数据库——可不敢删库跑路喽(建议收藏)
Posted 可乐好哇!
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据库——可不敢删库跑路喽(建议收藏)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
数据库——删库跑路喽
数据库简介
数据库是什么东东?
解决文件安全性、文件不利于数据查询和管理、文件不利于存储海量数据、文件在程序中控制不方便等问题,设计出更加利于管理数据的软件——数据库,管理数据会更有效。
数据库分类如何?
关系型数据库: 采用关系模型来组织数据的数据库(Oracle、mysql、SQL Server等)
非关系型数据库: 不规定基于SQL实现(Redis、MongoDB、HBASE、Neo4j等)
数据库基本操作
-
创建数据库
create database test;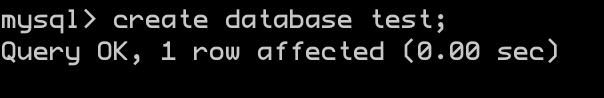
-
显示当前数据库
show databases;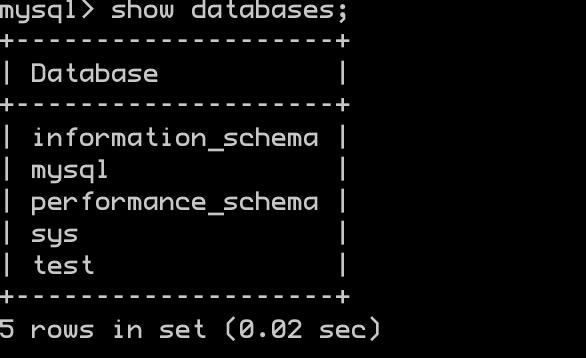
-
使用当前数据库
use test;
-
删除数据库
注意: 千万不敢,否则神也救不了你!!!

drop database test;
-
创建表格
create table test ( id int, name varchar(20) );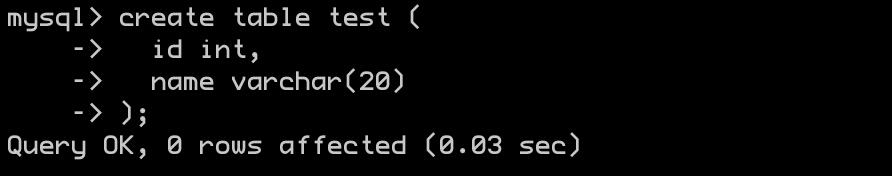
-
查看表格的结构
desc test;
-
删除表格
注意: 使劲儿删,这个比删库还厉害!!!

drop table test;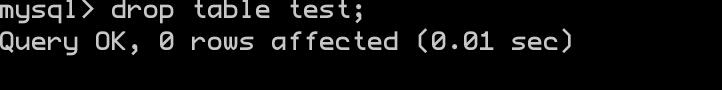
-
小二充电来

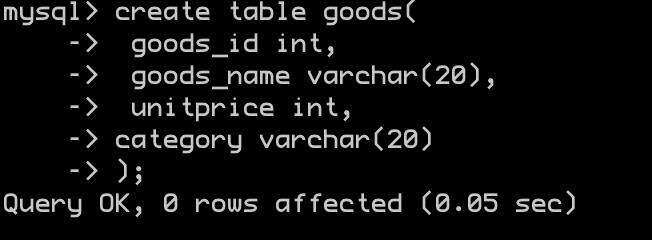
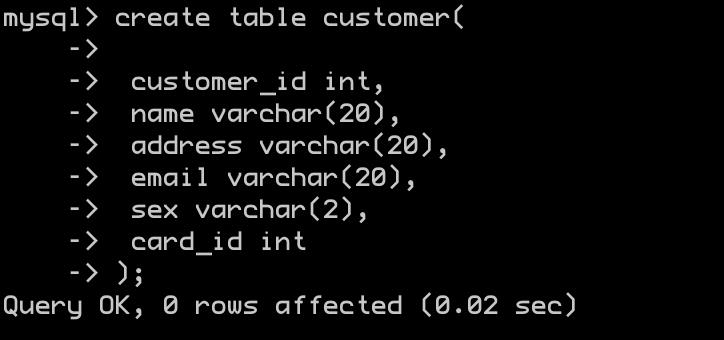
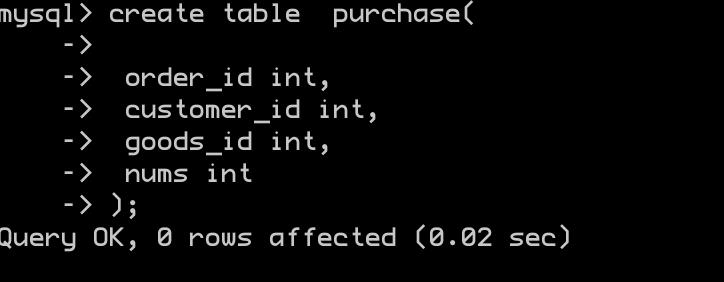
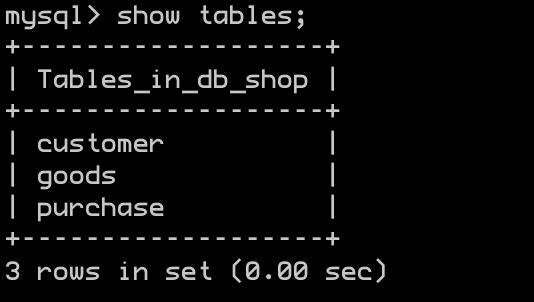

-
插入数据
insert into exam_result values(8, "毛爷爷", 99, 99 , 99);
还可以这样操作呦!(多条数据插入) insert into exam_result values(8, "毛爷爷", 99, 99 , 99), (8, "毛爷爷", 99, 99 , 99)...; -
查询数据(重点是它的进阶操作)
select * from exam_result;
-
修改数据
我要把毛爷爷的语数英都改为88 update exam_result set chinese=88, math=100, english=100 where name="毛爷爷";实际工作中不要轻易修改数据哦,不然老板会青睐你的。。。

-
删除数据
(建议把删除命令当做空气)
delete from exam_result where name = "毛爷爷";
-
数据进行规律排序(默认升序)
select * from exam_result order by chinese desc;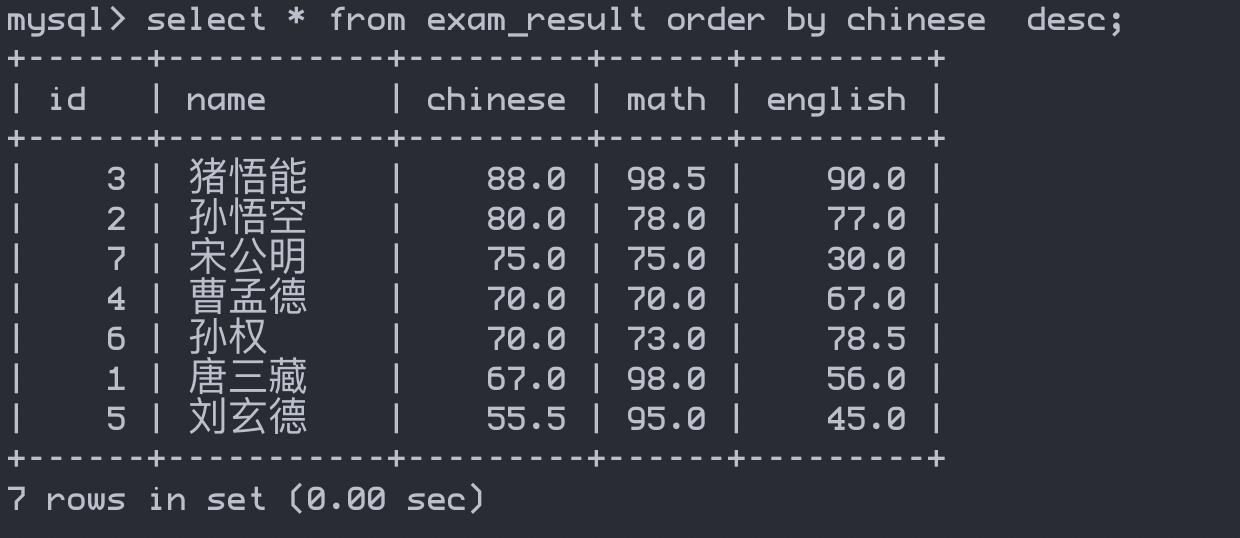
-
数据去重
select distinct chinese from exam_result;
-
数据模糊查询
select * from exam_result where name like '%明';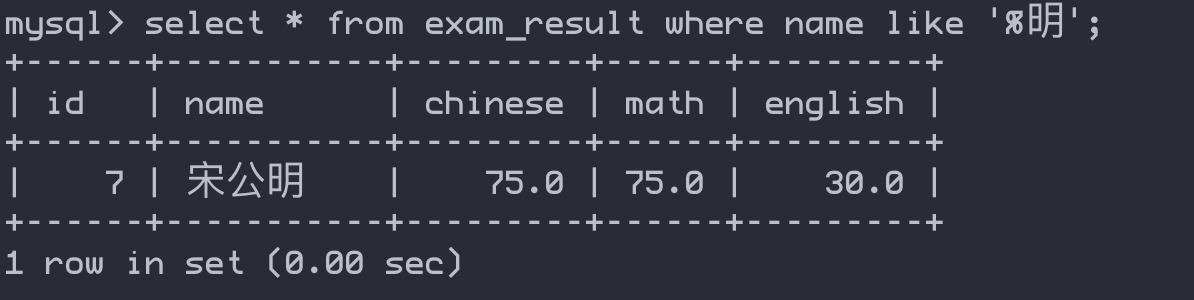
-
数据分页查询
select * from exam_result order by id limit 3 offset 0;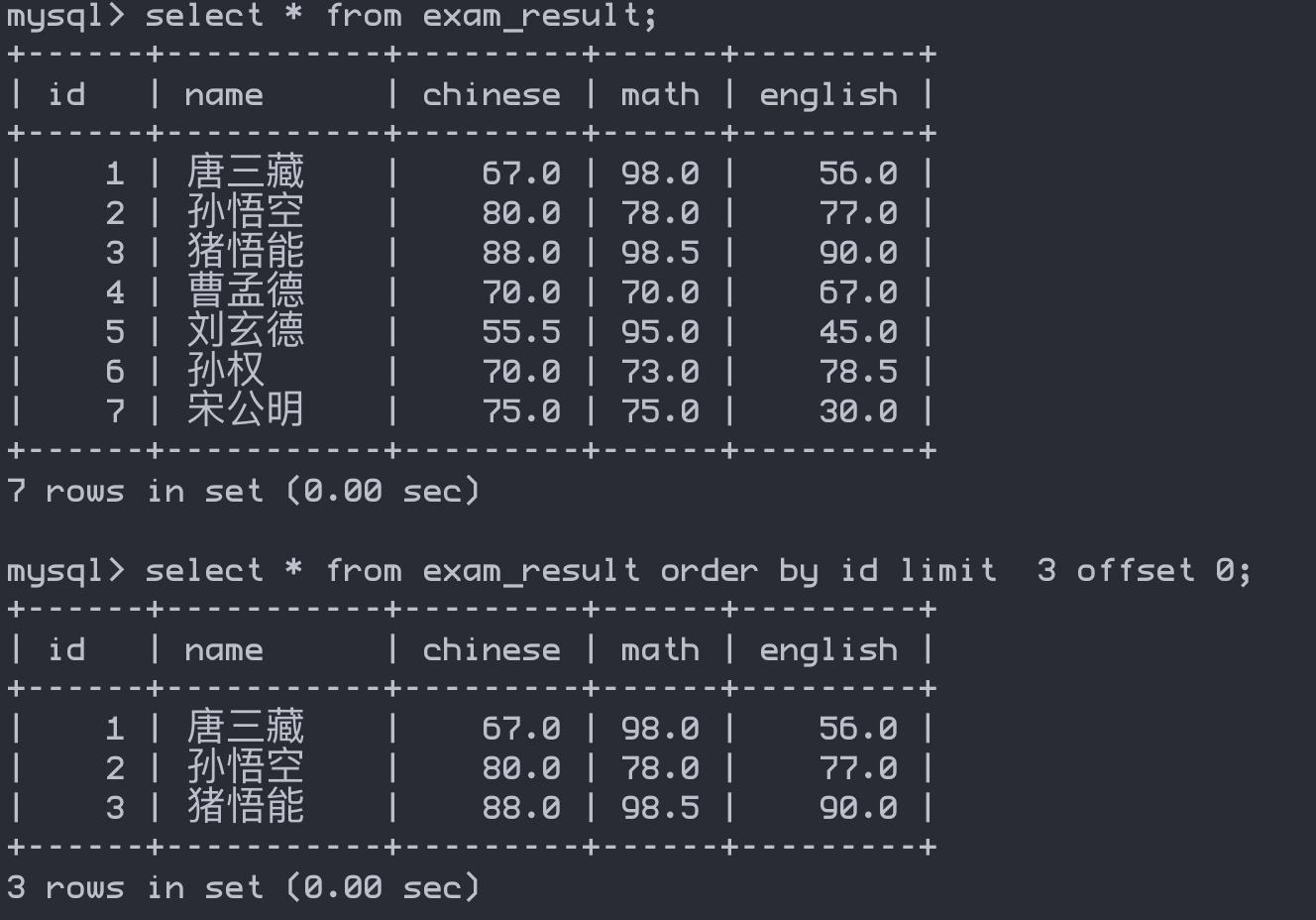
数据库的进阶操作
so easily!!!

-
not null — 那一列不能存储null值
create table student( id int not null, name varchar(20), sex varchar(4) ); -
unique — 保证那列的每行必须有唯一的值
create table student( id int not null, name varchar(20) unique, sex varchar(4) ); -
default — 给列赋指定的默认值
create table student( id int not null, name varchar(20) default, sex varchar(4) ); -
primary key — 是not null 和 unique 的结和,确保那列有唯一标识,有助于更容易更快速找到表中的特定记录
create table student( id int not null primary key auto_increment, -- auto_increment 自动增长 name varchar(20), sex varchar(4) ); -
foreign key — 保证一个表中的数据匹配另一个表中的值参照完整性
-- 创建班级表 create table classes( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), ); -- 创建学生表 create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) default 'unkown', classes_id int, foreign key (classes_id) references classes(id) ); -
check — 保证列中的值符合指定的条件,但是MySQL数据库忽略check语句(了解)
表的聚合查询(认真对待哦)
-
count(列名) — 返回查询到的数据数量
select count(*) from student;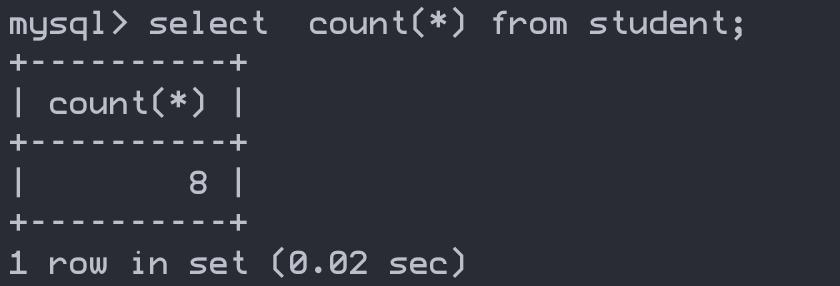
-
sum(列名) — 返回查询到的数据量总和,不是数字就没意义
select sum(math) from exam_result;
-
avg(列名) — 返回查询到的数据平均值,不是数字就没意义
select avg(chinese + math + english) as 平均总分 from exam_result;
-
max(列名) — 返回查询到的数据最大值,不是数字就没意义
select max(english) from exam_result;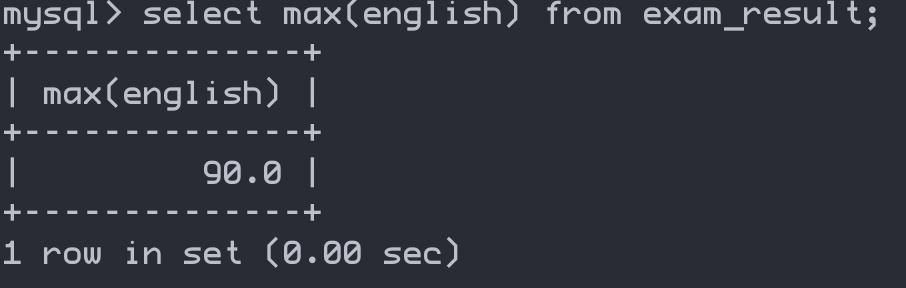
-
min(列名) — 返回查询到的数据最小值,不是数字就没意义
select min(math) from exam_result where math > 70;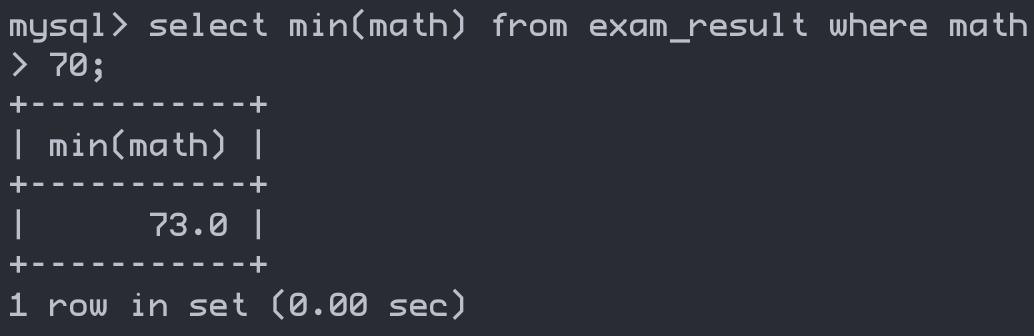
-
group by — 对数据进行分组查询(经常与having搭配)
select role, max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary) from emp group by role;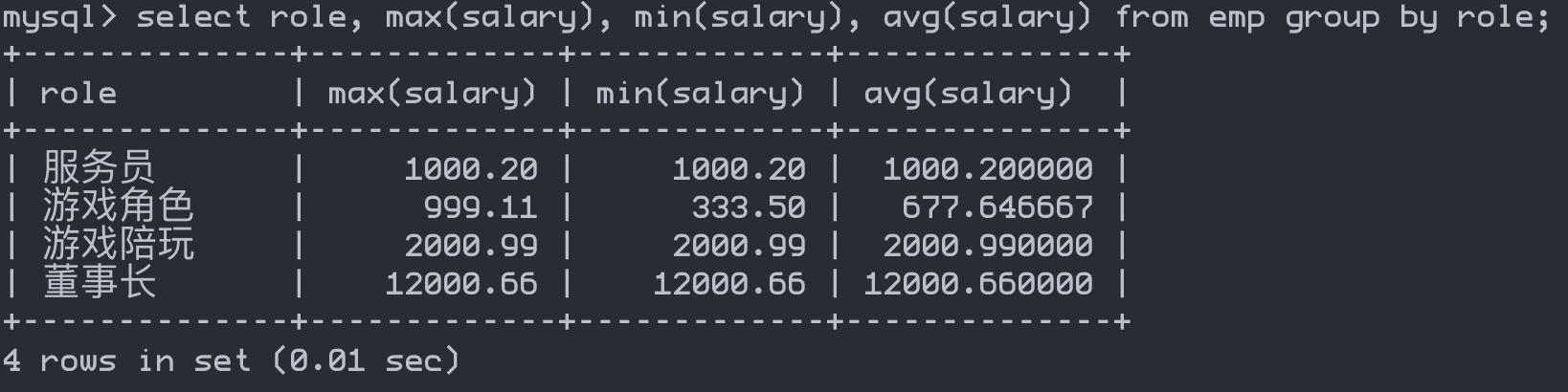
-
内连接
select sco.score from student as stu join score as sco on stu.id = sco.student_id and stu.name="许仙";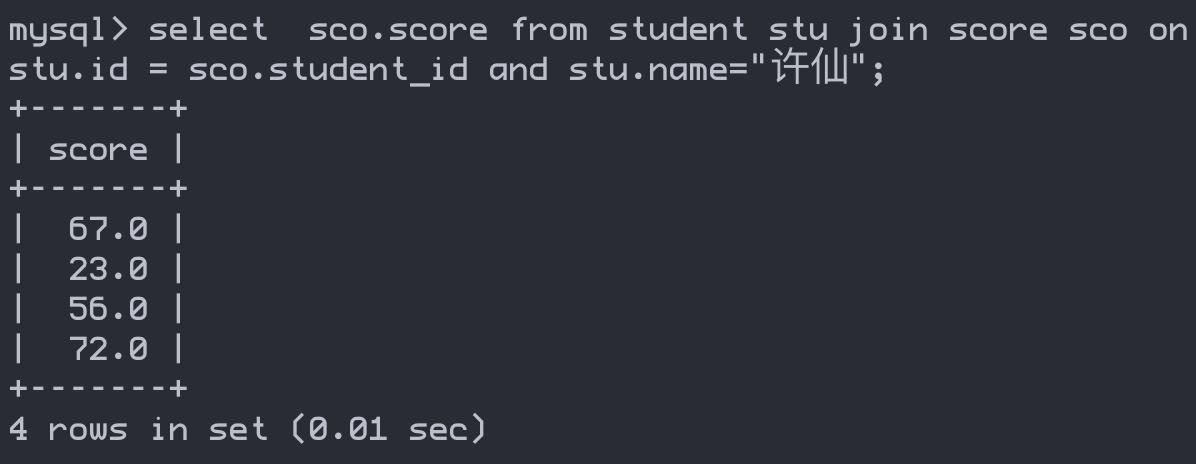
select sco.score from student as stu ,score as sco where stu.id = sco.student_id and stu.name = "许仙";
-
外连接 — 分为左外连接和右外连接,联合查询的时候左侧表完全显示,就是左外连接,反之,就是右外连接
select * from student left join score on student.id = score.student_id; select * from student right join score on student.id = score.student_id;
数据有点长就不截图啦
-
子查询 — 嵌入其他sql语句的select语句,也叫嵌套查询
select * from student where classes_id = (select classes_id from student where name='不想毕业');
select * from score where course_id in (select id from course where name="语文" or name="英文");
-
合并查询 — 实际应用中,合并多个select的执行结果,可以使用集合操作符union、union all,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要一致(不常用,了解即可)
select * from course where id < 3 union select * from course where name = "英文";
MySQL索引事务(简单了解)
-
概念
- 索引是一种特殊的文件,包含对数据表所有记录的引用指针,可以对表中的一列或多列创建索引并指定索引的类型,各类索引有各自的数据结构的实现
-
作用
- 数据库中的表、数据、索引之间的关系,类似书架上的图书、书籍目录的关系
- 索引所起的作用类似书籍目录,可用于快速定位、检索数据
- 索引对于提高数据库的性能有很大帮助
-
事务的概念
- 事务指逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败,在不同的环境下,都可以有事务,对应在数据库中就是数据库事务
Java的JDBC简单操作
简介
jdbc,java数据库连接,是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,它是Java中的数据库连接规范,它为Java程序猿操作数据库提供了一个标准的API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问
JDBC工作原理
JDBC为多种关系数据库提供了统一访问方式,作为特定厂商数据库访问API的一种高级抽象,它主要包含一些通用接口
- Java语言访问数据库操作完全面向抽象接口编程
- 开发数据库应用不用限定在特定数据库厂商的API
- 程序的可移植性大大增强
JDBC使用
-
准备数据库驱动包,并添加到项目的依赖中
-
建立数据库连接
// 加载JDBC驱动程序 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // 创建数据库连接 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cole?user=root&password=root&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"); -
创建操作命令(Statement)
Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); -
执行SQL语句
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select name from student"); -
处理结果集
while(resultSet.next()) String name = resultSet.getInt("name"); System.out.println(String.format("Student: name%s", name)); -
释放资源(关闭结果集、命令、连接)
// 关闭结果集 if(resultSet != null) try resultSet.close(); catch(SQLException e) e.printStackTrace(); // 关闭命令 if(statement != null) try statement.close(); catch(SQLException e) e.printStackTrace(); // 关闭连接命令 if(connection != null) try connection.close(); catch(SQLException e) e.printStackTrace();另一种连接方式:
// 1.先和数据库建立连接 // a) 先创建一个数据源(DataSource) DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource(); // b) 给数据源设置属性(为了让代码知道数据库在哪) ((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/火箭班2021?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true"); ((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root"); ((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("wangjin521"); // c) 通过 getConnection 方法来和服务器建立连接 Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
JDBC使用步骤
- 创建数据库连接(Connection)
- 创建操作命令(Statement)
- 使用操作命令来执行SQL
- 处理结果集(ResultSet)
- 释放资源
小结

-
数据库约束
约束类型 说明 实例 null约束 使用not null 指定列不为空 name varchar(20) not null unique唯一约束 指定列为唯一的、不重复的 name varchar(20) unique default默认约束 指定列为空时的默认值 age int defauult 20 主键约束 not null 和 unique 的结和 id int primary key 外键约束 关联其它表的主键或唯一键 foreign key (字段名) references 主表(列) check约束 保证列中的值符合指定的条件 check(sex=‘男’ or sex=‘女’) -
表的关系
- 一对一
- 一对多
- 多对多:需要创建中间表来映射两张表的关系
-
查询(重点掌握)
- 聚合函数:max、min、avg、count、sum
- 分组查询:group by…having…
- 内连接
- 外连接
- 嵌套查询
- 合并查询
- 事务索引简介
- Java中JDBC的简单使用
切记注意 :千万不敢轻易尝试删除修改操作,建议忘记这个命令哈,老板会善待你的!!!

以上是关于数据库——可不敢删库跑路喽(建议收藏)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章