Hyrax: Doubly-efficient zkSNARKs without trusted setup学习笔记
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Hyrax: Doubly-efficient zkSNARKs without trusted setup学习笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
Wahby等人2018年论文《Doubly-efficient zkSNARKs without trusted setup》。
代码实现参见:
https://github.com/hyraxZK
视频解说参见:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ScY9Z5tZZKU
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yq2AfLlMww0
论文要点:
- 基于standard cryptographic assumption,无需trusted setup,对Prover和Verifier均具有low communication complexity和low concrete cost的zkSNARKs for NP。
- Communication为 Θ ( d ⋅ log G + n w ) \\Theta(d\\cdot \\log G+\\sqrtn_w) Θ(d⋅logG+nw),其中 d , G d,G d,G分别为verifying circuit的depth和width, w n w_n wn为witness size。
- 当用于batched statements或者data-parallel statements时,Prover的runtime为linear in the verifying circuit size,Verifier的runtime为sub-linear in the verifying circuit size。两者均具有good constants。
- 通过使用a new commitment scheme for multilinear polynomials,witness-related communication可reduced,但verifier time会增加。
- 需要在setup、complexity assumptions、proof size和computational cost之间进行取舍平衡。
- 基于discrete log assumption,采用Fiat-Shamir heuristic 实现了zkSNARK in the random oracle model,本文称之为Hyrax。
- 将Hyrax与5种系统(BCCGP-sqrt, Bulletproofs, Ligero, ZKB++和libSTARK)进行了对比。对于modest problem sizes,Hyrax具有smaller proofs,most computationally costly baseline,prover和verifier速度快于5种系统中的3种。
其中5种方案分别为:
- BCCGP-sqrt:来源于Bootle等人2016年论文《Efficient zero-knowledge arguments for arithmetic circuits in the discrete log setting》。(在Groth [57] 和 Bayer and Groth [6] 的基础上,基于hardness of discrete logarithm,提供了2种ZK argument for Arithmetic Circuit C C C’s satisfiability。第一种proof size为 O ( M ) O(\\sqrtM) O(M),具有quasi-linear prover and verifier runtime for an AC with M M M multiplications;第二种proof size为 O ( log M ) O(\\log M) O(logM) at the cost of concretely longer prover and verifier runtimes。)
- Bulletproofs:来源于Bünz等人2018年论文《Bulletproofs: Efficient range proofs for confidential transactions》。(在BCCGP-sqrt的基础上进行改进,reduce proof size and runtimes in the log scheme ≈ 3 × \\approx 3\\times ≈3×)
- Ligero:来源于Ames等人2017年论文《Ligero: Lightweight sublinear arguments without a trusted setup》。(在ZKB++的基础上,使用了更成熟的secure computation protocol,可prove an Arithmetic Circuit C C C’s satisfiability with proof size O ( ∣ C ∣ ) O(\\sqrt|C|) O(∣C∣),prover和verifier work为quasi-linear in ∣ C ∣ |C| ∣C∣。)
- ZKB++:来源于Chase等人2017年论文《Post-quantum zero-knowledge and signatures from symmetric-key primitives》。(将a secure multi-party computation protocol into a ZK argument,为a ZK argument system for Boolean circuits with no trusted setup from collision-resistant hashes。concretely inexpensive for small circuits,但是costs scale linearly with circuit size。)
- libSTARK:来源于Ben-Sasson等人2018年论文《Scalable, transparent, and post-quantum secure computational integrity》。(zkSTARKs不需要trusted setup,no public-key cryptography,但是其soundness 基于non-standard conjecture related to Reed-Solomon codes。Both proof size and verifier runtime are logarithmic in circuit size (hundreds of kilobytes and tens of milliseconds, respectively, in practice), and prover runtime is quasi-linear。)
1.1 zero-knowledge proof
A zero-knowledge proof用于convince a verifier of a statement while revealing nothing but its own validity。
-
zero-knowledge proof概念由Goldwasser等人在1989年论文《The knowledge complexity of interactive proof systems》中首次提出。
-
Ben-Or等人1990年论文《Everything provable is provable in zero-knowledge》中指出:
any problem solvable by an interactive proof (IP) is also solvable by a computational zero-knowledge proof or pefect zero-knowledge argument。
也就是说,given an interactive proof for any NP-complete problem, one can construct zero-knowledge proofs or arguments for any NP statement。
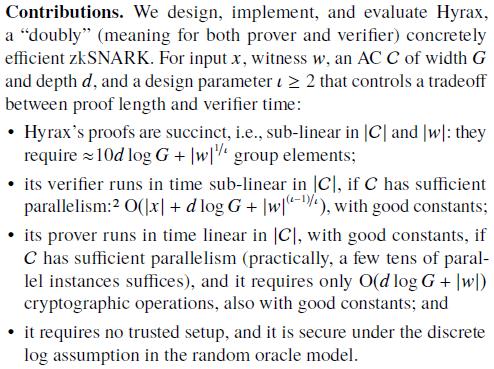
1.2 本文算法性能表现
本文主要关注的点有:
- proof应为succinct,sub-linear in the size of the statement and the witness to the statement’s validity;
- verifier应run in time linear in input plus proof size;
- prover,given a witness to the statement’s validity,应run in time linear in the cost of the NP verification procedure;
- 整个scheme应既不需要trusted setup,也不需要common reference string;
- soundness and zero-knowledge应为statistical或者基于standard cryptographic assumptions。实际上,security in the random oracle model就足够。
本文主要做了以下两方面的改进:
- 1)在verification procedure中整合了multi-commitment scheme和Schnorr-style proof。
- 2)设计了一种新的witness commitment scheme,可产生a succinct argument and asymptotically reducing the verifier’s cost associated with the witness。
具体的性能表现为:
1.3 Polynomial commitment scheme
- Polynomial commitment scheme 首次由Kate等人2010年论文《Constant-size commitments to polynomials and their applications》中提出,并基于pairing assumption 构建了单变量polynomial commitment。
- Papamanthou等人2013年论文《Signatures of correct computation》、Zhang等人2017年论文《vSQL: veriifying arbitrary SQL queries over dynamic outsourced databases》、Zhang等人2017年论文《A zero-knowledge version of vSQL》、Zhang等人2018年论文《vRAM: Faster verifiable RAM with program-independent preprocessing》等论文中,将其扩展为多变量polynomial commitment。
- Libert等人2016年论文《Functional Commitment Schemes: From Polynomial Commitments to Pairing-Based Accumulators》中构建了Functional Commitment (FC) for a linear functions based on constant-size assumptions in composite order groups endowed with a bilinear map。设置其challenge为 x ⃗ = ( 1 , x , ⋯ , x n − 1 ) \\vecx=(1,x,\\cdots,x^n-1) x=(1,x,⋯,xn−1)即可实现polynomial commitment。
- Fujisaki等人1997年论文《Statistical zero knowledge protocols to prove modular polynomial relations》中 give a construction for polynomial evaluation based on the RSA problem that can be immediately adapted to polynomial commitment。
- Bootle等人2017年论文《Linear-time zero-knowledge proofs for arithmetic circuit satisfiability》 和 Bootle等人2018年论文《Efficient batch zero knowledge arguments for low degree polynomials》中基于discrete log assumption构建了单变量polynomial commitment。本文主要在此基础上,将其扩展为了multilinear polynomials。同时,Bootle等人2018年论文《Efficient batch zero knowledge arguments for low degree polynomials》中还 give a framework for expressing simple relations between commitments and field elements。
1.4 一些定义

-
Arithmetic circuit (AC) C C C:
由加法门和乘法门组成,每个门最多由2个输入fan-in,所有计算基于finite field F \\mathbbF F。 C C C为分层设计,具有depth d d d,input x ⃗ \\vecx x with length ∣ x ∣ |x| ∣x∣。
目的是evaluate C C C on input x ⃗ \\vecx x。在interactive proof or argument中,prover发送 y y y,声称 y = C ( x ⃗ ) y=C(\\vecx) y=C(x)并提供相应的证明。
本文的目的是为这种arithmetic circuit satisfiability problem提供efficient protocol。
Let C ( ⋅ , ⋅ ) C(\\cdot,\\cdot) C(⋅,⋅)为layered arithmetic circuit of fan-in two。已知输入 x ⃗ \\vecx x和输出 y y y,目的是确认是否存在 witness w ⃗ \\vecw w,使得 C ( x ⃗ , w ⃗ ) = y C(\\vecx,\\vecw)=y C(x,w)=y 成立。相应的witness relation可表示为: R ( x ⃗ , y ) = w ⃗ : C ( x ⃗ , w ⃗ ) = y R_(\\vecx,y)=\\\\vecw:C(\\vecx,\\vecw)=y\\ R(x,y)=w:C(x,w)=y。 -
Interactive arguments and proofs:

-
Zero-knowledge (ZK):

-
Witness-extended emulation:


-
Generalized special soundness:

-
Collection of non-interactive commitment:
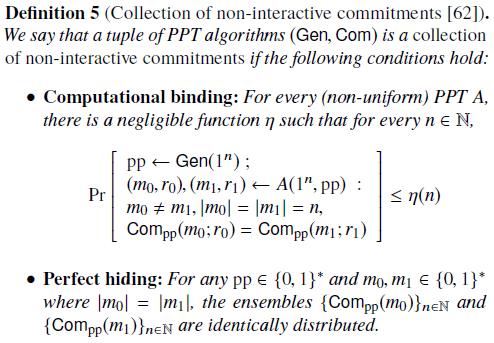
-
Additive homomorphism加法同态属性:
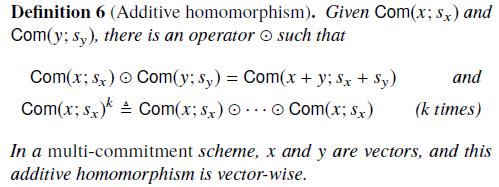
2. Arithmetic circuit evaluation problem
主要的研究有:(Arithmetic circuit C C C with depth d d d, input x x x, output y y y。)
- 【54】Goldwasser等人2015年论文《Delegating computation: Interactive proofs for muggles》中主要针对boolean circuit with depth d d d and input length n n n。其Verifier runs in time n ⋅ p o l y ( d , log ( n ) ) n\\cdot poly(d,\\log(n)) n⋅poly(d,log(n)) and space O ( log ( n ) ) O(\\log(n)) O(log(n)),communication complexity为 p o l y ( d , log ( n ) ) poly(d,\\log(n)) poly(d,log(n)),Prover runs in time p o l y ( n ) poly(n) poly(n)。
- 【37】【107】Cormode等人2012年论文《Practical verified computation with streaming interactive proofs》、Vu等人2013年论文《A hybrid architecture for interactive verifiable computation》中在【54】的基础上进行了改进,giving O ( ∣ C ∣ log ∣ C ∣ ) O(|C|\\log|C|) O(∣C∣log∣C∣) prover and O ( ∣ x ∣ + ∣ y ∣ + d log ∣ C ∣ ) O(|x|+|y|+d\\log|C|) O(∣x∣+∣y∣+dlog∣C∣) verifier runtimes, for AC C C C with depth d d d, input x x x, and output y y y。
- 【102】Thaler 2013年论文《Time-optimal interactive proofs for circuit evaluation》,针对
C
C
C 为data parallel,即包含
N
N
N个相同的sub-computations run on different inputs,可称其为sub-AC of
C
C
C(sub-AC的width为
G
以上是关于Hyrax: Doubly-efficient zkSNARKs without trusted setup学习笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章