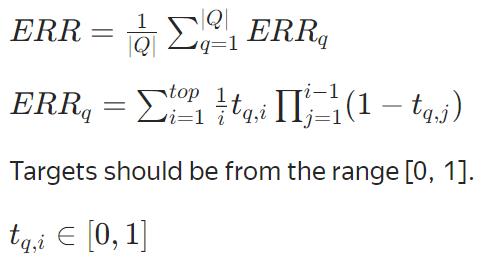
MRR(不可优化)

AUC、QueryAUC(不可优化)
通过AUC 类型,定义指标计算原则,与分类问题AUC和QueryAUC指标定义相同。
QueryAUC(不可优化)
题外话:
CatBoost中包含两个指标:
- loss_function:在训练中使用的指标。指定的值也决定了要解决的机器学习问题。The metric to use in training. The specified value also determines the machine learning problem to solve.
【包括】RMSE(默认)、Logloss、MAE、CrossEntropy、Quantile、LogLinQuantile、Lq、MultiRMSE、MultiClass、MultiClassOneVsAll、MultiLogloss、MultiCrossEntropy、MAPE、Poisson、PairLogit、PairLogitPairwise、QueryRMSE、QuerySoftMax、Tweedie、YetiRank、YetiRankPairwise、StochasticFilter、StochasticRank- eval_metric:用于过拟合检测(如果启用)和最佳模型选择(如果启用)的指标。The metric used for overfitting detection (if enabled) and best model selection (if enabled).
【包括】目标函数(默认)、RMSE、Logloss、MAE、CrossEntropy、Quantile、LogLinQuantile、Lq、MultiRMSE、MultiClass、MultiClassOneVsAll、MultiLogloss、MultiCrossEntropy、MAPE、Poisson、PairLogit、PairLogitPairwise、QueryRMSE、QuerySoftMax、Tweedie、SMAPE、Recall、Precision、F、F1、TotalF1、Accuracy、BalancedAccuracy、BalancedErrorRate、Kappa、WKappaLogLikelihoodOfPrediction、AUC、QueryAUC、R2、FairLoss、NumErrors、MCC、BrierScore、HingeLoss、HammingLoss、ZeroOneLoss、MSLE、MedianAbsoluteError、Huber、Expectile、MultiRMSE、PairAccuracy、AverageGain、PFound、NDCG、DCG、FilteredDCG、NormalizedGini、PrecisionAt、RecallAt、MAP、Quantile:alpha=0.3
自定义损失函数loss_function的说明
分类Logloss
class LoglossObjective(object):
def calc_ders_range(self, approxes, targets, weights):
assert len(approxes) == len(targets)
if weights is not None:
assert len(weights) == len(approxes)
result = []
for index in range(len(targets)):
e = np.exp(approxes[index])
p = e / (1 + e)
der1 = targets[index] - p
der2 = -p * (1 - p)
if weights is not None:
der1 *= weights[index]
der2 *= weights[index]
result.append((der1, der2))
return result
model = CatBoostClassifier(loss_function=LoglossObjective())
回归RMSE
class RmseObjective(object):
def calc_ders_range(self, approxes, targets, weights):
assert len(approxes) == len(targets)
if weights is not None:
assert len(weights) == len(approxes)
result = []
for index in range(len(targets)):
der1 = targets[index] - approxes[index]
der2 = -1
if weights is not None:
der1 *= weights[index]
der2 *= weights[index]
result.append((der1, der2))
return result
model = CatBoostRegressor(loss_function=RmseObjective())
多分类MultiClass
class MultiClassObjective(object):
def calc_ders_multi(self, approx, target, weight):
approx = np.array(approx) - max(approx)
exp_approx = np.exp(approx)
exp_sum = exp_approx.sum()
grad = []
hess = []
for j in range(len(approx)):
der1 = -exp_approx[j] / exp_sum
if j == target:
der1 += 1
hess_row = []
for j2 in range(len(approx)):
der2 = exp_approx[j] * exp_approx[j2] / (exp_sum**2)
if j2 == j:
der2 -= exp_approx[j] / exp_sum
hess_row.append(der2 * weight)
grad.append(der1 * weight)
hess.append(hess_row)
return (grad, hess)
model = CatBoostClassifier(loss_function=MultiClassObjective())
以上是关于总结-模型评价指标的定义(基于CatBoost文档)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章