java流总结 字节流
Posted yuanGrowing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java流总结 字节流相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、关于流的理论知识 在学习java的过程中,不可避免的会遇到各种流,各种Stream,开始的时候用的很烦,但是细细的总结之后其实也挺简单的。 1.1 什么是流? 按我自己的理解,这个流是一种工具,是程序和数据源之间进行数据交换的工具,但是这个流是单向的,也就是说只能存在程序向 数据源的流或者数据源向程序的流,而且这个流是不面向连接的。 举个例子,远古时期猿人还不会使用语言的时候,有一天一只猿人A开窍了,突然会说话了(说话这个功能你就可以理解 为outputstream,输出流),但是没人听懂它,后来有一只猿B突然能听懂了(听懂这个能力你可以理解为InputStream),这样 A就可以 向B诉说自己的想法,但是B很伤心,因为B还不会说呢。后来B也学会了OutputStream,而A也学会了InputStream,这 样A和B就能 愉快的交流了。 关于流的理论知识可以看 http://www.cnblogs.com/shitouer/archive/2012/12/19/2823641.html 。 1.2 流的分类和功能 a.根据流传输的格式可以分为字节流和字符流,字节流传输的是以字节为单位的数据,字符流是传输的是以字符(两字节的 Unicode 字符)为单位的数据。 b.根据流的方向分为输入流和输出流(输入和输出是针对于程序来说的,向程序输入是输入流) c.流的功能不同,分为节点流和处理流(我觉得用底层流和上层流来区分更好,节点流作为底层流最终是作为传输用的,处理流上 层流是 为了方便程序的使用而出现的可以包装底层流的流)。 下面的图可以帮助理解(只是选了一些我用过的流):
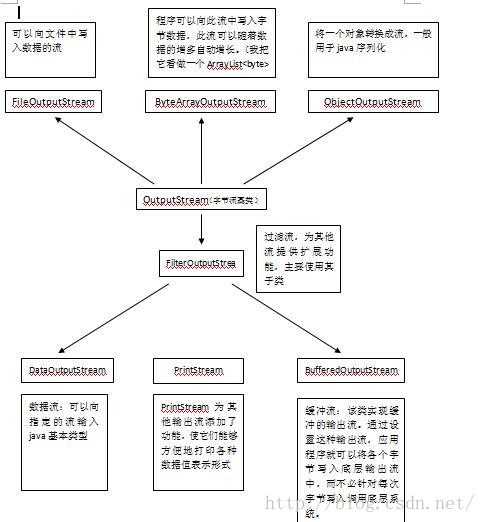
2、各种流的使用实践 以文件流为例,进行讲解。 2.1 利用最基础的inputstream和outputstream来操作文件(注意看注释) OutputStream:
| public static void main(String args[]) File file = new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\Administrator\\\\Desktop\\\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()) try file.createNewFile(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); OutputStream outputStream = null ; try outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); //OutputSteam 是最底层的输出流,只能操作字节数据 //向文件中写数据的时候要注意编码,否则文件中不能正常显示中文 outputStream.write(new String("你好".getBytes(),"utf8").getBytes()); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try outputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); |
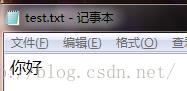
InputStream:
| InputStream inputStream = null ; try inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];//available可以获取到此流可以获得的字节数目 inputStream.read(bytes);//将文件中的数据通过字节流读到bytes数组中 for(int i=0;i<bytes.length;i++) System.out.print(bytes[i]+" "); System.out.println(); //将字节转换成字符串显示 System.out.println(new String(bytes,"utf8")); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try inputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); |
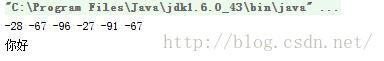 2.2 利用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream操作文件
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream是继承自最底层的输入输出流的,那么他们和基本的输入输出流有什么不同呢?
FileInputStream和InputStream基本上一样,只是FileInputStream提供了一个getChannel方法,可以使用java.nio中的
FileChannel类来操作文件,这个这里就先不研究了。
FileOutputStream:
如果你重复的执行之前的那个OutputStream的例子,你有没有发现每一次写入文件的时候都是完全重新写的文件,将文件原来
的值覆盖掉了。那我们如果需要向文件里面追加内容怎么办呢?有一个笨方法,就是将原来文件的内容读出来,然后将原来的内
容和要追加的内容一起放到文件里面去。但是这样显然很麻烦嘛。没关系,我们可以使用FileOutputStream。
2.2 利用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream操作文件
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream是继承自最底层的输入输出流的,那么他们和基本的输入输出流有什么不同呢?
FileInputStream和InputStream基本上一样,只是FileInputStream提供了一个getChannel方法,可以使用java.nio中的
FileChannel类来操作文件,这个这里就先不研究了。
FileOutputStream:
如果你重复的执行之前的那个OutputStream的例子,你有没有发现每一次写入文件的时候都是完全重新写的文件,将文件原来
的值覆盖掉了。那我们如果需要向文件里面追加内容怎么办呢?有一个笨方法,就是将原来文件的内容读出来,然后将原来的内
容和要追加的内容一起放到文件里面去。但是这样显然很麻烦嘛。没关系,我们可以使用FileOutputStream。
| FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null ; try fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file,true); fileOutputStream.write(new String("it is append!".getBytes(),"utf8").getBytes()); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try fileOutputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); |
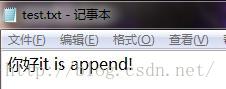
2.3 DataOutputStream和DataInputStream对编程的简化 之前我们程序的输入或者输出都必须是字节类型的数据,难道每一次输出之前输入之后都要转换一下格式吗?不,有了 DataOutputStream和DataInputStream妈妈再也不用担心我偷懒了。 这两者可以直接进行java基本类型的输入输出。
| DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null ; DataInputStream dataInputStream = null ; InputStream inputStream = null ; try inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream); dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file)); dataOutputStream.writeInt(12);//向文件中写入一个int类型的数字12 System.out.println(inputStream.available());//输出为4,证明写入的的确是4字节的int型数字,而不是byte System.out.println(dataInputStream.readInt()); catch (FileNotFoundException e) e.printStackTrace(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); finally try inputStream.close(); dataOutputStream.close(); dataInputStream.close(); catch (IOException e) e.printStackTrace(); |
以上是关于java流总结 字节流的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章