C语言显示系统时间
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C语言显示系统时间相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
自行编写一个C程序,求出你的程序在运行时系统时间是几点几分和几秒
已知在<time.h>中有如下定义:
struct tm
int tm_sec; /* 秒 */
int tm_min; /* 分 */
int tm_hour; /* 小时 */
…. /* 等其它 */
;
typedef long time_t;
通过如下代码段可获得指向当前系统时间的指针ptr
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
…. struct tm *ptr;
time_t lt;
lt = time(NULL); /* 获得当前系统时间 */
ptr = localtime(<);
/* 将ptr指向当前时间所在的结构变量 */
要求对指针ptr进行访问,以格式%d:%d:%d的形式输出当前运行时的系统时间是几点几分几秒
#include <time.h>
int main()
time_t rawtime;
struct tm * timeinfo;
time ( &rawtime );
timeinfo = localtime ( &rawtime );
printf ( "The current date/time is: %s", asctime (timeinfo) );
return 0;
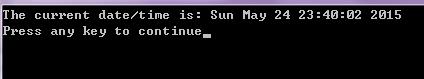
说明:
time_t // 时间类型(time.h 定义)struct tm // 时间结构,time.h 定义如下:
int tm_sec;
int tm_min;
int tm_hour;
int tm_mday;
int tm_mon;
int tm_year;
int tm_wday;
int tm_yday;
int tm_isdst;
time ( &rawtime ); // 获取时间,以秒计,从1970年1月一日起算,存于rawtime
localtime ( &rawtime ); //转为当地时间,tm 时间结构
asctime() // 转为标准ASCII时间格式:
//就是直接打印tm,tm_year 从1900年计算,所以要加1900,月tm_mon,从0计算,所以要加1 参考技术A
楼主你好!
根据你的要求写的供你参考!
#include<time.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
struct tm *ptr;
time_t it;
it=time(NULL);
ptr=localtime(&it);
printf("%4d年%02d月%02d日 %d:%d:%d\\n",ptr->tm_year+1900,ptr->tm_mon+1,ptr->tm_mday,ptr->tm_hour,ptr->tm_min,ptr->tm_sec);
return 0;
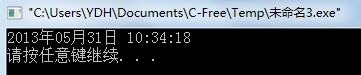
希望对你有帮助!
本回答被提问者采纳 参考技术B 我们可以使用strftime()函数将时间格式化为我们想要的格式。它的原型如下:size_t strftime(
char *strDest,
size_t maxsize,
const char *format,
const struct tm *timeptr
);
我们可以根据format指向字符串中格式命令把timeptr中保存的时间信息放在strDest指向的字符串中,最多向strDest中存放maxsize个字符。该函数返回向strDest指向的字符串中放置的字符数。
函数strftime()的操作有些类似于sprintf():识别以百分号(%)开始的格式命令集合,格式化输出结果放在一个字符串中。格式化命令说明串strDest中各种日期和时间信息的确切表示方法。格式串中的其他字符原样放进串中。格式命令列在下面,它们是区分大小写的。
%a 星期几的简写
%A 星期几的全称
%b 月分的简写
%B 月份的全称
%c 标准的日期的时间串
%C 年份的后两位数字
%d 十进制表示的每月的第几天
%D 月/天/年
%e 在两字符域中,十进制表示的每月的第几天
%F 年-月-日
%g 年份的后两位数字,使用基于周的年
%G 年分,使用基于周的年
%h 简写的月份名
%H 24小时制的小时
%I 12小时制的小时
%j 十进制表示的每年的第几天
%m 十进制表示的月份
%M 十时制表示的分钟数
%n 新行符
%p 本地的AM或PM的等价显示
%r 12小时的时间
%R 显示小时和分钟:hh:mm
%S 十进制的秒数
%t 水平制表符
%T 显示时分秒:hh:mm:ss
%u 每周的第几天,星期一为第一天 (值从0到6,星期一为0)
%U 第年的第几周,把星期日做为第一天(值从0到53)
%V 每年的第几周,使用基于周的年
%w 十进制表示的星期几(值从0到6,星期天为0)
%W 每年的第几周,把星期一做为第一天(值从0到53)
%x 标准的日期串
%X 标准的时间串
%y 不带世纪的十进制年份(值从0到99)
%Y 带世纪部分的十制年份
%z,%Z 时区名称,如果不能得到时区名称则返回空字符。
%% 百分号
如果想显示现在是几点了,并以12小时制显示,就象下面这段程序:
#include “time.h”
#include “stdio.h”
int main(void)
struct tm *ptr;
time_t lt;
char str[80];
lt=time(NULL);
ptr=localtime(<);
strftime(str,100,"It is now %I %p",ptr);
printf(str);
return 0;
其运行结果为:
It is now 4PM
而下面的程序则显示当前的完整日期:
#i nclude
#i nclude
void main( void )
struct tm *newtime;
char tmpbuf[128];
time_t lt1;
lt1 = time(NULL);
newtime=localtime(<1);
strftime( tmpbuf, 128, "Today is %A, day %d of %B in the year %Y.\n", newtime);
printf(tmpbuf);
运行结果:
Today is Saturday, day 30 of July in the year 2005.
C语言中 如何获取系统时间
各位高手帮手编写一个程序:
要求;用C语言编写,获取系统时间 年 月 日 只要 年月日 小时 分钟秒 不要!
并把 获取的 年月日 分别保存在 定义好的三个 int型 变量中!
并显示出来!
回复 zxl0714:
可以详细点 加点说明可以吗?
我看不明啊!!!
#include<time.h>
int main()
time_t timep;
struct tm *p;
time (&timep);
p=gmtime(&timep);
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_sec); /*获取当前秒*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_min); /*获取当前分*/
printf("%d\\n",8+p->tm_hour);/*获取当前时,这里获取西方的时间,刚好相差八个小时*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_mday);/*获取当前月份日数,范围是1-31*/
printf("%d\\n",1+p->tm_mon);/*获取当前月份,范围是0-11,所以要加1*/
printf("%d\\n",1900+p->tm_year);/*获取当前年份,从1900开始,所以要加1900*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_yday); /*从今年1月1日算起至今的天数,范围为0-365*/
拓展资料:
C语言是一门通用计算机编程语言,广泛应用于底层开发。C语言的设计目标是提供一种能以简易的方式编译、处理低级存储器、产生少量的机器码以及不需要任何运行环境支持便能运行的编程语言。
尽管C语言提供了许多低级处理的功能,但仍然保持着良好跨平台的特性,以一个标准规格写出的C语言程序可在许多电脑平台上进行编译,甚至包含一些嵌入式处理器(单片机或称MCU)以及超级电脑等作业平台。
二十世纪八十年代,为了避免各开发厂商用的C语言语法产生差异,由美国国家标准局为C语言制定了一套完整的美国国家标准语法,称为ANSI C,作为C语言最初的标准。目前2011年12月8日,国际标准化组织(ISO)和国际电工委员会(IEC)发布的C11标准是C语言的第三个官方标准,也是C语言的最新标准,该标准更好的支持了汉字函数名和汉字标识符,一定程度上实现了汉字编程。
C语言是一门面向过程的计算机编程语言,与C++,Java等面向对象的编程语言有所不同。
其编译器主要有Clang、GCC、WIN-TC、SUBLIME、MSVC、Turbo C等。
参考资料:C语言_百度百科
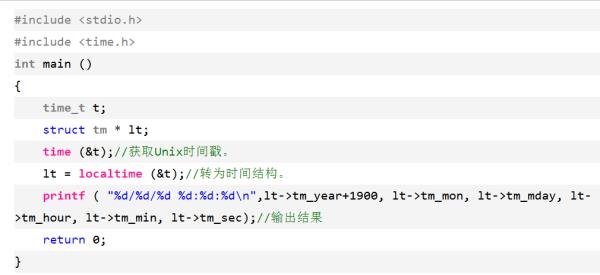
参考技术A#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main ()
time_t t
struct tm * lt; time (&t);//获取Unix时间戳。
lt = localtime (&t);//转为时间结构。
printf ( "%d/%d/%d %d:%d:%d\\n",lt->tm_year+1900, lt->tm_mon, lt->tm_mday, lt->tm_hour, lt->tm_min, lt->tm_sec);//输出结果
return 0;

扩展资料
#include -- 必须的时间函数头文件
time_t -- 时间类型(time.h 定义是typedef long time_t; 追根溯源,time_t是long)
struct tm -- 时间结构,time.h 定义如下:
int tm_sec;
int tm_min;
int tm_hour;
int tm_mday;
int tm_mon;
int tm_year;
int tm_wday;
int tm_yday;
int tm_isdst;
time ( &rawtime ); -- 获取时间,以秒计,从1970年1月一日起算,存于rawtime
localtime ( &rawtime ); -- 转为当地时间,tm 时间结构
asctime ()-- 转为标准ASCII时间格式:
星期 月 日 时:分:秒 年
参考资料:百度百科 time函数
参考技术B#include<time.h>
int main()
time_t timep;
struct tm *p;
time (&timep);
p=gmtime(&timep);
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_sec); /*获取当前秒*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_min); /*获取当前分*/
printf("%d\\n",8+p->tm_hour);/*获取当前时,这里获取西方的时间,刚好相差八个小时*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_mday);/*获取当前月份日数,范围是1-31*/
printf("%d\\n",1+p->tm_mon);/*获取当前月份,范围是0-11,所以要加1*/
printf("%d\\n",1900+p->tm_year);/*获取当前年份,从1900开始,所以要加1900*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_yday); /*从今年1月1日算起至今的天数,范围为0-365*/
扩展链接
使用其他的方法获取系统时间:

注意事项:
struct tm中的tm_year 值为实际年减去1900, 所以输出的时候要是lt->tm_year+1900。
参考技术C获取系统的时间需要借助time()函数,具体的代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
struct mydate
unsigned year;
unsigned month;
unsigned day;
struct mydate Today( )
struct mydate today;
time_t rawtime;
struct tm *timeinfo;
time ( &rawtime );
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
today.year = timeinfo->tm_year + 1900;
today.month = timeinfo->tm_mon + 1;
today.day = timeinfo->tm_mday;
return today;
int main( )
struct mydate today = Today( )
printf("%4d/%02d/%02d\\n",today.year,today.month,today.day);
return 0;
扩展资料:
使用其他的方法获取系统时间:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main ( )
time_t t;
struct tm * lt;
time (&t); //获取Unix时间戳。
lt = localtime (&t); //转为时间结构。
printf ( "%d/%d/%d %d:%d:%d\\n",lt->tm_year+1900, lt->tm_mon,,lt->tm_mday,,lt->tm_hour, lt->tm_min,,lt->tm_sec); //输出结果
return 0;
参考技术D方法一,#include<time.h>
int main()
time_t timep;
struct tm *p;
time (&timep);
p=gmtime(&timep);
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_sec); /*获取当前秒*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_min); /*获取当前分*/
printf("%d\\n",8+p->tm_hour);/*获取当前时,这里获取西方的时间,刚好相差八个小时*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_mday);/*获取当前月份日数,范围是1-31*/
printf("%d\\n",1+p->tm_mon);/*获取当前月份,范围是0-11,所以要加1*/
printf("%d\\n",1900+p->tm_year);/*获取当前年份,从1900开始,所以要加1900*/
printf("%d\\n",p->tm_yday); /*从今年1月1日算起至今的天数,范围为0-365*/
方法二.#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main ()
time_t t
struct tm * lt; time (&t);//获取Unix时间戳。
lt = localtime (&t);//转为时间结构。
printf ( "%d/%d/%d %d:%d:%d\\n",lt->tm_year+1900, lt->tm_mon, lt->tm_mday, lt->tm_hour, lt->tm_min, lt->tm_sec);//输出结果
return 0;

扩展资料
#include -- 必须的时间函数头文件
time_t -- 时间类型(time.h 定义是typedef long time_t; 追根溯源,time_t是long)
struct tm -- 时间结构,time.h 定义如下:
int tm_sec;
int tm_min;
int tm_hour;
int tm_mday;
int tm_mon;
int tm_year;
int tm_wday;
int tm_yday;
int tm_isdst;
time ( &rawtime ); -- 获取时间,以秒计,从1970年1月一日起算,存于rawtime
localtime ( &rawtime ); -- 转为当地时间,tm 时间结构
asctime ()-- 转为标准ASCII时间格式:
星期 月 日 时:分:秒 年
参考资料来源:百度百科 time函数
以上是关于C语言显示系统时间的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章