Java基础IO
Posted 3 ERROR(s)
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java基础IO相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、File文件操作类
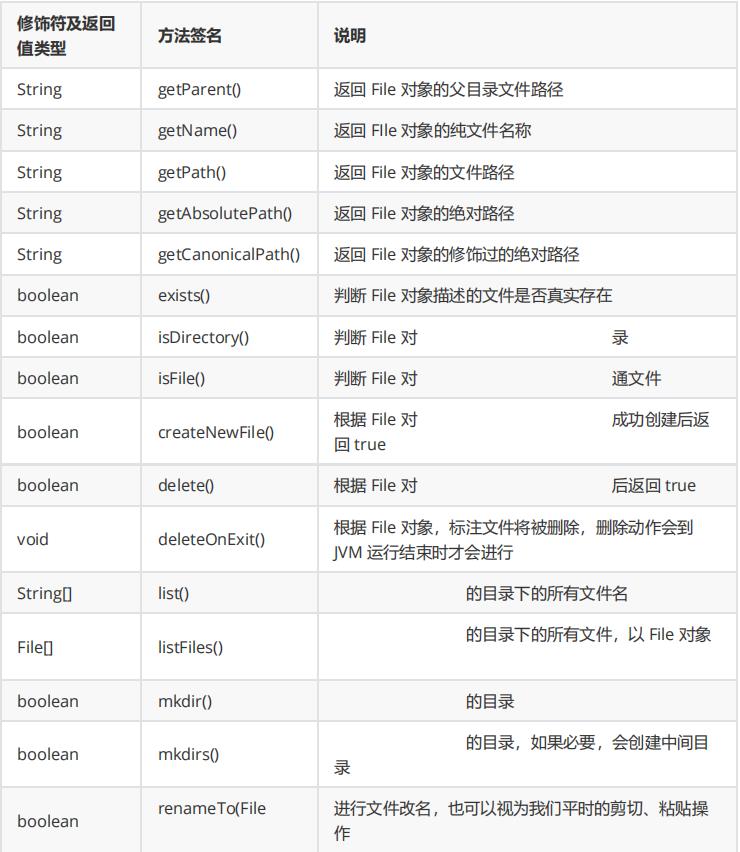
1. File类的常用方法
2.相对路径和绝对路径
- 绝对路径:从树型结构的角度来看,从根节点到这个节点的路径称之为绝对路径。
- 相对路径:从树形结构的角度来看,从任何一个结点到目标节点的路径称之为相对路径。
3.使用File类递归打印文件目录列表
//遍历输出一个文件夹下所有的文件
public class IODemo1
public static void main(String[] args)
File file = new File("D:/work");
listAll(file);
private static void listAll(File file)
if(file.isDirectory())
File [] files=file.listFiles();
for (File file2: files)
listAll(file2);
else
System.out.println(file);
二、IO流
1. IO流的概念
流:就像水流一样,一次可以读/写一个字节或多个字节
字节流:读写数据单位都是字节,读写二进制文件
字符流:读写数据的单位都是字符,读写文本文件
2. 复制字节流文件
步骤:
- 创建字节流输入输出对象。
- 读取字节流文件到磁盘。
- 从磁盘写入到目标地址
- 关闭文件(十分重要)
关闭文件十分的重要,每次一个进程打开一个文件都会占用文件描述表上的一个表项,一个进程可能对应多个PCB,(一个线程对应一个PCB)一个进程的若干PCB共享一个表,这个表项是有限的,当他满了的时候文件就打不开了。代码中每次打开一个文件本质上就是在文件描述符表中创建一个新的项,代码关闭一个项目,本质上就是白文件描述符表上的对应项删除。
1.0版本
/**
* @ClassName IODemo2
* @Description 字节流图片复制
* @Author Rcy
* @Data 2022/3/6 18:27
*/
public class IODemo2
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
copyFile("D:/Test/666.jpg","D:/Test/8888.jpg");
private static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws IOException
//1.先打开文件,创建InputStream和OutputStream对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(srcPath);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destPath);
//2.读取srcPath当中的内容
//bytes相当于磁盘 一次读取1024个字节 这就是缓冲区
byte [] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len=-1;
//3.将内容写入到destPath当中
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1)
//如果len是-1就明读取结束了,然后写入,写入的长度是len的长度。
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("文件复制成功");
上述代码有一个致命的问题:他的close方法可能不会被调用。因为在运行中一旦触发了IOException异常,此时方法就会被立刻终止,从而导致下面的colse方法不能被调用。
改进:使用finally关键字修饰
2.0版本
private static void copyFile2(String srcPath,String destPath)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try
fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(srcPath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destPath);
//2.读取srcPath当中的内容
//bytes相当于磁盘 一次读取1024个字节 这就是缓冲区
byte [] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len=-1;
//3.将内容写入到destPath当中
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1)
//如果len是-1就明读取结束了,然后写入,写入的长度是len的长度。
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
//用if判断他是否初始化成功,若不成功可能会造成空指针异常。
if(fileInputStream!=null)
fileInputStream.close();
if(fileOutputStream!=null)
fileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("文件复制成功");
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
上述代码还有一个问题,太丑了!
3.0版本
private static void copyFile3(String srcPath,String destPath)
//代码自动调用close方法。
try(FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(srcPath);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destPath))
byte [] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1)
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream类
这两个类自带缓冲区,什么是缓冲区呢?
缓冲区本质上是一片内存空间,其存在的意义就是提高读写效率。
其工作原理是因为程序访问内存要比访问磁盘快很多(3-4个数量级)。一次读1个数据读100次的效率要远远低于一次读100个数据。
下面是一段有无缓冲区的代码运行速度对比。
/**
* @ClassName IODemo3
* @Description 有无缓冲区对比
* @Author Rcy
* @Data 2022/3/7 16:31
*/
public class IODemo3
public static void main(String[] args)
copyFile("D:/Test/666.jpg","D:/Test/888856.jpg");
copyFile2("D:/Test/666.jpg","D:/Test/888856.jpg");
//不使用缓冲区
public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath)
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try(FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcPath))
int len=-1;
while ((len=fileInputStream.read())!=-1)
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("不使用缓冲区" + (end-begin)+"ms");
//使用缓冲区
public static void copyFile2(String srcPath, String destPath)
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try(BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcPath));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destPath)))
int len=-1;
while ((len=bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1)
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("使用缓冲区" + (end-begin)+"ms");
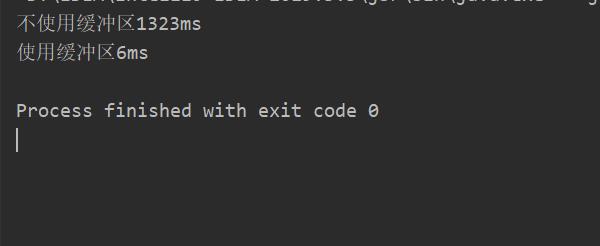
可以看到两者速度差距达到100多倍!
3.复制字符流文件
字节流文件和字符流文件的复制操作基本相同,区别在于字符流文件复制的时候采用的是FileReader和FileWriter这两个类。
/**
* @ClassName Demo4
* @Description 字符流的复制操作
* @Author Rcy
* @Data 2022/3/7 17:28
*/
public class IODemo4
public static void main(String[] args)
copyFile2("D:/Test/123.txt","D:/Test/321.txt");
//按照字符复制
private static void copyFile(String srcPath, String descPath)
try(FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(srcPath);
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(descPath))
int len=-1;
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
while((len=fileReader.read(buffer))!=-1)
fileWriter.write(buffer,0,len);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
字符流不仅可以一个字符一个字符的复制,还可以进行按行复制。
private static void copyFile2(String srcPath, String descPath)
try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcPath));
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(descPath)))
String len="";
//readLine()表示读一行,读到换行符为止,如果文件读取完毕就会返回null
while((len=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null)
bufferedWriter.write(len);
//因为他是按行读取的,所以他每次读都会少一个换行符,我们要手动加入这个换行符。
bufferedWriter.write("\\n");
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
三、 序列化和反序列化
1.什么是序列化和反序列化
序列化: 对象的寿命通常随着生成该对象的程序的终止而终止,有时候需要把在内存中的各种对象的状态(也就是实例变量,不是方法)保存下来,并且可以在需要时再将对象恢复。虽然你可以用你自己的各种各样的方法来保存对象的状态,但是Java给你提供一种应该比你自己的好的保存对象状态的机制,那就是序列化(将一个对象保存到二进制bit流中)
反序列化: 把二进制的byte流还原回原来的对象。
序列化和反序列化最大的作用就是让对象能通过网络传输/能够在文件中保存。在这个过程中要保证“信息不丢失!”
2.使用ObjectOutputStream类序列化/反序列化java对象
序列化的类必须实现支持持久化存储的Serializable接口,Serializable就像一个通行证,只有拥有这个通行证jvm才让他持久化到磁盘中。
import java.io.*;
/**
* @ClassName IODemo5
* @Description TODO
* @Author Rcy
* @Data 2022/3/7 20:15
*/
//Serializable显示说明这个类可以被序列化
class Student implements Serializable
//网络传输反序列化的时候需要比对UID,相同才可以反序列化。
//private static final long serialVersionUID = 123456789L;
public String name;
public int score;
public int age;
public Student()
public Student(String name, int score, int age)
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
this.age = age;
public class IODemo5
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
Student student = new Student("张三", 99, 20);
//serializeStudent(student);
System.out.println(deserializeStudent(student).name);
//序列化
private static void serializeStudent(Student student) throws IOException
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/Test/hehe.txt"));
// writeObject()继承序列化+写文件
// Student student = new Student("张三", 99, 20);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(student);
objectOutputStream.close();
//反序列化
private static Student deserializeStudent(Student student) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:/Test/hehe.txt"));
return (Student) objectInputStream.readObject();
以上是关于Java基础IO的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章