从Mapper到JavaBean源码层面解析ResultMap是怎么映射的
Posted 爱叨叨的程序狗
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从Mapper到JavaBean源码层面解析ResultMap是怎么映射的相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
起点:
源码下载:
Github:MyBatis源码下载
本文以3.3.x分支版本源码为例。
在源码工程的test中以NestedQueryCacheTest测试类下的testThatNestedQueryItemsAreRetrievedFromCache为例:
该方法中调的Mapper为:
<resultMap id="selectAuthor" type="org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.Author">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result property="username" column="username" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="bio" column="bio" />
<result property="favouriteSection" column="favourite_section" />
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAuthor" resultMap="selectAuthor">
select id, username, password, email, bio, favourite_section
from author where id = #id
</select>
resultMap工作原理
MyBatis中的标签主要用于返回javaType列和自定义列以及配合、标签实现一对一、一对多查询映射关系。MyBatis通过ResultMapElement类实现对的解析,解析过程中实质上是构造ResultMap对象,记录结果集中某一列与JavaBean中一个属性的一一对应关系
启动测试,在XMLMapperBuilder第108行打断点,通过XNode类型的context参数可获取到目标Mapper的包路径及名称,然后缓存下来,这样就保证了在多次访问时,Mapper文件我们只需要加载一次。
resultMap解析流程
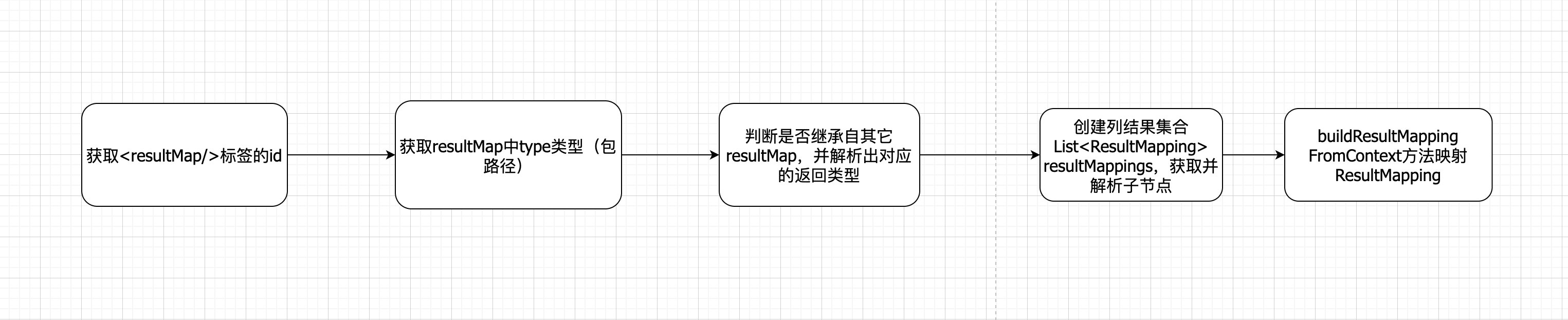
private void configurationElement(XNode context)
try
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals(""))
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
catch (Exception e)
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
在ResultMapElement中,resultMapElements中定义了resulteMap xml文件的解析方法。在该方法中,入参是XNode类型的List列表。xml是一种数据展现和存储的方式,为获取xml中的数据,我们需要Java-XML中间做一层转化,XNode就是MyBatis定义解析XML节点中属性和对应值的工具。
private void resultMapElements(List<XNode> list) throws Exception
for (XNode resultMapNode : list)
try
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
catch (IncompleteElementException e)
// ignore, it will be retried
在XMLMapperBuilder第242行断点,查看List的值:
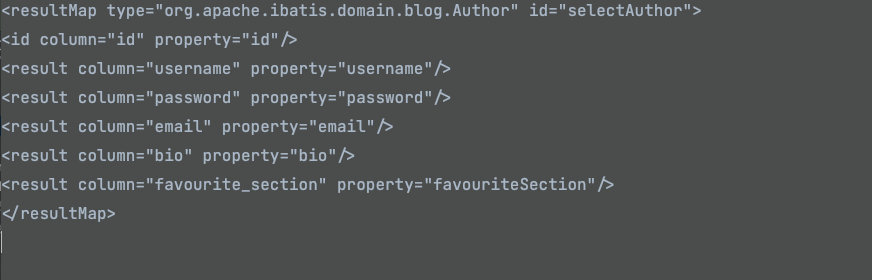
可见,MyBatis已经通过XNode获取到了xml文件中的resultMap编写的代码,接下来就是要在for循环中解析resultMap中每一行的数据。
解析resultMap每一行的映射关系
该方法的作用:
解析定义在xml中的SQL语句节点,将节点映射转化为ResultMap对象,嵌套对象如、等标签则根据对应的ResultType或ResulteMap的层级关系意义映射。
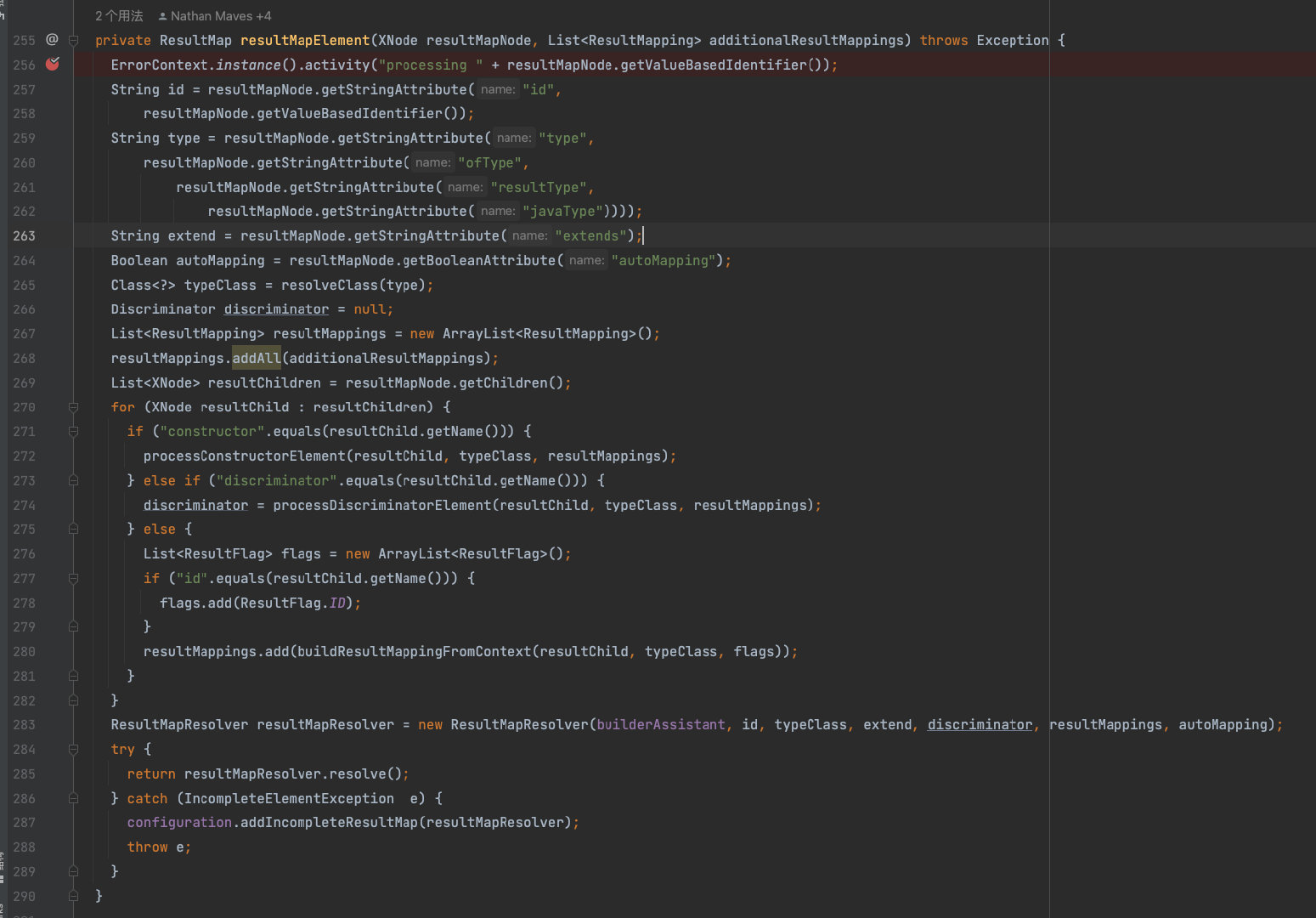
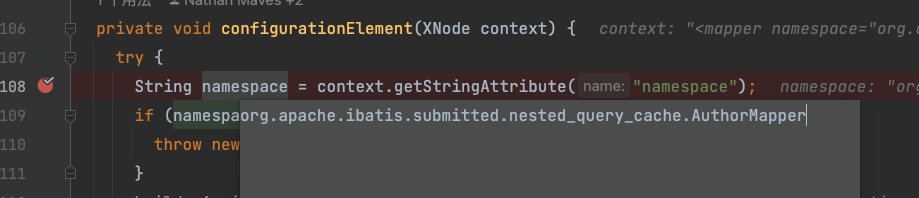
第一步获取id,默认拼装所有节点的resultId或property(唯一标识)
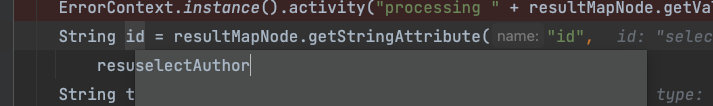
第二步,获取类型
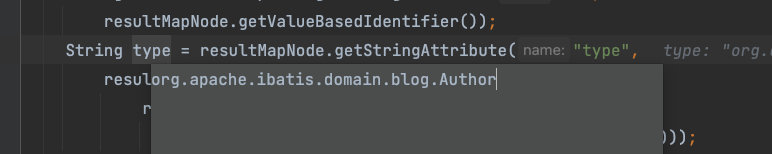
type是resultMap标签的,ofType是collection标签的,resultType是select、insert、update、delete标签的。标签允许多个type,优先级为:
【type】>【ofType】>【resultType】>【javaType】
第三步,判断该resultMap是否继承自其它resultMap,是否开启了自动映射配置。
autoMapping:自动映射:自动根据大小写实现SQL column <—>JavaBean(POJO) field转换
第四步,解析结果集的类型,根据type找到对应类
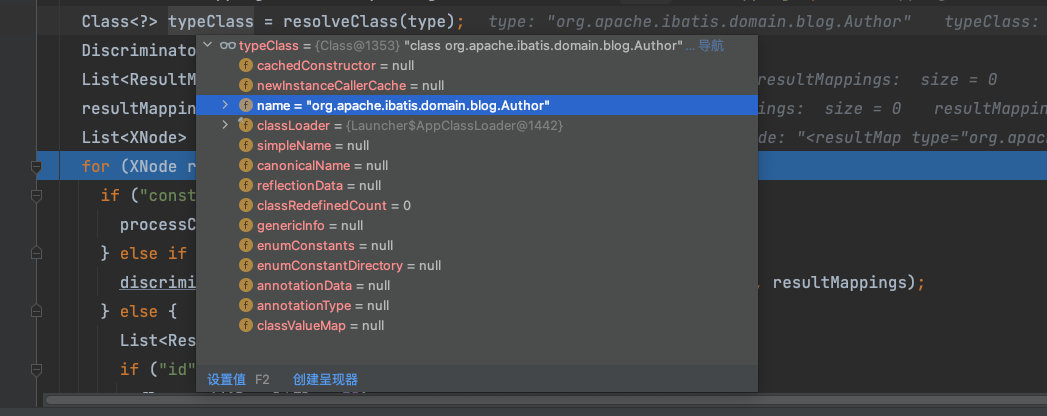
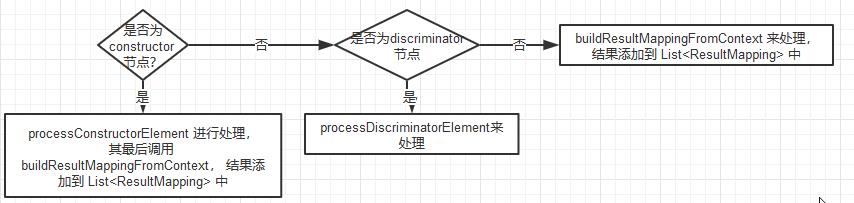
第五步,获取自定义的Mapper中所有的子节点,如外层嵌套了、子节点标签的Mapper,将在下面的for循环中解析构造函数元素,每一个子节点都会映射为一个对应的ResultMapping对象,与映射普通的节点一致。
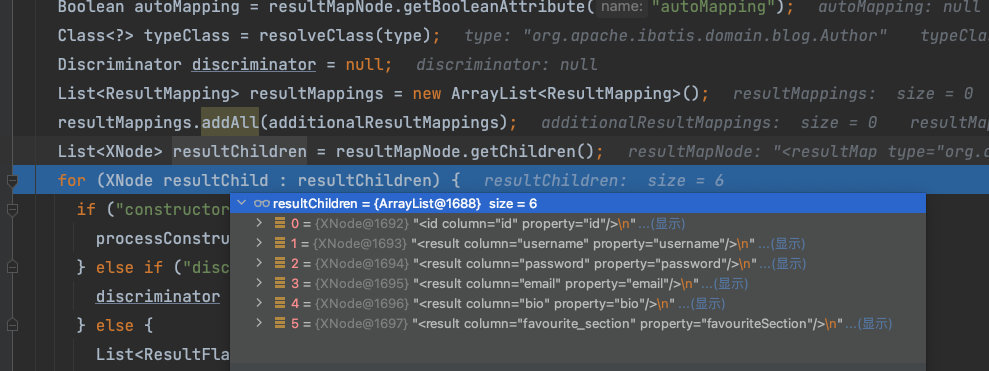
//处理子节点
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren)
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName()))
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName()))
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
else
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<ResultFlag>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName()))
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
// 创建 resultMapping 对象, 并添加到 resultMappings 中
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
引用处理子节点流程:
第六步,将从XNode中获取到的全部节点,将每一行数据都放入到List中,经buildResultMappingFromContext()完成映射。
/**
* 获取一行, 如result等, 取得他们所有的属性, 通过这些属性建立 ResultMapping 对象
* @param context 对于节点本身
* @param resultType resultMap 的结果类型
* @param flags flag 属性, 对应 ResultFlag 枚举中的属性。 一般情况下为空
* @return 返回 ResultMapping
* @throws Exception
*/
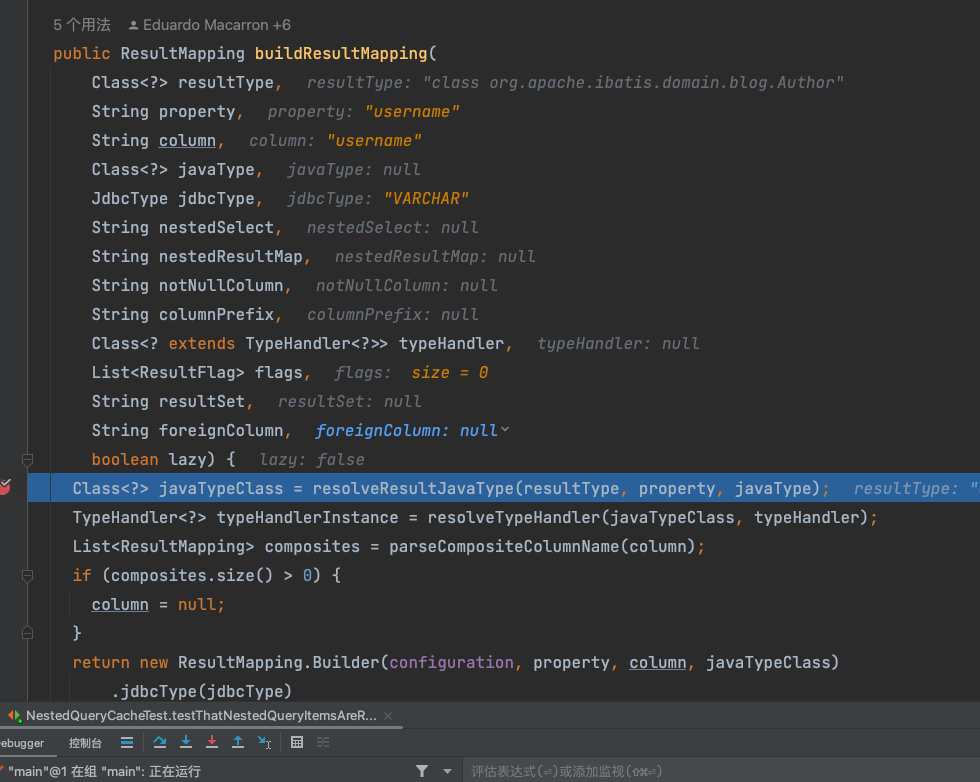
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception
// 列和字段对应关系
String property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
// 列和字段对应关系
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
// 列和字段对应关系
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
// 列和字段对应关系
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
//判断该标签中是否嵌套ResultMap
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap",
processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping> emptyList()));
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
String resulSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
//返回构造参数映射
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect, nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resulSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
/**
* 处理Constructor子节点
* @param resultChild 子节点数据
* @param resultType resultMap resultType类型
* @param resultMappings 结果集映射
* @throws Exception
*/
private void processConstructorElement(XNode resultChild, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception
List<XNode> argChildren = resultChild.getChildren();
for (XNode argChild : argChildren)
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<ResultFlag>();
flags.add(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR);
if ("idArg".equals(argChild.getName()))
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(argChild, resultType, flags));
补充:
构造参数映射(普通对象)
构造参数映射(嵌套对象)
private String processNestedResultMappings(XNode context, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception if ("association".equals(context.getName()) || "collection".equals(context.getName()) || "case".equals(context.getName())) if (context.getStringAttribute("select") == null) //递归调用解析元素方法 ResultMap resultMap = resultMapElement(context, resultMappings); return resultMap.getId(); return null;当解析到的Mapper中的方法中嵌套了另一个、的resultMap时,那么会递归调用映射方法,并将返回值做为本Map的一个参数返回。
从上面代码上能看得出成为嵌套ResultMap的规则为:association,collection,case标签,且不包含select属性.
以上是关于从Mapper到JavaBean源码层面解析ResultMap是怎么映射的的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章