数据结构--队列的实现(单向链表方式)
Posted 大扑棱蛾子
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构--队列的实现(单向链表方式)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
什么是链表
在阅读本章之前,需要您知道什么是链表?
说到链表,那么就需要聊一聊计算机中的存储方式。计算机中的存储方式主要分为两种,一种是顺序存储,一种是非顺序存储。可以扒一扒这篇文章看一看。
链表是一种非顺序存储结构,它允许保存的数据在内存中可以不连续。
链表有以下4种
- 单向链表:每个节点有一个指针(
next)指向下一个节点,最后一个节点指向null - 双向链表:每个节点有一个指针(
next)指向下一个节点和一个指针(prev)指向上一个节点。第一个节点的prev为null,最后一个节点的next为null。 - 单向循环链表:最后一个节点的
next指针指向第一个节点,如果只有一个节点,这个节点的next指向自己。 - 双向循环链表:第一个节点的
prev指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的next指向第一个节点,如果只有一个节点prev和next都指向自己。
这里只简单介绍链表,后面会写文章详细介绍链表及链表的实现。本文中我们用单向链表实现。
实现原理
定义两个指针front和rear。front指向第一个元素,rear指向最后一个元素。
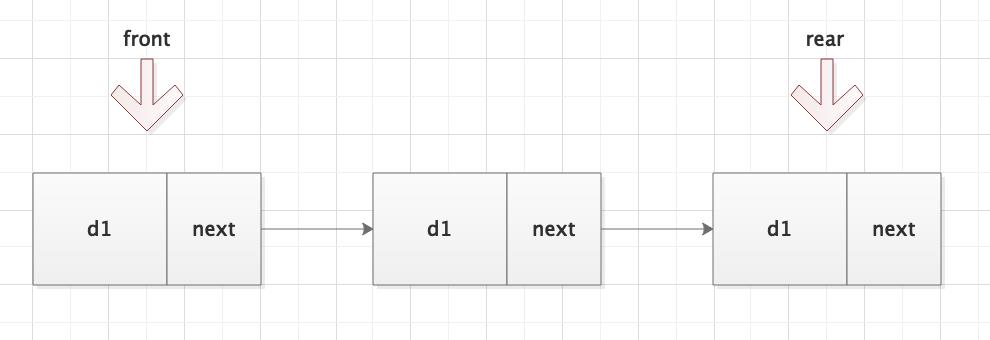
消费一个元素后,front指向这个元素的next。即下一个元素,当消费完最后一个元素后(next == null),front和rear都指向null。
添加元素后,rear所指向的元素的next指针指向新元素,同时rear也指向新元素。
需要在添加或者取出元素时维护队列长度。
使用链表来实现队列是比较简单的,而且可以实现没有长度限制的队列。
实现代码
package com.codestd.study.queue;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 链表方式实现队列
*
* @author jaune
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public class LinkedQueue<T> implements Queue<T>
private Node<T> front = null;
private Node<T> rear = null;
private int size = 0;
private final Integer maxSize;
/**
* 不设置最大长度,则队列的长度可以无限增加
*/
public LinkedQueue()
this.maxSize = null;
/**
* 设置队列的最大长度,达到最大长度后不能再添加元素。
* @param maxSize 最大长度
*/
public LinkedQueue(Integer maxSize)
this.maxSize = maxSize;
@Override
public T peek()
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("队列为空");
return this.front.item;
@Override
public void push(T t)
if (this.isFull())
throw new RuntimeException("队列已满,无法添加新的元素。");
if (this.size == 0)
this.front = new Node<>(t);
this.rear = this.front;
else
Node<T> node = new Node<>(t);
this.rear.next = node;
this.rear = node;
this.size++;
@Override
public T pop()
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("队列为空");
Node<T> node = this.front;
if (node.next == null)
this.front = null;
this.rear = null;
this.size = 0;
else
this.front = node.next;
this.size--;
return node.item;
@Override
public void clear()
// 这里清空所有引用,目的是为了便于垃圾回收。
Node<T> node = this.front;
while (node != null)
Node<T> next = node.next;
node.item = null;
node.next = null;
node = next;
this.front = this.rear = null;
this.size = 0;
@Override
public int size()
return this.size;
@Override
public boolean isEmpty()
return this.size == 0;
/**
* 链表队列不会有长度限制。
*/
@Override
public boolean isFull()
if (this.maxSize == null)
return false;
else
return size == maxSize;
private static class Node<T>
T item;
Node<T> next;
public Node(T item)
this.item = item;
注意clear方法,clear方法中是将所有引用都清空了。这样便于垃圾回收。java.util.LinkedList中的clear采用了另一种方法,下面将代码贴出来供大家参考。
public void clear()
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; )
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
以上是关于数据结构--队列的实现(单向链表方式)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章