LearnOpenGL学习笔记7:摄像机
Posted 键盘春秋
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LearnOpenGL学习笔记7:摄像机相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、 摄像机
1. 摄像机/观察空间
定义一个摄像机,我们需要一个摄像机在世界空间中的位置、观察的方向、一个指向它的右测的向量以及一个指向它上方的向量。
摄像机的位置
获取摄像机位置很简单。摄像机位置简单来说就是世界空间中代表摄像机位置的向量。我们把摄像机位置设置为前面教程中的那个相同的位置:
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);摄像机方向
用摄像机位置向量减去场景原点向量的结果就是摄像机指向向量。由于我们知道摄像机指向z轴负方向,我们希望方向向量指向摄像机的z轴正方向。如果我们改变相减的顺序,我们就会获得一个指向摄像机正z轴方向的向量。
glm::vec3 cameraTarget = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraDirection = glm::normalize(cameraPos - cameraTarget);右轴
我们需要的另一个向量是一个右向量(Right Vector),它代表摄像机空间的x轴的正方向。为获取右向量我们需要先使用一个小技巧:定义一个上向量(Up Vector)。我们把上向量和第二步得到的摄像机方向向量进行叉乘。两个向量叉乘的结果就是同时垂直于两向量的向量,因此我们会得到指向x轴正方向的那个向量(如果我们交换两个向量的顺序就会得到相反的指向x轴负方向的向量):
glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraRight = glm::normalize(glm::cross(up, cameraDirection));上轴
现在我们已经有了x轴向量和z轴向量,获取摄像机的正y轴相对简单;我们把右向量和方向向量(Direction Vector)进行叉乘:
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::cross(cameraDirection, cameraRight);使用这些摄像机向量我们就可以创建一个LookAt矩阵了,它在创建摄像机的时候非常有用。
2. LookAt
现在我们有了3个相互垂直的轴和一个定义摄像机空间的位置坐标,我们可以创建我们自己的LookAt矩阵了:
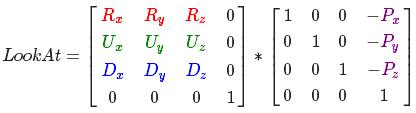
R是右向量,U是上向量,D是方向向量P是摄像机位置向量。注意,位置向量是相反的,因为我们最终希望把世界平移到与我们自身移动的相反方向。
GLM已经提供了这些支持。我们要做的只是定义一个摄像机位置,一个目标位置和一个表示上向量的世界空间中的向量(我们使用上向量计算右向量)。接着GLM就会创建一个LookAt矩阵,我们可以把它当作我们的观察矩阵:
glm::mat4 view;
view = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));3. 自由移动
首先我们必须设置一个摄像机系统,在我们的程序前面定义一些摄像机变量很有用:
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);LookAt函数现在成了:
view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);我们首先设置之前定义的cameraPos为摄像机位置。方向(Direction)是当前的位置加上我们刚刚定义的方向向量。这样能保证无论我们怎么移动,摄像机都会注视目标。我们在按下某个按钮时更新cameraPos向量。
我们已经为GLFW的键盘输入定义了一个key_callback函数,我们来添加几个新按键命令:
void key_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mode)
...
GLfloat cameraSpeed = 0.05f;
if (key == GLFW_KEY_W)
cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (key == GLFW_KEY_S)
cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (key == GLFW_KEY_A)
cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (key == GLFW_KEY_D)
cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
当我们按下WASD键,摄像机的位置都会相应更新。如果我们希望向前或向后移动,我们就把位置向量加上或减去方向向量。如果我们希望向旁边移动,我们做一个叉乘来创建一个右向量,沿着它移动就可以了。这样就创建了类似使用摄像机横向、前后移动的效果。
4. 视角移动
欧拉角
欧拉角(Euler Angle)是表示3D空间中可以表示任何旋转的三个值,由莱昂哈德·欧拉在18世纪提出。有三种欧拉角:俯仰角(Pitch)、偏航角(Yaw)和滚转角(Roll),下面的图片展示了它们的含义:
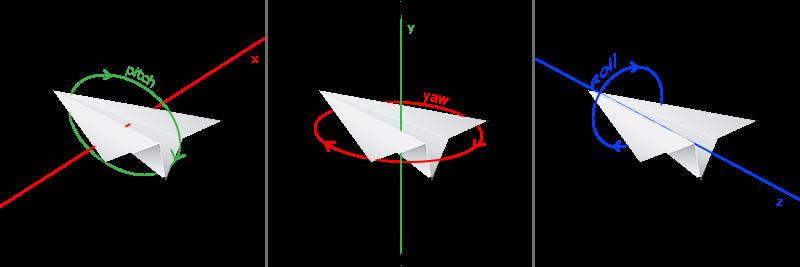
俯仰角是描述我们如何往上和往下看的角,它在第一张图中表示。第二张图显示了偏航角,偏航角表示我们往左和往右看的大小。滚转角代表我们如何翻滚摄像机。
对于我们的摄像机系统来说,我们只关心俯仰角和偏航角,所以我们不会讨论滚转角。用一个给定的俯仰角和偏航角,我们可以把它们转换为一个代表新的方向向量的3D向量。
direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * cos(glm::radians(yaw));//译注:direction代表摄像机的“前”轴,但此前轴是和本文第一幅图片的第二个摄像机的direction是相反的
direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * sin(glm::radians(yaw));5. 鼠标输入
首先我们要告诉GLFW,应该隐藏光标,并捕捉(Capture)它。捕捉鼠标意味着当应用集中焦点到鼠标上的时候光标就应该留在窗口中(除非应用拾取焦点或退出)。我们可以进行简单的配置:
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
这个函数调用后,无论我们怎么去移动鼠标,它都不会显示了,也不会离开窗口。对于FPS摄像机系统来说很好:
为计算俯仰角和偏航角我们需要告诉GLFW监听鼠标移动事件。我们用下面的原型创建一个回调函数来做这件事(和键盘输入差不多):
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);这里的xpos和ypos代表当前鼠标的位置。我们注册了GLFW的回调函数,鼠标一移动mouse_callback函数就被调用:
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);在处理FPS风格的摄像机鼠标输入的时候,我们必须在获取最终的方向向量之前做下面这几步:
- 计算鼠标和上一帧的偏移量。
- 把偏移量添加到摄像机和俯仰角和偏航角中。
- 对偏航角和俯仰角进行最大和最小值的限制。
- 计算方向向量。
我们必须先储存上一帧的鼠标位置,我们把它的初始值设置为屏幕的中心(屏幕的尺寸是800乘600):
GLfloat lastX = 400, lastY = 300;然后在回调函数中计算方向向量:
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
//第一次则将当前位置设置为上一帧的位置来避免抖动
if (firstMouse)
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
//计算偏移量并保存当前帧坐标为上一帧坐标
GLfloat xoffset = xpos - lastX;
GLfloat yoffset = lastY - ypos;
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
//缩放偏转量
GLfloat sensitivity = 0.05;
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity;
//计算偏转位置
yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset;
//控制偏转范围
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f;
//计算实际方向向量
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
6. 缩放
当视野变小时可视区域就会减小,产生放大了的感觉。我们用鼠标滚轮来放大。和鼠标移动、键盘输入一样我们需要一个鼠标滚轮的回调函数:
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
if (aspect >= 1.0f && aspect <= 45.0f)
aspect -= yoffset;
if (aspect <= 1.0f)
aspect = 1.0f;
if (aspect >= 45.0f)
aspect = 45.0f;
yoffset值代表我们滚动的大小。当scroll_callback函数调用后,我们改变全局aspect变量的内容。因为45.0f是默认的fov,我们将会把缩放级别限制在1.0f到45.0f。
我们现在在每一帧都必须把透视投影矩阵上传到GPU,但这一次使aspect变量作为它的fov:
projection = glm::perspective(aspect, (GLfloat)WIDTH / (GLfloat)HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);最后不要忘记注册滚动回调函数:
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);7. 摄像机类
直接贴出原教程给出的摄像机类:
#pragma once
// Std. Includes
#include <vector>
// GL Includes
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
// Defines several possible options for camera movement. Used as abstraction to stay away from window-system specific input methods
enum Camera_Movement
FORWARD,
BACKWARD,
LEFT,
RIGHT
;
// Default camera values
const GLfloat YAW = -90.0f;
const GLfloat PITCH = 0.0f;
const GLfloat SPEED = 3.0f;
const GLfloat SENSITIVTY = 0.25f;
const GLfloat ZOOM = 45.0f;
// An abstract camera class that processes input and calculates the corresponding Eular Angles, Vectors and Matrices for use in OpenGL
class Camera
public:
// Camera Attributes
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Front;
glm::vec3 Up;
glm::vec3 Right;
glm::vec3 WorldUp;
// Eular Angles
GLfloat Yaw;
GLfloat Pitch;
// Camera options
GLfloat MovementSpeed;
GLfloat MouseSensitivity;
GLfloat Zoom;
// Constructor with vectors
Camera(glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), GLfloat yaw = YAW, GLfloat pitch = PITCH) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
this->Position = position;
this->WorldUp = up;
this->Yaw = yaw;
this->Pitch = pitch;
this->updateCameraVectors();
// Constructor with scalar values
Camera(GLfloat posX, GLfloat posY, GLfloat posZ, GLfloat upX, GLfloat upY, GLfloat upZ, GLfloat yaw, GLfloat pitch) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
this->Position = glm::vec3(posX, posY, posZ);
this->WorldUp = glm::vec3(upX, upY, upZ);
this->Yaw = yaw;
this->Pitch = pitch;
this->updateCameraVectors();
// Returns the view matrix calculated using Eular Angles and the LookAt Matrix
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
return glm::lookAt(this->Position, this->Position + this->Front, this->Up);
// Processes input received from any keyboard-like input system. Accepts input parameter in the form of camera defined ENUM (to abstract it from windowing systems)
void ProcessKeyboard(Camera_Movement direction, GLfloat deltaTime)
GLfloat velocity = this->MovementSpeed * deltaTime;
if (direction == FORWARD)
this->Position += this->Front * velocity;
if (direction == BACKWARD)
this->Position -= this->Front * velocity;
if (direction == LEFT)
this->Position -= this->Right * velocity;
if (direction == RIGHT)
this->Position += this->Right * velocity;
// Processes input received from a mouse input system. Expects the offset value in both the x and y direction.
void ProcessMouseMovement(GLfloat xoffset, GLfloat yoffset, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
xoffset *= this->MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= this->MouseSensitivity;
this->Yaw += xoffset;
this->Pitch += yoffset;
// Make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (constrainPitch)
if (this->Pitch > 89.0f)
this->Pitch = 89.0f;
if (this->Pitch < -89.0f)
this->Pitch = -89.0f;
// Update Front, Right and Up Vectors using the updated Eular angles
this->updateCameraVectors();
// Processes input received from a mouse scroll-wheel event. Only requires input on the vertical wheel-axis
void ProcessMouseScroll(GLfloat yoffset)
if (this->Zoom >= 1.0f && this->Zoom <= 45.0f)
this->Zoom -= yoffset;
if (this->Zoom <= 1.0f)
this->Zoom = 1.0f;
if (this->Zoom >= 45.0f)
this->Zoom = 45.0f;
private:
// Calculates the front vector from the Camera's (updated) Eular Angles
void updateCameraVectors()
// Calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(this->Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(this->Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(this->Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(this->Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(this->Pitch));
this->Front = glm::normalize(front);
// Also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
this->Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(this->Front, this->WorldUp)); // Normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
this->Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(this->Right, this->Front));
;转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ylbs110/article/details/52506033
二、 示例
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// GLEW
#define GLEW_STATIC
#include <GL/glew.h>
// GLFW
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
// SOIL
#include <SOIL\\SOIL.h>
#include <glm\\glm.hpp>
#include <glm\\gtc\\matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm\\gtc\\type_ptr.hpp>
#include "Shader.h"
#include "Camera.h"
const GLuint WIDTH = 800, HEIGHT = 600;
void key_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mode);
GLuint loadTexture(string fileName, GLint REPEAT, GLint FILTER);
void do_movement();
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
// Shaders
const GLchar* vertexShaderSource = "#version 330 core\\n"
"layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;\\n"//顶点数据传入的坐标
"layout (location = 1) in vec3 color;\\n"//顶点数据传入的颜色
"layout (location = 2) in vec2 texCoord;\\n"//顶点数据传入的颜色
"uniform vec4 offset;\\n"
"uniform float mixPar;\\n"
"uniform mat4 model;\\n"
"uniform mat4 view;\\n"
"uniform mat4 projection;\\n"
"out vec3 Color;\\n"
"out vec2 TexCoord;\\n"
"out vec4 vertexColor;\\n"//将顶点坐标作为颜色传入片段着色器,测试所得效果
"out float MixPar;\\n"
"void main()\\n"
"\\n"
"gl_Position =projection * view * model* vec4(position.x, position.y, position.z, 1.0)+offset;\\n"
"vertexColor=gl_Position*0.2f;\\n"
"Color=color*0.2f;\\n"
"TexCoord=texCoord;\\n"
"MixPar=mixPar;\\n"
"\\0";
const GLchar* fragmentShaderSource = "#version 330 core\\n"
"out vec4 color;\\n"
"in vec4 vertexColor;\\n"
"in vec3 Color;\\n"
"in vec2 TexCoord;\\n"
"in float MixPar;\\n"
"uniform sampler2D ourTexture1;\\n"
"uniform sampler2D ourTexture2;\\n"
"void main()\\n"
"\\n"
"color =mix(texture(ourTexture1, TexCoord),texture(ourTexture2, vec2(TexCoord.x,1-TexCoord.y)),MixPar)+vec4(Color, 1.0f)+vertexColor;\\n"//合成两张纹理并对第二张纹理进行翻转操作,混合比例由上下键控制
"\\n\\0";
Camera mainCamera;
Shader shader;//shader
GLuint texContainer, texAwesomeface;//纹理id
float key_UD = 0.5f;//混合比例
GLuint VBO, VAO;
GLfloat deltaTime = 0.0f; // 当前帧遇上一帧的时间差
GLfloat lastFrame = 0.0f; // 上一帧的时间
bool keys[1024];
GLfloat lastX = 400, lastY = 300;
GLfloat scrollSpeed = 0.05f;
bool firstMouse = true;
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
void shaderInit()
shader = Shader(vertexShaderSource, fragmentShaderSource);
void textureInit()
texContainer = loadTexture("container.jpg", GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE, GL_LINEAR);
texAwesomeface = loadTexture("awesomeface.png", GL_MIRRORED_REPEAT, GL_NEAREST);
GLuint loadTexture(string fileName,GLint REPEAT, GLint FILTER)
//创建纹理
GLuint texture;
glGenTextures(1, &texture);
//绑定纹理
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture);
// 为当前绑定的纹理对象设置环绕、过滤方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, FILTER);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, FILTER);
//glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
//glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// 加载纹理
int width, height;
unsigned char* image = SOIL_load_image(fileName.c_str(), &width, &height, 0, SOIL_LOAD_RGB);
// 生成纹理
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, image);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
//释放图像的内存并解绑纹理对象
SOIL_free_image_data(image);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0);
return texture;
void vertexObjectInit()
//不使用索引缓冲对象用两个三角形绘制一个梯形
// 设置顶点缓存和属性指针
GLfloat vertices[] =
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
;
//创建索引缓冲对象
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
// 把顶点数组复制到缓冲中供OpenGL使用
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// 位置属性
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// 颜色属性
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(3 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(6 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);// 这个方法将顶点属性指针注册到VBO作为当前绑定顶点对象,然后我们就可以安全的解绑
glBindVertexArray(0);// 解绑 VAO (这通常是一个很好的用来解绑任何缓存/数组并防止奇怪错误的方法)
int main()
//初始化GLFW
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_RESIZABLE, GL_FALSE);
//创建窗口对象
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(WIDTH, HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", nullptr, nullptr);
if (window == nullptr)
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
//注册键盘回调
glfwSetKeyCallback(window, key_callback);
//注册鼠标回调
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
//注册鼠标滚轮回到
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
//设置光标隐藏并捕获
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
//初始化GLEW
glewExperimental = GL_TRUE;
if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK)
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLEW" << std::endl;
return -1;
//告诉OpenGL渲染窗口尺寸大小
int width, height;
glfwGetFramebufferSize(window, &width, &height);
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
//初始化并绑定shaders
shaderInit();
//初始化textures
textureInit();
//初始化顶点对象数据
vertexObjectInit();
mainCamera = Camera();
//让窗口接受输入并保持运行
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
GLfloat currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
//检查事件
glfwPollEvents();
do_movement();
//渲染指令
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
//设置根据时间变换的x,y偏移值,最终效果为圆周运动
GLfloat timeValue = glfwGetTime();
GLfloat offsetx = (sin(timeValue) / 2) + 0.5;
GLfloat offsety = (cos(timeValue) / 2) + 0.5;
//绘制长方形
shader.Use();
//绑定两张贴图
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texContainer);
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "ourTexture1"), 0);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texAwesomeface);
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "ourTexture2"), 1);
// 更新uniform值
//设置运动轨迹
//GLint vertexorangeLocation = glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "offset");
//glUniform4f(vertexorangeLocation, offsetx, offsety, 0.0f, 1.0f);
//设置混合比例
GLint mixPar = glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "mixPar");
glUniform1f(mixPar, key_UD);
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::rotate(model, (GLfloat)glfwGetTime() * 5.0f, glm::vec3(0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
glm::mat4 view;
view = mainCamera.GetViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 projection;
projection = glm::perspective(mainCamera.Zoom*scrollSpeed, (float)(WIDTH / HEIGHT), 0.1f, 100.0f);
GLint modelLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "model");
glUniformMatrix4fv(modelLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(model));
GLint viewLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "view");
glUniformMatrix4fv(viewLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(view));
GLint projectionLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shader.Program, "projection");
glUniformMatrix4fv(projectionLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(projection));
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] =
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f)
;
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
for (GLuint i = 0; i < 10; i++)
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
if (i < 4)
GLfloat angle = (GLfloat)glfwGetTime()*5.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, angle, glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
glUniformMatrix4fv(modelLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(model));
else
glUniformMatrix4fv(modelLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(model));
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
glBindVertexArray(0);
//交换缓冲
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
//释放资源
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
void do_movement()
// 摄像机控制
GLfloat cameraSpeed = 5.0f* deltaTime;
if (keys[GLFW_KEY_W])
mainCamera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
if (keys[GLFW_KEY_S])
mainCamera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
if (keys[GLFW_KEY_A])
mainCamera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
if (keys[GLFW_KEY_D])
mainCamera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime);
void key_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mode)
// 当用户按下ESC键,我们设置window窗口的WindowShouldClose属性为true
// 关闭应用程序
if (key == GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE && action == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, GL_TRUE);
if (key == GLFW_KEY_UP&& action == GLFW_PRESS)//按下UP键增加混合比例
key_UD = key_UD + 0.1f;
if (key == GLFW_KEY_DOWN&& action == GLFW_PRESS)//按下DOWN减小混合比例
key_UD = key_UD - 0.1f;
if (action == GLFW_PRESS)
keys[key] = true;
else if (action == GLFW_RELEASE)
keys[key] = false;
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
if (firstMouse)
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
GLfloat xoffset = xpos - lastX;
GLfloat yoffset = lastY - ypos; // Reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to left
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
mainCamera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
cout << yoffset << endl;
mainCamera.ProcessMouseScroll(yoffset);
结果:
wsad可以控制上下左右,鼠标控制摄像头方向,滚轮可以拉伸:

以上是关于LearnOpenGL学习笔记7:摄像机的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章