Android 架构 3.实现
Posted H_bolin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 架构 3.实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
以实现最小化可用产品(MVP)的目标,用最简单的方式来搭建架构和实现代码。
IDE采用android Studio,Demo实现的功能为用户注册、登录和展示一个券列表,数据采用我们现有项目的测试数据,接口也是我们项目中的测试接口。
项目搭建
根据架构篇所讲的,将项目分为了四个层级:模型层、接口层、核心层、界面层。四个层级之间的关系如下图所示:
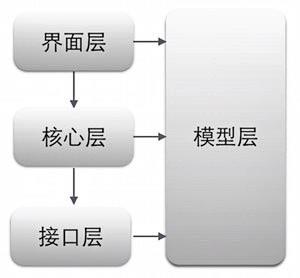
实现上,在Android Studio分为了相应的四个模块(Module):model、api、core、app。
model为模型层,api为接口层,core为核心层,app为界面层。
model、api、core这三个模块的类型为library,app模块的类型为application。
四个模块之间的依赖设置为:model没有任何依赖,接口层依赖了模型层,核心层依赖了模型层和接口层,界面层依赖了核心层和模型层。
项目搭建的步骤如下:
创建新项目,项目名称为KAndroid,包名为com.keegan.kandroid。默认已创建了app模块,查看下app模块下的build.gradle,会看到第一行为:
apply plugin: \'com.android.application\'
这行表明了app模块是application类型的。
分别新建模块model、api、core,Module Type都选为Android Library,在Add an activity to module页面选择Add No Activity,这三个模块做为库使用,并不需要界面。创建完之后,查看相应模块的build.gradle,会看到第一行为:
apply plugin: \'com.android.library\'
建立模块之间的依赖关系。有两种方法可以设置:
第一种:通过右键模块,然后Open Module Settings,选择模块的Dependencies,点击左下方的加号,选择Module dependency,最后选择要依赖的模块,下图为api模块添加了model依赖;

第二种:直接在模块的build.gradle设置。打开build.gradle,在最后的dependencies一项里面添加新的一行:compile project(\':ModuleName\'),比如app模块添加对model模块和core模块依赖之后的dependencies如下:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: \'libs\', include: [\'*.jar\'])
compile \'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.0\'
compile project(\':model\')
compile project(\':core\')
}
通过上面两种方式的任意一种,创建了模块之间的依赖关系之后,每个模块的build.gradle的dependencies项的结果将会如下:
model:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: \'libs\', include: [\'*.jar\'])
compile \'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.0\'
}
api:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: \'libs\', include: [\'*.jar\'])
compile \'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.0\'
compile project(\':model\')
}
core:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: \'libs\', include: [\'*.jar\'])
compile \'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.0\'
compile project(\':model\')
compile project(\':api\')
}
app:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: \'libs\', include: [\'*.jar\'])
compile \'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.0\'
compile project(\':model\')
compile project(\':core\')
}
创建业务对象模型
业务对象模型统一存放于model模块,是对业务数据的封装,大部分都是从接口传过来的对象,因此,其属性也与接口传回的对象属性相一致。在这个Demo里,只有一个业务对象模型,封装了券的基本信息,以下是该实体类的代码:

/** * 券的业务模型类,封装了券的基本信息。 * 券分为了三种类型:现金券、抵扣券、折扣券。 * 现金券是拥有固定面值的券,有固定的售价; * 抵扣券是满足一定金额后可以抵扣的券,比如满100减10元; * 折扣券是可以打折的券。 * * @version 1.0 创建时间:15/6/21 */ public class CouponBO implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8022957276104379230L; private int id; // 券id private String name; // 券名称 private String introduce; // 券简介 private int modelType; // 券类型,1为现金券,2为抵扣券,3为折扣券 private double faceValue; // 现金券的面值 private double estimateAmount; // 现金券的售价 private double debitAmount; // 抵扣券的抵扣金额 private double discount; // 折扣券的折扣率(0-100) private double miniAmount; // 抵扣券和折扣券的最小使用金额 // TODO 所有属性的getter和setter }
接口层的封装
在这个Demo里,提供了4个接口:一个发送验证码的接口、一个注册接口、一个登录接口、一个获取券列表的接口。这4个接口具体如下:
发送验证码接口
URL:http://uat.b.quancome.com/platform/api
参数:
| 参数名 | 描述 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| appKey | ANDROID_KCOUPON | String |
| method | service.sendSmsCode4Register | String |
| phoneNum | 手机号码 | String |
输出样例:
{ "event": "0", "msg": "success" }
注册接口
URL:http://uat.b.quancome.com/platform/api
参数:
| 参数名 | 描述 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| appKey | ANDROID_KCOUPON | String |
| method | customer.registerByPhone | String |
| phoneNum | 手机号码 | String |
| code | 验证码 | String |
| password | MD5加密密码 | String |
输出样例:
{ "event": "0", "msg": "success" }
登录接口
URL:http://uat.b.quancome.com/platform/api
其他参数:
| 参数名 | 描述 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| appKey | ANDROID_KCOUPON | String |
| method | customer.loginByApp | String |
| loginName | 登录名(手机号) | String |
| password | MD5加密密码 | String |
| imei | 手机imei串号 | String |
| loginOS | 系统,android为1 | int |
输出样例:
{ "event": "0", "msg": "success" }
券列表
URL:http://uat.b.quancome.com/platform/api
其他参数:
| 参数名 | 描述 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| appKey | ANDROID_KCOUPON | String |
| method | issue.listNewCoupon | String |
| currentPage | 当前页数 | int |
| pageSize | 每页显示数量 | int |
输出样例:
{ "event": "0", "msg": "success", "maxCount": 125, "maxPage": 7, "currentPage": 1, "pageSize": 20, "objList":[
{"id": 1, "name": "测试现金券", "modelType": 1, ...},
{...},
...
]}
在架构篇已经讲过,接口返回的json数据有三种固定结构:
{"event": "0", "msg": "success"}
{"event": "0", "msg": "success", "obj":{...}}
{"event": "0", "msg": "success", "objList":[{...}, {...}], "currentPage": 1, "pageSize": 20, "maxCount": 2, "maxPage": 1}
因此可以封装成实体类,代码如下:

public class ApiResponse<T> { private String event; // 返回码,0为成功 private String msg; // 返回信息 private T obj; // 单个对象 private T objList; // 数组对象 private int currentPage; // 当前页数 private int pageSize; // 每页显示数量 private int maxCount; // 总条数 private int maxPage; // 总页数 // 构造函数,初始化code和msg public ApiResponse(String event, String msg) { this.event = event; this.msg = msg; } // 判断结果是否成功 public boolean isSuccess() { return event.equals("0"); } // TODO 所有属性的getter和setter }
上面4个接口,URL和appKey都是一样的,用来区别不同接口的则是method字段,因此,URL和appKey可以统一定义,method则根据不同接口定义不同常量。而除去appKey和method,剩下的参数才是每个接口需要定义的参数。因此,对上面4个接口的定义如下:

public interface Api { // 发送验证码 public final static String SEND_SMS_CODE = "service.sendSmsCode4Register"; // 注册 public final static String REGISTER = "customer.registerByPhone"; // 登录 public final static String LOGIN = "customer.loginByApp"; // 券列表 public final static String LIST_COUPON = "issue.listNewCoupon"; /** * 发送验证码 * * @param phoneNum 手机号码 * @return 成功时返回:{ "event": "0", "msg":"success" } */ public ApiResponse<Void> sendSmsCode4Register(String phoneNum); /** * 注册 * * @param phoneNum 手机号码 * @param code 验证码 * @param password MD5加密的密码 * @return 成功时返回:{ "event": "0", "msg":"success" } */ public ApiResponse<Void> registerByPhone(String phoneNum, String code, String password); /** * 登录 * * @param loginName 登录名(手机号) * @param password MD5加密的密码 * @param imei 手机IMEI串号 * @param loginOS Android为1 * @return 成功时返回:{ "event": "0", "msg":"success" } */ public ApiResponse<Void> loginByApp(String loginName, String password, String imei, int loginOS); /** * 券列表 * * @param currentPage 当前页数 * @param pageSize 每页显示数量 * @return 成功时返回:{ "event": "0", "msg":"success", "objList":[...] } */ public ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>> listNewCoupon(int currentPage, int pageSize); }
Api的实现类则是ApiImpl了,实现类需要封装好请求数据并向服务器发起请求,并将响应结果的数据转为ApiResonse返回。而向服务器发送请求并将响应结果返回的处理则封装到http引擎类去处理。另外,这里引用了gson将json转为对象。ApiImpl的实现代码如下:

public class ApiImpl implements Api { private final static String APP_KEY = "ANDROID_KCOUPON"; private final static String TIME_OUT_EVENT = "CONNECT_TIME_OUT"; private final static String TIME_OUT_EVENT_MSG = "连接服务器失败"; // http引擎 private HttpEngine httpEngine; public ApiImpl() { httpEngine = HttpEngine.getInstance(); } @Override public ApiResponse<Void> sendSmsCode4Register(String phoneNum) { Map<String, String> paramMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); paramMap.put("appKey", APP_KEY); paramMap.put("method", SEND_SMS_CODE); paramMap.put("phoneNum", phoneNum); Type type = new TypeToken<ApiResponse<Void>>(){}.getType(); try { return httpEngine.postHandle(paramMap, type); } catch (IOException e) { return new ApiResponse(TIME_OUT_EVENT, TIME_OUT_EVENT_MSG); } } @Override public ApiResponse<Void> registerByPhone(String phoneNum, String code, String password) { Map<String, String> paramMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); paramMap.put("appKey", APP_KEY); paramMap.put("method", REGISTER); paramMap.put("phoneNum", phoneNum); paramMap.put("code", code); paramMap.put("password", EncryptUtil.makeMD5(password)); Type type = new TypeToken<ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>>>(){}.getType(); try { return httpEngine.postHandle(paramMap, type); } catch (IOException e) { return new ApiResponse(TIME_OUT_EVENT, TIME_OUT_EVENT_MSG); } } @Override public ApiResponse<Void> loginByApp(String loginName, String password, String imei, int loginOS) { Map<String, String> paramMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); paramMap.put("appKey", APP_KEY); paramMap.put("method", LOGIN); paramMap.put("loginName", loginName); paramMap.put("password", EncryptUtil.makeMD5(password)); paramMap.put("imei", imei); paramMap.put("loginOS", String.valueOf(loginOS)); Type type = new TypeToken<ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>>>(){}.getType(); try { return httpEngine.postHandle(paramMap, type); } catch (IOException e) { return new ApiResponse(TIME_OUT_EVENT, TIME_OUT_EVENT_MSG); } } @Override public ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>> listNewCoupon(int currentPage, int pageSize) { Map<String, String> paramMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); paramMap.put("appKey", APP_KEY); paramMap.put("method", LIST_COUPON); paramMap.put("currentPage", String.valueOf(currentPage)); paramMap.put("pageSize", String.valueOf(pageSize)); Type type = new TypeToken<ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>>>(){}.getType(); try { return httpEngine.postHandle(paramMap, type); } catch (IOException e) { return new ApiResponse(TIME_OUT_EVENT, TIME_OUT_EVENT_MSG); } } }
而http引擎类的实现如下:

public class HttpEngine { private final static String SERVER_URL = "http://uat.b.quancome.com/platform/api"; private final static String REQUEST_MOTHOD = "POST"; private final static String ENCODE_TYPE = "UTF-8"; private final static int TIME_OUT = 15000; private static HttpEngine instance = null; private HttpEngine() { } public static HttpEngine getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new HttpEngine(); } return instance; } public <T> T postHandle(Map<String, String> paramsMap, Type typeOfT) throws IOException { String data = joinParams(paramsMap); HttpUrlConnection connection = getConnection(); connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(data.getBytes().length)); connection.connect(); OutputStream os = connection.getOutputStream(); os.write(data.getBytes()); os.flush(); if (connection.getResponseCode() == 200) { // 获取响应的输入流对象 InputStream is = connection.getInputStream(); // 创建字节输出流对象 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 定义读取的长度 int len = 0; // 定义缓冲区 byte buffer[] = new byte[1024]; // 按照缓冲区的大小,循环读取 while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { // 根据读取的长度写入到os对象中 baos.write(buffer, 0, len); } // 释放资源 is.close(); baos.close(); connection.disconnect(); // 返回字符串 final String result = new String(baos.toByteArray()); Gson gson = new Gson(); return gson.fromJson(result, typeOfT); } else { connection.disconnect(); return null; } } private HttpURLConnection getConnection() { HttpURLConnection connection = null; // 初始化connection try { // 根据地址创建URL对象 URL url = new URL(SERVER_URL); // 根据URL对象打开链接 connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // 设置请求的方式 connection.setRequestMethod(REQUEST_MOTHOD); // 发送POST请求必须设置允许输入,默认为true connection.setDoInput(true); // 发送POST请求必须设置允许输出 connection.setDoOutput(true); // 设置不使用缓存 connection.setUseCaches(false); // 设置请求的超时时间 connection.setReadTimeout(TIME_OUT); connection.setConnectTimeout(TIME_OUT); connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"); connection.setRequestProperty("Connection", "keep-alive"); connection.setRequestProperty("Response-Type", "json"); connection.setChunkedStreamingMode(0); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return connection; } private String joinParams(Map<String, String> paramsMap) { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (String key : paramsMap.keySet()) { stringBuilder.append(key); stringBuilder.append("="); try { stringBuilder.append(URLEncoder.encode(paramsMap.get(key), ENCODE_TYPE)); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } stringBuilder.append("&"); } return stringBuilder.substring(0, stringBuilder.length() - 1); } }
至此,接口层的封装就完成了。接下来再往上看看核心层吧。
核心层的逻辑
核心层处于接口层和界面层之间,向下调用Api,向上提供Action,它的核心任务就是处理复杂的业务逻辑。先看看我对Action的定义:

public interface AppAction { // 发送手机验证码 public void sendSmsCode(String phoneNum, ActionCallbackListener<Void> listener); // 注册 public void register(String phoneNum, String code, String password, ActionCallbackListener<Void> listener); // 登录 public void login(String loginName, String password, ActionCallbackListener<Void> listener); // 按分页获取券列表 public void listCoupon(int currentPage, ActionCallbackListener<List<CouponBO>> listener); }
首先,和Api接口对比就会发现,参数并不一致。登录并没有iemi和loginOS的参数,获取券列表的参数里也少了pageSize。这是因为,这几个参数,跟界面其实并没有直接关系。Action只要定义好跟界面相关的就可以了,其他需要的参数,在具体实现时再去获取。
另外,大部分action的处理都是异步的,因此,添加了回调监听器ActionCallbackListener,回调监听器的泛型则是返回的对象数据类型,例如获取券列表,返回的数据类型就是List,没有对象数据时则为Void。回调监听器只定义了成功和失败的方法,如下:

public interface ActionCallbackListener<T> { /** * 成功时调用 * * @param data 返回的数据 */ public void onSuccess(T data); /** * 失败时调用 * * @param errorEvemt 错误码 * @param message 错误信息 */ public void onFailure(String errorEvent, String message); }
接下来再看看Action的实现。首先,要获取imei,那就需要传入一个Context;另外,还需要loginOS和pageSize,这定义为常量就可以了;还有,要调用接口层,所以还需要Api实例。而接口的实现分为两步,第一步做参数检查,第二步用异步任务调用Api。具体实现如下:

public class AppActionImpl implements AppAction { private final static int LOGIN_OS = 1; // 表示Android private final static int PAGE_SIZE = 20; // 默认每页20条 private Context context; private Api api; public AppActionImpl(Context context) { this.context = context; this.api = new ApiImpl(); } @Override public void sendSmsCode(final String phoneNum, final ActionCallbackListener<Void> listener) { // 参数为空检查 if (TextUtils.isEmpty(phoneNum)) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_NULL, "手机号为空"); } return; } // 参数合法性检查 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("1\\\\d{10}"); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(phoneNum); if (!matcher.matches()) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_ILLEGAL, "手机号不正确"); } return; } // 请求Api new AsyncTask<Void, Void, ApiResponse<Void>>() { @Override protected ApiResponse<Void> doInBackground(Void... voids) { return api.sendSmsCode4Register(phoneNum); } @Override protected void onPostExecute(ApiResponse<Void> response) { if (listener != null && response != null) { if (response.isSuccess()) { listener.onSuccess(null); } else { listener.onFailure(response.getEvent(), response.getMsg()); } } } }.execute(); } @Override public void register(final String phoneNum, final String code, final String password, final ActionCallbackListener<Void> listener) { // 参数为空检查 if (TextUtils.isEmpty(phoneNum)) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_NULL, "手机号为空"); } return; } if (TextUtils.isEmpty(code)) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_NULL, "验证码为空"); } return; } if (TextUtils.isEmpty(password)) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_NULL, "密码为空"); } return; } // 参数合法性检查 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("1\\\\d{10}"); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(phoneNum); if (!matcher.matches()) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_ILLEGAL, "手机号不正确"); } return; } // TODO 长度检查,密码有效性检查等 // 请求Api new AsyncTask<Void, Void, ApiResponse<Void>>() { @Override protected ApiResponse<Void> doInBackground(Void... voids) { return api.registerByPhone(phoneNum, code, password); } @Override protected void onPostExecute(ApiResponse<Void> response) { if (listener != null && response != null) { if (response.isSuccess()) { listener.onSuccess(null); } else { listener.onFailure(response.getEvent(), response.getMsg()); } } } }.execute(); } @Override public void login(final String loginName, final String password, final ActionCallbackListener<Void> listener) { // 参数为空检查 if (TextUtils.isEmpty(loginName)) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_NULL, "登录名为空"); } return; } if (TextUtils.isEmpty(password)) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_NULL, "密码为空"); } return; } // TODO 长度检查,密码有效性检查等 // 请求Api new AsyncTask<Void, Void, ApiResponse<Void>>() { @Override protected ApiResponse<Void> doInBackground(Void... voids) { TelephonyManager telephonyManager = (TelephonyManager) context.getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE); String imei = telephonyManager.getDeviceId(); return api.loginByApp(loginName, password, imei, LOGIN_OS); } @Override protected void onPostExecute(ApiResponse<Void> response) { if (listener != null && response != null) { if (response.isSuccess()) { listener.onSuccess(null); } else { listener.onFailure(response.getEvent(), response.getMsg()); } } } }.execute(); } @Override public void listCoupon(final int currentPage, final ActionCallbackListener<List<CouponBO>> listener) { // 参数检查 if (currentPage < 0) { if (listener != null) { listener.onFailure(ErrorEvent.PARAM_ILLEGAL, "当前页数小于零"); } } // TODO 添加缓存 // 请求Api new AsyncTask<Void, Void, ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>>>() { @Override protected ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>> doInBackground(Void... voids) { return api.listNewCoupon(currentPage, PAGE_SIZE); } @Override protected void onPostExecute(ApiResponse<List<CouponBO>> response) { if (listener != null && response != null) { if (response.isSuccess()) { listener.onSuccess(response.getObjList()); } else { listener.onFailure(response.getEvent(), response.getMsg()); } } } }.execute(); } }
简单的实现代码就是这样,其实,这还有很多地方可以优化,比如,将参数为空的检查、手机号有效性的检查、数字型范围的检查等等,都可以抽成独立的方法,从而减少重复代码的编写。异步任务里的代码也一样,都是可以通过重构优化的。另外,需要扩展时,比如添加缓存,那就在调用Api之前处理。
核心层的逻辑就是这样了。最后就到界面层了。
界面层
在这个Demo里,只有三个页面:登录页、注册页、券列表页。在这里,也会遵循界面篇提到的三个基本原则:规范性、单一性、简洁性。
首先,界面层需要调用核心层的Action,而这会在整个应用级别都用到,因此,Action的实例最好放在Application里。代码如下:
